- COVID-19 travel advice
Considering travel during the pandemic? Take precautions to protect yourself from COVID-19.
A coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccine can prevent you from getting COVID-19 or from becoming seriously ill due to COVID-19 . But even if you're vaccinated, it's still a good idea to take precautions to protect yourself and others while traveling during the COVID-19 pandemic.
If you've had all recommended COVID-19 vaccine doses, including boosters, you're less likely to become seriously ill or spread COVID-19 . You can then travel more safely within the U.S. and internationally. But international travel can still increase your risk of getting new COVID-19 variants.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that you should avoid travel until you've had all recommended COVID-19 vaccine and booster doses.

Before you travel
As you think about making travel plans, consider these questions:
- Have you been vaccinated against COVID-19 ? If you haven't, get vaccinated. If the vaccine requires two doses, wait two weeks after getting your second vaccine dose to travel. If the vaccine requires one dose, wait two weeks after getting the vaccine to travel. It takes time for your body to build protection after any vaccination.
- Have you had any booster doses? Having all recommended COVID-19 vaccine doses, including boosters, increases your protection from serious illness.
- Are you at increased risk for severe illness? Anyone can get COVID-19 . But older adults and people of any age with certain medical conditions are at increased risk for severe illness from COVID-19 .
- Do you live with someone who's at increased risk for severe illness? If you get infected while traveling, you can spread the COVID-19 virus to the people you live with when you return, even if you don't have symptoms.
- Does your home or destination have requirements or restrictions for travelers? Even if you've had all recommended vaccine doses, you must follow local, state and federal testing and travel rules.
Check local requirements, restrictions and situations
Some state, local and territorial governments have requirements, such as requiring people to wear masks, get tested, be vaccinated or stay isolated for a period of time after arrival. Before you go, check for requirements at your destination and anywhere you might stop along the way.
Keep in mind these can change often and quickly depending on local conditions. It's also important to understand that the COVID-19 situation, such as the level of spread and presence of variants, varies in each country. Check back for updates as your trip gets closer.
Travel and testing
For vaccinated people.
If you have been fully vaccinated, the CDC states that you don't need to get tested before or after your trip within the U.S. or stay home (quarantine) after you return.
If you're planning to travel internationally outside the U.S., the CDC states you don't need to get tested before your trip unless it's required at your destination. Before arriving to the U.S., you need a negative test within the last day before your arrival or a record of recovery from COVID-19 in the last three months.
After you arrive in the U.S., the CDC recommends getting tested with a viral test 3 to 5 days after your trip. If you're traveling to the U.S. and you aren't a citizen, you need to be fully vaccinated and have proof of vaccination.
You don't need to quarantine when you arrive in the U.S. But check for any symptoms. Stay at home if you develop symptoms.
For unvaccinated people
Testing before and after travel can lower the risk of spreading the virus that causes COVID-19 . If you haven't been vaccinated, the CDC recommends getting a viral test within three days before your trip. Delay travel if you're waiting for test results. Keep a copy of your results with you when you travel.
Repeat the test 3 to 5 days after your trip. Stay home for five days after travel.
If at any point you test positive for the virus that causes COVID-19 , stay home. Stay at home and away from others if you develop symptoms. Follow public health recommendations.
Stay safe when you travel
In the U.S., you must wear a face mask on planes, buses, trains and other forms of public transportation. The mask must fit snugly and cover both your mouth and nose.
Follow these steps to protect yourself and others when you travel:
- Get vaccinated.
- Keep distance between yourself and others (within about 6 feet, or 2 meters) when you're in indoor public spaces if you're not fully vaccinated. This is especially important if you have a higher risk of serious illness.
- Avoid contact with anyone who is sick or has symptoms.
- Avoid crowds and indoor places that have poor air flow (ventilation).
- Don't touch frequently touched surfaces, such as handrails, elevator buttons and kiosks. If you must touch these surfaces, use hand sanitizer or wash your hands afterward.
- Wear a face mask in indoor public spaces. The CDC recommends wearing the most protective mask possible that you'll wear regularly and that fits. If you are in an area with a high number of new COVID-19 cases, wear a mask in indoor public places and outdoors in crowded areas or when you're in close contact with people who aren't vaccinated.
- Avoid touching your eyes, nose and mouth.
- Cover coughs and sneezes.
- Wash your hands often with soap and water for at least 20 seconds.
- If soap and water aren't available, use a hand sanitizer that contains at least 60% alcohol. Cover all surfaces of your hands and rub your hands together until they feel dry.
- Don't eat or drink on public transportation. That way you can keep your mask on the whole time.
Because of the high air flow and air filter efficiency on airplanes, most viruses such as the COVID-19 virus don't spread easily on flights. Wearing masks on planes has likely helped lower the risk of getting the COVID-19 virus on flights too.
However, air travel involves spending time in security lines and airport terminals, which can bring you in close contact with other people. Getting vaccinated and wearing a mask when traveling can help protect you from COVID-19 while traveling.
The Transportation Security Administration (TSA) has increased cleaning and disinfecting of surfaces and equipment, including bins, at screening checkpoints. TSA has also made changes to the screening process:
- Travelers must wear masks during screening. However, TSA employees may ask travelers to adjust masks for identification purposes.
- Travelers should keep a distance of 6 feet apart from other travelers when possible.
- Instead of handing boarding passes to TSA officers, travelers should place passes (paper or electronic) directly on the scanner and then hold them up for inspection.
- Each traveler may have one container of hand sanitizer up to 12 ounces (about 350 milliliters) in a carry-on bag. These containers will need to be taken out for screening.
- Personal items such as keys, wallets and phones should be placed in carry-on bags instead of bins. This reduces the handling of these items during screening.
- Food items should be carried in a plastic bag and placed in a bin for screening. Separating food from carry-on bags lessens the likelihood that screeners will need to open bags for inspection.
Be sure to wash your hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds directly before and after going through screening.
Public transportation
If you travel by bus or train and you aren't vaccinated, be aware that sitting or standing within 6 feet (2 meters) of others for a long period can put you at higher risk of getting or spreading COVID-19 . Follow the precautions described above for protecting yourself during travel.
Even if you fly, you may need transportation once you arrive at your destination. You can search car rental options and their cleaning policies on the internet. If you plan to stay at a hotel, check into shuttle service availability.
If you'll be using public transportation and you aren't vaccinated, continue physical distancing and wearing a mask after reaching your destination.
Hotels and other lodging
The hotel industry knows that travelers are concerned about COVID-19 and safety. Check any major hotel's website for information about how it's protecting guests and staff. Some best practices include:
- Enhanced cleaning procedures
- Physical distancing recommendations indoors for people who aren't vaccinated
- Mask-wearing and regular hand-washing by staff
- Mask-wearing indoors for guests in public places in areas that have high cases of COVID-19
- Vaccine recommendations for staff
- Isolation and testing guidelines for staff who've been exposed to COVID-19
- Contactless payment
- Set of rules in case a guest becomes ill, such as closing the room for cleaning and disinfecting
- Indoor air quality measures, such as regular system and air filter maintenance, and suggestions to add air cleaners that can filter viruses and bacteria from the air
Vacation rentals, too, are enhancing their cleaning procedures. They're committed to following public health guidelines, such as using masks and gloves when cleaning, and building in a waiting period between guests.
Make a packing list
When it's time to pack for your trip, grab any medications you may need on your trip and these essential safe-travel supplies:
- Alcohol-based hand sanitizer (at least 60% alcohol)
- Disinfectant wipes (at least 70% alcohol)
- Thermometer
Considerations for people at increased risk
Anyone can get very ill from the virus that causes COVID-19 . But older adults and people of any age with certain medical conditions are at increased risk for severe illness. This may include people with cancer, serious heart problems and a weakened immune system. Getting the recommended COVID-19 vaccine and booster doses can help lower your risk of being severely ill from COVID-19 .
Travel increases your chance of getting and spreading COVID-19 . If you're unvaccinated, staying home is the best way to protect yourself and others from COVID-19 . If you must travel and aren't vaccinated, talk with your health care provider and ask about any additional precautions you may need to take.
Remember safety first
Even the most detailed and organized plans may need to be set aside when someone gets ill. Stay home if you or any of your travel companions:
- Have signs or symptoms, are sick or think you have COVID-19
- Are waiting for results of a COVID-19 test
- Have been diagnosed with COVID-19
- Have had close contact with someone with COVID-19 in the past five days and you're not up to date with your COVID-19 vaccines
If you've had close contact with someone with COVID-19 , get tested after at least five days. Wait to travel until you have a negative test. Wear a mask if you travel up to 10 days after you've had close contact with someone with COVID-19 .
- How to protect yourself and others. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/prevention.html. Accessed Feb. 4, 2022.
- Domestic travel during COVID-19. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/travelers/travel-during-covid19.html. Accessed Feb. 4, 2022.
- Requirement for face masks on public transportation conveyances and at transportation hubs. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/travelers/face-masks-public-transportation.html. Accessed Feb. 4, 2022.
- International travel. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/travelers/international-travel/index.html. Accessed Feb. 4, 2022.
- U.S citizens, U.S. nationals, U.S. lawful permanent residents, and immigrants: Travel to and from the United States. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/travelers/international-travel-during-covid19.html. Accessed Feb. 4, 2022.
- Non-US. citizen, non-U.S. immigrants: Air travel to the United States. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/travelers/noncitizens-US-air-travel.html. Accessed Feb. 4, 2022.
- People with certain medical conditions. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/need-extra-precautions/people-with-medical-conditions.html. Accessed Feb. 4, 2022.
- Stay up to date with your vaccines. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/stay-up-to-date.html. Accessed Feb. 4, 2022.
- Pack smart. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/page/pack-smart. Accessed Feb. 4, 2022.
- Travel: Frequently asked questions. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/travelers/faqs.html. Accessed Feb. 7, 2022.
- Coronavirus (COVID-19) information. Transportation Security Administration. https://www.tsa.gov/coronavirus. Accessed Feb. 7, 2022.
- WHO advice for international traffic in relation to the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant (B.1.1.529). World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/news-room/articles-detail/who-advice-for-international-traffic-in-relation-to-the-sars-cov-2-omicron-variant. Accessed Feb. 7, 2022.
- VRHP/VRMA Cleaning guidelines for COVID-19. Vacation Rental Management Association. https://www.vrma.org/page/vrhp/vrma-cleaning-guidelines-for-covid-19. Accessed Feb. 7, 2022.
- Safe stay. American Hotel & Lodging Association. https://www.ahla.com/safestay. Accessed Feb. 7, 2022.
- Khatib AN, et al. COVID-19 transmission and the safety of air travel during the pandemic: A scoping review. Current Opinion in Infectious Diseases. 2021; doi:10.1097/QCO.0000000000000771.
Products and Services
- A Book: Endemic - A Post-Pandemic Playbook
- Begin Exploring Women's Health Solutions at Mayo Clinic Store
- A Book: Future Care
- Antibiotics: Are you misusing them?
- COVID-19 and vitamin D
- Convalescent plasma therapy
- Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
- COVID-19: How can I protect myself?
- Herd immunity and coronavirus
- COVID-19 and pets
- COVID-19 and your mental health
- COVID-19 antibody testing
- COVID-19, cold, allergies and the flu
- COVID-19 drugs: Are there any that work?
- Long-term effects of COVID-19
- COVID-19 tests
- COVID-19 in babies and children
- Coronavirus infection by race
- COVID-19 vaccine: Should I reschedule my mammogram?
- COVID-19 vaccines for kids: What you need to know
- COVID-19 vaccines
- COVID-19 variant
- COVID-19 vs. flu: Similarities and differences
- COVID-19: Who's at higher risk of serious symptoms?
- Debunking coronavirus myths
- Different COVID-19 vaccines
- Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO)
- Fever: First aid
- Fever treatment: Quick guide to treating a fever
- Fight coronavirus (COVID-19) transmission at home
- Honey: An effective cough remedy?
- How do COVID-19 antibody tests differ from diagnostic tests?
- How to measure your respiratory rate
- How to take your pulse
- How to take your temperature
- How well do face masks protect against COVID-19?
- Is hydroxychloroquine a treatment for COVID-19?
- Loss of smell
- Mayo Clinic Minute: You're washing your hands all wrong
- Mayo Clinic Minute: How dirty are common surfaces?
- Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C)
- Nausea and vomiting
- Pregnancy and COVID-19
- Safe outdoor activities during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Safety tips for attending school during COVID-19
- Sex and COVID-19
- Shortness of breath
- Thermometers: Understand the options
- Treating COVID-19 at home
- Unusual symptoms of coronavirus
- Vaccine guidance from Mayo Clinic
- Watery eyes
U.S. travel resources
- Check CDC recommendations for travel within the U.S.
- Review testing requirements for travel to the U.S.
- Look up restrictions at your destination .
- Review airport security measures .
Related resources
Make twice the impact.
Your gift can go twice as far to advance cancer research and care!
National Geographic content straight to your inbox—sign up for our popular newsletters here

A traveler walks through Amsterdam’s Schiphol Airport May 13, 2020. Netherlands-based KLM Royal Dutch Airlines, like most carriers, now requires passengers to cover their faces to board planes.
- CORONAVIRUS COVERAGE
Is it safe to travel now? It depends.
Here are the best practices for getting on the road without endangering your health—or anyone else’s.
Although many restrictions are still in place, travel is slowly starting up again. People locked down for months want to stretch their legs, see something other than a screen, and boost the economy. Restaurants and some tourist attractions (Florida’s Universal Orlando Resort, The Museum of Fine Arts, Houston) are opening for local and domestic travel. A few countries (Greece, Italy) are starting to welcome international travelers.
But how can you safely explore a world of potentially deadly encounters with friendly people who might infect you (or who you might expose to the virus)? Is the airplane really a soaring petri dish? Is visiting a national park possible while social distancing? And if you choose a seemingly safer road trip, can you stop to use a public restroom?
A poll by National Geographic and Morning Consult finds that just 2 percent of 2,200 Americans said they’d jump on a plane now, and only another 8 percent would consider it later this summer. That’s wise with travel advisories still in place, including the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) warnings against international travel and cautions about travel within the U.S. , and with many countries and states ( Maine , Hawaii ) still requiring 14 days of post-travel self-isolation regardless of symptoms.
As we recently report, travel planning is good for your mental health . Knowing more about real and perceived COVID-19 risks might help you feel better about getting out as roadblocks lift. Here are best practices for travelers.
Should I get on an airplane?
Challenge: Being crammed next to strangers in a flying metal tube
Best practice: It’s reassuring to know that “data to date suggest only rare possible occurrences of in-flight transmission” of COVID-19, says Dr. Lin H. Chen , associate professor at Harvard Medical School and director of Cambridge’s Travel Medicine Center at Mount Auburn . She explains that if everyone follows the World Health Organization’s guidelines , the risk of transmission aboard planes, and anywhere else, is significantly reduced.

A plastic drape covers an airline check-in counter at Amsterdam’s Schiphol Airport on March 27, 2020. Barriers like this between workers and travelers are meant to help prevent the spread of COVID-19.
“Many people think they get sick on an airplane, but the reality is that the air quality on an airplane is actually really good—high amounts of clean outdoor air and all recirculated air passes through a HEPA filter,” says Joe Allen . An assistant professor and director of the Healthy Buildings Program at Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Allen explains that you’re more likely to pick up a bug standing in line at airport security, at the boarding gate, or on the subway.
Airports and airlines are trying to minimize the risks of contagions in their often-crowded environments. Intensive cleaning is now the norm; planes are now being fogged with electrostatic disinfectant that sticks to surfaces like seatbelts. Some airlines give you wipes and the Transportation Security Administration has upped the size of hand sanitizer bottles you can bring on board from 3.4 ounces to 12.
(Related: What’s the safest seat to claim on the plane?)
Face coverings are required to board most flights. Airlines are trying to seat people so they have more space. But that doesn’t necessarily mean middle seats are remaining empty, especially with reductions in numbers of flights. There’s no national U.S. policy yet, but several airlines are checking for fevers. They won’t let you fly with a temperature above 100.4℉ (though testing is far from foolproof).
Internationally, some destinations require proof of a negative COVID-19 test; other destinations test passengers on arrival. Many have mandatory 14-day quarantines, sometimes requiring you to submit a quarantine plan for approval, download an app, or get a tracking bracelet to ensure you follow the rules. Vaccination certification may eventually be needed for travel, but so far the science doesn’t support “immunity passports” or proof that a person has had COVID-19 and is, in theory, immune.
Should I head to a national park?
Challenge: Avoiding big crowds in the great outdoors
Best practice: “There are many health benefits to being outside in nature, and the risks are low and manageable,” says Allen. The key is keeping a six-foot distance. A good practice at a park is to pretend that other people are grizzly bears and stay away from them.
Check the National Park Service’s find-a-park website to see if the park is closed or partially closed (restrooms and food services, in particular), for limits on numbers of visitors, and other rules like mask-wearing. Avoid group activities that involve close contact and practice social distancing at camp sites. Joyce Sanchez , an infectious disease specialist and medical director of the Travel Health Clinic at Froedtert and the Medical College of Wisconsin, reminds us that “summer is tick and mosquito season,” so don’t forget your bug spray and sunscreen (though perhaps a face-mask tan will become a badge of honor that you’re doing your part to protect others).
(Related: Learn how COVID closures are impacting the small town bordering Yellowstone and Grand Teton National Parks.)
Should I rent a cottage by the sea?
Challenge : Assessing the safety of beaches and vacation rentals
Best practice: Like park trips, seaside vacations are great if you can stay away from others and obey beach closure rules. There’s no evidence you can catch COVID-19 from the water (it’s other people you should be concerned about). Remember to bring your two best beach friends: reef-safe sunscreen free of oxybenzone and hand sanitizer.

