Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Employee Exit Interviews
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Market Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- Customer Journey Mapping
- Customer Journey Stages

See how XM for Customer Frontlines works
The complete guide to customer journey stages.
12 min read If you want to turn a potential customer into a lifetime one, you’ll need to get to know every step of the entire customer journey. Here’s why the secret to customer retention lies in knowing how to fine-tune your sales funnel…
What is the customer journey?
What do we actually mean when we talk about the customer journey? Well, the simplest way to think about it is by comparing it to any other journey: a destination in mind, a starting point, and steps to take along the way.
In this case, the destination is not only to make a purchase but to have a great experience with your product or service – sometimes by interacting with aftersale customer support channels – and become a loyal customer who buys again.
And, just like how you can’t arrive at your vacation resort before you’ve done you’ve found out about it, the customer journey starts with steps to do with discovery, research, understanding, and comparison, before moving on to the buying process.
“Maximizing satisfaction with customer journeys has the potential not only to increase customer satisfaction by 20% but also lift revenue up by 15% while lowering the cost of serving customers by as much as 20%”
– McKinsey, The Three Cs of Customer Satisfaction
In short, the customer journey is the path taken by your target audience toward becoming loyal customers. So it’s really important to understand – both in terms of what each step entails and how you can improve each one to provide a maximally impressive and enjoyable experience.
Every customer journey will be different, after all, so getting to grips with the nuances of each customer journey stage is key to removing obstacles from in front of your potential and existing customers’ feet.
Free Course: Customer Journey Management & Improvement
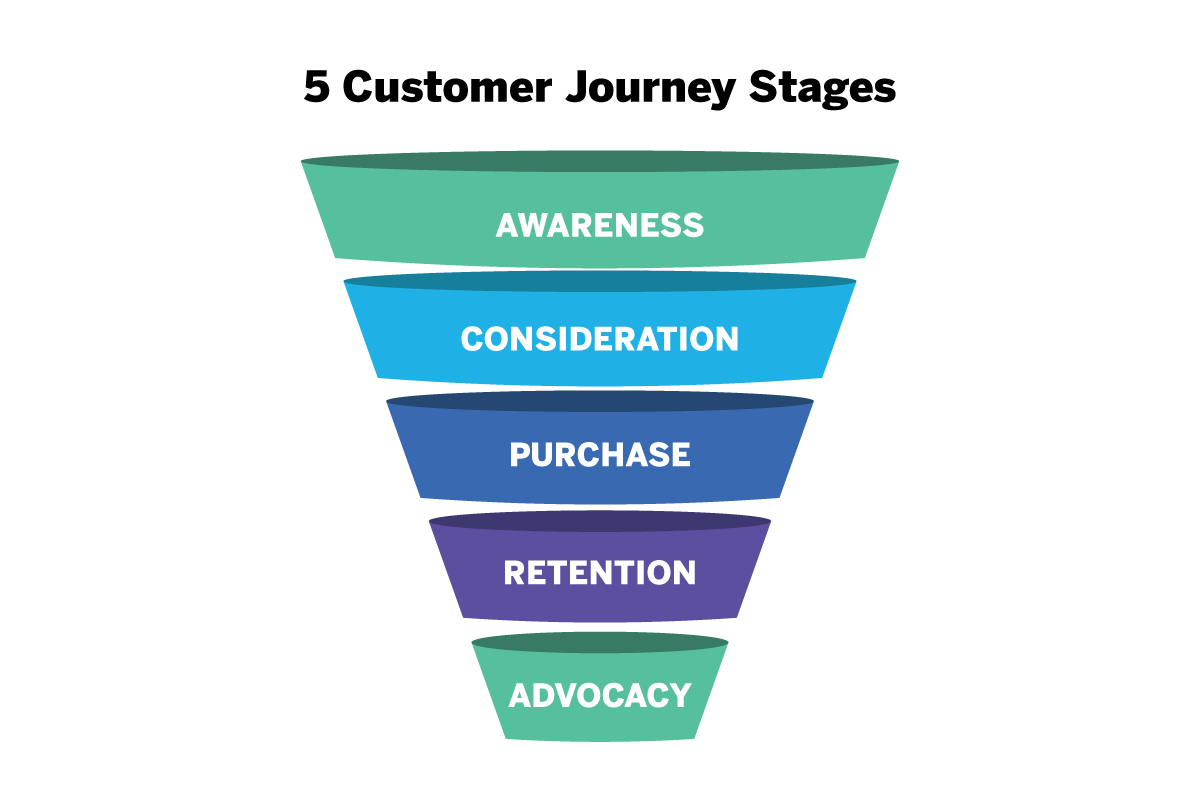
What are the essential customer journey stages?
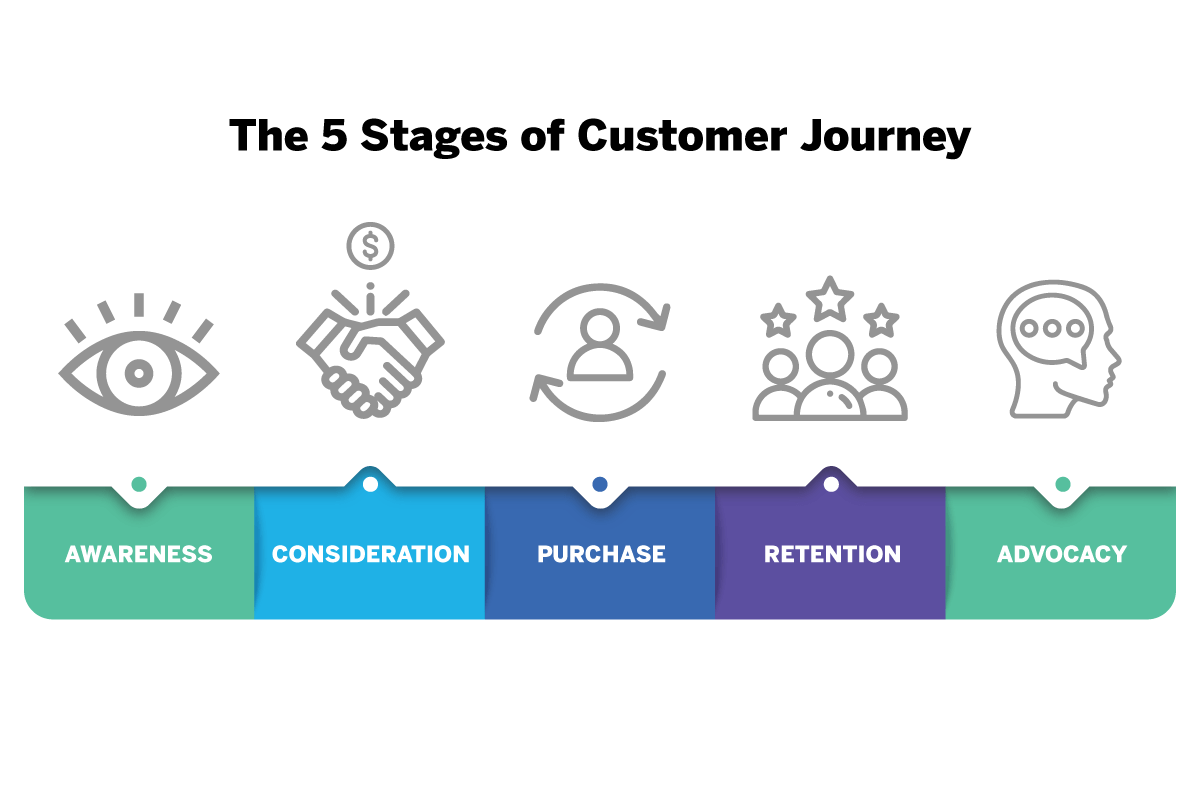
While many companies will put their own spin on the exact naming of the customer journey stages, the most widely-recognized naming convention is as follows:
- Consideration
These steps are often then sub-categorized into three parts:
- Sale/Purchase
It’s important to understand every part of the puzzle, so let’s look at each sub-category and stage in turn, from the awareness and consideration stage, right through to advocacy:
Customer journey: Pre-sale
In the pre-sale phase, potential customers learn about products, evaluate their needs, make comparisons, and soak up information.
Awareness stage
In the awareness stage, your potential customer becomes aware of a company, product, or service. This might be passive – in that they’re served an ad online, on TV, or when out and about – or active in that they have a need and are searching for a solution. For example, if a customer needs car insurance, they’ll begin searching for providers.
Consideration stage
In the consideration stage, the customer has been made aware of several possible solutions for their particular need and starts doing research to compare them. That might mean looking at reviews or what others are saying on social media, as well as absorbing info on product specs and features on companies’ own channels. They’re receptive to information that can help them make the best decision.
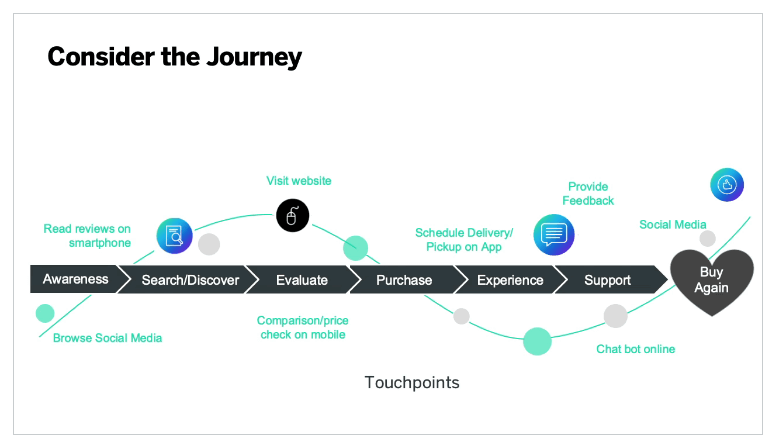
Customer journey: Sale
The sale phase is short but pivotal: it’s when the crucial decision on which option to go with has been made.
Decision stage
The customer has all the information they need on the various options available to them, and they make a purchase. This can be something that’s taken a long time to decide upon, like buying a new computer, or it can be as quick as quickly scouring the different kinds of bread available in the supermarket before picking the one they want.
Customer journey: Post-sale
Post-sale is a really important part of the puzzle because it’s where loyal customers , who come back time and again, are won or lost.
Retention stage
The retention stage of the customer journey is where you do whatever you can to help leave a lasting, positive impression on the customer, and entice them to purchase more. That means offering best-in-class customer support if they have any issues, but it also means being proactive with follow-up communications that offer personalized offers, information on new products, and rewards for loyalty.
Advocacy stage
If you nail the retention phase, you’ll have yourself a customer who not only wants to keep buying from you but will also advocate on your behalf. Here, the customer will become one of the most powerful tools in your arsenal, in that they’ll actively recommend you to their friends, family, followers, and colleagues.
What’s the difference between the customer journey and the buyer’s journey?
Great question; the two are similar, but not exactly the same. The buyer’s journey is a shorter, three-step process that describes the steps taken to make a purchase. So that’s awareness , consideration, and decision . That’s where things stop, however. The buyer’s journey doesn’t take into account the strategies you’ll use to keep the customer after a purchase has been made.
Why are the customer journey stages important?
The short answer? The customer journey is what shapes your entire business. It’s the method by which you attract and inform customers, how you convince them to purchase from you, and what you do to ensure they’re left feeling positive about every interaction.
Why this matters is that the journey is, in a way, cyclical. Customers who’ve had a smooth ride all the way through their individual journeys are more likely to stay with you, and that can have a massive effect on your operational metrics.
It’s up to five times more expensive to attract a new customer than it is to keep an existing customer, but even besides that: satisfied customers become loyal customers , and customer loyalty reduces churn at the same time as increasing profits .
So companies looking to really make an impact on the market need to think beyond simply attracting potential customers with impressive marketing, and more about the journey as a whole – where the retention and advocacy stages are equally important.
After all, 81% of US and UK consumers trust product advice from friends and family over brand messaging, and 59% of American consumers say that once they’re loyal to a brand, they’re loyal to it for life.
Importantly, to understand the customer journey as a whole is to understand its individual stages, recognize what works, and find things that could be improved to make it a more seamless experience. Because when you do that, you’ll be improving every part of your business proposition that matters.
How can you improve each customer journey stage?
Ok, so this whole customer journey thing is pretty important. Understanding the customer journey phases and how they relate to the overall customer experience is how you encourage customers to stick around and spread the news via word of mouth.
But how do you ensure every part of the journey is performing as it should? Here are some practical strategies to help each customer journey stage sing…
1. Perform customer journey mapping
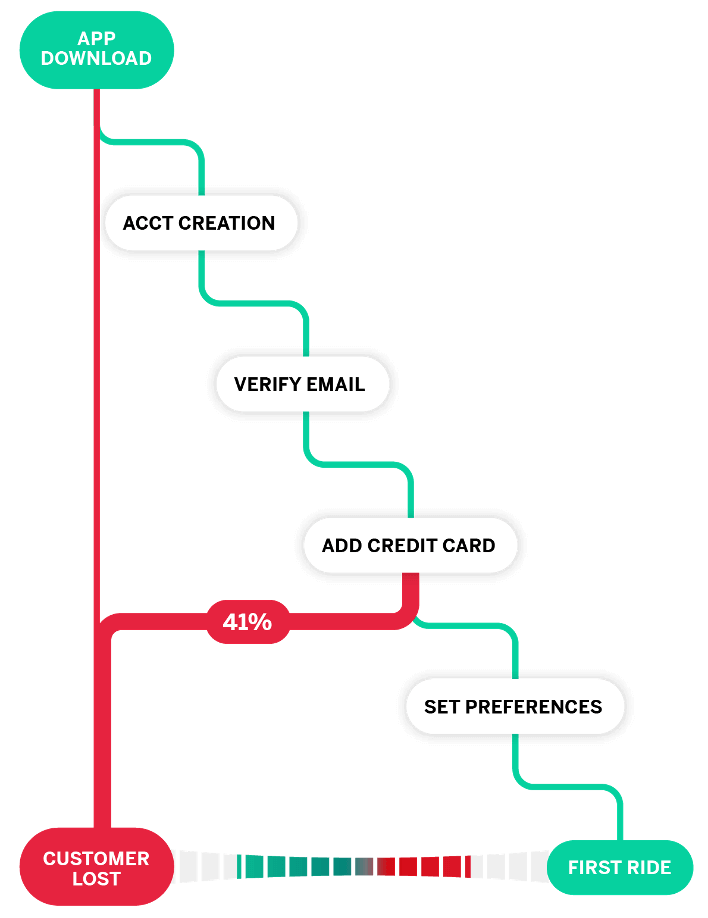
A customer journey map takes all of the established customer journey stages and attempts to plot how actual target audience personas might travel along them. That means using a mix of data and intuition to map out a range of journeys that utilize a range of touch points along the way.
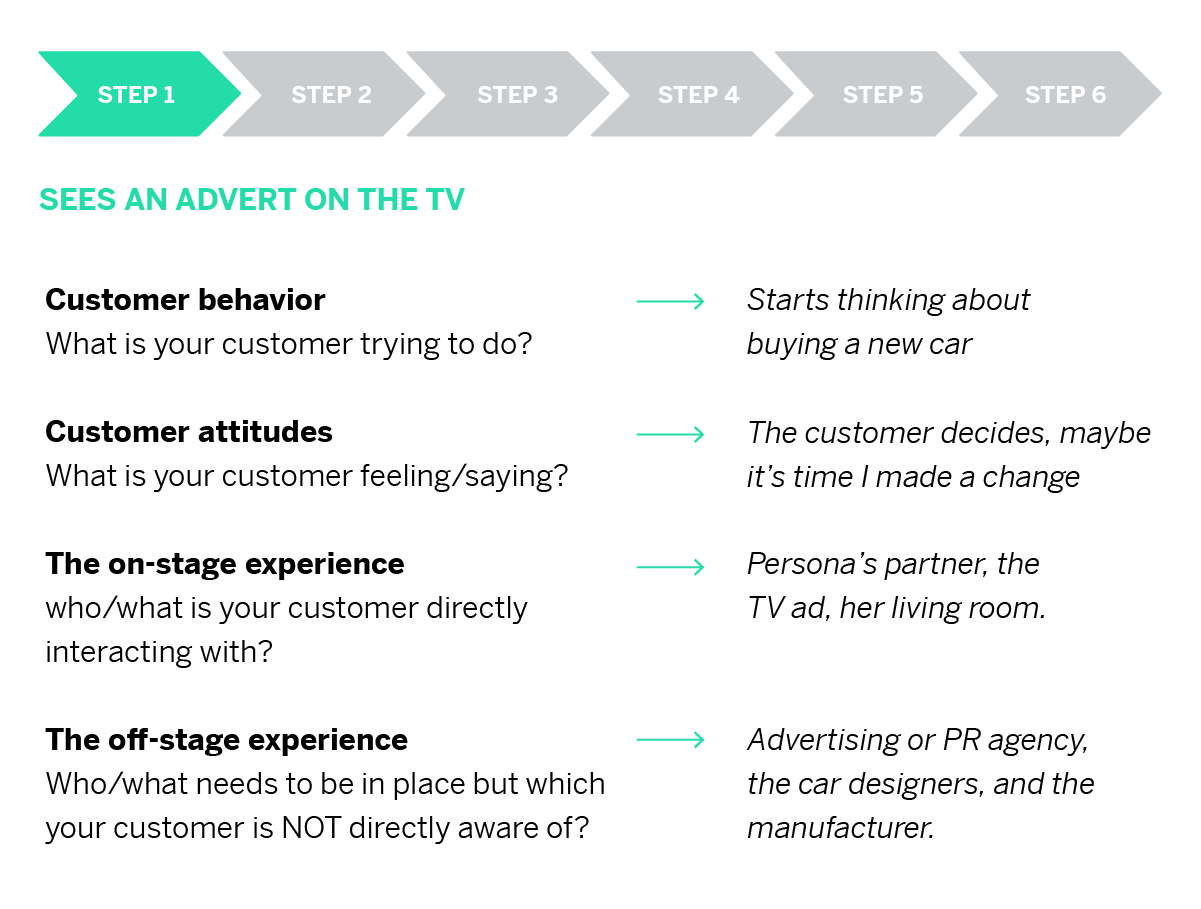
One customer journey map, for example, might start with a TV ad, then utilize social media and third-party review sites during the consideration stage, before purchasing online and then contacting customer support about you your delivery service. And then, finally, that customer may be served a discount code for a future purchase. That’s just one example.
Customer journey mapping is really about building a myriad of those journeys that are informed by everything you know about how customers interact with you – and then using those maps to discover weaker areas of the journey.
2. Listen like you mean it
The key to building better customer journeys is listening to what customers are saying. Getting feedbac k from every stage of the journey allows you to build a strong, all-encompassing view of what’s happening from those that are experiencing it.
Maybe there’s an issue with the customer sign-up experience, for example. Or maybe the number advertised to contact for a demo doesn’t work. Or maybe you have a customer service agent in need of coaching, who only makes the issue worse. By listening, you’ll understand your customers’ issues and be able to fix them at the source. That customer service agent, for example, may just feel disempowered and unsupported, and in need of the right tools to help them perform better. Fixing that will help to optimize a key stage in the customer journey.
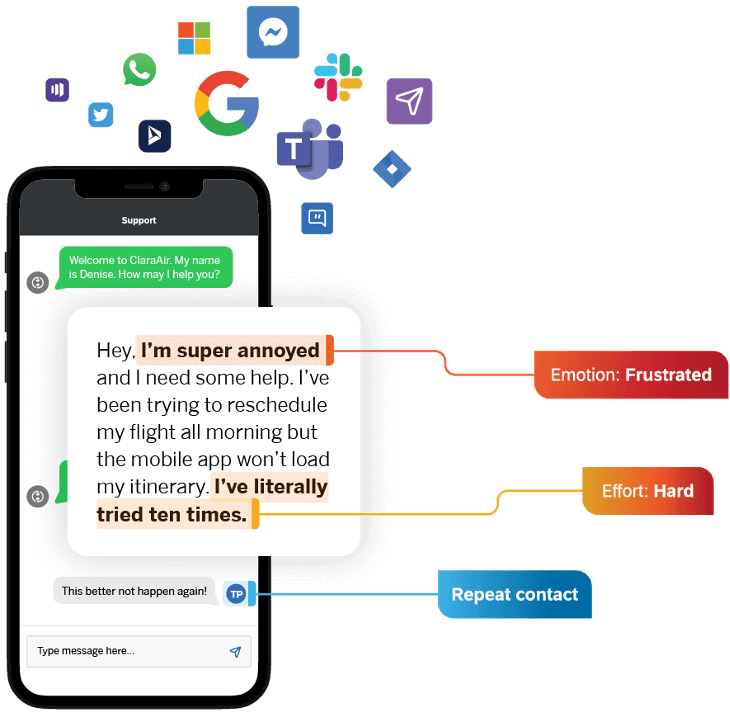
The key is to listen at every stage, and we can do that by employing the right technology at the right customer journey stages.
Customer surveys, for instance, can help you understand what went wrong from the people who’re willing to provide that feedback, but conversational analytics and AI solutions can automatically build insights out of all the structured and unstructured conversational data your customers are creating every time they reach out, or tweet, or leave a review on a third party website.
3. Get personal
The other side of the ‘listening’ equation is that it’s worth remembering that each and every customer’s journey is different – so treating them with a blanket approach won’t necessarily make anything better for them.
The trick instead is to use the tools available to you to build out a personalized view of every customer journey, customer journey stage, and customer engagemen t, and find common solutions.
Qualtrics Experience iD , for example, is an intelligent system that builds customer profiles that are unique to them and can identify through AI, natural language processing , and past interactions what’s not working – and what needs fixing.
On an individual basis, that will help turn each customer into an advocate. But as a whole, you’ll learn about experience gaps that are common to many journeys.
Listening to and understanding the customer experience at each customer journey stage is key to ensuring customers are satisfied and remain loyal on a huge scale.
It’s how you create 1:1 experiences, because, while an issue for one person might be an issue for many others, by fixing it quickly you can minimize the impact it might have on future customers who’re right at the start of their journey.
Free Course: Customer Journey Management Improvement
Related resources
Customer Journey
Buyer's Journey 16 min read
Customer journey analytics 13 min read, how to create a customer journey map 22 min read, b2b customer journey 13 min read, customer interactions 11 min read, consumer decision journey 14 min read, customer journey orchestration 12 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
The customer journey — definition, stages, and benefits