A woman sunbathes in a roped-off social-distancing zone on the beach in La Grande Motte in southern France.
Regarding rentals, ask whether properties are cleaned according to public health guidelines, such as the WHO’s accommodation sector advice . Airbnb’s Enhanced Cleaning Initiative includes a 24- to 72-hour vacancy period between guests (though cleaners may visit during that window), but it’s likely unnecessary given evidence that the coronavirus floats in the air only up to three hours. Since it’s possible for the virus to live on surfaces for two or three days , you could give high-touch surfaces an extra clean. As Chen says, “good hand washing should overcome potentially contaminated touching.” If anxiety outweighs the benefits of a vacation, it’s a sign you’re not ready to venture out yet.
Should I stay in a hotel?
Challenge: Distancing safely and trusting housekeeping
Best practice: Hotels that take better care of their employees (by providing them with personal protective equipment and paid sick leave) are more likely to take better care of you. Check the website of any hotel you’re considering to determine how they’re responding to COVID-19. Many U.S. hotels are following the American Hotel and Lodging Association’s new Safe Stay guidelines .
Choose properties that base their protocols on science, rather than things that sound good but have little effect or take focus away from areas that really matter. Look for hotels that have installed plexiglass at reception and that require staff to wear masks, or where you can check-in online and use your phone as your room key.
(Related: Want to stay healthy on the road? Follow these germ-fighting tips.)

In Pristina, Kosovo, a worker in a protective suit sprays disinfectant in a hotel room to prevent the spread of coronavirus.
Avoid elevators and, if able, “take the opportunity to exercise and use the stairs,” advises Sanchez. Room service may be safer than the restaurant. Go for a swim if the pool isn’t crowded: Standard pool cleaning kills viruses, so the pool is probably safe; it’s the people you need to worry about. While clean rooms are important, what’s more important is staying six feet away from others. And, of course, wash your hands when you arrive in your room and again before you leave.
Should I use a public restroom?
Challenge: Taking care of business in busy bathrooms
Best practice: Assume public restrooms “are not properly disinfected and treat surfaces as if they have live virus on them,” says Sanchez. That said, it’s often necessary to use. When you do, choose single-stall and well-ventilated bathrooms if you can, and keep your distance from others.
Chen says that “good hand hygiene is key after using a public bathroom,” meaning wash and dry your hands; if there’s no soap, use hand sanitizer. She adds “I am unaware of any data to show that flushing aerosolizes SARS-CoV-2 and transmits the virus.” Regardless, it’s always good practice to put the lid down before you flush .
What about people who don’t wear masks?
Challenge: Staying safe while respecting others’ boundaries
Best practice: Following all the new COVID-19 protocols takes some getting used to. It’s easy to revert to pre-pandemic habits in new situations, when we’re stressed, and when we’re trying to relax and have fun. Being as kind and understanding as possible helps minimize stress.
Setting a good example is the best way to encourage others. Jonathon Day , associate professor and graduate program director at Purdue’s School of Hospitality and Tourism Management , says “safety when traveling (and when out and about in general) is a ‘co-creation.’”
“If it’s someone you know who is non-mask-wearing [or] non-social-distancing, it might be worth discussing the reasoning behind these measures,” says Chen. Remember that not everyone can wear a mask and that we’re all human and can forget the new norms. You could politely ask anyone who gets too close “would you mind giving us a bit more space, please?” but it might be easier just to move away from them. It’s likely not worth the risk, or the stress, to confront a stranger. If you can’t escape the situation, ask a store manager or flight attendant for help.
Remember that, with communicable diseases, “if everyone is responsible to themselves and community/society, then we would all be safer,” says Chen.
Know the safety basics
We’re still learning about COVID-19. But one consensus is that it seems to spread most easily by close contact between people. The CDC says that touching objects isn’t the main way of contracting it .
This means that whenever you’re away from home, the most important thing you can do is maintain a six-foot (or more) distance from people you don’t live with. Wearing a face covering also minimizes the chance you’ll pass a virus or other illness to others.
Other key prevention measures, outlined by the World Health Organization and other public health authorities: washing your hands well, avoiding touching your face, coughing and sneezing into your elbow, disinfecting frequently touched items like your phone, and staying home if you’re sick. Practicing these measures keeps you—and everyone else—safer, regardless of how far you roam. “COVID-19 has shown that we have shared responsibilities to reduce spread,” says Chen, who’s president of the International Society of Travel Medicine .
General considerations for travel
During a pandemic, going to the grocery store—let alone traveling to another city or country—requires new protocols. Follow policies about lockdown restrictions and mandatory quarantines, both at home and at your planned destination. The CDC provides links to the rules of each state’s and territory’s health departments . Many international borders remain closed to nonessential travel, and some countries also limit domestic travel between regions.
Examine your personal situation. Extra cautions are needed for anyone at elevated risk of contracting COVID-19 . Check post-travel quarantine rules, including your employer’s. Just as important as protecting you and your loved ones is shielding other people. You don’t want to bring the virus from your community, especially to places with low case numbers, or bring it home (the CDC tracks cases and deaths by state and county ). Consider whether the benefits of travel outweigh the risk that you might spread the virus.
When deciding where to go and how you’ll get there, scrutinize how easy it will be to stay away from other people. “Generally speaking, driving is going to be safer than flying commercially from an infection standpoint because you can control how you reach your destination—who is sharing the car with you, what measures are used for disinfecting surfaces, where you stop along the way, and when you return,” says Sanchez.
Related Topics
- CORONAVIRUS
- BEACH ACTIVITIES
You May Also Like

9 travel stories our readers loved in 2023

6 tips to make your next beach trip more sustainable
Free bonus issue.

New tools offer peace of mind for pandemic travel

A break in Llandudno, a vintage Welsh beachside resort with enduring appeal

10 best things to do in Alaska

A UK break in Falmouth: Cornish maritime history on the South West Coast Path

10 of the best hotels in Rio de Janeiro, from party houses to beach boltholes
- Environment
- Perpetual Planet
History & Culture
- History & Culture
- History Magazine
- Mind, Body, Wonder
- Paid Content
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Coronavirus Updates
The u.s. lifts the pandemic travel ban and opens the doors to international visitors.
The Associated Press

Passengers walk through Salt Lake City International Airport, Oct. 27, 2020. More than a year and a half after COVID-19 concerns prompted the U.S. to close its borders to international travelers from countries including Brazil, China, India, South Africa, the U.K. and much of Europe, restrictions are shifting to focus on vaccine status. Rick Bowmer/AP hide caption
Passengers walk through Salt Lake City International Airport, Oct. 27, 2020. More than a year and a half after COVID-19 concerns prompted the U.S. to close its borders to international travelers from countries including Brazil, China, India, South Africa, the U.K. and much of Europe, restrictions are shifting to focus on vaccine status.
The U.S. lifted restrictions Monday on travel from a long list of countries including Mexico, Canada and most of Europe, allowing tourists to make long-delayed trips and family members to reconnect with loved ones after more than a year and a half apart because of the pandemic.
Starting Monday, the U.S. is accepting fully vaccinated travelers at airports and land borders, doing away with a COVID-19 restriction that dates back to the Trump administration. The new rules allow air travel from previously restricted countries as long as the traveler has proof of vaccination and a negative COVID-19 test. Land travel from Mexico and Canada will require proof of vaccination but no test.
Airlines are expecting more travelers from Europe and elsewhere. Data from travel and analytics firm Cirium showed airlines are increasing flights between the United Kingdom and the U.S. by 21% this month over last month.
The change will have a profound effect on the borders with Mexico and Canada, where traveling back and forth was a way of life until the pandemic hit and the U.S. shut down nonessential travel.
Malls, restaurants and Main Street shops in U.S. border towns have been devastated by the lack of visitors from Mexico. On the boundary with Canada, cross-border hockey rivalries were community traditions until being upended by the pandemic. Churches that had members on both sides of the border are hoping to welcome parishioners they haven't seen during COVID-19 shutdown.
Loved ones have missed holidays, birthdays and funerals while nonessential air travel was barred, and they are now eager to reconnect.
River Robinson's American partner wasn't able to be in Canada for the birth of their baby boy 17 months ago because of pandemic-related border closures. She was thrilled to hear the U.S. is reopening its land crossings to vaccinated travelers.
"I'm planning to take my baby down for the American Thanksgiving," said Robinson, who lives in St. Thomas, Ontario. "If all goes smoothly at the border I'll plan on taking him down as much as I can. Is crazy to think he has a whole other side of the family he hasn't even met yet."
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the U.S. will accept travelers who have been fully vaccinated with any of the vaccines approved for emergency use by the World Health Organization, not just those in use in the U.S. That means that the AstraZeneca vaccine, widely used in Canada, will be accepted.
For air travelers, the airlines are required to verify vaccine records and match them against ID, and if they don't, they could face fines of up to nearly $35,000 per violation. Airlines will also collect information about passengers for contact tracing efforts. There will be CDC workers spot-checking travelers for compliance in the U.S. At land borders, Customs and Border Protection agents will check vaccine proof.
The moves come as the U.S. has seen its COVID-19 outlook improve dramatically in recent weeks since the summer delta surge that pushed hospitals to the brink in many locations.
How 2020 and COVID-19 changed travel forever – and what that means for you
This is the year that changed travel forever.
It's difficult to understate the devastation of COVID-19. A recent study by the U.S. Travel Association projected a 45% decline in industry revenues. That translates into a $519 billion loss for the year – roughly nine times the impact of 9/11 on travel revenue.
"2020 has been a year like no other," says Roger Block, president of Travel Leaders Network . "The pandemic has put a halt on all types of international travel, changing the face and the mindset of travelers. Travelers are now more cautious, aware of cleanliness standards and practices which have forced airlines and hotels to impose new sanitation protocols."
But which of these changes are permanent? That's a harder question, mostly because no one knows the future. But industry experts have a pretty good idea, based on how people are traveling now. Taken together, their predictions paint a sobering but ultimately upbeat picture of travel in 2021 and beyond.
In the future, you'll pay more attention to health and safety, and you'll probably pay more for your trips. You'll also see fewer business travelers and stay closer to home. And travel experts say all of these changes could stick.
It's all about health now
No question about it, the pandemic has made travelers obsessive about their health. "We'll see a bigger focus on traveler well-being post-COVID-19 – and rightly so," says Sarah Wilson, CEO of ACE Travel . "Travelers will need to ensure that they’re aware of safety protocols, better hygiene, and more efficient and safer booking experiences, such as paperless online booking and self-check-in services." These changes are permanent. The contactless credit card readers and self-check-in kiosks are here to stay.
New mask guidelines: CDC advises booting travelers who refuse to wear masks on planes, trains, buses, other transportation
Travel insurance is mandatory
And by "mandatory," I don't just mean it's a good idea. If you're visiting another country, it may literally be mandatory. Thailand, for example, which is currently only accepting visa applications from residents of low-risk countries , requires $100,000 in medical coverage, according to the Thai Consulate in Los Angeles . "During the year ahead, it's especially important for travelers to make sure they understand their risks, exposures and insurance coverage before they take a trip," says John Thompson, the division president of international accident and health at Chubb, which bills itself as "the world’s largest publicly-traded property and casualty insurance company."
Somebody is watching you
Contact tracing, already required at many destinations, could become standard for travelers. "Eventually, surveillance technology could assign each passenger a digital identity, with access to anything from geolocation to virus test results or immunity certificates," predicts Annalisa Nash Fernandez, an intercultural strategist at BecauseCulture . Current contact tracing uses smartphone apps as sensors to detect proximity and exposure to infected people. But she says there will be privacy concerns, just as there were after 9/11. As contact tracing becomes standardized, health officials will need to address these worries.
You'll pay more for a planned vacation
Another travel change: Vacations won't be thrown together at the last minute and they'll cost more. A once-in-a-century pandemic can change that – and it has. The travel insurance site Squaremouth reports that spending on international trips is up 18% to an average of $4,343. And domestic trips are up 27% for an average trip cost of $3,513. Travelers are also making their reservations sooner: four months before their departure for international trips, or 50% further out than last year. Domestic travelers are planning trips 19% further out than last year, an average of 79 days before departure. Experts say these trends will stay with us for a long time.
Bye-bye, business travelers
During the pandemic, a large percentage of the workforce switched to virtual meetings. Even the most optimistic studies predict a lengthy recovery for business travel. "A percentage of business travel will never return as companies realize that employees can be as productive virtually as they are holding in-person meetings," predicts Deborah Friedland , the practice leader of hospitality advisory services for EisnerAmper , a business advisory firm. Problem is, corporate traveler has traditionally subsidized cheap airline tickets. So the price of flying will probably rise.
Lodging doesn't necessarily mean hotels
The shift to vacation rentals and other nontraditional lodging was well underway before the pandemic. But COVID-19 accelerated it and made it one of the biggest permanent travel changes. "There's a decreased desire for large hotels ," says Joli Moniz, owner of A Vontade Tours , which specializes in trips to the islands of Cabo Verde off the west coast of Africa. "Instead, people want boutique hotels or private villas with fewer people and limited interactions." Social distancing may not outlast this pandemic, but the need for space and privacy could be permanent.
COVID-19 travelers are flocking to Airbnb, Vrbo: Consumers prefer vacation rentals to hotels amid pandemic. But why?
We're discovering America again
Another permanent travel change: an inward focus when it comes to tourism. In 2020, did we even have a choice? "Travelers who previously would never consider taking a domestic vacation are enjoying exploring destinations close to home," says Kristiana Choquet, a travel agent with EMBARK Beyond . "People are discovering the beauty and wonders of their own countries."
Travel has changed for good. Future travelers will be healthier and safer and will plan their vacations farther in advance. Yes, they'll pay more, but each vacation will also be an adventure.
"The next incarnation of tourism is on the way," says Richard Bangs, the chief adventure officer for Steller , a travel-inspired storytelling platform. "As we go out and redefine how we experience the world – with our senses re-attuned, our situational awareness reengaged – let it bring awakenings and inventions, the way we travelers have always risen to the greatest challenges."
Beyond 2020: Tips for the future of travel
Prepare for travel change . If you haven't traveled since the pandemic, get ready for a few changes. You'll have to learn to use those new self-service kiosks and touchless room keys. (Don't be afraid to ask for help.) Authorities will enforce mask and social distancing rules. It's the new normal.
Plan ahead. Whether you're booking your vacation or buying travel insurance, you'll want to give yourself plenty of preparation time in 2021 and beyond. Waiting until the last minute may mean you don't qualify for certain coverages or even that you can't travel because of paperwork requirements. Do everything in advance – everything.
If you find a deal, book it. Experts predict travel companies will try to raise their fares and prices quickly to recover lost revenue. The fire sales of late 2020 will almost certainly give way to higher rates. So if you see a deal now, don't wait.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
A Year Without Travel
How Bad Was 2020 for Tourism? Look at the Numbers.
The dramatic effects of the coronavirus pandemic on the travel industry and beyond are made clear in six charts.

By Stephen Hiltner and Lalena Fisher
Numbers alone cannot capture the scope of the losses that have mounted in the wake of the coronavirus pandemic. Data sets are crude tools for plumbing the depth of human suffering , or the immensity of our collective grief .
But numbers can help us comprehend the scale of certain losses — particularly in the travel industry , which in 2020 experienced a staggering collapse.
Around the world, international arrivals are estimated to have dropped to 381 million in 2020, down from 1.461 billion in 2019 — a 74 percent decline . In countries whose economies are heavily reliant on tourism , the precipitous drop in visitors was, and remains, devastating.
According to recent figures from the United Nations World Tourism Organization, the decline in international travel in 2020 resulted in an estimated loss of $1.3 trillion in global export revenues. As the agency notes, this figure is more than 11 times the loss that occurred in 2009 as a result of the global economic crisis.
The following charts — which address changes in international arrivals, emissions, air travel, the cruise industry and car travel — offer a broad overview of the effects of the coronavirus pandemic within the travel industry and beyond.
International arrivals in tourism-dependent economies

Macau, a top gambling destination, is highly dependent on travelers, as measured by the share
of its G.D.P. that is generated by tourism. Its international visitor numbers plummeted in 2020:
ARRIVALS IN 2020
The following countries are also among the world’s most dependent on travel, in terms of both their
G.D.P. and their international tourism receipts as a percent of total exports:
U.S. Virgin Islands
The Bahamas
Antigua and Barbuda
Saint Lucia
Cook Islands
0.5 million

Macau, a gambling destination, is dependent on travelers,
as measured by the share of its G.D.P. that is generated by
tourism. Its international visitor numbers plummeted in 2020:
The following countries are also among the world’s most
dependent on travel, in terms of both their G.D.P. and their
international tourism receipts as a percent of total exports:
Before the pandemic, tourism accounted for one out of every 10 jobs around the world. In many places, though, travel plays an even greater role in the local economy.
Consider the Maldives, where in recent years international tourism has accounted for around two-thirds of the country’s G.D.P. , when considering direct and indirect contributions.
As lockdowns fell into place worldwide, international arrivals in the Maldives plunged; from April through September of 2020, they were down 97 percent compared to the same period in 2019. Throughout all of 2020, arrivals were down by more than 67 percent compared with 2019. (Arrival numbers slowly improved after the country reopened in July; the government, eager to promote tourism and mitigate losses, lured travelers with marketing campaigns and even courted influencers with paid junkets .)
Similar developments played out in places such as Macau, Aruba and the Bahamas: shutdowns in February and March, followed by incremental increases later in the year.
The economic effect of travel-related declines has been stunning. In Macau, for example, the G.D.P. contracted by more than 50 percent in 2020.
And the effects could be long-lasting; in some areas, travel is not expected to return to pre-pandemic levels until 2024.
Travelers passing through T.S.A. airport security checkpoints

The pandemic upended commercial aviation. One way to visualize the effect of lockdowns on air travel is to consider the number of passengers screened on a daily basis at Transportation Security Administration checkpoints.
Traveler screenings plunged in March before hitting a low point on April 14, when 87,534 passengers were screened — a 96 percent decline as compared with the same date in 2019.
Numbers have risen relatively steadily since then, though today the screening figures still sit at less than half of what they were a year earlier.
According to the International Air Transport Association, an airline trade group, global passenger traffic in 2020 fell by 65.9 percent as compared to 2019, the largest year-on-year decline in aviation history.
Daily carbon dioxide emissions from aviation

3.0 million metric tons

Another way to visualize the drop-off in air travel last year is to consider the amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) emitted by aircraft around the world.
According to figures from Carbon Monitor , an international initiative that provides estimates of daily CO2 emissions, worldwide emissions from aviation fell by nearly 50 percent last year — to around 500 million metric tons of CO2, down from around 1 billion metric tons in 2019. (Those numbers are expected to rebound, though the timing will depend largely on how long corporate and international travel remain sidelined .)
All told, CO2 emissions from fossil fuels dropped by 2.6 billion metric tons in 2020, a 7 percent reduction from 2019, driven in large part by transportation declines.
Yearly revenues of three of the biggest cruise lines

$20 billion
ROYAL CARIBBEAN

Few industries played as central and public a role in the early months of the coronavirus pandemic as did the major cruise lines — beginning with the outbreak aboard the Diamond Princess .
In a scathing rebuke of the industry issued in July, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention blamed cruise companies for widespread transmission of the virus, pointing to 99 outbreaks aboard 123 cruise ships in U.S. waters alone.
While precise passenger data for 2020 is not yet available, the publicly disclosed revenues — which include ticket sales and onboard purchases — from three of the largest cruise lines offer a dramatic narrative: strong revenues in the early months of 2020, followed by a steep decline.
Third-quarter revenues for Carnival Corporation, the industry’s biggest player, showed a year-to-year decline of 99.5 percent — to $31 million in 2020, down from $6.5 billion in 2019.
The outlook remains bleak for the early months of 2021: For now, most cruise lines have canceled all sailings into May or June.
Long-distance car travel, before and during the pandemic

Driving trips at least 50 miles from home, with stays of two hours or more, based on a daily index from
mobile location data.

Trips at least 50 miles from home, with stays of two hours
or more, based on a daily index from mobile location data.
Air travel, both international and domestic, was markedly curtailed by the pandemic. But how was car travel affected?
One way to measure the change is to look at the Daily Travel Index compiled by Arrivalist , a company that uses mobile location data to measure consumer road trips of 50 miles or more in all 50 U.S. states.
The figures tell the story of a rebound that’s slightly stronger than that of air travel: a sharp drop in March and April, as state and local restrictions fell into place , followed by a gradual rise to around 80 percent of 2019 levels.
Difference in visits to four popular national parks, 2019 to 2020

1.0 MILLION
GREAT SMOKY
GRAND CANYON
CUYAHOGA VALLEY
YELLOWSTONE

1.0 million
Another way to consider car travel in 2020 — and domestic travel in the U.S. more broadly — is to look at the visitation numbers for America’s national parks.
Over all, national park visitation decreased by 28 percent in 2020 — to 237 million visitors, down from 327.5 million in 2019, largely because of temporary park closures and pandemic-related capacity restrictions.
The caveat, though, is that several parks saw record numbers of visitors in the second half of the year, as a wave of travel-starved tourists began looking for safe and responsible forms of recreation.
Consider the figures for recreational visits at Yellowstone National Park. After a shutdown in April, monthly visitation at the park quickly rose above 2019 levels. The months of September and October of 2020 were both the busiest on record, with numbers in October surpassing the previous monthly record by 43 percent .
Some national parks located near cities served as convenient recreational escapes throughout the pandemic. At Cuyahoga Valley National Park, 2020 numbers exceeded 2019 numbers from March through December. At Great Smoky Mountains National Park, numbers surged after a 46-day closure in the spring and partial closures through August; between June and December, the park saw one million additional visits compared to the same time period in 2019.
Stephen Hiltner is an editor on the Travel desk. You can follow his work on Instagram and Twitter . More about Stephen Hiltner
Come Sail Away
Love them or hate them, cruises can provide a unique perspective on travel..
Cruise Ship Surprises: Here are five unexpected features on ships , some of which you hopefully won’t discover on your own.
Icon of the Seas: Our reporter joined thousands of passengers on the inaugural sailing of Royal Caribbean’s Icon of the Seas . The most surprising thing she found? Some actual peace and quiet .
Th ree-Year Cruise, Unraveled: The Life at Sea cruise was supposed to be the ultimate bucket-list experience : 382 port calls over 1,095 days. Here’s why those who signed up are seeking fraud charges instead.
TikTok’s Favorite New ‘Reality Show’: People on social media have turned the unwitting passengers of a nine-month world cruise into “cast members” overnight.
Dipping Their Toes: Younger generations of travelers are venturing onto ships for the first time . Many are saving money.
Cult Cruisers: These devoted cruise fanatics, most of them retirees, have one main goal: to almost never touch dry land .
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Data Descriptor
- Open access
- Published: 23 September 2021
A database of travel-related behaviors and attitudes before, during, and after COVID-19 in the United States
- Rishabh Singh Chauhan ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7188-557X 1 ,
- Matthew Wigginton Bhagat-Conway ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1210-2982 2 ,
- Denise Capasso da Silva ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-1414-8439 3 ,
- Deborah Salon ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-2240-8408 2 ,
- Ali Shamshiripour 1 ,
- Ehsan Rahimi ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8649-7542 1 ,
- Sara Khoeini 3 ,
- Abolfazl (Kouros) Mohammadian ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3595-3664 1 ,
- Sybil Derrible ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-2939-6016 1 &
- Ram Pendyala 3
Scientific Data volume 8 , Article number: 245 ( 2021 ) Cite this article
8663 Accesses
13 Citations
2 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Interdisciplinary studies
- Research data
The COVID-19 pandemic has impacted billions of people around the world. To capture some of these impacts in the United States, we are conducting a nationwide longitudinal survey collecting information about activity and travel-related behaviors and attitudes before, during, and after the COVID-19 pandemic. The survey questions cover a wide range of topics including commuting, daily travel, air travel, working from home, online learning, shopping, and risk perception, along with attitudinal, socioeconomic, and demographic information. The survey is deployed over multiple waves to the same respondents to monitor how behaviors and attitudes evolve over time. Version 1.0 of the survey contains 8,723 responses that are publicly available. This article details the methodology adopted for the collection, cleaning, and processing of the data. In addition, the data are weighted to be representative of national and regional demographics. This survey dataset can aid researchers, policymakers, businesses, and government agencies in understanding both the extent of behavioral shifts and the likelihood that changes in behaviors will persist after COVID-19.
Machine-accessible metadata file describing the reported data: https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.15141945
Similar content being viewed by others
Worldwide divergence of values

Interviews in the social sciences
Persistent interaction patterns across social media platforms and over time
Background & summary.
The COVID-19 pandemic has spread across the world, infecting tens of millions and killing over one million people 1 . By March 2021, the United States (U.S.) had recorded the highest number of confirmed COVID-19 cases and COVID-19 related deaths in the world 1 . Since social distancing is one of the most effective measures in containing the spread of the infection 2 , several U.S. states issued various restrictions including stay at home orders. Moreover, numerous restaurants and bars closed for dine-in services, various recreation facilities were shut down, many offices and schools switched from meeting in-person to meeting online, and travel restrictions were imposed. These measures had a profound impact on how people in the U.S. went about their daily lives.
To understand the current and future impacts of the pandemic, we conducted a nationwide online survey. The goal of the survey is to capture attitudes and shifts in travel-related choices of people across the nation both during the pandemic and once COVID-19 is no longer a threat. The data are shared publicly in order to help government agencies and businesses prepare for the future. We are conducting additional survey waves with the same respondents to monitor how people’s choices evolve over the course of the pandemic and beyond.
An early version of the survey took place from April to June 2020, when the stay at home orders were in place in most parts of the country 3 , 4 ; this portion of the data collection is referenced as Wave 1 A . A slightly-modified larger-scale survey, Wave 1B ,was deployed between late June and October 2020. Subsequent survey waves are being conducted as the situation evolves. The collected data are released as they become available and necessary procedures for cleaning, documenting, and weighting the data are completed. This procedures for data processing are detailed in this paper. The present article focuses on data from the first wave of the survey.
In the months following the beginning of the spread of COVID-19, several efforts have been made to collect data related to COVID-19. In fact, many datasets have been compiled, specifically on COVID-19 testing 5 , medical imaging of COVID-19 cases 6 , the timeline of government interventions 7 , policy announcements 8 , implementation and relaxation of public health and social measures 9 , epidemiological data 10 , mobility-related data 11 , and out-of-home activity information 12 , to name a few. Researchers also turned to social media platforms, like Twitter and Instagram, to gather COVID-19-related data 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 . Furthermore, several surveys have been conducted to measure the impacts of the pandemic 17 , 18 , 19 , some of which are now released for public use 20 , 21 .
Our survey data are different from most others in several ways. First, it is comprehensive insofar as it includes data about a wide range of topics including commuting, daily travel, air travel, working from home, online learning, shopping, attitudes, risk perception, and socioeconomic and demographic details. Second, it captures detailed information about behaviors before and during the COVID-19 pandemic, as well as the choices that people expect to make when the COVID-19 virus is no longer a threat. Third, it was collected from respondents across the U.S., covering diverse socio-economic backgrounds, professions, education levels, and ages. Fourth, the survey is a true longitudinal panel survey, collecting data in multiple waves from the same individuals at regular intervals. Finally, the data are made publicly available to promote data-driven analysis and research.
The next section describes the data collection methodology, the questions included in the survey, the survey deployment process, and the participant recruitment strategy. Next, the data records section describes the data file types and metadata. Subsequently, the technical validation section explains the procedure for the survey data cleaning and weighting. Lastly, the final section provides additional notes for data users.
Ethical compliance
Our study protocol was approved by both Arizona State University (ASU) and University of Illinois at Chicago (UIC) Institutional Review Board offices. Participants were informed that their participation is voluntary, and that their responses are shared anonymously. An online informed consent was obtained from everyone who responded to the survey.
Survey questions
The data were collected through an extensive online survey with over 120 questions. The survey questions can be broadly divided into three categories: (1) retrospective questions focusing on the period before COVID-19, (2) questions about the period during COVID-19, and (3) prospective questions on respondent expectations for a future period in which COVID-19 is no longer a threat. The questions cover a wide variety of subjects including commuting habits, discretionary travel choices, work-related questions, study-related questions, shopping, dining, and so on – all before, during, and expected after the pandemic.
The survey questions can be classified into eight categories based on question subject type, namely: demographics, work, study, shopping and dining, transportation, and general attitudes. Table 1 describes each of these categories.
Survey recruitment
From April to mid-June 2020, initial Wave 1A responses were collected from a convenience sample via mailing lists, social media outreach, and mainstream media articles. A total of 1,110 responses were collected during this phase.
From late June onward, Wave 1B, the modified version of the survey, was deployed through survey invitations sent to a random email list purchased from a data marketing company. The list contained 350,000 email addresses belonging to people in 24 metropolitan areas across the U.S., as well as the state of Ohio (see Fig. 1 ). We purchased 100,000 additional email addresses of people randomly selected from across the country, including rural areas and excluding the areas covered by the first 350,000 emails. A total of 1,116 responses were received from the email list. Unfortunately, major email service providers quickly began marking our survey invitations as spam, while some smaller providers did not. While we took several steps to mitigate this issue, including changing the wording of the emails, changing the source of the emails (a uic.edu, asu.edu, or covidfuture.org email address), we were ultimately not able to fully solve this problem and saw a lower response rate from individuals with addresses from major email providers.
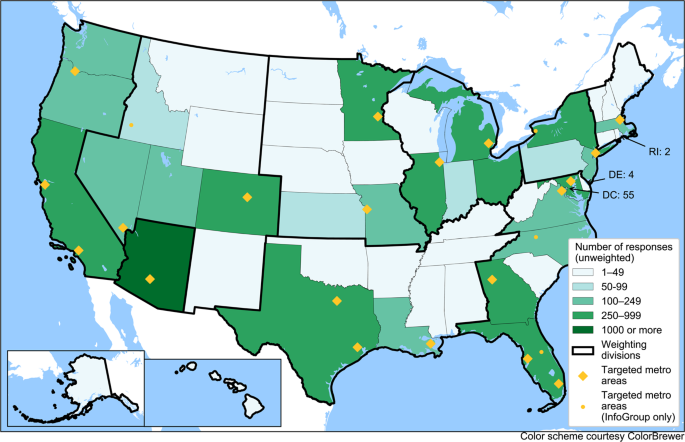
Distribution of survey respondents by the state of residence for survey dataset version 1.0. Alaska and Hawai’i are in the same weighting division as California, Oregon, and Washington.
Survey invitation emails were also sent to an additional list of approximately 39,000 email addresses from the Phoenix metropolitan area purchased for a previous survey effort 22 . This list yielded 782 responses. The survey invitation emails were sent using Amazon Web Services (AWS) and through the Qualtrics platform. Every 20 th respondent who was invited through the purchased email addresses received a $10 incentive as a gift card. Respondents also had the option to donate their survey incentive to a charity. Invitees received two reminders as part of efforts to maximize response rates.
An additional 5,250 responses to the Wave 1B survey were collected through a Qualtrics Online Panel. Qualtrics recruits these respondents from a variety of panels maintained by other firms and uses quota sampling to recruit respondents that are demographically representative of the nation. The Qualtrics quotas were set to collect information from 20 U.S. metropolitan areas, mostly consistent with the metropolitan areas sampled from the purchased email list, as well as the states of Ohio, Utah, North Carolina, upstate New York, and rural areas. In order to obtain samples that would represent the population in each of the selected geographies, quotas were imposed in the Qualtrics online panel subsample to guarantee representation based on income, age, race and ethnicity, and education. We requested all respondents to provide their email addresses in order to recontact them for subsequent survey waves. Since the Qualtrics respondents are professional survey takers, we designated most questions as mandatory, and we included attention check questions, which are shown to improve response quality 23 .
The distribution of responses by geography, as well as the targeted metropolitan areas, are shown in Fig. 1 . Figure 2 shows the distribution of responses by recruitment method, available in the “org” variable in the dataset. The geographical targets were chosen based on geographic and metropolitan area size diversity, as well as the state of the virus spread in May 2020.
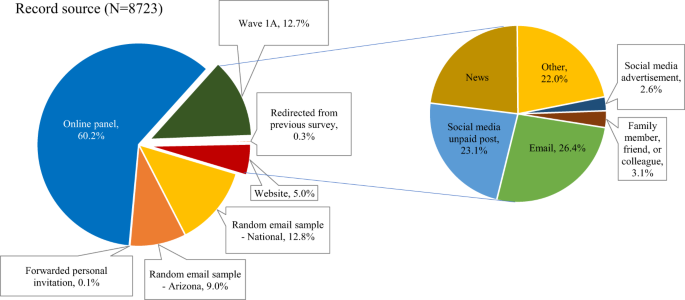
Distribution of Record by Source (from the survey dataset version 1.0).
Figure 1 shows the distribution of survey respondents across the U.S. (50 states and the District of Columbia). Following our recruitment strategy, a greater number of responses come from larger and more urban states. Arizona is overrepresented due to the oversample of Arizona respondents in the email-based deployment. The respondents from the initial Wave 1A sample are also more likely to hail from Arizona as the Arizona State University survey team’s network is heavily Arizona-based. When the data are weighted, any geographic discrepancies at the census division level are controlled and overrepresentation of Arizona is controlled/corrected separately.