Businesses need to understand their customers to increase engagement, sales, and retention. But building an understanding with your customers isn’t easy.
The customer journey is the road a person takes to convert, but this journey isn’t always obvious to business owners. Understanding every step of that journey is key to business success. After reading this article, you’ll understand the customer journey better and how to use it to improve the customer experience while achieving your business goals.
This post will discuss:
- What a customer journey is
Customer journey stages
Benefits of knowing the customer journey.
- What a customer journey map is
How to create a customer journey map
Use the customer journey map to optimize the customer experience, what is a customer journey.
The customer journey is a series of steps — starting with brand awareness before a person is even a customer — that leads to a purchase and eventual customer loyalty. Businesses use the customer journey to better understand their customers’ experience, with the goal of optimizing that experience at every touchpoint.
Giving customers a positive customer experience is important for getting customers to trust a business, so optimizing the customer journey has never mattered more. By mastering the customer journey, you can design customer experiences that will lead to better customer relationships, loyalty, and long-term retention .
Customer journey vs. the buyer journey
The stages of the customer’s journey are different from the stages of the buyer’s journey. The buyer’s journey follows the customer experience from initial awareness of a brand to buying a product. The customer journey extends beyond the purchase and follows how customers interact with your product and how they share it with others.
Every lead goes through several stages to become a loyal customer. The better this experience is for customers at each stage, the more likely your leads are to stick around.
Ensure that your marketing, sales, and customer service teams optimize for these five stages of the customer journey:

1. Awareness
In the awareness phase, your target audience is just becoming aware of your brand and products. They need information or a solution to a problem, so they search for that information via social media and search engines.
For example, if someone searches on Google for pens for left-handed people, their customer journey begins when they’re first aware of your brand’s left-handed pen.
At this stage, potential customers learn about your business via web content, social media, influencers, and even their friends and family. However, this isn’t the time for hard sells. Customers are simply gathering information at this stage, so you should focus first on answering their questions and building trust.
2. Consideration
In the consideration phase, customers begin to consider your brand as a solution to their problem. They’re comparing your products to other businesses and alternative solutions, so you need to give these shoppers a reason to stick around.
Consideration-stage customers want to see product features that lean heavily toward solving problems and content that doesn’t necessarily push a sale. At this stage, businesses need to position their solution as a better alternative. For example, a nutrition coaching app might create content explaining the differences between using the app and working with an in-person nutritionist — while subtly promoting the benefits of choosing the app.
3. Purchase
The purchase stage is also called the decision stage because at this stage customers are ready to make a buying decision. Keep in mind that their decision might be to go with a competing solution, so purchase-stage buyers won’t always convert to your brand.
As a business, it’s your job to persuade shoppers at this stage to buy from you. Provide information on pricing, share comparison guides to showcase why you’re the superior option, and set up abandoned cart email sequences.
4. Retention
The customer journey doesn’t end once a shopper makes their first purchase. Once you’ve converted a customer, you need to focus on keeping them around and driving repeat business. Sourcing new customers is often more expensive than retaining existing clients, so this strategy can help you cut down on marketing costs and increase profits.
The key to the retention stage is to maintain positive, engaging relationships between your brand and its customers. Try strategies like regular email outreach, coupons and sales, or exclusive communities to encourage customer loyalty.
5. Advocacy
In the advocacy stage, customers are so delighted with your products and services that they spread the word to their friends and family. This goes a step beyond retention because the customer is actively encouraging other people to make purchases.
Customer journeys don’t have a distinct end because brands should always aim to please even their most loyal customers. In the advocacy stage of the customer journey, you can offer referral bonuses, loyalty programs, and special deals for your most active customers to encourage further advocacy.
Being aware of the customer journey helps shed more light on your target audience’s expectations and needs. In fact, 80% of companies compete primarily on customer experience. This means optimizing the customer journey will not only encourage your current customers to remain loyal but will also make you more competitive in acquiring new business.
More specifically, acknowledging the customer journey can help you:

- Understand customer behavior. Classifying every action your customers take will help you figure out why they do what they do. When you understand a shopper’s “why,” you’re better positioned to support their needs.
- Identify touchpoints to reach the customer. Many businesses invest in multichannel marketing, but not all of these touchpoints are valuable. By focusing on the customer journey, you’ll learn which of these channels are the most effective for generating sales. This helps businesses save time and money by focusing on only the most effective channels.
- Analyze the stumbling blocks in products or services. If leads frequently bail before buying, that could be a sign that something is wrong with your product or buying experience. Being conscious of the customer journey can help you fix issues with your products or services before they become a more expensive problem.
- Support your marketing efforts. Marketing requires a deep familiarity with your target audience. Documenting the customer journey makes it easier for your marketing team to meet shoppers’ expectations and solve their pain points.
- Increase customer engagement. Seeing the customer journey helps your business target the most relevant audience for your product or service. Plus, it improves the customer experience and increases engagement. In fact, 29.6% of customers will refuse to embrace branded digital channels if they have a poor experience, so increasing positive customer touchpoints has never been more important.
- Achieve more conversions. Mapping your customers’ journey can help you increase conversions by tailoring and personalizing your approach and messages to give your audience exactly what they want.
- Generate more ROI. You need to see a tangible return on your marketing efforts. Fortunately, investing in the customer journey improves ROI across the board. For example, brands with a good customer experience can increase revenue by 2–7% .
- Improve customer satisfaction and loyalty. Today, 94% of customers say a positive experience motivates them to make future purchases. Optimizing the customer journey helps you meet shopper expectations, which increases satisfaction and loyalty.

What is a customer journey map?
A customer journey map is a visual representation of every step your customer takes from being a lead to eventually becoming an advocate for your brand. The goal of customer journey mapping is to simplify the complex process of how customers interact with your brand at every stage of their journey.
Businesses shouldn’t use a rigid, one-size-fits-all customer journey map. Instead, they should plan flexible, individual types of customer journeys — whether they’re based on a certain demographic or on individual customer personas. To design the most effective customer journey map, your brand needs to understand a customer’s:
- Actions. Learn which actions your customer takes at every stage. Look for common patterns. For example, you might see that consideration-stage shoppers commonly look for reviews.
- Motivations. Customer intent matters. A person’s motivations change at every stage of the customer journey, and your map needs to account for that. Include visual representation of the shopper’s motivations at each stage. At the awareness stage, their motivation might be to gather information to solve their problem. At the purchase stage, it might be to get the lowest price possible.
- Questions. Brands can take customers’ common questions at every stage of the customer journey and reverse-engineer them into useful content. For example, shoppers at the consideration stage might ask, “What’s the difference between a DIY car wash and hiring a professional detailer?” You can offer content that answers their question while subtly promoting your car detailing business.
- Pain points. Everybody has a problem that they’re trying to solve, whether by just gathering intel or by purchasing products. Recognizing your leads’ pain points will help you craft proactive, helpful marketing campaigns that solve their biggest problems.
Customer journey touchpoints
Every stage of the customer journey should also include touchpoints. Customer touchpoints are the series of interactions with your brand — such as an ad on Facebook, an email, or a website chatbot — that occur at the various stages of the customer journey across multiple channels. A customer’s actions, motivations, questions, and pain points will differ at each stage and at each touchpoint.
For example, a customer searching for a fishing rod and reading posts about how they’re made will have very different motivations and questions from when later comparing specs and trying to stay within budget. Likewise, that same customer will have different pain points when calling customer service after buying a particular rod.

It might sound like more work, but mapping the entire customer journey helps businesses create a better customer experience throughout the entire lifecycle of a customer’s interaction with your brand.
Before jumping into the steps of how to create the customer journey map, first be clear that your customer journey map needs to illustrate the following:
- Customer journey stages. Ensure that your customer journey map includes every stage of the customer journey. Don’t just focus on the stages approaching the purchase — focus on the retention and advocacy stages as well.
- Touchpoints. Log the most common touchpoints customers have at every stage. For example, awareness-stage touchpoints might include your blog, social media, or search engines. Consideration-stage touchpoints could include reviews or demo videos on YouTube. You don’t need to list all potential touchpoints. Only list the most common or relevant touchpoints at each stage.
- The full customer experience. Customers’ actions, motivations, questions, and pain points will change at every stage — and every touchpoint — during the customer journey. Ensure your customer journey map touches on the full experience for each touchpoint.
- Your brand’s solutions. Finally, the customer journey map needs to include a branded solution for each stage and touchpoint. This doesn’t necessarily mean paid products. For example, awareness-stage buyers aren’t ready to make a purchase, so your brand’s solution at this stage might be a piece of gated content. With these necessary elements in mind, creating an effective customer journey map is a simple three-step process.
1. Create buyer personas
A buyer persona is a fictitious representation of your target audience. It’s a helpful internal tool that businesses use to better understand their audience’s background, assumptions, pain points, and needs. Each persona differs in terms of actions, motivations, questions, and pain points, which is why businesses need to create buyer personas before they map the customer journey.
To create a buyer persona, you will need to:
- Gather and analyze customer data. Collect information on your customers through analytics, surveys, and market research.
- Segment customers into specific buying groups. Categorize customers into buying groups based on shared characteristics — such as demographics or location. This will give you multiple customer segments to choose from.
- Build the personas. Select the segment you want to target and build a persona for that segment. At a minimum, the buyer persona needs to define the customers’ basic traits, such as their personal background, as well as their motivations and pain points.

For example, ClearVoice created a buyer persona called “John The Marketing Manager.” The in-depth persona details the target customer’s pain points, pet peeves, and potential reactions to help ClearVoice marketers create more customer-focused experiences.
2. List the touchpoints at each customer journey stage
Now that you’ve created your buyer personas, you need to sketch out each of the five stages of the customer journey and then list all of the potential touchpoints each buyer persona has with your brand at every one of these five stages. This includes listing the most common marketing channels where customers can interact with you. Remember, touchpoints differ by stage, so it’s critical to list which touchpoints happen at every stage so you can optimize your approach for every buyer persona.
Every customer’s experience is different, but these touchpoints most commonly line up with each stage of the customer journey:
- Awareness. Advertising, social media, company blog, referrals from friends and family, how-to videos, streaming ads, and brand activation events.
- Consideration. Email, sales calls, SMS, landing pages, and reviews.
- Purchase. Live chat, chatbots, cart abandonment emails, retargeting ads, and product print inserts.
- Retention. Thank you emails, product walkthroughs, sales follow-ups, and online communities.
- Advocacy. Surveys, loyalty programs, and in-person events.
Leave no stone unturned. Logging the most relevant touchpoints at each stage eliminates blind spots and ensures your brand is there for its customers, wherever they choose to connect with you.
3. Map the customer experience at each touchpoint
Now that you’ve defined each touchpoint at every stage of the customer journey, it’s time to detail the exact experience you need to create for each touchpoint. Every touchpoint needs to consider the customer’s:
- Actions. Describe how the customer got to this touchpoint and what they’re going to do now that they’re here.
- Motivations. Specify how the customer feels at this moment. Are they frustrated, confused, curious, or excited? Explain why they feel this way.
- Questions. Every customer has questions. Anticipate the questions someone at this stage and touchpoint would have — and how your brand can answer those questions.
- Pain points. Define the problem the customer has — and how you can solve that problem at this stage. For example, imagine you sell women’s dress shoes. You’re focusing on the buyer persona of a 36-year-old Canadian woman who works in human resources. Her touchpoints might include clicking on your Facebook ad, exploring your online shop, but then abandoning her cart. After receiving a coupon from you, she finally buys. Later, she decides to exchange the shoes for a different color. After the exchange, she leaves a review. Note how she acts at each of these touchpoints and detail her likely pain points, motivations, and questions, for each scenario. Note on the map where you intend to respond to the customer’s motivations and pain points with your brand’s solutions. If you can create custom-tailored solutions for every stage of the funnel, that’s even better.
A positive customer experience is the direct result of offering customers personalized, relevant, or meaningful content and other brand interactions. By mapping your customers’ motivations and pain points with your brand’s solutions, you’ll find opportunities to improve the customer experience. When you truly address their deepest needs, you’ll increase engagement and generate more positive reviews.
Follow these strategies to improve the customer experience with your customer journey map:
- Prioritize objectives. Identify the stages of the customer journey where your brand has the strongest presence and take advantage of those points. For example, if leads at the consideration stage frequently subscribe to your YouTube channel, that gives you more opportunities to connect with loyal followers.
- Use an omnichannel approach to engage customers. Omnichannel marketing allows businesses to gather information and create a more holistic view of the customer journey. This allows you to personalize the customer experience on another level entirely. Use an omnichannel analytics solution that allows you to capture and analyze the true cross-channel experience.
- Personalize interactions at every stage. The goal of mapping the customer journey is to create more personalized, helpful experiences for your audience at every stage and touchpoint. For example, with the right data you can personalize the retail shopping experience and customer’s website experience.
- Cultivate a mutually trusting relationship. When consumer trust is low, brands have to work even harder to earn their customers’ trust. Back up your marketing promises with good customer service, personalized incentives, and loyalty programs.
Getting started with customer journeys
Customer journeys are complicated in an omnichannel environment, but mapping these journeys can help businesses better understand their customers. Customer journey maps help you deliver the exact experience your customers expect from your business while increasing engagement and sales.
When you’re ready to get started, trace the interactions your customers have at each stage of their journey with your brand. Adobe Customer Journey Analytics — a service built on Adobe Experience Platform — can break down, filter, and query years’ worth of data and combine it from every channel into a single interface. Real-time, omnichannel analysis and visualization let companies make better decisions with a holistic view of their business and the context behind every customer action.
Learn more about Customer Journey Analytics by watching the overview video .
https://business.adobe.com/blog/perspectives/introducing-adobes-customer-journey-maturity-model
https://business.adobe.com/blog/how-to/create-customer-journey-maps
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/what-is-customer-journey-map

Blog • Customer Experience
Customer Journey Stages: Guide, How-To & Best Practices