Additional survey waves
To monitor how people’s attitudes and behaviors evolve, survey respondents are contacted again with at least two shorter follow-up surveys, approximately four months apart in spring and fall 2021.
Data Records
The survey dataset 24 can be accessed from the ASU Dataverse at: https://doi.org/10.48349/ASU/QO7BTC . The dataset is available in CSV (comma-separated value) format. Since the data will be updated periodically, the data are versioned—in this article, results from the survey dataset version 1.0 are reported. The dataverse also contains the database codebook containing the metadata and explaining the variables. The codebook contains a changelog for each new version.
The respondents to Waves 1A and 1B received similar but not identical surveys. We have merged the responses to these two versions of the survey into the final dataset wherever possible. For some variables, the questions were identical, whereas for other variables, harmonization of similar responses was required. In the dataset, variables ending in ‘_harm’ are harmonized between the two datasets, variables ending in ‘_w1a’ are available only for Wave 1A respondents, variables ending in ‘_w1b’ are available only for respondents from our Qualtrics Online Panel, purchased email lists, and anyone who found the survey via the COVIDFuture web site or email lists after June 19, 2020 (start date of Wave 1B). Variables with no suffix were asked the same way between the two surveys, and no harmonization was necessary. We also provide a file containing only Wave 1B responses and variables, which simplifies analysis of the Wave 1B data.
Technical Validation
Data cleaning.
To monitor respondents’ attention to survey questions in the Qualtrics online panel, attention check questions were included. Respondents were allowed to miss one attention check and be given an opportunity to answer that section again. If they missed an attention check twice, or both attention checks once, their survey was terminated.
We additionally undertook several quality checks to help ensure that the collected data were valid. We removed any respondents who reported that they shop for groceries both in-store and online every day, or expect to after the pandemic, as these are likely to be invalid responses. We also removed respondents who reported strongly agreeing or strongly disagreeing with all COVID-related attitudes, as some of these were worded positively and some negatively. Several additional quality checks were undertaken in the Qualtrics Online Panel as part of Qualtrics’ data cleaning process, including a check for people finishing the survey too quickly.
Respondents that did not report a state of residence, reported living outside the 50 states and the District of Columbia, or did not provide answers to all of the control variables used in the data weighting process described in the next section were removed from the data. Due to this restriction, 558 records with missing control variable information, 59 records with missing home location, and one response from Puerto Rico were not included in the final dataset encompassing responses received through October 14, 2020. Further steps in data preparation will include imputation of missing data, which will allow for some of these omitted records to be recovered in the next version of the dataset. Among the respondents who were not included in the dataset due to missing control variable information, there are 34 respondents who declared their gender as Other; these respondents could not be included because the Census offers no control marginals to weight these records. Further data weighting procedures will attempt to incorporate non-binary gendered individuals on the dataset. Due to the data cleaning and filtering process applied to responses obtained through October 14, 2020, a total of 618 records were not included in the published dataset.
Data weighting
Because the raw data are not fully representative of the U.S. population, weights were calculated using the following control variables: age, education, gender, Hispanic status, household income, presence of children, and number of household vehicles. The weighting procedure accounts for the true population characteristics at the person level. Household-level variables (i.e., income, presence of children, and number of vehicles) were controlled at the person level as well. For example, the marginal distribution used for presence of children refers to the share of adults aged 18 years and older living in household with children, instead of the share of households that have children as it is usually represented. Those marginal distributions were computed using data from the Integrated Public Use Microdata Sample and the American Community Survey (ACS) 2018 1-year data 25 using the sample 18 and older in each of the weighting region boundaries. A noteworthy consequence of this approach is that adjusted household weights are necessary to evaluate household-level characteristics since individuals from larger households are more likely to be represented in the survey (given there are more individuals in these households), and thus have a higher probability of being selected. Weights for household-level analysis can be computed by dividing the person-level weight (provided in the data) by the number of adults in the household.
The national sample was divided into nine regions based on the reported home state (Table 2 ). Each region’s sample was then weighted to match the distributions observed in ACS 2018 1-year estimates 25 , meaning that the survey is demographically representative at the level of each region as well as the entire U.S. The unweighted and weighted survey results are shown in Table 3 ; the weighted results closely replicate population distributions, with inevitable minor deviations on variables that were not controlled in the weighting process.
Weights were calculated using iterative proportional fitting (IPF) procedures embedded within the synthetic population generator PopGen2.0 26 , 27 , 28 . Univariate marginal control distributions were derived from the Integrated Public Use Microdata Sample, American Community Survey (ACS) 2018 1-year data 25 .
Usage Notes
Since the survey will be followed by at least two follow-up survey waves, the database will be updated periodically after the data for each wave is collected, cleaned, and weighted. Each version of the data will be uploaded to the ASU Dataverse and assigned a new DOI number, and all previous versions will remain available to promote reproducibility.
The weights were developed to produce a sample that is representative of the U.S. population, as well as representative of nine divisions within the U.S.: eight census regions (with East and West South Central combined due to small samples in these regions), and a separate category for Arizona due to its large number of respondents. The weights are not guaranteed to produce a representative sample for other (smaller) geographies. When evaluating subsamples at a finer geography (e.g., state or metropolitan area), data users should compare marginal distributions of key demographic variables with the census, and re-weight the data if needed to be representative of the area being analyzed.
Some questions differ between Waves 1A and 1B. Therefore, we have weighted the dataset twice: once including all respondents (Waves 1A and 1B), and once excluding respondents to the Wave 1A sample. Data users should use the Wave 1B weights whenever using variables that are not present in the convenience sample. Since Wave 1A data deviates significantly in terms of population representativeness 4 , there are no weights for questions asked only of Wave 1A respondents. In the file with only Wave 1B responses, only Wave 1B weights are presented.
This unique dataset provides insights on attitudes and behaviors not just before and during pandemic, but also on what might be expected after the pandemic. Possible use cases include modeling of during-pandemic and longer-term changes in mode use, air travel, transit ridership, work from home, and traffic congestion (especially for peak period traffic planning). Published uses of this dataset are documented in Capasso da Silva et al . 29 , Chauhan et al . 30 , Mirtich et al . 31 , and Salon et al . 32 .
Code availability
No codes were developed for this research.
COVID-19 Map. Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html (2020).
CDC. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/social-distancing.html (2020).
Shamshiripour, A., Rahimi, E., Shabanpour, R. & Mohammadian, A. K. How is COVID-19 reshaping activity-travel behavior? Evidence from a comprehensive survey in Chicago. Transp. Res. Interdiscip. Perspect. 7 , 100216 (2020).
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Conway, M. W., Salon, D., da Silva, D. C. & Mirtich, L. How will the COVID-19 pandemic affect the future of urban life? Early evidence from highly-educated respondents in the United States. Urban Sci. 4 , 50 (2020).
Article Google Scholar
Hasell, J. et al . A cross-country database of COVID-19 testing. Sci. Data 7 , 1–7 (2020).
Kalkreuth, R. & Kaufmann, P. COVID-19: a survey on public medical imaging data resources. ArXiv Prepr. ArXiv200404569 (2020).
Desvars-Larrive, A. et al . A structured open dataset of government interventions in response to COVID-19. medRxiv (2020).
Cheng, C., Barceló, J., Hartnett, A. S., Kubinec, R. & Messerschmidt, L. Covid-19 government response event dataset (coronanet v. 1.0). Nat. Hum. Behav. 4 , 756–768 (2020).
Zheng, Q. et al . HIT-COVID, a global database tracking public health interventions to COVID-19. Sci. Data 7 , 1–8 (2020).
Xu, B. et al . Epidemiological data from the COVID-19 outbreak, real-time case information. Sci. Data 7 , 1–6 (2020).
Pepe, E. et al . COVID-19 outbreak response, a dataset to assess mobility changes in Italy following national lockdown. Sci. Data 7 , 1–7 (2020).
Killeen, B. D. et al . A County-level dataset for informing the United States’ response to COVID-19. ArXiv Prepr. ArXiv200400756 (2020).
Chen, E., Lerman, K. & Ferrara, E. Tracking social media discourse about the COVID-19 pandemic: Development of a public coronavirus Twitter data set. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 6 , e19273 (2020).
Zarei, K., Farahbakhsh, R., Crespi, N. & Tyson, G. A first Instagram dataset on COVID-19. ArXiv Prepr. ArXiv200412226 (2020).
Alqurashi, S., Alhindi, A. & Alanazi, E. Large arabic twitter dataset on covid-19. ArXiv Prepr. ArXiv200404315 (2020).
Lopez, C. E., Vasu, M. & Gallemore, C. Understanding the perception of COVID-19 policies by mining a multilanguage Twitter dataset. ArXiv Prepr. ArXiv200310359 (2020).
Gensler. US Work from home survey 2020. Gensler-US-Work-From-Home-Survey-2020-Briefing-1.pdf (2020).
Kleinberg, B., van der Vegt, I. & Mozes, M. Measuring emotions in the covid-19 real world worry dataset. ArXiv Prepr. ArXiv200404225 (2020).
Grashuis, J., Skevas, T. & Segovia, M. S. Grocery shopping preferences during the COVID-19 pandemic. Sustainability 12 , 5369 (2020).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Shuja, J., Alanazi, E., Alasmary, W. & Alashaikh, A. Covid-19 open source data sets: A comprehensive survey. Appl. Intell . 1–30 (2020).
Trung, T. et al . Dataset of Vietnamese student’s learning habits during COVID-19. Data Brief 105682 (2020).
Khoeini, S. et al . Attitudes Towards Emerging Mobility Options and Technologies – Phase 2: Pilot and Full Survey Deployment . https://tomnet-utc.engineering.asu.edu/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/TOMNET-Year-2-Project-Report-All-Universities_-Attitudes-Towards-Mobility-Options-Technologies.pdf (2019).
Shamon, H. & Berning, C. Attention check items and instructions in online surveys: Boon or bane for data quality? Surv. Res. Methods Forthcom . (2019).
Salon, D. et al . COVID Future Wave 1 Survey Data v1.0.0. ASU Library Research Data Repository https://doi.org/10.48349/ASU/QO7BTC (2020).
Ruggles, S. et al . IPUMS USA: Version 10.0 Minneapolis, MN: IPUMS https://doi.org/10.18128/D010.V10.0 (2020).
PopGen. MARG - Mobility Analytics Research Group https://www.mobilityanalytics.org/popgen.html (2020).
Ye, X., Konduri, K., Pendyala, R. M., Sana, B. & Waddell, P. A methodology to match distributions of both household and person attributes in the generation of synthetic populations. In 88th Annual Meeting of the Transportation Research Board, Washington, DC (2009).
Konduri, K. C., You, D., Garikapati, V. M. & Pendyala, R. M. Enhanced synthetic population generator that accommodates control variables at multiple geographic resolutions. Transp. Res. Rec. 2563 , 40–50 (2016).
Capasso da Silva, D. et al . How are attitudes toward COVID-19 associated with traveler behavior during the pandemic? Findings https://doi.org/10.32866/001c.24389 (2021).
Chauhan, R. S. et al . COVID-19 related attitudes and risk perceptions across urban, rural, and suburban areas in the United States. Findings https://doi.org/10.32866/001c.23714 (2021).
Mirtich, L. et al . How stable are transport-related attitudes over time? Findings https://doi.org/10.32866/001c.24556 (2021).
Salon, D. et al . The potential stickiness of pandemic-induced behavior changes in the United States. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 118 (27), e2106499118, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2106499118 (2021).
Download references
Acknowledgements
This research was supported in part by the National Science Foundation (NSF) RAPID program under grants no. 2030156 and 2029962 and by the Center for Teaching Old Models New Tricks (TOMNET), a University Transportation Center sponsored by the U.S. Department of Transportation through grant no. 69A3551747116, as well as by the Knowledge Exchange for Resilience at Arizona State University. This COVID-19 Working Group effort was also supported by the NSF-funded Social Science Extreme Events Research (SSEER) network and the CONVERGE facility at the Natural Hazards Center at the University of Colorado Boulder (NSF Award #1841338) and the NSF CAREER award under grant no. 155173. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the funders.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Civil, Materials, and Environmental Engineering, University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, IL, USA
Rishabh Singh Chauhan, Ali Shamshiripour, Ehsan Rahimi, Abolfazl (Kouros) Mohammadian & Sybil Derrible
School of Geographical Sciences and Urban Planning, Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ, USA
Matthew Wigginton Bhagat-Conway & Deborah Salon
School of Sustainable Engineering and the Built Environment, Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ, USA
Denise Capasso da Silva, Sara Khoeini & Ram Pendyala
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
R.P., A.M., S.D., D.S. and S.K. planned the project. D.S., M.C., D.C.S., R.C., E.R. and A.M. prepared the survey questions. M.C., D.C.S. and D.S. designed the survey flow logic. R.C., D.C.S., M.C., D.S. and S.D. deployed the survey. M.C. and D.C.S. performed data cleaning and survey data analysis. D.C.S. weighted the dataset. M.C. and D.S. worked on sending out the incentives to the selected respondents. R.C. prepared the first draft. All the authors made significant contributions to manuscript editing and approving the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Rishabh Singh Chauhan .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ applies to the metadata files associated with this article.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Chauhan, R.S., Bhagat-Conway, M.W., Capasso da Silva, D. et al. A database of travel-related behaviors and attitudes before, during, and after COVID-19 in the United States. Sci Data 8 , 245 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-021-01020-8
Download citation
Received : 14 December 2020
Accepted : 29 July 2021
Published : 23 September 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-021-01020-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
Covid future panel survey: a unique public dataset documenting how u.s. residents’ travel-related choices changed during the covid-19 pandemic.
- R. S. Chauhan
- M. Bhagat-Conway
Transportation (2024)
Response willingness in consecutive travel surveys: an investigation based on the National Household Travel Survey using a sample selection model
- F. Atiyya Shaw
- Kari E. Watkins
Transportation (2023)
Tracking the state and behavior of people in response to COVID-19 through the fusion of multiple longitudinal data streams
- Mohamed Amine Bouzaghrane
- Hassan Obeid
- Joan Walker
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

COVID-19 international travel advisories
If you plan to visit the U.S., you do not need to be tested or vaccinated for COVID-19. U.S. citizens going abroad, check with the Department of State for travel advisories.
COVID-19 testing and vaccine rules for entering the U.S.
- As of May 12, 2023, noncitizen nonimmigrant visitors to the U.S. arriving by air or arriving by land or sea no longer need to show proof of being fully vaccinated against COVID-19.
- As of June 12, 2022, people entering the U.S. no longer need to show proof of a negative COVID-19 test .
U.S. citizens traveling to a country outside the U.S.
Find country-specific COVID-19 travel rules from the Department of State.
See the CDC's COVID-19 guidance for safer international travel.
LAST UPDATED: December 6, 2023
Have a question?
Ask a real person any government-related question for free. They will get you the answer or let you know where to find it.
This is the impact of COVID-19 on the travel sector

A full recovery of the global tourism sector isn't expected until 2024. Image: UNSPLASH/Eva Darron

.chakra .wef-9dduvl{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-9dduvl{font-size:1.125rem;}} Explore and monitor how .chakra .wef-15eoq1r{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;color:#F7DB5E;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-15eoq1r{font-size:1.125rem;}} COVID-19 is affecting economies, industries and global issues