What Is the Customer Journey?
Why is it important to understand the different customer journey stages, how to create an effective customer journey, best practices for an efficient customer journey stages.
It’s easy to fall into an if it ain’t broke, don’t fix it mindset when thinking about customer journeys—why mess with a system that’s served you well so far? The rather unsurprising answer is that your customer journey isn’t nearly as efficient, enjoyable, and profitable as it could be.
According to McKinsey , when the average business makes systematic, targeted improvements to their customer journey, they increase revenue by 15-20% while also cutting service costs by 15-20%.
Interested in this win-win scenario? You’re going to need a solid understanding of the journey stages and what they mean to your business. And in this Customerly guide, we’ll be giving you a crash course to get you started.
Let’s dive in.
A customer journey is the life cycle of a customer’s relationship with your business—from the point of initial contact to post-purchase follow-up.
The customer journey is a fluid spectrum—but that’s not an especially helpful way of thinking about it. To simplify things, people usually break the customer journey down into stages (five, to be exact) that are defined by customer needs, behaviors, and touchpoints.
When you understand each stage, you’re much better equipped to give each customer the experience they’re looking for at any given moment.
Check out how Feed Donkey uses Customerly to engage with their clients at every stage of the journey.
What are those stages? Let’s go over them now.
The Stages of a Customer Journey
- Awareness : The customer becomes aware of your product or service. Maybe they saw an ad, or maybe they clicked on a blog post—the important point is that they know your company exists.
- Consideration : The customer isn’t simply aware of your existence; they’re actively considering your company as a solution to their problem(s). This usually involves fairly surface-level research and comparison.
- Purchase : This is the point when a customer has decided to purchase something from your company. They’ve put aside any hesitations or doubts and moved forward with their purchase.
- Retention : The customer made a purchase (congrats)—now your goal is to retain their business. In practice, that means offering incredible post-purchase support, demonstrating that you value the relationship (e.g., offers and rewards), and delivering an excellent overall experience.
- Advocacy : This is one of the most powerful stages in terms of impact on your bottom line. In this stage, the customer is not only satisfied—they actively champion your product or service to their friends and family. This can create a snowball effect that fast-tracks growth.
We already covered two very good reasons to care about customer journey stages—increased revenue and decreased costs. But those benefits are really side effects of far more important reasons:
Allocate Resources Effectively
Your customer journey is a complex mess of touchpoints, channels, mediums, features, benefits, use cases, landing pages… you get the idea.
When you understand the stages (and what they mean for customers), it helps you identify where to invest, what features and tools to prioritize, and how best to engage with customers along their entire purchase journey. The result is a system that’s working as close to maximum efficiency as possible when it comes to generating revenue.
Personalized Customer Experience
On a related note, these stages also give you a quick and easy way to segment leads and customers into intuitive groups. These groups are easy to target for personalized messages, tailored content, and relevant product recommendations.
With Customerly, you can build custom lists of customers in our CRM using a range of characteristics, including:
- contact properties
- company properties
This helps you create much more rewarding experiences for each customer group—the kinds of experiences that earn purchases, retention, and advocacy.
Build Longer-Term Relationships
Customers want their experiences with businesses to be simple, straightforward, and rewarding—no moments of confusion, no moments of frustration. If you consciously work to make that dream a reality, you’re setting yourself apart from the competition and earning long-term advocates.
1. Create a Customer Profile
If you want to create an effective journey for your customer, you need to know who that is—in clear, concrete terms.
A customer profile (or ideal customer persona ) is like a character sheet for a TV show, movie, or D&D campaign. It’s a generalization of a customer group that’s important to your business, either because they make up a sizable portion of your total customer base or revenue.
For each customer profile you create, you’ll want to cover:
- Demographics : Who the customer is (e.g., “Chief Customer Officer at a growing B2B SaaS”).
- Psychographics : What their needs and interests are (e.g., “looking for a partner to guide the process”).
- Goals : What they hope to achieve in their journey (e.g., “boost customer support efficiency”).
- Pain Points : What keeps them awake at night (e.g., “confusing onboarding processes”).
- Current Solutions : How (if at all) they’re meeting their needs without your solution.
To get your hands on the data needed to make these generalizations, you’re going to need to run surveys to supplement CRM data. With Customerly, you can create and run custom surveys or use our pre-built customer persona template to speed the process up.
All the data you collect is automatically added to your CRM for use in analysis and automated marketing campaigns.
2. Make a List of Customer Touchpoints
Once you have a customer profile, it’s time to make a list of the customer touchpoints—or, the points of contact between them and your business.
There are an absolute ton of touchpoints that you can use to your advantage, but there’s a caveat here—not every touchpoint is well-suited to every customer at every stage of their journey.
There’s some overlap, but here’s a simplified list of common touchpoints and the stages they apply to:
- Awareness : SEO, PPC, word-of-mouth, blog content, PR, etc.
- Consideration : Organic social, case studies, demos, website visits, etc.
- Purchase : Reviews, testimonials, sales staff, branded content, etc.
- Retention : Surveys, email campaigns, etc.
- Advocacy : Loyalty programs, offers, organic social, etc.
3. Identify the Pain Points
Pain points are reliable predictors of behavior.
If you really understand a problem someone is having and know for a fact that you can solve it, it’s much easier to make a sale. So, the next step in this process is listing the pain points that bring customers to you—either on a segment-by-segment basis or in general.
Not sure where to start?
A product positioning survey is a great way to find out why customers choose your company over the competition. Start by using Customerly to target a valuable segment (paid customers, perhaps?) and launch our product positioning template to start generating data.
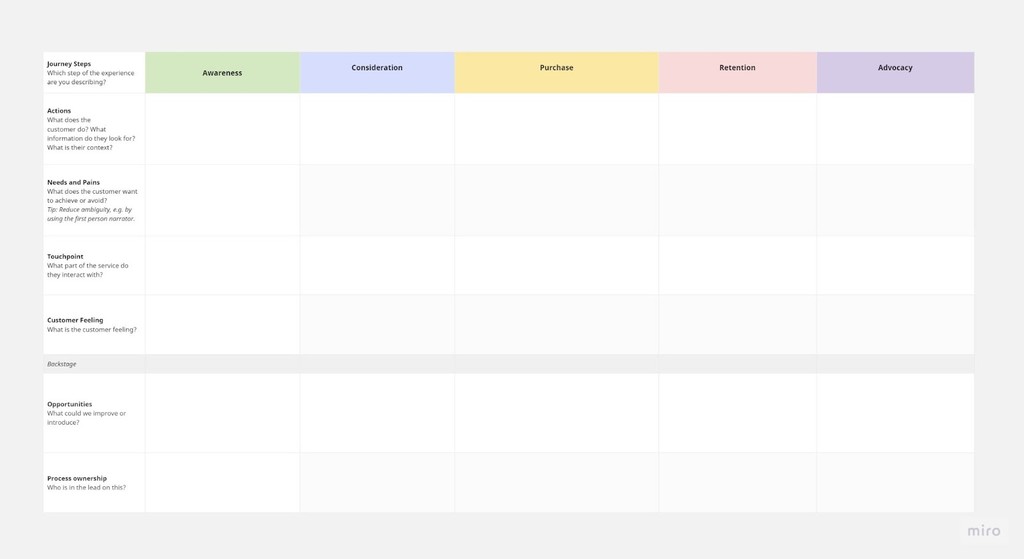
4. Create a Customer Journey Map
Now that you have a customer profile, touchpoints, and pain points identified—you can create a customer journey map. This is an interactive diagram that shows (in broad strokes) how a customer segment progresses from awareness to advocacy.
The map should include key touchpoints, pain points, needs, customer emotions, and the owner(s) for each stage. You should also be creating a map for each persona you identified in the first step.
Here’s an example of what this might look like:
5. Determine the Course of Action
This final step is where you start using your customer journey map to fine-tune your processes.
Start by finding out which touchpoints are influencing customer satisfaction the most. Identify what’s working well and what needs improvement.
Then, brainstorm ways to improve each stage of the journey and measure success at each stage. This includes optimizing processes, running experiments, and implementing changes that will make customers feel heard and valued—ultimately leading to better engagement.
1. Establish a Good First Impression
The first impression is the most important one. That’s why it’s so important to establish a good one from the very start—especially in the awareness and consideration stages.
2. Understand What the Customer Is Getting and Why
In every stage of the customer journey, it’s important to understand what your customer is getting and why. Your messaging should be focused on communicating the value they get from your product or service—not just on pitching them something.
3. Demonstrate Value
Withholding value is an important sales tactic—but it’s important to find a balance. Demonstrate your product or service’s value without revealing too much. Simple, transparent free trials let customers experience the offering fully and allow you to showcase its value. The trial serves as a reference for informed decision-making once it ends.
4. Stay in Contact with Customers After-Sale
It’s not enough to just make a sale—you also need to stay in contact with customers after they’ve made their purchase. This will help you build a strong relationship with them and encourage repeat business. Make sure your post-sale messaging is focused on customer success—not just upselling or cross-selling.
5. Measure Your Success
To create an effective customer journey, measuring success is crucial. Track customer satisfaction , purchase frequency, and lifetime value to understand how your strategy is performing. Use tools like analytics software, surveys, and user tests.
Every well-designed customer journey begins with a deep understanding of the stages that make it up.
At Customerly , we arm businesses with all the tools they need to understand and enhance every stage of their customer journey. From marketing automation tools to intelligent live chat support, we’re here to help you create a seamless customer experience that will increase satisfaction and loyalty.
Want to see for yourself? Start your 14-day free trial and take Customerly for a test drive.
14-day free trial
Create a seamless customer experience that will increase satisfaction and loyalty
- Customer Advocacy
- customer experience
- Customer Journey Analysis
- Customer Journey Mapping
- Customer Journey Optimization.
- Customer Journey Stages
- Customer Pain Points
- Customer Relationship Management
- customer retention
- Customer Touchpoints
Luca Micheli
Luca Micheli is a serial tech entrepreneur with one exited company and a passion for bootstrap digital projects. He's passionate about helping companies to succeed with marketing and business development tips.
Related articles

The Role of AI Tools in Personalizing Customer Experiences for Marketing Success

Best Customer Satisfaction Software for Every Use
- Customer Service
- Marketing Automation
- Customer Satisfaction
- Video Live Chat
- Help Center
- Marketing Funnel
- Email Marketing
- Email Template Builder
- In-App Surveys
- Alternatives
- Success stories
- Terms Of Service
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Submit Guest Post
- Merchandising
Send us an email
What is a customer journey map and how to make your own [examples included]
Written by by Kiran Shahid
Published on November 2, 2023
Reading time 12 minutes
Do you know what your customers see and do before they purchase from you?
They see your ads, interact with you on social media and explore your website before they buy. All these interactions—from the first ad impression to every “Please help” DM customers send—define your customer journey. To keep up with it all and better inform your social media marketing strategy , create a customer journey map as a blueprint to help you understand your customers at each stage.
Let’s explore what customer journey mapping is and how it helps your brand.

Social Customer Care by Sprout Social
What is customer journey mapping?
A customer journey map is a visual representation of each point of interaction your customers have with your company. You can style the map like a flowchart, timeline, table or even on sticky notes.
Creating the map is a great internal exercise. Along the way, you might find pain points or touchpoints you didn’t know existed. A basic customer journey map includes the buying stages (and support touchpoints) a customer goes through.

More detailed maps include:
- actions your customers take
- good and bad emotions your customers experienced
- departments involved in customer touchpoints
- content types you serve your customers
- solutions to pain points
What is a customer touchpoint?
A touchpoint on the customer journey map is the point of interaction a customer has with your brand. It doesn’t need to be a two-way interaction. Seeing a social media ad, getting a branded newsletter and asking a friend for a product recommendation are all touchpoints.
Customers may experience emotions and actions at touchpoints. When someone asks for product recommendations, people might mention your brand. You might not serve that recommendation to them directly but someone still introduces you to a potential customer.
What are the benefits of customer journey mapping?
A customer journey map puts the customer first by giving you a deeper understanding of how your customers interact with your brand. This enable you to make better decisions and improve customer experiences.
When coupled with social media market research , they help brands:
- Provide an overview of the resources your customers use . This helps determine the ROI of customer-centric engagement and service. For example, if blogs are your highest traffic sources, investing more in those channels makes sense.
- Identify content gaps . Pain points without solutions are an excellent source for content ideation and development . If customers need help with a specific product issue, for example, but find limited guidance, create in-depth video tutorials to address this pain point.
- Identify inefficiencies . Maybe some processes are repetitive, or some solutions cause more friction. If your customers have trouble checking out due to a complicated form, for example, simplify it to reduce cart abandonment rates.
- Generate marketing campaign ideas . A clear understanding of customer motivations and journey stages creates targeted campaigns. You can provide them with relevant content and incentives to move them closer to a purchase.
- Guide multiple departments. Streamline content creation, social customer care strategy and messaging optimization across every touchpoint. Departments use the customer journey map as a central reference to ensure a consistent and customer-focused approach.
- Enhance customer communication . Customer journey maps reveal critical touchpoints, like social media interactions, for timely and meaningful engagement. In fact, The Sprout Social Index™ shows 51% of customers believe the most memorable brands on social respond to customers.
Every business and industry has its unique customer journey maps, but the fundamentals remain the same.
Recently, our social team talked about using social media for the customer journey in the auto industry. Watch the video below to hear their discussion on touchpoints, customer experience and how legacy brands are going beyond traditional tactics like targeted ads to tell their story.
It’s a great example of how industry-specific customer journey follows the fundamentals but also has touchpoints specific to them.
What’s included in a customer journey map?
A customer journey map is like a detailed travel itinerary for your customer’s experience with your brand. It includes elements like:
1. The buying process
The buying process is the step-by-step path a customer follows to make a purchase decision. It tells you where customers drop off or face obstacles during making purchases.
Use prospecting tools, content management systems (CMS) and behavior analytics tools to gather data. Facebook Shops, Instagram Shopping and TikTok Shop data also provide valuable insights into how customers find products and engage with content via social commerce .
Pro tip : Categorize the journey into stages like awareness, consideration and decision to map these steps horizontally on the customer journey map.
Don’t forget to integrate feedback mechanisms, such as customer surveys or user testing. These offer qualitative insights into the buying process. Understanding the “why” behind customer behavior can be as important as knowing the “what.”
2. Emotions
Emotions show how customers feel at different touchpoints in their interaction with your brand. Emotions heavily influence purchase decisions and brand loyalty which is exactly why it’s so important to include them.
Think about it: When someone has a great experience with your brand and feels happy, they’re more likely to buy from you again. On the flip side, if they feel frustrated or unhappy, they’ll knock on your competitor’s door.
Use surveys or feedback forms to ask customers how they felt during their experience. You might have come across these smileys during your own shopping experience:

These scales are a convenient way to gauge how your customers feel at any point.
Pay attention to what they say on social media and in reviews. You can tell if they’re happy or upset by their tone.
Tools like Sprout Social use AI-driven sentiment analysis to dig into social listening data to give you insights on what people think about your brand.

These insights are handy when creating emotional marketing campaigns . When you know how customers feel, take actionable steps to solve any negative experiences and encourage positive ones.
3. User actions
User actions are the steps customers take when they interact with your brand. They include steps like visiting your website, clicking on a product, adding items to their cart or signing up for your newsletter.
Actions highlight what people do at each stage. Each of these actions tells you something about what customers are interested in and how close they are to making a purchase.
Analytics tools for your website or app are your best bet for such data. These tools show you which pages customers visit, what they click on and where they drop off.
Once you have this information, tailor your marketing efforts and content to align with the actions customers take at each stage.
4. User research
User research examines what customers search for or where they turn for information during the buying process. This part of the customer journey map helps you understand how customers gather information.
For example, in the awareness stage, buyers often rely on search engines like Google to research solutions to their problems. But it’s not just about where they go—it’s about what they’re looking for. Knowing their specific research topics allows you to address their pain points.
What’s the trick? Keep an eye on what customers search for online. Tracking keywords and phrases they use on search engines, as well as social media market research are good places to start.
Also, monitor discussions and conversations to get a deeper understanding of the questions, concerns and topics that are top-of-mind for your potential customers.
The key is to use this information to provide potential customers with what they need at each stage. Targeted content delivery positions your brand as a valuable source of information.
5. Solutions
This section outlines the actions and strategies your brand implements to address customer pain points and improve their overall experience.
It documents the specific solutions or improvements applied at each stage of the customer journey. These include steps like changes to website design that resolve issues and improve the customer experience.
It visualizes how your brand responds to customer needs and challenges at different touchpoints. Besides that, it’s a good reference to ensure your team implements the solutions and refines them to increase customer satisfaction.
What are the 7 steps to map the customer journey?
A strategic approach to building a map ensures you capture every touchpoint, anticipate customer desires and address potential pain points. Here are seven steps to build a journey map unique to your customers and business needs.
1. Set your goals
What do you want to get out of this process? And why does it matter to your business? Knowing your goals sets the stage for how you assemble your map.
Some examples of goals include:
- Identify the top three customer pain points. Use these pain points to create content.
- Understand customer interests and motivations to develop better products and services.
- Total the cost of customer interactions to set a better social media budget .
2. Decide on a customer journey map type
There are several different customer journey maps and each one has its advantages. When you decide which map to work with, you know which details to focus on.
These are four of the most common types of customer journey maps: current state, future state, day in the life and service blueprint. We’ll go further into detail on each one later on.
Understanding your goals and where your brand stands in its evolution will guide you in selecting the appropriate map type.
3. Create and define your customer personas
Which customers will you focus on? It’s difficult to map a customer journey if you don’t have a customer in mind. Customer personas are fictional characters that represent each of your target customer groups. They’re detailed with everything from demographics to interests to buying behavior.

If you’ve already created social media personas to understand your audience, you’re more than halfway there. But if you haven’t, then our buyer persona template or Xtensio’s will be useful. To really get to know someone’s purchase decisions and shopping processes, interview existing customers.
Pro tip: If you have distinctively different personas—such as, if you serve both a B2C and B2B market—set up different customer journey maps.
4. Break it down: touchpoints and stages

The customer journey map is divided into stages that usually fit within the funnel illustrated above. List out the stages to begin. Next, list out the main customer touchpoints that exist for your company. When you’re done with both lists, place the touchpoints into the different stages.
To get even more detailed, assign department owners to each touchpoint. You can identify where certain social media channels fit into the mix. And, you can assign predicted customer sentiment or emotions to different stages of the journey. It’s up to you how detailed you want the map to be.
5. Gather data and customer feedback
You need rock-solid data on how customers interact with your brand to create an accurate customer journey map. Focus on these three aspects:
Analyze existing data
Jump into the data you already have—more specifically website performance, chats with customer support and sales records. This information can tell you loads about how customers act, what they like and what frustrates them.
This quantitative data offers a foundational perspective on how customers interact with your brand, helping you identify both strengths and areas of improvement.
Conduct customer interviews
Get personal with one-on-one chats with customers. Ask them about their experiences, what bugs them and what they expect when they deal with your brand. These talks reveal qualitative insights that numbers can’t, like understanding the emotional and psychological aspects of the customer journey.
Create surveys and questionnaires
Turn to surveys and questionnaires for a more structured and broader approach to gathering feedback. Send them out to a bunch of customers and get structured feedback. Ask questions about their journey with your brand, how happy they are and where they think things could get better.
A combination of these three aspects gives you a 360-degree view of what your customers really experience with your brand.
6. Test and identify pain points
To confirm your customer touchpoints, you probably checked in on various departments and spoke to customers. This is great work but you need to take another step further: test it yourself. Go through the customer journey from the viewpoint of the customer.
While you’re testing the journey, keep an eye out for challenges, confusion or any frustrating moments. For example, if the website takes forever to load, if instructions aren’t clear or if reaching customer support is a headache, make detailed notes of these issues.
It’s also a smart move to collect feedback from both colleagues and customers who’ve gone through the journey. This way, you double-check and confirm your findings for a more complete picture.
A hands-on approach ensures your customer journey map reflects the real-world experience and equips you to take targeted actions to improve the overall customer journey.
7. Make changes and find solutions
So your map is complete. What’s next? You need to find or create solutions to the pain points you identified in the previous step.
Now’s the time to check in on the goals you established in step one and make the moves to smooth out the journey. Give yourself time and space to implement some of the solutions, whether a quarter or six months, and check back on the map to update it.
As you put these changes into action, make sure to watch your customer journey map closely. Don’t forget to keep it up to date to show the improvements and how they affect the customer experience. This keeps your customer journey map fresh and super useful for steering your brand toward delivering an exceptional customer experience.
4 types of customer journey maps and examples
Let’s take a look at the four most common customer journey maps and examples of each.
1. Current state
Current state customer journey maps are like an audit. You document how your customers experience their buying and service paths in your company’s current state. These are especially helpful to establish a baseline for your customer service experience.
Take a look at this simplified current state customer journey map from Nielsen-Norman.

The map follows the journey of “Jumping Jamie” as they navigate the process of switching to a different mobile plan. The map defines the current journey into four stages. Apart from the journey, it also highlights opportunities and metrics to track.
Current state maps are fantastic for sharing user frustrations with all departments. This helps you get everyone on board with investing in solutions and brainstorming ways to address user pain points.
2. Future state
Future state customer journey maps follow the same format as current state maps except they represent the ideal journey. You can use them alongside your current state maps to identify painpoints and areas to improve.
Here’s an example of a future state journey map:

Why does this visual work? It covers different states, feelings and even touchpoints in a cohesive format.
The map visualizes the best-case scenario to create a north star vision for your brand. It aligns your efforts toward achieving the ideal customer journey.
3. Day-in-the-life
Day-in-the-life customer journey maps outline one of your persona’s schedules as they go about their day. The interactions may or may not involve your company. Creating one of these maps helps you identify the best times and areas to interact with your customer.
Here’s a “day-in-the-life” visual from Pipedrive.

The map doesn’t just highlight when the persona does something, but it also highlights different touchpoints and the different people they interact with throughout the day. And, notice those thumbs ups and downs? Those highlight how the child feels during different activities too.
4. Service blueprint

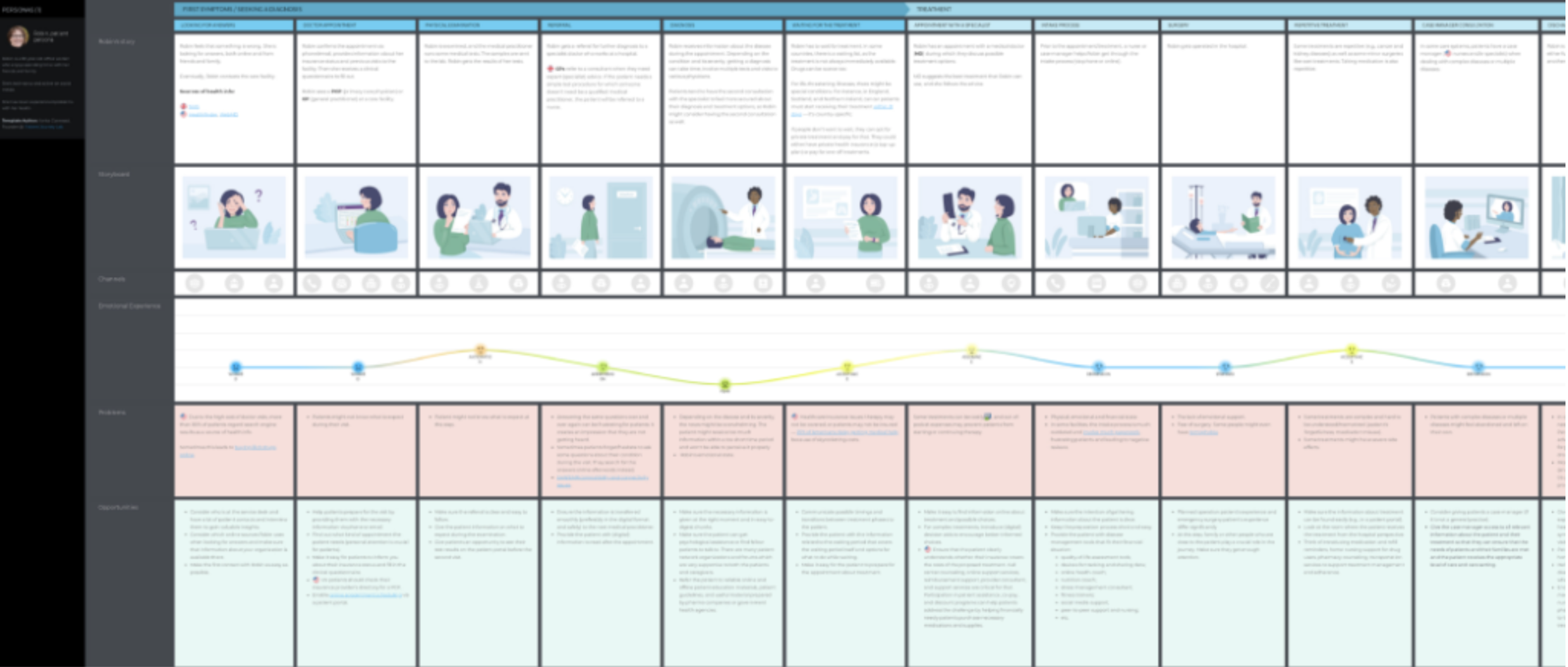
A service blueprint customer journey map focuses solely on when you provide customer service. It ignores components like ads that might exist in other maps.
Miro, a collaborative online whiteboard for teams, created the above map with a bank in mind. You’ll notice how this map is only about a customer’s visit to the bank. This type of map helps brands look at individual service areas and interactions. It’s a macro version of the current and future state maps.
Get started with customer journey map templates
Creating a customer journey map doesn’t have to be overwhelming. There are plenty of free and paid templates out there to help you create one. If you think you’ll need more guidance or many maps, some companies offer special software to design a custom map. Build your first journey map or improve your existing one with these options.
- Current state template , provided by Bright Vessel.

- Customer journey map template by Moqups, a design and collaboration tool.

- Service blueprint template by Miro

- Customer journey map template by Mural, a planning tool.