.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;color:#2846F8;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{font-size:1.125rem;}} Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:.
- The tourism sector is one of the worst affected by the impacts of COVID-19.
- International arrivals have increased by just 4% in the second year of the pandemic; with 1 billion fewer arrivals when compared to pre-pandemic levels.
- 63% of experts from the World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) believe the sector won't fully recover until 2024.
While few industries have been spared by the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, even fewer have been hit as hard as the tourism sector . As 2021 drew to a close with severe limitations to travel still in place, the World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) reported that international tourist arrivals increased by just 4 percent last year, remaining 72 percent below 2019 levels. That equates to more than 1 billion fewer international arrivals compared to pre-pandemic levels, keeping the industry at levels last seen in the late 1980s.
Prior to the coronavirus outbreak, the global tourism sector had seen almost uninterrupted growth for decades. Since 1980, the number of international arrivals skyrocketed from 277 million to nearly 1.5 billion in 2019. As our chart shows, the two largest crises of the past decades, the SARS epidemic of 2003 and the global financial crisis of 2009, were minor bumps in the road compared to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Looking ahead, most experts no longer expect a full recovery until until 2024 or later. While the UNWTO Panel of Experts is confident to see an uptick in travel activity this year, just 4 percent of the surveyed experts expect a full recovery in 2022. Roughly one third of respondents believe that international arrivals will return to pre-pandemic levels in 2023, while 63 percent think it will take even longer than that. UNWTO scenarios predict that international tourist arrivals could grow between 30 and 78 percent in 2022 compared to 2021. While that sounds like a significant improvement, it would still be more than 50 percent below pre-pandemic levels.
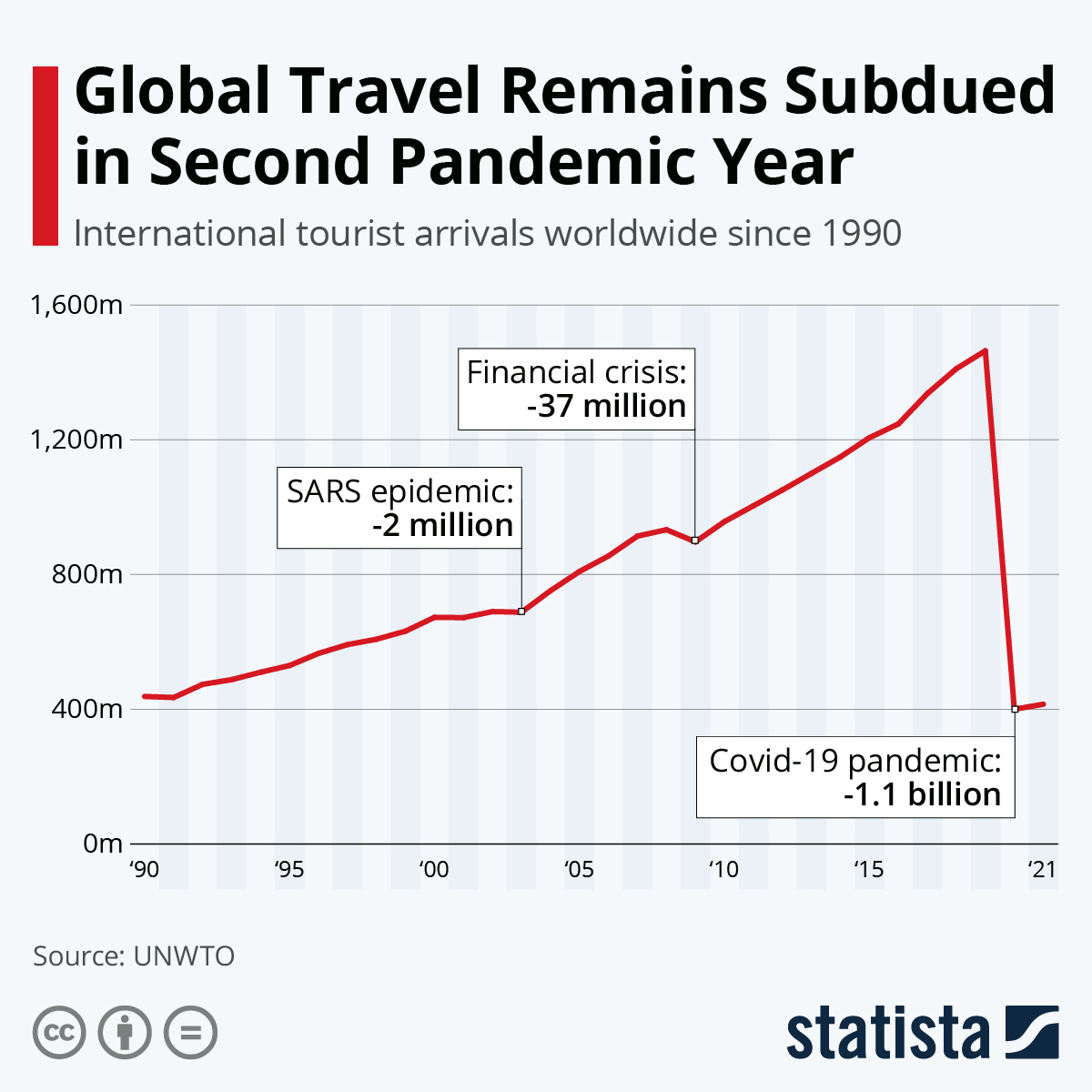
Have you read?
.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} business travel won’t be more sustainable post-covid unless companies take action, a travel boom is looming. but is the industry ready, how virtual tourism can rebuild travel for a post-pandemic world, don't miss any update on this topic.
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The agenda .chakra .wef-n7bacu{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-weight:400;} weekly.
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
.chakra .wef-1dtnjt5{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;} More on Health and Healthcare Systems .chakra .wef-17xejub{-webkit-flex:1;-ms-flex:1;flex:1;justify-self:stretch;-webkit-align-self:stretch;-ms-flex-item-align:stretch;align-self:stretch;} .chakra .wef-nr1rr4{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;white-space:normal;vertical-align:middle;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:0.75rem;border-radius:0.25rem;font-weight:700;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;line-height:1.2;-webkit-letter-spacing:1.25px;-moz-letter-spacing:1.25px;-ms-letter-spacing:1.25px;letter-spacing:1.25px;background:none;padding:0px;color:#B3B3B3;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;box-decoration-break:clone;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;}@media screen and (min-width:37.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:0.875rem;}}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:1rem;}} See all

Market failures cause antibiotic resistance. Here's how to address them
Katherine Klemperer and Anthony McDonnell
April 25, 2024

Equitable healthcare is the industry's north star. Here's how AI can get us there
Vincenzo Ventricelli

Bird flu spread a ‘great concern’, plus other top health stories
Shyam Bishen
April 24, 2024

This Earth Day we consider the impact of climate change on human health
Shyam Bishen and Annika Green
April 22, 2024

Scientists have invented a method to break down 'forever chemicals' in our drinking water. Here’s how
Johnny Wood
April 17, 2024

Young people are becoming unhappier, a new report finds
Free webinar May 9: How to spot and stop a scam. Sign up now.
AARP daily Crossword Puzzle
Hotels with AARP discounts
Life Insurance
AARP Dental Insurance Plans
AARP MEMBERSHIP — $12 FOR YOUR FIRST YEAR WHEN YOU SIGN UP FOR AUTOMATIC RENEWAL
Get instant access to members-only products and hundreds of discounts, a free second membership, and a subscription to AARP the Magazine.
- right_container
Work & Jobs
Social Security
AARP en Español
- Membership & Benefits
- AARP Rewards
- AARP Rewards %{points}%
Conditions & Treatments
Drugs & Supplements
Health Care & Coverage
Health Benefits

Staying Fit
Your Personalized Guide to Fitness

AARP Hearing Center
Ways To Improve Your Hearing

Brain Health Resources
Tools and Explainers on Brain Health

A Retreat For Those Struggling
Scams & Fraud
Personal Finance
Money Benefits
View and Report Scams in Your Area

AARP Foundation Tax-Aide
Free Tax Preparation Assistance

AARP Money Map
Get Your Finances Back on Track

How to Protect What You Collect
Small Business
Age Discrimination

Flexible Work
Freelance Jobs You Can Do From Home

AARP Skills Builder
Online Courses to Boost Your Career

31 Great Ways to Boost Your Career

ON-DEMAND WEBINARS
Tips to Enhance Your Job Search

Get More out of Your Benefits

When to Start Taking Social Security

10 Top Social Security FAQs

Social Security Benefits Calculator

Medicare Made Easy
Original vs. Medicare Advantage

Enrollment Guide
Step-by-Step Tool for First-Timers

Prescription Drugs
9 Biggest Changes Under New Rx Law

Medicare FAQs
Quick Answers to Your Top Questions
Care at Home
Financial & Legal
Life Balance

LONG-TERM CARE
Understanding Basics of LTC Insurance

State Guides
Assistance and Services in Your Area

Prepare to Care Guides
How to Develop a Caregiving Plan

End of Life
How to Cope With Grief, Loss
Recently Played
Word & Trivia
Atari® & Retro
Members Only
Staying Sharp
Mobile Apps
More About Games

Right Again! Trivia

Right Again! Trivia – Sports

Atari® Video Games

Throwback Thursday Crossword
Travel Tips
Vacation Ideas
Destinations
Travel Benefits

Beach vacation ideas
Vacations for Sun and Fun

Plan Ahead for Tourist Taxes

AARP City Guide
Discover Seattle

25 Ways to Save on Your Vacation
Entertainment & Style
Family & Relationships
Personal Tech
Home & Living
Celebrities
Beauty & Style

TV for Grownups
Best Reality TV Shows for Grownups

Robert De Niro Reflects on His Life

Looking Back
50 World Changers Turning 50

Sex & Dating
Spice Up Your Love Life
Navigate All Kinds of Connections

Life & Home
Couple Creates Their Forever Home

Store Medical Records on Your Phone?

Maximize the Life of Your Phone Battery

Virtual Community Center
Join Free Tech Help Events

Create a Hygge Haven

Soups to Comfort Your Soul

Your Ultimate Guide to Mulching
Driver Safety
Maintenance & Safety
Trends & Technology

AARP Smart Guide
How to Keep Your Car Running

We Need To Talk
Assess Your Loved One's Driving Skills

AARP Smart Driver Course

Building Resilience in Difficult Times

Tips for Finding Your Calm

Weight Loss After 50 Challenge

Cautionary Tales of Today's Biggest Scams

7 Top Podcasts for Armchair Travelers

Jean Chatzky: ‘Closing the Savings Gap’

Quick Digest of Today's Top News

AARP Top Tips for Navigating Life

Get Moving With Our Workout Series
You are now leaving AARP.org and going to a website that is not operated by AARP. A different privacy policy and terms of service will apply.
Go to Series Main Page
Should You Plan Travel as the Pandemic Continues?
Some opt for 'trip stacking,' while weighing covid-19 health risks at destinations around the world.

Americans were finally starting to vacation and visit loved ones again last summer, both domestically and internationally, but the recent surge in the omicron variant and continued COVID-19 spikes have led to new travel restrictions and added fear and uncertainty about travel. Cities, states and countries are introducing rules that seem to change almost daily, as do U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) travel advisories and the agency’s roster of “high risk” destinations. What hasn't changed: The CDC continues to advise against travel unless you are fully vaccinated . (You are considered fully vaccinated two weeks after receiving the second dose of either the Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna vaccine, or the one-dose Johnson & Johnson vaccine.)
On the plus side, global vaccination levels continue to increase, and airlines, cruise ships, hotels and tour companies have introduced infection prevention measures, some quite stringent. But children under 5 still can’t get vaccinated, adding anxiety to family travel that includes young kids, while the enforcement (or even existence) of health protocols varies widely by location.

AARP Membership — $12 for your first year when you sign up for Automatic Renewal
Given this uncertainty, is now the right time to travel or even plan a vacation?
We asked travel industry and health experts to weigh in on the subject.
Evaluating travel's risks vs. rewards
“Travel now is a matter of balancing risks with benefits,” says Paul Holtom, M.D., infectious diseases specialist and chief epidemiologist at the LAC+USC Medical Center in Los Angeles. “I agree there is a mental health and wellness benefit to travel, but there are inherent risks as well, with seniors in a higher risk group. If you want to travel, you should do everything you can to reduce those risks.”
And everyone's risk tolerance is different, says Joost Schreve, chief executive officer of the Boulder, Colorado-based travel service company kimkim. “The decision of whether or not to travel is a personal choice that mostly depends on your health risk profile and willingness to deal with potential logistical challenges,” he notes.
Some travelers are, if not throwing caution out the window, taking a carpe diem attitude toward travel, says Jack Ezon, founder of Embark Beyond, a New York-based travel agency specializing in the luxury market. “Most of our clients have recognized from the past two years that you only live once. With the right precautions, they value their freedom to travel, to explore and most of all to connect with the world. And right now there are great values and most places aren’t overcrowded,” adds Ezon, communicating while on vacation with his family in South Africa. “While omicron of course poses challenges, we actually took advantage of the public fear and were able to get prime space at some of the most sought-after lodges in South Africa.”
The most obvious way to dramatically lower your risk: Get vaccinated for COVID-19, including a booster shot. But even vaccinated people face some risk of getting a breakthrough infection of COVID-19 while traveling. “While it’s unlikely that a vaccinated person contracts COVID, it’s not impossible,” Holtom cautions, particularly in light of the recent surge in breakthrough cases (where vaccinated people are becoming infected). “These cases will more likely be mild or asymptomatic, but given testing requirements to return to the U.S., this still means you’ll have to quarantine for two weeks in a foreign country [if traveling abroad]. And if you should happen to suffer another type of serious illness or injury while traveling, you’ll have to use local health care facilities that may be substandard or overburdened from COVID patients.”
In terms of timing, Holtom says that “historically we’ve seen a virus surge in winter with lower temperatures and increased indoor gatherings. But none of us have a crystal ball; we really don’t know what’s coming.”
Given the uncertainly of virus trends and travel restrictions, reducing the risk for travel now comes down to being as well-informed as possible about your destination and modes of travel, as well as your own health — both physical and mental. You won’t benefit from the soothing benefits of travel if you’re stressed the entire time, says Schreve: “While traveling, you’ll find yourself in airports and other places that can get crowded. If you’re uncomfortable with those kinds of situations in your hometown, traveling now might not be ideal for you. But if you’re living a fairly normal life at the moment, we’ve found that most of our travelers have had no issues and in many cases enjoyed a relative lack of crowds since many places have fewer visitors.”
ARTICLE CONTINUES AFTER ADVERTISEMENT
Traveling within the U.S.
Domestic U.S. travel, particularly travel by car, has enjoyed great popularity during the pandemic, allowing Americans to avoid confusing border restrictions, as well as crowded airplanes. There are are varying restrictions within the U.S., however. Hawaii has particularly strict rules about vaccination and testing for visitors, requiring enrollment in the Hawaii Safe Travels program, and a five-day quarantine for those who don’t meet requirements. Los Angeles County and Las Vegas are among the jurisdictions that require everyone to wear masks in indoor public areas, and Washington, D.C., and New York City require customers to show proof of COVID-19 vaccination to enter restaurants and other venues.
If you're considering a trip in the U.S., Holtom recommends researching the COVID-19 status at your destination, while many cities and counties continue to experience dramatic spikes in infection rates. And think about where you're least likely to become infected, according to the CDC: outside. That's likely why road trips to outdoor destinations such as the U.S. national parks have been receiving record numbers of visitors. Many travelers have also been turning to home rentals, where, unlike at a hotel, travelers generally don't need to interact with anyone outside their group. Last summer, available short-term rentals grew scarce at popular beach destinations like Wisconsin's Door County and Cape Cod, Massachusetts, which saw a more than 30 percent increase in home-rental demand compared with the pre-pandemic summer of 2019, according to online rental giant VRBO.
AARP® Dental Insurance Plan administered by Delta Dental Insurance Company
Dental insurance plans for members and their families
Traveling to other countries
Any international travel right now requires careful planning, including checking the CDC's COVID-19-related warnings for international destinations. The agency currently lists more than 100 countries and territories as “Very High Risk — avoid travel," with dozens more considered “High Risk.” (You can check its color-coded map .) Travelers should also check recommendations from the State Department, which may have stronger warnings for certain countries, often due to factors other than COVID-19, plus any advisories from the U.S. embassy in the country you're planning to visit. And, of course, you need to stay on top of your destination's entry rules, which vary widely by country and can change quickly.
Then there are rules for coming back into the U.S.: All travelers — regardless of vaccination status or nationality — arriving from international locations need to show proof of a negative COVID-19 test taken within one day of their flight to the U.S. (Until recently, fully vaccinated U.S. travelers could offer tests taken within three days of their flight home.) The CDC also continues to advise all U.S. travelers to get tested for COVID-19 three to five days after arriving back in the country and to watch for symptoms.
Plenty of Americans are heading overseas, despite the regulations and omicron, however. “We have seen a surge in new short-term international booking requests, up 83 percent this January," says Ezon. For those planning to travel internationally, Ezon, who caters to a high-end clientele, has these recommendations: “First, make sure the place you are going to allows you to quarantine in a luxury hotel or resort and not a government facility [in case you test positive for COVID-19]. Second, make sure the locale has good medical facilities, in case you need more help, and, three, always be sure to take travel insurance that includes medical evacuation insurance.”
You also can reduce the risk and stress of international travel with strategic planning that lowers your risk of complications and, possibly, COVID-19 infection, Schreve says, such as booking direct flights to avoid the additional exposure to crowds and potential snafus that can come with connecting flights.
Matt Berna, the California-based managing director for Intrepid Travel North America, suggests an outdoorsy vacation as a good option for international travelers in the age of COVID-19. Intrepid’s hikes through the Italian Dolomites and around Mont Blanc in France have been popular, as well as the lesser-known Rota Vicentina along the Portuguese coast.
Even in countries the CDC labels “high risk,” all-inclusive resorts can provide safe havens, says Joshua Bush, chief executive officer of Avenue Two Travel in Bryn Mawr, Pennsylvania. “Lots of resorts in the Caribbean and Los Cabos, for example, offer a feeling of security with on-site testing and by containing guests while still offering plenty to do so that the vacation experience isn’t hindered. Travel agencies partnering with the large luxury brands usually have inventory and access to great value-added amenities to defray costs.”
The cruise industry has been hit hard over over the past two years, with early pandemic-era stories of massive outbreaks on ships and long-term quarantines at sea. All of the big cruise lines have vaccine requirements and new shipboard health protocols in place, but the recent omicron surge has caused yet another series of cruise cancellations, COVID-19 outbreaks onboard, and ports refusing ships’ entry.
The CDC, meanwhile, is clear on its current recommendations for cruising: Don't do it. Earlier this month it raised its warning level for cruising to Level 4 (Do Not Travel) "regardless of vaccination status." The agency states, "It is especially important that travelers who are at increased risk of severe illness from COVID-19 avoid travel on cruise ships. The chance of getting COVID-19 on cruise ships is high because the virus spreads easily between people in close quarters aboard ships.”
It also says that even those passengers who are fully vaccinated should get a COVID-19 viral test one to three days before departure, and three to five days after their trip.
Perhaps not surprisingly, Bob Levinstein, chief executive officer of Iowa-based Cruise Compete, still calls cruises a great travel choice now, going so far as to label cruising “the safest vacation out there.” Levinstein adds that “cruise ships have an advantage over other modes of travel in that they have total control over their environment and rules.” He cites cruise lines’ strict new vaccine and testing requirements and their newly installed shipboard air filtration devices. “And if you do get sick on board,” he says, “every ship has trained medical staff on call and COVID tests readily available. You’re not going to have that in any other type of travel.”
But, regardless of your risk tolerance, a cruise vacation is currently vulnerable to disruption, as passengers continue to test positive on ships, warns Gene Sloan, cruise writer for The Points Guy. Your cruise “might miss a port call or two, as some ports are turning ships away due to COVID worries or adding new COVID-related requirements that make it more difficult for ships to visit," he notes. For example, multiple Caribbean ports recently instituted temporary bans or tight restrictions for cruise ship visits. Shore excursions may be limited, and itineraries may change mid-cruise. "There’s also the relatively small chance that [passengers] could get quarantined on a ship,” Sloan adds.
Planning far ahead? Both Levinstein and Sloan agree this could be a great time to book cruises with departures several months or even a year or two away, as long as you are able to keep your plans flexible. There are some great deals out there," Levinstein says, "and cruise lines have introduced generous cancellation policies.”
Holtom does not consider cruising a safe option when it comes to infection avoidance, however — pandemic or no. “It would be hard for me to ever get on a cruise ship, even without coronavirus, given other shipboard outbreaks like norovirus,” he says. “Cruise ships have an inherently higher risk of disease spread given their setup with large groups in confined indoor spaces.”
Considering the 'travel stacking' strategy
One increasingly popular way to manage travel uncertainty and improve flexibility: trip stacking. “It’s a strategy employed by those who don’t want to be disappointed if a trip cancels or they have narrow travel windows. By booking multiple trips for the same date, they’re guaranteed one of them,” Bush says. “The challenge is to know the terms and conditions of that trip inside and out and to not be stuck in a financial penalty when you cancel or change the timing on one of them.”
Ezon is seeing the same thing at Embark Beyond. “We have many clients trip stacking in order to ensure they can get somewhere over a certain time frame. As a travel agency, we try to negotiate very liberal cancellation penalties to avoid losing money,” he says.
What everyone seems to agree on: With the continued uncertainty in travel, booking trips with any sort of lead time is going to require evaluating your personal risk tolerance and staying flexible. And whether your strategy is trip stacking or simply having a tentative “plan B,” you should confirm a trip only with careful consideration of cancellation policies and an awareness of the latest health situation and COVID-19 restrictions at your planned destination.
Bill Fink is an award-winning travel writer who has covered cultural travel for Lonely Planet, Frommer's, The San Francisco Chronicle and many other outlets.
Editor's note: This article was originally published on September 29, 2021. It's been updated to reflect new information.
Bill Fink is an award-winning travel writer who has covered cultural travel for Lonely Planet , Frommer’ s, the San Francisco Chronicle and many other outlets.
More on travel