- UXPressia’s customer journey map online tool , made specifically to create presentation-ready customer journey maps.
Create a strong foundation with a well-integrated customer journey map
A customer journey map gives you the recipe for crafting personalized, impactful interactions that build customer satisfaction and loyalty.
When you know what they are and why they’re important, it’s time to make yours. Use data to create a solid customer journey map that exceeds customer expectations at every touchpoint.
Check out how you can turn your B2B social media data into a revenue-driving powerhouse and create a memorable brand.
- Customer Care
- Customer Experience
How to build customer relationships with social media
Omnichannel customer experience: exploring seamless customer journeys
The role of AI in creating a more human customer experience
- Social Listening
How to use voice of customer data to grow your brand
- Now on slide
Build and grow stronger relationships on social
Sprout Social helps you understand and reach your audience, engage your community and measure performance with the only all-in-one social media management platform built for connection.
Learn / Guides / Customer journey mapping (CJM) guide
Back to guides
Customer journey mapping in 2 and 1/2 days
How to create a customer journey map that improves customer success.
Last updated
Reading time.
There’s a common saying that you can’t understand someone until you’ve walked a mile in their shoes—and that’s exactly what customer journey maps do: they help you put yourself in different customers’ shoes and understand your business from their point of view.
Why should you do it? How should you do it? Find the answers in this guide, which we wrote after interviewing 10+ customer journey experts who shared methodologies, dos and don’ts, and pro tips with us.
On this page:
What is a customer journey map?
How to create a customer journey map in 2 and ½ working days
4 benefits of customer journey mapping for your business
In later chapters, we dive deeper into customer journey analytics, workshops, and real-life examples.
Start mapping your customer journey
Hotjar lets you experience the customer journey through their eyes, so you can visualize what’s working and what needs improvement.
A customer journey map (CJM) is a visual representation of how customers interact with and experience your website, products, or business across multiple touchpoints.
By visualizing the actions, thoughts, and emotions your customers experience, a customer journey map helps you better understand them and identify the pain points they encounter. This is essential if you want to implement informed, customer-focused optimizations on your site.
Mapping the customer journey: narrow vs. wide focus
A customer journey map can have a very narrow focus and only look at a few, specific steps of the customer experience or buyer’s journey (for example, a product-to-purchase flow on a website), or it can take into account all the touchpoints, online and offline, someone goes through before and after doing business with you.
Each type of customer journey map has its advantages:
A CJM with a narrow focus allows you to zero in on an issue and effectively problem-solve
A CJM with a wide focus gives you a broader, holistic understanding of how customers experience your business
Regardless of their focus, the best customer journey maps have one thing in common: they are created with real customer data that you collect and analyze . The insights are usually organized into a map (hence the name), diagram, or flowchart during a group workshop, which is later shared across the entire business so everyone gets a clear and comprehensive overview of a customer’s journey.
How to create your first customer journey map in 2 and ½ working days
The process of creating a customer journey map can be as long or short as you need. Depending on how many people and stakeholders you involve, how much data you collect and analyze, and how many touchpoints there are across the business, you could be looking at days or even weeks and months of work.
If you’re new to customer journey mapping, start from a narrower scope before moving on to mapping every single customer touchpoint .
Here’s our beginner customer journey mapping framework to help you create your first complete map in 2 and ½ working days:
Day 1: preliminary customer journey mapping work
Day 2: prep and run your customer journey mapping workshop.
Final ½ day: wrap up and share your results
Download your free customer journey map checklist (as seen below), to mark off your tasks as you complete them.
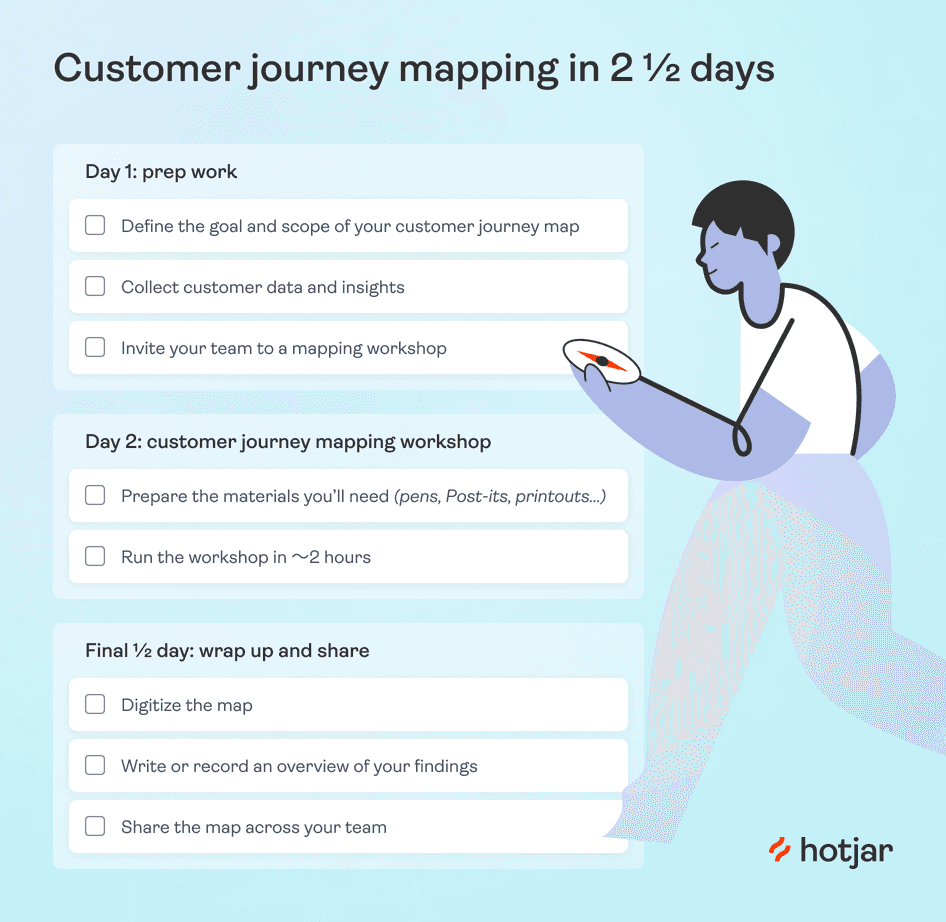
On your first day, you have three essential tasks:
Define the goal and scope of your CJM
Collect customer data and insights
Invite your team to a customer journey mapping workshop
Step 1: define the goal and scope of your CJM
Clarifying what part(s) of the journey you're looking at, and why, helps you stay focused throughout the mapping process.
If this is your first map, start from a known issue or problematic area of your website. Keep the scope small, and focus on anything you can break down into four or five steps. For example:
If you have a high drop-off on a pricing page with five calls-to-action, each of which takes users to a different page, that’s enough for a mappable journey
If your purchase flow is made of five self-contained pages, each of which loses you potential customers, that’s a good candidate for mapping
✅ The output: a one- or two-sentence description of what your map will cover, and why, you can use whenever you need to explain what the process is about. For example: this map looks at the purchase flow on our website, and helps us understand how customers go through each step and the issues or obstacles they encounter. The map starts after users click ‘proceed to checkout’ and ends when they reach the 'Thank You' page .
Step 2: collect customer data and insights
Once you identify your goal and scope, the bulk of your first day should be spent collecting data and insights you’ll analyze as part of your mapping process. Because your map is narrow in focus, don’t get distracted by wide-scale demographics or data points that are interesting and nice to know, but ultimately irrelevant.
Get your hands on as much of the following information as you can:
Metrics from traditional analytics tools (such as Google Analytics) that give you insight into what’s happening, across the pages and stages your customer journey map covers
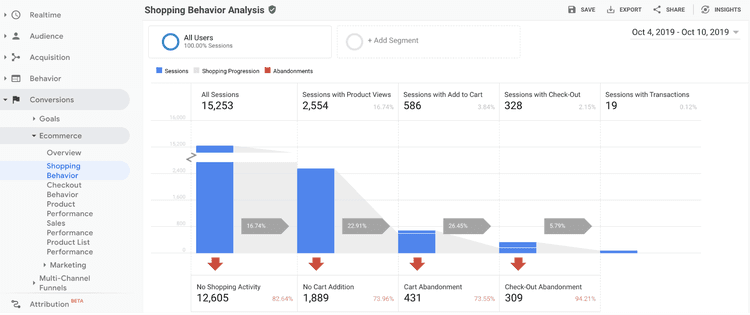
Data from analyzing your conversion ‘funnels’ , which record how many visitors end up at each stage of the user journey, so you can optimize those steps for potential customers and increase conversions
Behavior analytics data (from platforms like Hotjar) that show you how people interact with your site. For example, heatmaps give you an aggregate view of how users click, move and scroll on specific pages, and session recordings capture a user’s entire journey as they navigate your site
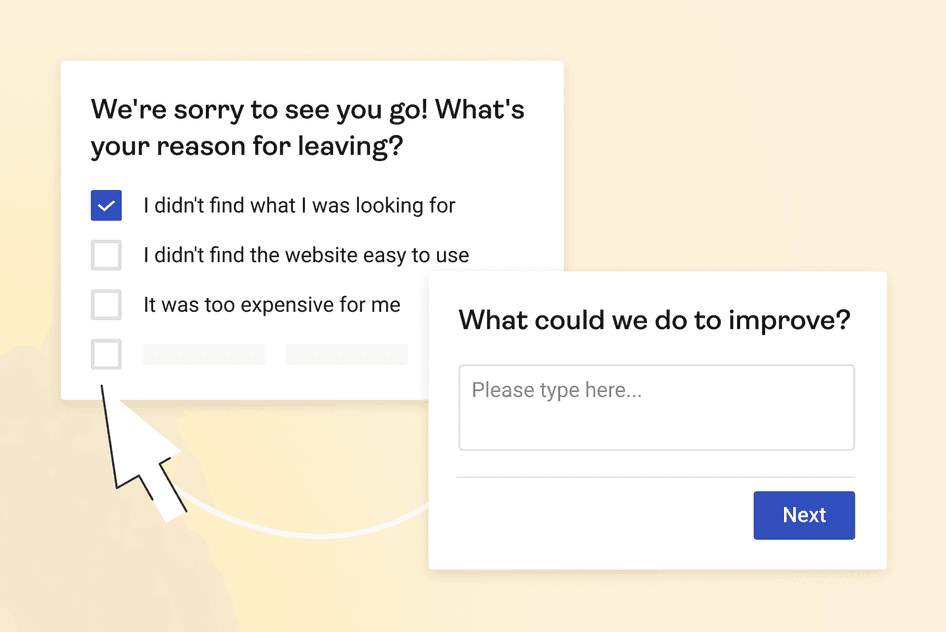
Quantitative and qualitative answers to on-site surveys relevant to the pages you’re going to investigate, as customer feedback will ultimately guide your roadmap of changes to make to improve the journey
Any demographic information about existing user and customer personas that helps you map the journey from the perspective of a real type of customer, rather than that of any hypothetical visitor, ensuring the journey makes sense for your target audience
Any relevant data from customer service chat logs, emails, or even anecdotal information from support, success, and sales teams about the issues customers usually experience
✅ The output: quantitative and qualitative data about your customers' interactions and their experiences across various touchpoints. For example, you’ll know how many people drop off at each individual stage, which page elements they interact with or ignore, and what stops them from converting.
💡Pro tip: as you read this guide, you may not yet have most of this data, particularly when it comes to heatmaps, recordings, and survey results. That’s ok.
Unless you’re running your CJM workshop in the next 12 hours, you have enough time to set up Hotjar on your website and start collecting insights right now. The platform helps you:
Learn where and why users drop off with Funnels
Visualize interactions on key pages with Heatmaps
Capture visitor sessions across your website with Recordings
Run on-site polls with Surveys
When the time comes for you to start your customer journey mapping process, this data will be invaluable.
Step 3: invite your team to a customer journey mapping workshop
In our experience, the most effective way to get buy-in is not to try and convince people after things are done—include them in the process from the start. So while you can easily create a customer journey map on your own, it won’t be nearly as powerful as one you create with team members from different areas of expertise .
For example, if you’re looking at the purchase flow, you need to work with:
Someone from the UX team, who knows about the usability of the flow and can advocate for design changes
Someone from dev or engineering, who knows how things work in the back end, and will be able to push forward any changes that result from the map
Someone from success or support, who has first-hand experience talking to customers and resolving any issues they experience
✅ The output: you’ve set a date, booked a meeting space, and invited a group of four to six participants to your customer journey mapping workshop.
💡Pro tip: for your first map, stay small. Keep it limited to four to six people, and no main stakeholders . This may be unpopular advice, especially since many guides out there mention the importance of having stakeholders present from the start.
However, when you’re not yet very familiar with the process, including too many people early on can discourage them from re-investing their time into future CJM tasks. At this stage, it’s more helpful to brainstorm with a small team, get feedback on how to improve, and iterate a few times. Once you have a firm handle on the process, then start looping in your stakeholders.
On workshop day, you’ll spend half your time prepping and the other half running the actual session.
Step 1: prepare all your materials
To run a smooth workshop, ensure you do the following:
Bring stationery: for an interactive workshop, you’ll need basic materials such as pens, different colored Post-its, masking tape, and large sheets of paper to hang on the wall
Collect and print out the data: use the data you collected on Day 1. It’s good to have digital copies on a laptop or tablet for everybody to access, but print-outs could be the better alternative as people can take notes and scribble on them.
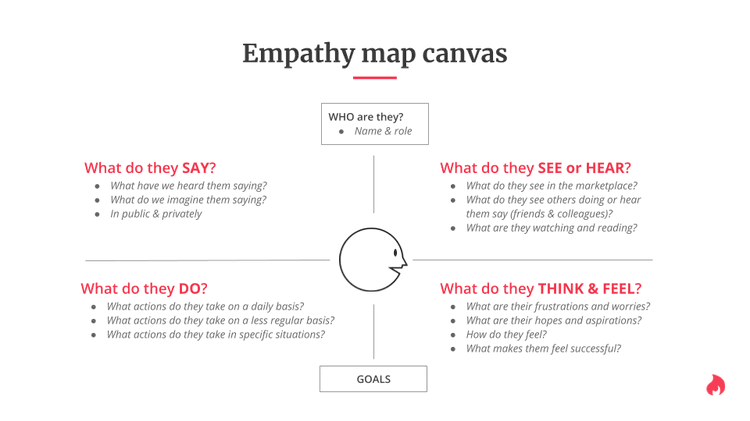
Print out an empathy map canvas for each participant: start the workshop with an empathy mapping exercise (more on this in Step 2). For this, hand each participant an empty empathy map canvas you can recreate from the template below.
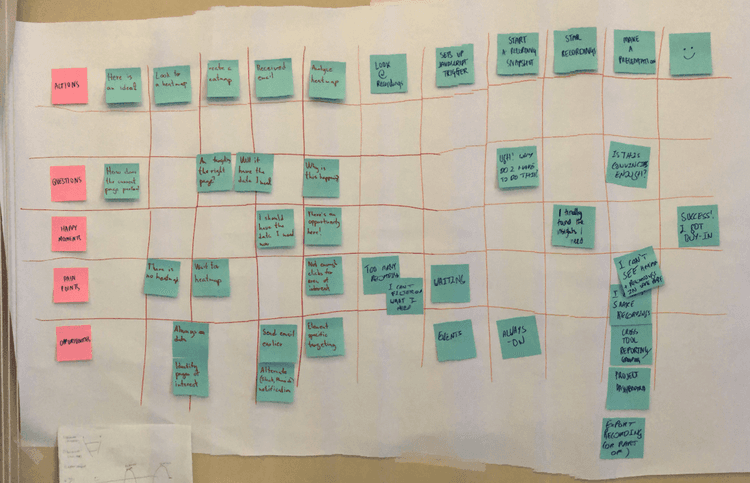
Set up a customer journey map template on the wall: use a large sheet of paper to create a grid you'll stick to the wall and fill in as part of the workshop. On the horizontal axis, write the customer journey steps you identified during your Day 1 prep work; on the vertical axis, list the themes you want to analyze for each step. For example:
Actions your customers take
Questions they might have
Happy moments they experience
Pain points they experience
Tech limits they might encounter
Opportunities that arise
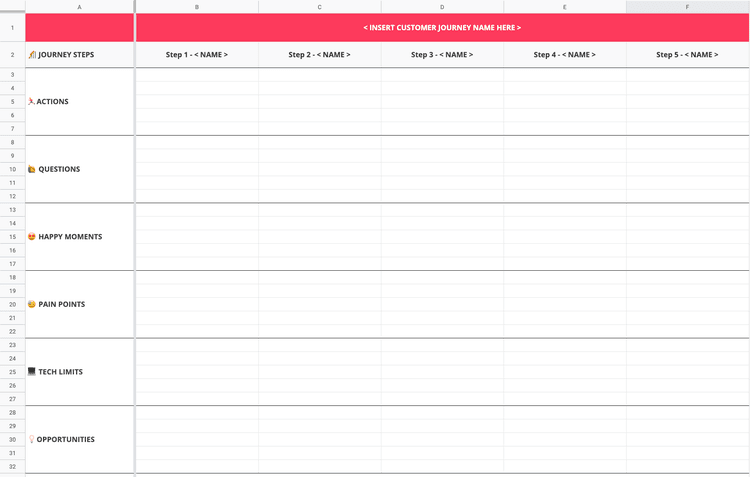
Step 2: run the workshop
This is the most interactive (and fun) part of the process. Follow the framework below to go from zero to a completed draft of a map in just under 2 hours .
Introduction [🕒 5–10 min]
Introduce yourself and your participants to one another
Using the one-two sentence description you defined on Day 1, explain the goal and scope of the workshop and the activities it will involve
Offer a quick summary of the customer persona you’ll be referring to throughout the session
Empathy mapping exercise [🕒 30 min]
Using the personas and data available, have each team member map their observations onto sticky notes and paste them on the relevant section of the empathy mapping canvas
Have all participants take turns presenting their empathy map
Facilitate group discussions where interesting points of agreement or disagreement appear
Customer journey mapping [🕒 60 min]
Using Post-its, ask each participant to fill in parts of the map grid with available information. Start by filling in the first row together, so everybody understands the process, then do each row individually (15–20 min). At the end of the process, you should have something like this:

Looking at the completed map, encourage your team to discuss and align on core observations (and take notes: they’ll come in handy on your final half day). At this point, customer pain points and opportunities should become evident for everybody involved. Having a cross-functional team means people will naturally start discussing what can, or cannot, immediately be done to address them (35–40 min).
Wrap up [🕒 5 min]
Congratulations! Your first customer journey map is complete. Finish the session by thanking your participants and letting them know the next steps.
Final half-day: wrap up and share
Once you’ve gone through the entire customer journey mapping workshop, the number one thing you want to avoid is for all this effort to go to waste. Instead of leaving the map hanging on the wall (or worse: taking it down, folding it, and forgetting about it), the final step is to wrap the process up and communicate the results to the larger team.
Digitize the map so you can easily update and share it with team members: it may be tempting to use dedicated software or invest time into a beautiful design, but for the first few iterations, it’s enough to add the map to your team’s existing workflows (for example, our team digitized our map and added it straight into Jira, where it’s easily accessible)
Offer a quick write-up or a 5-minute video introduction of the activity: re-use the description you came up with on Day 1, including who was involved and the top three outcomes
Clearly state the follow-up actions: if you’ve found obvious issues that need fixing, that’s a likely next step. If you’ve identified opportunities for change and improvement, you may want to validate these findings via customer interviews and usability testing.
4 benefits of customer journey mapping
In 2023, it’s almost a given that great customer experience (CX) provides any business or ecommerce site with a competitive advantage. But just how you’re supposed to deliver on the concept and create wow-worthy experiences is often left unsaid, implied, or glossed over.
Customer journey maps help you find answers to this ‘How?’ question, enabling you to:
Visualize customer pain points, motivations, and drivers
Create cross-team alignment around the business
Remove internal silos and clarify areas of ownership
Make improvements and convert more visitors into customers
We’ve done a lot of customer journey work here at Hotjar, so we know that the above is true—but don’t just take our word for it: all the people we interviewed for this guide confirmed the benefits of journey mapping. Let’s take a look at what they shared.
1. Visualize customer pain points, motivations, and drivers
It’s one thing to present your entire team with charts, graphs, and trends about your customers, and quite another to put the same team in front of ONE map that highlights what customers think, want, and do at each step of their journey.
I did my first customer journey map at MADE.COM within the first three months of joining the company. I was trying to map the journey to understand where the pain points were.
For example, people who want to buy a sofa from us will be coming back to the site 8+ times over several weeks before making a purchase. In that time, they may also visit a showroom. So now I look at that journey, at a customer’s motivation for going to the website versus a physical store, and I need to make sure that the experience in the showroom complements what they're doing on-site, and vice-versa, and that it all kind of comes together.
The map helps in seeing that journey progress right up to the time someone becomes a customer. And it also continues after: we see the next touchpoints and how we're looking to retain them as a customer, so that they come back and purchase again.
A customer journey map is particularly powerful when you incorporate empathy into it, bringing to light specific emotions that customers experience throughout the journey.

2. Create cross-team alignment around the business
The best, most effective customer journey maps are not the solo project of the user experience (UX) or marketing team (though they may originate there).
Customer journey maps are a quick, easy, and powerful way to help everybody in your business get a clearer understanding of how things work from a customers’ perspective and what the customers’ needs are—which is the first step in your quest towards creating a better experience for them.
Our first goal for preparing a customer journey map was to improve understanding customers across the company, so that every employee could understand the entire process our clients go through.
For example, people from the shipping department didn't know how the process works online; people from marketing didn't know how customers behave after filing a complaint. Everything seems obvious, but when we shared these details, we saw that a lot of people didn't know how the company itself works—this map made us realize that there were still gaps we needed to fill.
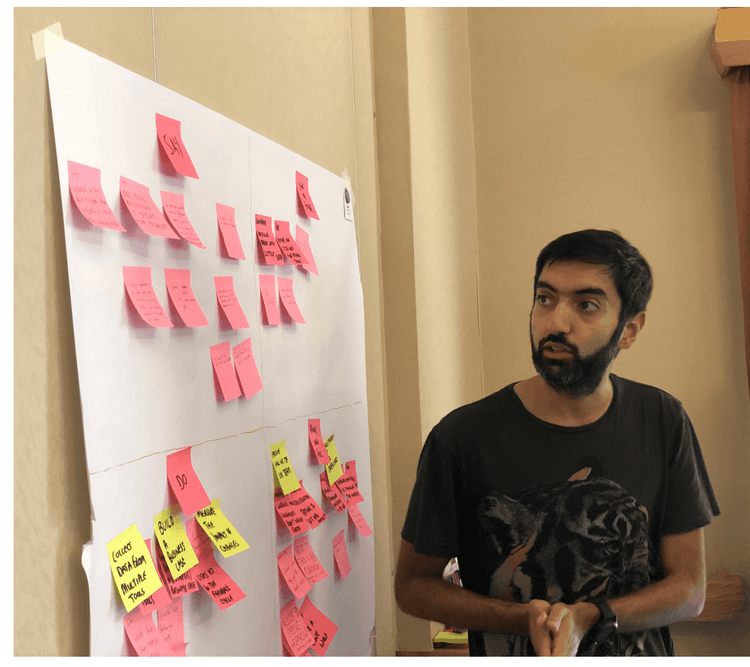

If we discover that customers have a pain point in a specific section of the map, different teams can look at the same section from several angles; customer support can communicate why something is not possible, and engineering can explain why it’s going to take X amount of effort to get it done. Especially in cross-functional teams where we all come from really different disciplines, I find these maps to be an incredible way for us all to speak the same language.
3. Remove internal silos and clarify areas of ownership
As a company grows in size and complexity, the lines of ownership occasionally become blurry. Without clarity, a customer might get bounced like a ping pong ball across Sales, Success, and Support departments—not great for the seamless and frictionless customer experience we all want to offer.
A central source of ‘truth’ in the form of a customer journey map that everybody can refer to helps clarify areas of ownership and handover points.
We were growing as a team, and we realized we needed to operationalize a lot of the processes that, before then, had just been manually communicated. We did it through a customer journey map. Our goal was to better understand where these hand-off points were and how to create a more seamless experience for our customers, because they were kind of being punted from team to team, from person to person—and often, it was really hard to keep tabs on exactly where the customer was in that entire journey.
4. Make improvements and convert more visitors into customers
A customer journey map will take your team from 'It appears that 30% of people leave the website at this stage' to 'Wow, people are leaving because the info is incomplete and the links are broken.' Once everyone is aligned on the roadblocks that need to be addressed, changes that have a positive impact on the customer experience and customer satisfaction will happen faster.
The customer journey map brings it all together: it doesn't matter who you've got in the room. If you’re doing a proper journey map, they always get enlightened in terms of ‘Oh, my word. I did not know the customer's actually experiencing this.’ And when I walk out of the session, we have often solved issues in the business. Accountability and responsibilities have been assigned, and I find that it just works well.

Shaheema (right) working on a customer journey map
Collect the right data to create an effective customer journey map
The secret of getting value from customer journey mapping is not just building the map itself: it's taking action on your findings. Having a list of changes to prioritize means you can also measure their effect once implemented, and keep improving your customers' experience.
This all starts with collecting customer-centric data—the sooner you begin, the more information you’ll have when the time comes to make a decision.
Start mapping your customer journey today
Hotjar lets you experience your customer’s journey through their eyes, so you can visualize what’s working and what needs improvement.
FAQs about customer journey mapping
How do i create a customer journey map.
To create a useful customer journey map, you first need to define your objectives, buyer personas, and the goals of your customers (direct customer feedback and market research will help you here). Then, identify all the distinct touchpoints the customer has with your product or service in chronological order, and visualize the completion of these steps in a map format.
What are the benefits of customer journey mapping?
Customer journey mapping provides different teams in your company with a simple, easily understandable visualization that captures your customers’ perspective and needs, and the steps they’ll take to successfully use your product or service.
Consider customer journey mapping if you want to accomplish a specific objective (like testing a new product’s purchase flow) or work towards a much broader goal (like increasing overall customer retention or customer loyalty).
What is the difference between a customer journey map and an experience map?
The main difference between an experience map and a customer journey map is that customer journey maps are geared specifically toward business goals and the successful use of a product or service, while experience maps visualize an individual’s journey and experience through the completion of any task or goal that may not be related to business.
Sprinklr Service
Sprinklr Social
Works Best With
Sprinklr Insights
Sprinklr Marketing
Marketing Teams
Customer Service Teams
- Unified-CXM
- Customers Customer Stories Sprinklr Champions
- Company Our Story Leadership Newsroom Partners Careers Culture & Talent Investor Relations Security & Data Privacy
- Resources Learn Services Support CX-WISE Podcast Analyst Reports Product Demo Days eBooks & Reports Events & Webinars Blog Unified-CXM Guide Our Services Training For Agencies Help Center Release Notes Contact Us
.css-14us1xl{box-sizing:border-box;margin:0;min-width:0;white-space:pre-wrap;} Customer Journey: Stages, Mapping & Examples
Customer journeys can be elusive. Learn more about customer journey mapping and how it can help brands create better experiences for their customers.
Share this Topic
What is a customer journey?
What is a customer journey map, five stages of customer journey [key phases], examples of successful customer journey implementation by brands.
The customer journey is the sum of all the interactions a customer has with a brand before, during and after a purchase. A smooth, effortless customer journey can ensure a prospect converts into a customer in the quickest time possible.
Brands need to factor in consumer needs and behavioral patterns when mapping out customer journeys to deliver a great end-to-end customer experience (CX) and achieve their business goals faster.
A customer journey map helps brands visualize all the interactions a prospect or customer has with the brand, product, or service. These interactions, also called touchpoints, can vary in number depending on your customers’ preferences, their end goals, and the channels through which they interact with your brand. A detailed customer journey map can help you understand your customer pain points and customize individual touchpoints accordingly.
Why is the customer journey important?
Having a firm understanding of how customers engage with your brand lets you accomplish the following:
Having a firm understanding of how customers engage with your brand lets you accomplish the following:
Today’s customers have more options than ever and have much higher expectations regarding product, price and service than ever before. To meet and exceed those expectations, brands must identify their customers’ likes and preferences.
With a clear view of the customer journey and the various phases a customer navigates to address their objective, brands can deliver superior experiences to their customers.
#2. Faster conversion
If this transition isn’t smooth, your customers may not feel invested enough to continue their journey to achieve their goals, whatever they may be. A customer journey that is free from obstacles, such as an inconsistent experience when switching between touchpoints, impacts your conversion rate.
#3. Customer delight
A customer’s journey doesn’t come to an end immediately after they’ve made a purchase. A happy and satisfied customer often comes back for more. In fact, they become loyal brand advocates, increasing brand affinity.
Audience analysis and designing persona-driven journeys will help create more positive “moments of truth” — a significant brand-customer interaction whereby the customer forms or changes their impression of your brand — ultimately leading to customer delight.