Current Airline Policies During COVID-19 Pandemic

The Battle Over 5G Cell Service and Air Travel Safety

The Latest TSA Security Procedures During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Or Call: 1-800-675-4318
Enter a valid from location
Enter a valid to location
Enter a valid departing date
Enter a valid returning date
Age of children:
Child under 2 must either sit in laps or in seats:
+ Add Another Flight
Enter a valid destination location
Enter a valid checking in date
Enter a valid checking out date
Occupants of Room
Occupants of Room 1:
Occupants of Room 2:
Occupants of Room 3:
Occupants of Room 4:
Occupants of Room 5:
Occupants of Room 6:
Occupants of Room 7:
Occupants of Room 8:
Enter a valid date
You didn't specify child's age
There are children in room 1 without an adult
You didn't specify child's age for room 1
There are children in room 2 without an adult
You didn't specify child's age in room 2
There are children in room 3 without an adult
You didn't specify child's age in room 3
There are children in room 4 without an adult
You didn't specify child's age in room 4
There are children in room 5 without an adult
You didn't specify child's age in room 5
You have more than 6 people total
Please select a trip duration less than 28 days
There must be at least 1 traveler (age 12+) for each infant in a lap
Enter a valid From location
Enter a valid start date
Enter a valid drop location
Enter a valid drop off date
Select a valid to location
Select a month
Enter a valid going to location
Enter a valid from date
Enter a valid to date
AARP VALUE &
MEMBER BENEFITS

Denny's
15% off dine-in and pickup orders

AARP Travel Center Powered by Expedia: Vacation Packages
$50 gift card of your choice when booking any flight package

$20 off a Walmart+ annual membership

AARP® Staying Sharp®
Activities, recipes, challenges and more with full access to AARP Staying Sharp®
SAVE MONEY WITH THESE LIMITED-TIME OFFERS

Interactive visualization requires JavaScript
Related research and data
- COVID-19: International and Domestic Travel
- Policy Responses to the Coronavirus Pandemic
- Are children eligible for COVID-19 vaccination?
- Biweekly change in confirmed COVID-19 cases
- Biweekly change in confirmed COVID-19 deaths
- Biweekly confirmed COVID-19 cases
- Biweekly confirmed COVID-19 cases per million people
- Biweekly confirmed COVID-19 deaths
- Biweekly confirmed COVID-19 deaths per million people
- COVID-19 Containment and Health Index
- COVID-19 testing policies
- COVID-19 vaccination policy
- COVID-19 vaccinations vs. COVID-19 deaths
- COVID-19 vaccine boosters administered
- COVID-19 vaccine boosters administered per 100 people
- COVID-19 vaccine doses administered by manufacturer
- COVID-19 vaccine doses administered per 100 people, by income group
- COVID-19 vaccine doses donated to COVAX
- COVID-19 vaccine doses donated to COVAX, per capita
- COVID-19 vaccine doses donated to COVAX, per dose administered
- COVID-19 vaccine doses donated to COVAX, per million dollars of GDP
- COVID-19: Daily tests vs. daily new confirmed cases
- COVID-19: Daily tests vs. daily new confirmed cases per million
- COVID-19: Where are the world's unvaccinated people?
- Cancellation of public events during COVID-19 pandemic
- Chile: COVID-19 weekly death rate by vaccination status
- Confirmed COVID-19 deaths per million vs. GDP per capita
- Cumulative confirmed COVID-19 cases and deaths
- Cumulative confirmed COVID-19 cases by world region By Region
- Cumulative confirmed COVID-19 deaths by world region
- Cumulative confirmed COVID-19 deaths vs. cases
- Daily COVID-19 tests
- Daily COVID-19 tests per 1,000 people Rolling 7-day average
- Daily COVID-19 vaccine doses administered
- Daily and total confirmed COVID-19 deaths
- Daily confirmed COVID-19 cases by world region Stacked area chart – by world region
- Daily confirmed COVID-19 deaths by world region
- Daily new confirmed COVID-19 cases and deaths
- Daily new confirmed COVID-19 deaths in Sweden
- Daily new estimated COVID-19 infections from the ICL model
- Daily new estimated COVID-19 infections from the IHME model
- Daily new estimated COVID-19 infections from the LSHTM model
- Daily new estimated COVID-19 infections from the YYG model
- Daily new estimated infections of COVID-19
- Daily share of the population receiving a COVID-19 vaccine dose
- Daily vs. total confirmed COVID-19 cases per million people
- Debt or contract relief during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Economic decline in the second quarter of 2020
- Economic decline in the second quarter of 2020 vs. confirmed COVID-19 cases per million people
- Economic decline in the second quarter of 2020 vs. total confirmed COVID-19 deaths (as of August 2020)
- England: COVID-19 monthly death rate by vaccination status
- Estimated cumulative excess deaths during COVID Faceted Explorer version
- Estimated cumulative excess deaths during COVID, from the WHO
- Estimated cumulative excess deaths during COVID-19 Non-Explorer, single-entity version
- Estimated cumulative excess deaths per 100,000 people during COVID, from The Economist
- Estimated cumulative excess deaths, from The Economist and the WHO
- Estimated daily excess deaths during COVID Faceted Explorer version
- Estimated daily excess deaths during COVID Non-Explorer, single-entity version
- Estimated daily excess deaths per 100,000 people during COVID, from The Economist
- Excess mortality: Cumulative deaths from all causes compared to projection based on previous years Absolute deaths
- Excess mortality: Cumulative deaths from all causes compared to projection based on previous years Percentage
- Excess mortality: Cumulative deaths from all causes compared to projection based on previous years, per million people
- Excess mortality: Deaths from all causes compared to average over previous years P-scores, average baseline
- Excess mortality: Deaths from all causes compared to average over previous years, by age P-scores, average baseline
- Excess mortality: Deaths from all causes compared to projection P-scores, projected baseline
- Excess mortality: Deaths from all causes compared to projection based on previous years, by age P-scores, projected baseline
- Excess mortality: Raw number of deaths from all causes compared to projection based on previous years Raw death counts, stacked years
- Excess mortality: Raw number of deaths from all causes compared to projection based on previous years Raw death counts, extended series
- Face covering policies during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Grocery and pharmacy stores: How did the number of visitors change relative to before the pandemic?
- How did the number of visitors change since the beginning of the pandemic?
- How do key COVID-19 metrics compare to the early 2021 peak in Israel?
- How do key COVID-19 metrics compare to the early 2021 peak in Spain?
- How do key COVID-19 metrics compare to the early 2021 peak?
- Income support during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Number of COVID-19 patients in ICU per million
- Number of COVID-19 patients in hospital
- Number of COVID-19 patients in hospital per million
- Number of COVID-19 patients in intensive care (ICU)
- Number of people who completed the initial COVID-19 vaccination protocol
- Parks and outdoor spaces: How did the number of visitors change relative to before the pandemic?
- Public information campaigns on the COVID-19 pandemic
- Public transport closures during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Residential areas: How did the time spent at home change relative to before the pandemic?
- Restrictions on internal movement during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Restrictions on public gatherings in the COVID-19 pandemic
- Retail and recreation: How did the number of visitors change relative to before the pandemic?
- SARS-CoV-2 sequences by variant
- SARS-CoV-2 variants in analyzed sequences
- School closures during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Share of SARS-CoV-2 sequences that are the delta variant
- Share of SARS-CoV-2 sequences that are the omicron variant
- Share of global daily COVID-19 vaccine doses administered as boosters
- Share of people who completed the initial COVID-19 vaccination protocol
- Share of people who completed the initial COVID-19 vaccination protocol by age
- Share of people who received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine Line chart
- Share of people with a COVID-19 booster dose by age
- Share of people with at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine by age
- Share of total COVID-19 tests that were positive
- Stay-at-home requirements during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Sweden: Daily new confirmed COVID-19 deaths, by date of death
- Switzerland: COVID-19 weekly death rate by vaccination status
- Tests and new confirmed COVID-19 cases per day
- Tests conducted per new confirmed case of COVID-19
- The share of COVID-19 tests that are positive
- Total COVID-19 tests Line chart
- Total COVID-19 tests conducted vs. confirmed cases
- Total COVID-19 tests conducted vs. confirmed cases per million
- Total COVID-19 tests per 1,000 people Line chart
- Total COVID-19 tests per 1,000 vs. GDP per capita
- Total COVID-19 tests per confirmed case Bar chart
- Total COVID-19 vaccine doses administered
- Total COVID-19 vaccine doses administered per 100 people
- Total confirmed COVID-19 cases vs. deaths per million
- Total confirmed COVID-19 cases, by source
- Total confirmed COVID-19 deaths and cases per million people
- Total confirmed deaths due to COVID-19 vs. population
- Total confirmed deaths from COVID-19, by source
- Total number of people who received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine
- Transit stations: How did the number of visitors change relative to before the pandemic?
- UK: Cumulative confirmed COVID-19 deaths per 100,000
- UK: Daily new confirmed COVID-19 cases
- UK: Daily new confirmed COVID-19 cases per 100,000
- UK: Daily new confirmed COVID-19 deaths
- UK: Daily new hospital admissions for COVID-19
- UK: Number of COVID-19 patients in hospital
- UK: Share of COVID-19 tests that are positive
- US: Daily COVID-19 vaccine doses administered
- US: Daily COVID-19 vaccine doses administered per 100 people
- US: Number of people who completed the initial COVID-19 vaccination protocol
- US: Number of people who received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine
- US: Share of available COVID-19 vaccine doses that have been used
- US: Share of people who completed the initial COVID-19 vaccination protocol
- US: Share of people who received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine
- US: Total COVID-19 vaccine doses administered
- US: Total COVID-19 vaccine doses administered per 100 people
- US: Total COVID-19 vaccine doses distributed
- US: Total COVID-19 vaccine doses distributed per 100 people
- United States: COVID-19 weekly death rate by vaccination status
- Week by week change in confirmed COVID-19 cases
- Week by week change of confirmed COVID-19 deaths
- Weekly confirmed COVID-19 cases
- Weekly confirmed COVID-19 cases per million people
- Weekly confirmed COVID-19 deaths
- Weekly confirmed COVID-19 deaths per million people
- Weekly new ICU admissions for COVID-19
- Weekly new ICU admissions for COVID-19 per million
- Weekly new hospital admissions for COVID-19
- Weekly new hospital admissions for COVID-19 per million
- What is the youngest age group eligible for COVID-19 vaccination?
- Which countries do COVID-19 contact tracing?
- Willingness to get vaccinated against COVID-19 by month
- Workplace closures during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Workplaces: How did the number of visitors change relative to before the pandemic?
Our World in Data is free and accessible for everyone.
Help us do this work by making a donation.
China’s Golden Week Holiday: What’s Driving Outbound Travel
Peden Doma Bhutia , Skift
April 24th, 2024 at 3:30 AM EDT
Understanding what Chinese travelers want is crucial for stakeholders in the tourism industry to tailor offerings and experiences that match these changing preferences.
Peden Doma Bhutia
Destinations in the Middle East are emerging as favorites for China’s upcoming May Day holiday, commonly known as Golden Week.
Overall outbound travel from China during this year’s holiday is still lagging behind 2019 levels by 13%. But travel to the United Arab Emirates (UAE) has surged by 66%, and Turkey has experienced a significant growth of 56%, according to ticket sales data from ForwardKeys.
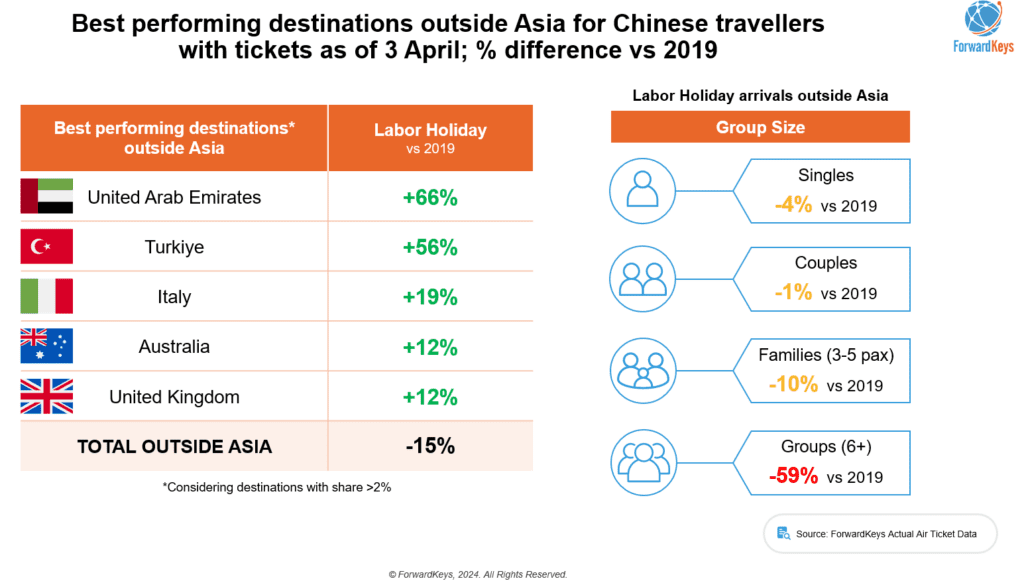
Increased seat capacity from Africa and the Middle East, which is set to expand by 75% in the second quarter, has led to this surge in travel.
Corresponding increases in seat capacity to China have backed the travel growth rates of 56% to Turkey, 19% to Italy, and 12% to the UK.
Last month, Trip.com, China’s biggest online travel agency, announced record bookings in Abu Dhabi, exceeding 57,000 room nights over the past 12 months. From 2022 to 2023, outbound travel orders across all products from Chinese travelers to the UAE surged by more than threefold.
Chinese outbound travel to Middle East had already reached pre-pandemic levels during the Chinese New Year period in February.
Pre-Pandemic Travel Patterns
ForwardKeys anticipates that the May holiday will witness notable travel peaks around April 27 and May 1, closely resembling pre-pandemic travel patterns.
In the Asian region, Malaysia has emerged as the top-performing destination for Chinese travelers, with flight bookings currently 42% ahead of 2019 levels. Because of more lenient visa policies, including visa-free travel to Malaysia and Singapore, and streamlined procedures for South Korea, travel to these destinations is expected to surpass 2019 levels in May.
These findings align with insights from Dragon Trail’s Chinese Traveler Sentiment Report , releasing later on Wednesday. According to the report, visa-free policies, direct flights, and simplified application procedures are also making outbound travel more appealing and accessible.
According to ForwardKeys, a notable shift in passenger profiles is the decrease in group travellers, which has dropped by 53% compared to 2019 levels. In contrast, solo travellers are showing a strong interest in exploring Asian destinations, with a 9% increase.
The Dragon Trail report also highlights growing preference for independent travel among Chinese tourists. Travelers also prefer, semi-self-guided travel and boutique groups of 6-10 people, which offer flexibility and convenience.
Value-Oriented Approach
Along with flexibility and convenience, Chinese travelers are also seeking relaxation and comfort in their trips.
Amidst the challenges posed by the Covid-19 pandemic and China’s economic downturn in 2023, Chinese travelers are prioritizing relaxation and comfort in their trips.
The economic pressures have led to a value-oriented approach to travel planning, with a majority carefully considering their spending to maximize value and opting for affordable travel options.
Around 20% of respondents who said they would not travel outbound in 2024 cite limited income as a barrier. Only a small percentage (11%) are willing to pay a premium for superior products and services.
Most travelers allocate less than 20% of their income for travel, with budgets typically ranging from RMB10,000 to RMB30,000 for upcoming trips.
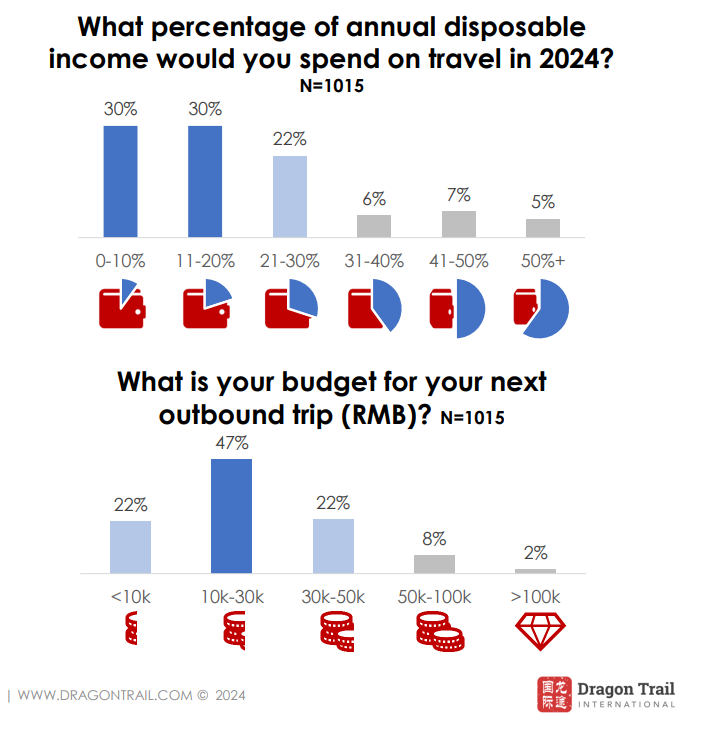
Despite budget-consciousness, shopping remains an integral part of outbound travel, with more than two-thirds of travelers spending a minimum of RMB2,000 (US$276) per trip. Local foods and souvenirs are the primary shopping categories, followed by cosmetics, clothing, shoes and bags.
The Daily Newsletter
Our daily coverage of the global travel industry. Written by editors and analysts from across Skift’s brands.
Have a confidential tip for Skift? Get in touch
Tags: asia monthly , budget travel , china , china outbound , golden week , middle east , shopping , turkey , uae
Photo credit: Overall outbound travel from China during this year's May holiday is 13% behind 2019. Florence Lo / Reuters
Every product is independently selected by (obsessive) editors. Things you buy through our links may earn us a commission.
What I Can't Live Without
- What Joey Fatone Can’t Live Without What Joey Fatone Can’t Live Without
- What Chanel Iman Can’t Live Without What Chanel Iman Can’t Live Without
- What Author Young Kim Can’t Live Without What Author Young Kim Can’t Live Without
- What Todd Selby Can’t Live Without What Todd Selby Can’t Live Without
- What Smokey Robinson Can’t Live Without What Smokey Robinson Can’t Live Without
- What DJ Khaled Can’t Live Without What DJ Khaled Can’t Live Without
- What Myha’la Herrold Can’t Live Without What Myha’la Herrold Can’t Live Without
- What Jimmy Butler Can’t Live Without What Jimmy Butler Can’t Live Without
- What Rachel Antonoff (Still) Can’t Live Without What Rachel Antonoff (Still) Can’t Live…
- What Simu Liu Can’t Live Without What Simu Liu Can’t Live Without
- What Jena Malone Can’t Live Without What Jena Malone Can’t Live Without
- What Waxahatchee Can’t Live Without What Waxahatchee Can’t Live Without
- What Steve Aoki (Still) Can’t Live Without What Steve Aoki (Still) Can’t Live Witho…
- What June Diane Raphael Can’t Live Without What June Diane Raphael Can’t Live Witho…
- What Leslie Bibb Can’t Live Without What Leslie Bibb Can’t Live Without
- What JJ Johnson Can’t Live Without What JJ Johnson Can’t Live Without
- What Ashlee Simpson and Evan Ross Can’t Live Without What Ashlee Simpson and Evan Ross Can’t…
- What Miss Fame Can’t Live Without What Miss Fame Can’t Live Without
- What Rapper Tierra Whack Can’t Live Without What Rapper Tierra Whack Can’t Live With…
- What Tailor Rich Fresh Can’t Live Without What Tailor Rich Fresh Can’t Live Withou…
- What Musician Andrew McMahon Can’t Live Without What Musician Andrew McMahon Can’t Live…
- What PIN-UP Magazine’s Felix Burrichter Can’t Live Without What PIN-UP Magazine’s Felix Burrichter…
- What Kyle Kuzma of the Washington Wizards Can’t Live Without What Kyle Kuzma of the Washington Wizard…
- What Sean Paul Can’t Live Without What Sean Paul Can’t Live Without
- What Performer Todrick Hall Can’t Live Without What Performer Todrick Hall Can’t Live W…
- What Activist Dr. Akilah Cadet Can’t Live Without What Activist Dr. Akilah Cadet Can’t Liv…
- What Musician Angélique Kidjo Can’t Live Without What Musician Angélique Kidjo Can’t Live…
- What Photographer Catherine Opie Can’t Live Without What Photographer Catherine Opie Can’t L…
- What Ray McGuire Can’t Live Without What Ray McGuire Can’t Live Without
- What Curtis Sliwa Can’t Live Without What Curtis Sliwa Can’t Live Without
- What Kathryn Garcia Can’t Live Without What Kathryn Garcia Can’t Live Without
- What Dianne Morales Can’t Live Without What Dianne Morales Can’t Live Without
- What Fernando Mateo Can’t Live Without What Fernando Mateo Can’t Live Without
- What Scott Stringer Can’t Live Without What Scott Stringer Can’t Live Without
- What Shaun Donovan Can’t Live Without What Shaun Donovan Can’t Live Without
- What 10 New York City Mayoral Candidates Can’t Live Without What 10 New York City Mayoral Candidates…
- What Andrew Yang Can’t Live Without What Andrew Yang Can’t Live Without
- What Florist Ryan Norville Can’t Live Without What Florist Ryan Norville Can’t Live Wi…
- What Curator Larry Ossei-Mensah Can’t Live Without What Curator Larry Ossei-Mensah Can’t Li…
- What Miguel Can’t Live Without What Miguel Can’t Live Without
- What Model-Musician Shaun Ross Can’t Live Without What Model-Musician Shaun Ross Can’t Liv…
- What Astrologer Susan Miller Can’t Live Without What Astrologer Susan Miller Can’t Live…
- What Actress Ryan Destiny Can’t Live Without What Actress Ryan Destiny Can’t Live Wit…
- What Artist Shantell Martin Can’t Live Without What Artist Shantell Martin Can’t Live W…
- What Chef Kwame Onwuachi Can’t Live Without What Chef Kwame Onwuachi Can’t Live With…
- What Actor Emile Hirsch Can’t Live Without What Actor Emile Hirsch Can’t Live Witho…
- What Singer Michael Bublé Can’t Live Without What Singer Michael Bublé Can’t Live Wit…
- What Rapper Big Freedia Can’t Live Without What Rapper Big Freedia Can’t Live Witho…
- What Hike Clerb’s Evelynn Escobar-Thomas Can’t Live Without What Hike Clerb’s Evelynn Escobar-Thomas…
- What the Glazed NYC Designers Can’t Live Without What the Glazed NYC Designers Can’t Live…
What Joey Fatone Can’t Live Without

If you’re like us, you’ve probably wondered what everyday stuff famous people add to their carts — like hair spray or an electric toothbrush . We talked to singer, actor, and television host Joey Fatone — who recently partnered with Screwball Whiskey — about the gaming console he travels with, his favorite pink sneakers, and the boxer briefs he can’t live without.

A friend of mine actually suggested I try this. She was like, “Trust me. People will like it.” I smelled it and liked it, so I got myself a bottle. I’m not kidding you: I’ve never gotten many compliments with any other cologne I’ve worn. For some odd reason, when I started wearing Creed, people suddenly started asking me, “Hey what is that? You smell really good.” I bought myself the family-size bottle, which is expensive as hell. However, it lasted me for almost two years. I literally just ran out of it the other day and am about to restock.

My dad would say to me, “You always have to have clean underwear .” So it’s essential for me. I prefer boxer briefs. Boxers are very loosey loosey. They’re not the greatest. When I’m dancing around on stage, I want things to be in place so I don’t hurt myself. Stance’s boxer briefs are comfortable, and they have this little pouch, which sounds kind of funny even saying it out loud. And they come in lots of different fun designs, sometimes with cartoon characters on them. Because why not? You can still be a kid as an adult, right?

Speaking of being a kid, this is another thing I don’t really leave home without, even when I’m traveling. God forbid there’s nothing around and I can’t get WiFi, but I can watch movies on it, get on social media, and play video games . I play the heck out of Population , which is kind of like Fortnite . I also play Ghostbusters with my buddies. I haven’t played lately, but sometimes three or four of us get on at the same time, and we bust ghosts. I’m huge with VR. I got hooked on it when it first came out and was still called Oculus.

VocalMist is a necessity, especially when I’m traveling for work. It’s been a real game-changer for me on the tour I’ve been doing with AJ from the Backstreet Boys. It’s like a personal mister or humidifier with saline. It’s this itty-bitty thing that comes in a little case. I’ll use it before the show, during breaks, or even sometimes onstage to help open up my vocal cords. It loosens and warms everything up and lubricates my vocal cords.

My SBs. Nike, obviously, comes out with great sneakers, and I love them a lot. Lately I’ve been on a kick with the SBs, the Dunks. I love all the colors, but I just keep going back to the pink ones with the orange swoosh on it. They’re dope. They’re comfortable. I love ’em.

More shoes. I’ve been traveling lately, so I needed slippers . People wear Crocs and other brands, but I like these Simpsons Adidas ones. They look like clouds and they’re boxy. And they’re comfortable as hell. It’s like I’m actually walking on clouds. I’m also a huge Simpsons fan. Back in the day, NSYNC did an episode on the show. Funnily enough, Adidas did a whole line of Simpsons sneakers, so I have those ones, too. They’re made to look like the house. The front of the shoe is the rug, the tongue of the shoe has the pink wall and frame of the sailboat, and the back has Santa’s Little Helper and Snowball. I’m a sneakerhead. I can’t help it.

I’m not gonna lie. I think I was drunk at one point during the pandemic when I bought this online. When it came in, I was like, Well, is this thing going to work? It is awesome. It’s almost like a little AC unit that cools your bed. You can even travel with it. I mean, you would need a bigger suitcase , but it’s doable. It goes in between the sheets, so it kind of puffs up when you’re lying in bed. The cool thing is that it has a dual sheet, so if your spouse or whoever you’re sleeping next to you wants to be warm and you want it cold, it can adjust the airflow and temperature on each side. It’s a game-changer, especially if you’re a hot person or you heat up like I do. Dropping it down to a cold temp feels amazing.

I am a dork with these theme parks. I can’t help it. A friend of mine actually is a Club 33 member, so he hooked me up with an annual pass for my daughter. And then we love Universal, too. We live in Orlando, Florida, so we can’t live without those passes. For instance, if we want to go somewhere when my kid’s done with school or something, we just take a break and walk around the park. We don’t have to necessarily even go on the rides; it’s just to go out. It’s right in my backyard, so I never leave home without these.

I’m not a huge whiskey person to be completely honest. But, I’m a huge peanut-butter fan. With this, you can’t really taste that it’s whiskey. Screwball came up with this idea to do a take on a Moscow mule called a “PB&G” for the Kentucky Derby. The drink’s the Screwball peanut-butter whiskey with ginger beer, pomegranate juice, and lime juice. At first, I was like, I don’t know about that . But holy crap, it’s fricking amazing.
The Strategist is designed to surface the most useful, expert recommendations for things to buy across the vast e-commerce landscape. Some of our latest conquests include the best acne treatments , rolling luggage , pillows for side sleepers , natural anxiety remedies , and bath towels . We update links when possible, but note that deals can expire and all prices are subject to change.
- what i can't live without
- celebrity shopping
Every product is independently selected by (obsessive) editors. Things you buy through our links may earn us a commission.
Deal of the Day
Micro sales, greatest hits, most viewed stories.
- The 17 Very Best Protein Powders
- All the Best Walking Shoes We’ve Ever Written About
- All of My Friends Have These Trompe l’oeil Sweatpant Jeans
- The Very Best Body Washes
- I Only Packed One Outfit for My Weeklong Vacation
Today’s Top Clicked

- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
Where Americans Are Traveling in 2024: By the Numbers

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
Americans are traveling abroad in droves.
The number of U.S. citizens flying to international destinations reached nearly 6.5 million passengers in March, according to the International Trade Administration. That’s the highest March total in over five years and shows that the post-pandemic “revenge travel” trend is the new normal.
It wasn’t just March, which usually sees a spike in international departures for spring break. In every month of 2024 so far, more Americans left the country than last year and 2019. These trends point to a blockbuster summer for overseas travel.
Nearly half of Americans (45%) plan to travel by air and/or stay in a hotel this summer and expect to spend $3,594 on average, on these expenses, according to a survey of 2,000 U.S. adults, conducted online by The Harris Poll and commissioned by NerdWallet.
That's despite rising travel prices that have caused some hesitancy among would-be travelers. About 22% of those choosing not to travel this summer cite inflation making travel too expensive as a reason for staying home, according to the poll.
So where are traveling Americans going? And what does it mean for those looking to avoid crowds of tourists and higher travel prices?
New travel patterns
Nearly every region in the world saw an increase in U.S. visitors in March 2024 compared with March 2023, according to International Trade Administration data. Only the Middle East saw a decline of 9%. Yet not every region saw the same year-over-year bump. U.S. visitors to Asia saw a 33% jump, while Oceania and Central America each saw a 30% increase.
Comparing 2024 with 2023 only tells part of the story, however. The new patterns really emerge when comparing international travel trends to 2019. For example, Central America received 50% more U.S. visitors in March 2024 compared with March 2019. Nearly 1.5 million Americans visited Mexico, up 39% compared with before the pandemic. That’s almost as many visitors as the entire continent of Europe, which has seen a more modest 10% increase since 2019.
Only Canada and Oceania saw fewer visitors in March 2024 than in 2019, suggesting that interest in these locations has not rebounded. Indeed, the trends indicate a kind of tourism inertia from COVID-19 pandemic-era lockdowns: Those destinations that were more open to U.S. visitors during the pandemic, such as Mexico, have remained popular, while those that were closed, such as Australia, have fallen off travelers’ radars.
Price pressures
How these trends play out throughout the rest of the year will depend on a host of factors. Yet, none will likely prove more important than affordability. After months of steadiness, the cost of travel, including airfare, hotels and rental cars, has begun to sneak up again.
About 45% of U.S. travelers say cost is their main consideration when planning their summer vacation, according to a survey of 2,000 Americans by the travel booking platform Skyscanner.
That’s likely to weigh further on U.S. travelers’ appetite for visiting expensive destinations such as Europe, while encouraging travel to budget-friendly countries. It could also depress overall international travel as well, yet so far, Americans seem to be traveling more.
For those looking to avoid crowds while maintaining a budget, Skyscanner travel trends expert Laura Lindsay offered a recommendation many of us might need help finding on a map.
“Albania has been on the radar of travelers looking for something different,” Lindsay said. "Most people have yet to discover it, but flights and tourism infrastructure are in place, and there are fewer crowds in comparison to trending European destinations like Italy, Greece, or Portugal.”
On the flip side, American travelers looking to avoid crowds of compatriots would do well to avoid Japan, which has seen a staggering 50% increase in U.S. tourists between March 2019 and 2024.
How to maximize your rewards
You want a travel credit card that prioritizes what’s important to you. Here are our picks for the best travel credit cards of 2024 , including those best for:
Flexibility, point transfers and a large bonus: Chase Sapphire Preferred® Card
No annual fee: Bank of America® Travel Rewards credit card
Flat-rate travel rewards: Capital One Venture Rewards Credit Card
Bonus travel rewards and high-end perks: Chase Sapphire Reserve®
Luxury perks: The Platinum Card® from American Express
Business travelers: Ink Business Preferred® Credit Card
On a similar note...


Travel costs have soared since the pandemic — with one mode now absurdly expensive
Ay, car-rumba.
A new study shows the cost of travel has skyrocketed since 2019 — with rental car prices far and away the most inflated, compared to pre-COVID.
NerdWallet found that the expense of having your own wheels away from home was a whopping 39.3% higher in March 2024 versus five years ago, in March 2019 — and that’s after an 8.8% decline from March 2023.
The research revealed that Chicago’s O’Hare was the priciest airport for car rentals, with an eye-watering average weekly rate of $671.
Phoenix Sky Harbor International Airport came in second at $598, then Las Vegas’ Harry Reid Airport at $588. Los Angeles International Airport was priced at $568 — just slightly above Seattle-Tacoma International Airport’s $566.
Researchers found Enterprise to be the cheapest and National to be the most expensive.
They also noted that booking in advance was more costly than at the last minute, when rental car companies are now sometimes found offering better deals.
Although rental cars saw the steepest increase, there are plenty of other culprits keeping the cost of hitting the road higher than normal.
Restaurant prices have soared for example, by 29.3% between 2019 to 2024. During the past year alone, they’ve risen 4.2%.
Tickets to plays, movies, and concerts also shot up 22.6% — 5% more than a year ago.
Hotel rooms are far from immune.
Over the five-year period, lodging costs increased by 16.3% . They have risen by 6.7% between February and March of this year.
The biggest shock, however, is that airfare has only increased 2.6% during the past five years.
It is currently down 7.1% from 2023. American and Southwest both announced losses in the first quarter of 2024; Southwest said it will limit hiring and pull out of four airports as a result.

- Skip to content
The Cornell Lab of Ornithology builds the eBird global platform for communities and partners around the world to advance data-driven science, education, and conservation.
Change Region
- News & Resources
- Recent Checklists
- Trip Reports
- Illustrated Checklist
- Hotspot Map
- Rare Bird Alerts
- Printable Checklist
Lockdowns & Less Travel May Have Altered the Behavior of Birds
Available languages.

- Macaulay Library
Ithaca, New York & Winnipeg, Manitoba —Eighty percent of bird species examined in a new study were reported in greater numbers in human-altered habitats during pandemic lockdowns. Researchers compared online eBird observations from the United States and Canada from before and during the pandemic. They focused on areas within about 100 km of urban areas, major roads, and airports. Their findings were just published in the journal Science Advances .
“A lot of species we really care about became more abundant in human landscapes during the pandemic,” says study senior author Nicola Koper at the University of Manitoba, which led the research. “I was blown away by how many species were affected by decreased traffic and activity during lockdowns.”
Reports of Bald Eagles increased in cities with the strongest lockdowns. Ruby-throated Hummingbirds were three times more likely to be reported within a kilometer of airports than before the pandemic. Barn Swallows, a threatened species in Canada, were reported more often within a kilometer of roads than before the pandemic.
A few species decreased their use of human-altered habitat during the pandemic. Red-tailed Hawk reports decreased near roads, perhaps because there was less roadkill when traffic declined. But far more species had increased counts in these human-dominated landscapes.
The authors filtered pandemic and pre-pandemic eBird reports so that the final data sets had the same characteristics, such as location, number of lists, and level of birdwatcher effort.
“We also needed to be aware of the detectability issue,” explains co-author Alison Johnston from the Cornell Lab of Ornithology. “Were species being reported in higher numbers because people could finally hear the birds without all the traffic noise, or was there a real ecological change in the numbers of birds present?”
The study tested whether better detectability might be a factor in the larger bird numbers reported. If it was, the scientists expected that to be more noticeable for smaller birds, which are harder to detect beneath traffic noise. However, effects were noticed across many species, from hawks to hummingbirds, suggesting that the increased numbers were not only caused by increased detectability in the quieter environments.
Vast amounts of data from a likewise vast geographic area were vital for this study. The researchers used more than 4 million eBird observations of 82 bird species from across Canada and the U.S.
“Having so many people in North America and around the world paying attention to nature has been crucial to understanding how wildlife react to our presence,” says lead author Michael Schrimpf, a postdoctoral fellow at the University of Manitoba. “Studies such as this one rely on volunteer birdwatchers, so if you enjoy watching wildlife, there are many projects out there, like eBird and iNaturalist , that can use your help.”
Reference :
Reduced human activity during COVID-19 alters avian land use across North America . Michael B. Schrimpf, Paulson G. Des Brisay, Alison Johnston, Adam C. Smith, Jessica Sánchez-Jasso, Barry G. Robinson, Miyako H. Warrington, Nancy A. Mahony, Andrew G. Horn, Matthew Strimas-Mackey, Lenore Fahrig, Nicola Koper. 2021. Science Advances. DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abf5073.
This study was funded by Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada with in-kind support provided by Environment and Climate Change Canada and the Cornell Lab of Ornithology.
US travel sector faces long wait for China tourism to hit 2019 highs
- Medium Text

Sign up here.
Reporting by Aishwarya Jain in Bengaluru; Editing by Devika Syamnath
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

Brazil's central bank chief said on Friday that the environment of greater uncertainties does not have a mechanical relationship with the conduct of monetary policy, emphasizing that U.S. interest rates are currently a major beacon.

Markets Chevron

Global stocks gain on Big Tech lift; yen slides to fresh 34-yr low
Global stocks were higher on Friday as Big Tech gains lifted Wall Street shares, while Japan's yen hit a fresh 34-year low after the Bank of Japan (BOJ) opted to keep monetary policy loose at its latest meeting.

More From Forbes
Airline industry expected to soar with record summer travel.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
travel bags and passport flight travel traveller
The airline industry is gearing up for what could be a record-breaking summer travel season, if forecasts turn out to be correct. Despite challenges such as the Boeing 737 MAX 9 grounding and aircraft delivery delays, airlines are reporting strong demand and growth, particularly in international markets. For investors, this could be a unique opportunity to gain exposure to a sector that’s poised for takeoff.
Not every carrier has reported results for the March quarter yet, but what I’ve seen has been encouraging. Delta Air Lines reported record quarterly revenue and expects continued strong momentum, targeting earnings of $6 to $7 per share and free cash flow of $3 to $4 billion for the full year. United Airlines, despite a pre-tax loss that’s largely attributed to the MAX 9 grounding, saw a $92 million improvement over the same quarter last year.
“Demand continued to be strong, and we see a record spring and summer travel season with our 11 highest sales says in our history all occurring this calendar year,” Delta CEO Ed Bastian said during the company’s earnings call.
Passenger Figures Off To A Record Start
The big takeaway is that the U.S. economy and air travel remain healthy, with airlines experiencing record numbers of travelers. Checkpoint volumes provided by the Transportation Security Administration (TSA) are off to a record start in 2024, with carriers in the U.S. handling an average of 2.26 million passengers each day, a 5.6% increase over the same period in 2019.
Air passenger volumes exceeded pre-pandemic levels in the first quarter
The Best Romantic Comedy Of The Last Year Just Hit Netflix
Rudy giuliani and mark meadows indicted in arizona fake electors case, tupac shakur s estate challenges drake over ai vocals in kendrick lamar diss song.
This bodes well for the industry, as higher passenger volumes translate to increased revenue and potentially better margins.
International Travel Boom Despite Supply Constraints
International travel is driving the recovery, with U.S.-international air travel rising 15% year-over-year in the first three months of 2024, according to Airlines for America (A4A). This trend is also reflected in the latest data from Airports Council International (ACI), which shows that while domestic airport markets grew over 20% in 2023, international markets drove the recovery with a 36.5% growth rate.
The airline industry is not without its challenges. The global airline industry is facing a summer squeeze as travel demand is expected to surpass pre-pandemic levels while aircraft deliveries drop sharply due to production problems at Boeing and Airbus. Airlines are spending billions on repairs to keep flying older, less fuel-efficient jets and paying a premium to secure aircraft from lessors. This has led to increased costs and could potentially impact margins in the short term.
Why Airline Stocks Could Soar In The Coming Years
Nevertheless, I believe the long-term outlook for the airline industry remains positive. The shift toward hybrid work has created a new segment of travelers who have the time and money to spend on air travel. This trend, coupled with the pent-up demand for leisure travel, should help support the industry’s growth in the coming years.
Additionally, airlines have prioritized debt reduction, which should help improve their balance sheets and credit ratings over time. At the end of 2023, the domestic industry reported a collective $143 billion in debt, an approximately 15% decrease from 2021 levels.
U.S. airlines have prioritized debt reduction
As we head into the summer travel season, I believe now may be the time for investors to consider adding exposure to this sector. With a long-term outlook and a diversified approach, investors can potentially benefit from the industry’s recovery and growth in the coming years.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions

IMAGES
COMMENTS
By Mayo Clinic Staff. A coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccine can prevent you from getting COVID-19 or from becoming seriously ill due to COVID-19. But even if you're vaccinated, it's still a good idea to take precautions to protect yourself and others while traveling during the COVID-19 pandemic. If you've had all recommended COVID-19 ...
But in order to avoid riding in style with germs, there are some precautions you should take before you hit the road. Start by cleaning and disinfecting your vehicle thoroughly. Wipe down all high ...
A COVID-19 testing centre for travellers at Heathrow Airport. During the COVID-19 pandemic, many countries and regions imposed quarantines, entry bans, or other travel restrictions for citizens of or recent travelers to the most affected areas. [1] Some countries and regions imposed global restrictions that apply to all foreign countries and ...
Curaçao has lifted its pandemic-related travel restrictions. However, visitors must complete a digital immigration card before travel. The C.D.C. risk assessment for Covid-19 is Level 3: High.
During a pandemic, going to the grocery store—let alone traveling to another city or country—requires new protocols. Follow policies about lockdown restrictions and mandatory quarantines, both ...
The change will have a profound effect on the borders with Mexico and Canada, where traveling back and forth was a way of life until the pandemic hit and the U.S. shut down nonessential travel.
Numerous studies on that question have been published in the months since the pandemic brought travel to a halt in March. Many of them suggest that the risk of contracting coronavirus while flying ...
Section 1. Policy. Science-based public health measures are critical to preventing the spread of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) by travelers within the United States and those who enter the ...
All →. Since October 2020, the WHO Guideline Development Group for International Travel and Health (WHO ITH GDG) is tasked with regularly evaluating the scientific evidence around the effectiveness, safety and impact of public health measures for reducing travel-associated spread of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, while avoiding ...
Given the resumption of air travel as worldwide restrictions due to the COVID-19 pandemic begin to ease, these policies will, consistent with the measures required by Executive Order 13998 of ...
Bye-bye, business travelers. During the pandemic, a large percentage of the workforce switched to virtual meetings. Even the most optimistic studies predict a lengthy recovery for business travel.
Should you travel via plane this winter considering the explosion of cases of Covid-19 around the world? Know the pitfalls of flying during a pandemic and how to reduce the risk if you must fly.
The main risk of air travel during the COVID-19 pandemic is sitting or standing close to other people for potentially long periods of time. Risk is particularly high while waiting to board the ...
Long-distance car travel, before and during the pandemic. Driving trips at least 50 miles from home, with stays of two hours or more, based on a daily index from . mobile location data.
The COVID-19 pandemic has spread across the world, infecting tens of millions and killing over one million people 1.By March 2021, the United States (U.S.) had recorded the highest number of ...
COVID-19 testing and vaccine rules for entering the U.S. As of May 12, 2023, noncitizen nonimmigrant visitors to the U.S. arriving by air or arriving by land or sea no longer need to show proof of being fully vaccinated against COVID-19. As of June 12, 2022, people entering the U.S. no longer need to show proof of a negative COVID-19 test. U.S. citizens traveling to a country outside the U.S.
While few industries have been spared by the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, even fewer have been hit as hard as the tourism sector.As 2021 drew to a close with severe limitations to travel still in place, the World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) reported that international tourist arrivals increased by just 4 percent last year, remaining 72 percent below 2019 levels.
March was by far the busiest month for COVID-19-related travel restrictions. After the World Health Organization (WHO) declared COVID-19 a pandemic on March 11, the Trump administration issued a travel ban on non-Americans who visited more than two dozen European countries within 14 days of coming to the United States. On March 17, the United States and Canada mutually agreed to close their ...
Traveling within the U.S. Domestic U.S. travel, particularly travel by car, has enjoyed great popularity during the pandemic, allowing Americans to avoid confusing border restrictions, as well as crowded airplanes. There are are varying restrictions within the U.S., however. Hawaii has particularly strict rules about vaccination and testing for ...
Of those people who traveled since the start of the pandemic, 27% of respondents said they took one to two trips, 12% said they took three to four trips and 6% took more than four trips. One-third ...
The states with the greatest declines in travel, tourism and outdoor recreation employment were Rhode Island (decline of 37.9%), Vermont (37.4%), Connecticut (36.4%), Massachusetts (32.1%), New York (31.5%), and Washington (24.9%). These states reflect locations of initial outbreaks at the start of the pandemic and the disproportionate impact ...
Cancellation of public events during COVID-19 pandemic. Chile: COVID-19 weekly death rate by vaccination status. Confirmed COVID-19 deaths per million vs. GDP per capita. Cumulative confirmed COVID-19 cases and deaths. Cumulative confirmed COVID-19 cases by world region By Region.
Overall outbound travel from China during this year's holiday is still lagging behind 2019 levels by 13%. But travel to the United Arab Emirates (UAE) has surged by 66%, and Turkey has ...
We spoke to musician, actor, and television host Joey Fatone about his favorite things, including comfortable slides and sneakers, video games, and more.
Indeed, the trends indicate a kind of tourism inertia from COVID-19 pandemic-era lockdowns: Those destinations that were more open to U.S. visitors during the pandemic, such as Mexico, have ...
During the past year alone, they've risen 4.2%. Tickets to plays, movies, and concerts also shot up 22.6% — 5% more than a year ago. ... Travel costs have soared since the pandemic — with ...
Ruby-throated Hummingbirds were three times more likely to be reported within a kilometer of airports than before the pandemic. Barn Swallows, a threatened species in Canada, were reported more often within a kilometer of roads than before the pandemic. A few species decreased their use of human-altered habitat during the pandemic.
The U.S. travel sector will have to wait at least two more years for lucrative Chinese tourism to recover to pre-pandemic levels as slow growth and high costs in the Asian country keep its ...
journals.lww.com
The global airline industry is facing a summer squeeze as travel demand is expected to surpass pre-pandemic levels while aircraft deliveries drop sharply due to production problems at Boeing and ...