Get the Sprinklr Service Strategic Handbook
Customer journey vs. Customer experience
Customer journey and customer experience might sound similar, but they represent distinct aspects of the customer's interaction with a brand.
Read More: Top 7 Customer Experience Metrics to Track
The customer journey phases represent the different stages your prospects and customers go through as they interact with your brand. These phases usually include multiple touchpoints and are classified as follows.
This is when a prospect is looking for a solution to their business problem(s) through research on search engines and, in the process, comes across your brand and product.
Customers become aware of your brand and products.
Initial interaction via social media, search engines or recommendations.
Roadmap for brands : Focus on providing informational content that answers questions and builds trust.
Example: In this initial stage, the call center leader becomes aware of a problem - growing agent attrition. To find solutions, they turn to Quora, a popular platform for information and discussion. Here, they search for "Why are agents leaving my call center?" and stumble upon a highly informative response from a Sprinklr representative. This response lists the top reasons for agent attrition, instantly grabbing the leader's attention. The trust is established as the information is accurate and relevant, positioning Sprinklr as a knowledgeable source.
🤔Consideration
The prospect then tries to identify the most appropriate solution for their specific business needs by visiting your website and your competitors to evaluate their options.
Customers consider your brand as a solution.
They compare products and alternatives.
Roadmap for brands: Provide content highlighting problem-solving features without aggressive sales tactics.
Example: At this point, the call center leader is intrigued and motivated to explore Sprinklr's solutions further. They visit Sprinklr's website, where they find a wealth of valuable content related to call management , employee engagement and call center guide to agent retention .
Impressed by the depth and relevance of the content, the leader signs up for Sprinklr's blog, showing interest in staying updated with industry insights. This indicates a growing consideration for Sprinklr as a potential solution provider to address their attrition issue.
The prospect shortlists potential solutions that they think will solve their needs and then proceeds to shortlist your product or service along with a few others. Then, after a period of deliberation, decide to buy or adopt your offering.
Customers develop preferences for reading through the available content on the internet
They decide to take a demo or a free trial
Based on their experience, customers decide to make a buying choice
Roadmap for brands : Persuade customers with pricing, comparison guides and abandoned cart emails.
Example: As the leader continues to engage with Sprinklr's content and resources, they begin to develop a preference for the company's offerings. They reach out to Sprinklr's sales team or request a demo of the Unified-CXM platform.
After a successful demo and discussions with Sprinklr's sales representatives, they decide to make a purchase. This stage involves the leader becoming a paying customer, signaling their commitment to solving the agent attrition challenge with Sprinklr's assistance.
🙌Retention
After a while, the customer may have issues with your product or service and decide to reach your customer support for help. Or they may wish to renew or upgrade their existing product or service, and subsequently land on your FAQ pages to understand their options.
Roadmap for brands : Focus on keeping existing customers and driving repeat business. Maintain positive relationships with email outreach, coupons and exclusive communities.
Example: The call center leader and their team receive onboarding assistance, training and ongoing support from Sprinklr's team to ensure a smooth implementation. In this stage, the call center leader's success and satisfaction with Sprinklr's solutions are crucial to building a long-term customer relationship, potentially leading to future collaborations and referrals.
After implementing Sprinklr's Unified-CXM platform to address agent attrition, the call center leader began to witness significant improvements in employee retention. The attrition rate decreases and job satisfaction among the call center agents increases due to better working conditions, streamlined processes and improved support systems offered by Sprinklr's solution.
The call center leader decides to continue using Sprinklr’s Unified-CXM platform and reap its benefits in the form of better productivity and great customer experiences.
Read more: The Call Center Guide to Agent Retention
The final stage involves the customer being so happy with their experience with your brand that they recommend your solution to others. They do this through word of mouth – text, calls and by leaving positive reviews on the platform of their choice. Delighted customers actively encourage others to make purchases.
Roadmap for brands : Offer referral bonuses, loyalty programs and special deals to promote advocacy further.
Example: In the Advocacy stage, the call center leader becomes a vocal advocate for Sprinklr. Their success story becomes a powerful testimonial for Sprinklr's solution. The leader is now not only retaining their team but also sharing their positive experiences with colleagues in the industry, both online and in professional networking events.
The call center leader might write a blog post or participate in industry webinars, sharing how Sprinklr's Unified-CXM platform helped them combat agent attrition effectively. They recommend Sprinklr to peers and industry forums where similar challenges are discussed. The leader's advocacy not only enhances Sprinklr's reputation but also leads to potential referrals and new business opportunities for the company.
Dig Deeper: How to Turn Customers into Brand Advocates
A customer journey map is a visual representation of the entire experience a customer has with a business, from initial awareness to post-purchase interactions.
It helps businesses understand and improve the customer's path, enabling them to identify pain points and opportunities for engagement to enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty ultimately.
These interactions, also called customer touchpoints, can vary in number depending on your customers' preferences, their end goals and the customer service channels through which they interact with your brand. Regardless, customer journey mapping is the foundation of customer lifecycle management.
How to create a customer journey map
To create an efficient customer journey map, understand these four key elements.
Customer journey stages : Your map should cover every stage of the customer journey, from initial awareness to post-purchase advocacy. Don't limit your focus to just the buying stages; consider the entire customer lifecycle.
Touchpoints : Identify and document the most common touchpoints that customers encounter at each stage of their journey. These touchpoints could include your blog, social media, reviews or email. Prioritize the most relevant touchpoints to ensure a comprehensive view.
The full customer experience : Recognize that customers' actions, motivations, questions and pain points change as they progress through the journey and interact with different touchpoints. Your map should encompass the entire customer experience at each touchpoint.
Your brand's solutions : Provide solutions tailored to each stage and touchpoint. These solutions may not always involve a direct purchase; for instance, an awareness-stage solution could be a blog, video or social media post aimed at furthering the reader’s understanding of the topic.
With these essential elements in mind, creating an effective customer journey map becomes a straightforward three-step process.
1st Step: Create buyer personas
Before mapping the customer journey, it's crucial to understand your audience. To do this, create buyer personas - fictional representations of your target customers . These personas should encompass their background, motivations, pain points and needs.
Here's how you can create a buyer persona:
Gather and analyze customer data : Collect information through analytics, surveys, and market research to understand your customers better.
Segment customers : Categorize customers into groups with shared characteristics, such as demographics or location.
Build personas : Select a segment to target and create a persona for that group. Include basic traits, motivations and pain points.
For example, Steve, “a marketing manager” might be a persona for marketing platforms like Marketo with detailed information about his pain points and preferences.
2nd Step : List touchpoints at each customer journey stage
Now that you have your buyer personas, it's time to identify touchpoints at each stage of the customer journey. This step involves listing the marketing channels where customers can interact with your brand. Key touchpoints at each stage typically include:
Awareness : Advertising, social media, blogs, referrals, and more
Consideration : Email, sales calls, landing pages and reviews
Purchase : Live chat, cart abandonment emails and more
Retention : Thank-you emails, product walkthroughs and online communities
Advocacy : Surveys, loyalty programs and events
By thoroughly identifying these touchpoints, you can ensure you engage with your customers effectively and consistently throughout their journey.
3rd Step: Map the customer experience at each touchpoint
Now, it's time to detail the experience you want to create for customers at each touchpoint. For each touchpoint, consider the customer's:
Actions : Describe how the customer arrives at the touchpoint and what they are likely to do there.
Motivations : Understand the customer's emotional state at that moment. Are they curious, frustrated, or excited? Explore why they feel this way.
Questions : Anticipate customers' questions at each stage and how your brand can provide answers.
Pain points : Identify the problems customers encounter and how your brand can address these issues.
Make sure your brand's solutions cater to each of these stages in the customer's journey, from the time the customer becomes aware of your solution to the consideration stage to the decision stage and finally towards the delight stage.
By mapping out these details, you can respond effectively to your customer's needs at every step of their journey. The goal is to deliver the exact experience they expect from your business, ultimately increasing engagement and sales.
The global audio streaming giant decided to enhance the music-sharing experience for its users. They partnered with a marketing firm to craft a customer journey map to achieve this.
The objective was crystal clear: pinpoint where music-sharing features could seamlessly integrate into the user experience.
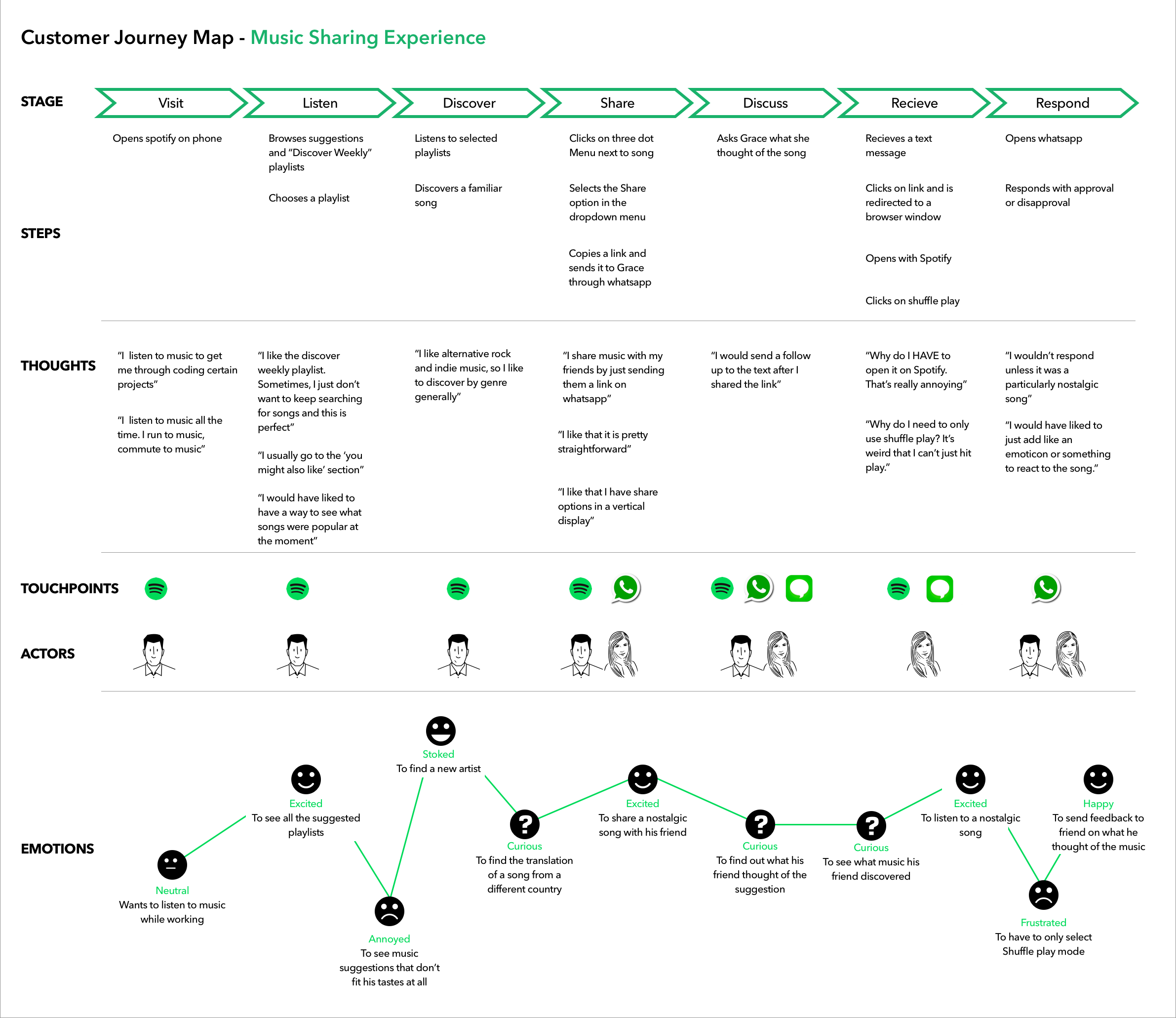
Spotify's map meticulously traces the user's voyage from opening the Spotify app on a mobile device to their engagement with shared songs. At each stage and touchpoint, it delves into what users engage with, do, think, and feel. This thorough analysis leveraged data research and customer surveys to grasp user sentiments at various points in the customer journey.
Using this valuable map, Spotify identified pain points and tailored solutions to create a smoother, more enjoyable music-sharing experience.
The result? Elevated customer satisfaction, leading to a seamless buying journey, stronger customer loyalty and often, customers evolving into enthusiastic brand advocates .
boAt , one of the top wearable electronics brands, started with audio devices and gadgets and then charted a course toward smart wearables. Their focus? Placing customers at the heart of their journey, delivering luxury audio and entertainment technology at attractive prices. They embarked on a digital transformation to navigate this mission, seeking a data-driven foundation to steer their growth.
Challenge : To truly understand customers' desires, boAt needed to be in tune with the market's pulse. They aspired to decipher consumer conversations, identify desired product features and maintain affordability.
A data analytics practice was established from the ground up to become an intelligent enterprise guided by data-driven insights, with Sprinklr as a key platform.
Solution : By harnessing Sprinklr's Unified-CXM platform, boAt is weaving together multiple solutions, culminating in a seamless experience for both customers and employees. Since the launch, they've welcomed 140 team members to the Sprinklr platform, delving into over 10,000 customer touchpoints and swiftly validating 6,000 warranty claims in real-time. This newfound visibility into customer interactions perfectly aligns with boAt's digital transformation journey.
From quality and speed metrics to a unified platform for workflow transparency, boAt ensured that its customers received uninterrupted cross-channel support. They leveraged AI technology to speed up claims and warranty processes and transitioned from reactive to proactive, predictive and preventive measures.
Interesting Read: The Very “Undigital” Truth About Digital Transformation
Outcome : boAt transformed its operations by integrating numerous solutions into Sprinklr's Unified-CXM platform. Since its implementation, boAt has seamlessly onboarded 140 employees to the Sprinklr platform, meticulously analyzed over 10,000 customer touchpoints and swiftly validated more than 6,000 warranty claims in real-time.
This enhanced visibility into customer interactions is precisely what boAt sought when commencing its digital transformation journey.
If you want to map better customer experiences, just like boAt did, take a free trial of Sprinklr Service for 30 days and let us know how you find it.
Frequently Asked Questions
Touchpoints in the customer journey are key moments when customers interact with a brand. These can be online or offline encounters, such as website visits, social media engagement, emails or in-store experiences.
The perfect customer journey is one that's highly personalized, seamless and aligns with the customer's needs and preferences. It's a path that anticipates their desires, provides relevant information and offers exceptional support at each touchpoint.
A bad customer journey is one fraught with inconsistency, inconvenience, and frustration. It involves disjointed touchpoints, irrelevant information and a lack of support when needed.
Yes, customer journeys can and should be personalized for each customer. Leveraging data and technology, businesses can tailor interactions, content and touchpoints to match individual preferences and behaviors.
related products
Related Topics
Thank you for contacting us.
A Sprinklr representative will be in touch with you shortly.
Contact us today, and we'll create a customized proposal that addresses your unique business needs.
Request a Demo
Welcome Back,
No need to fill out any forms — you're all set.
Related Content

Learn from Jay Baer’s customer experience insights: how to create experiences that customers not only remember but also want to share, turning satisfaction into advocacy.

Unveiling the Essence of Agent Training and Coaching in Modern Workforce
Annette Franz March 28, 2024 • 5 min read

Introducing the judges of the 2024 CXUnifier Awards
Meet the judges for Sprinklr’s 2024 CXUnifier Awards.
Jordana Gustafson Wright March 21, 2024 • 4 min read
What is a Customer Journey Map? [Free Templates]
Learn what the customer journey mapping process is and download a free template that you can use to create your own customer journey map.
Table of Contents
Mapping the customer journey can give you a way to better understand your customers and their needs. As a tool, it allows you to visualize the different stages that a customer goes through when interacting with your business; their thoughts, feelings, and pain points.
And, it’s shown that the friction from those pain points costs big: in 2019, ecommerce friction totaled an estimated 213 billion in lost US revenue .
Customer journey maps can help you to identify any problems or areas where you could improve your customer experience . In this article, we’ll explain what the customer journey mapping process is and provide a free template that you can use to create your own map. Let’s get started!
Bonus: Get our free, fully customizable Customer Experience Strategy Template that will help you understand your customers and reach your business goals.
What is a customer journey map?
So, what is customer journey mapping? Essentially, customer journey maps are a tool that you can use to understand the customer experience. Customer journey maps are often visual representations showing you the customer’s journey from beginning to end. They include all the touchpoints along the way.
There are often four main stages in your sales funnel, and knowing these can help you create your customer journey maps:
- Inquiry or awareness
- Interest, comparison, or decision-making
- Purchase or preparation
- Installation, activation, or feedback
Customer journey maps are used to track customer behavior and pinpoint areas where the customer experiences pain points. With this information uncovered, you can improve the customer experience, giving your customers a positive experience with your company.
You can use customer journey mapping software like Excel or Google sheets, Google Decks, infographics, illustrations, or diagrams to create your maps. But you don’t actually need customer journey mapping tools. You can create these maps with a blank wall and a pack of sticky notes.
Though they can be scribbled on a sticky note, it’s often easier to create these journeys digitally. That way, you have a record of your journey map, and you can share it with colleagues. We’ve provided free customer journey mapping templates at the end of this article to make your life a little easier.
The benefits of using customer journey maps
The main benefit of customer journey mapping is a better understanding of how your customers feel and interact with your business touchpoints. With this knowledge, you can create strategies that better serve your customer at each touchpoint.
Give them what they want and make it easy to use, and they’ll keep coming back. But, there are a couple of other great knock-on benefits too.
Improved customer support
Your customer journey map will highlight moments where you can add some fun to a customer’s day. And it will also highlight the pain points of your customer’s experience. Knowing where these moments are will let you address them before your customer gets there. Then, watch your customer service metrics spike!
Effective marketing tactics
A greater understanding of who your customers are and what motivates them will help you to advertise to them.
Let’s say you sell a sleep aid product or service. A potential target market for your customer base is young, working mothers who are strapped for time.
The tone of your marketing material can empathize with their struggles, saying, “The last thing you need is someone asking if you’re tired. But we know that over half of working moms get less than 6 hours of sleep at night. While we can’t give you more time, we know how you can make the most of those 6 hours. Try our Sleep Aid today and sleep better tonight.”
Building out customer personas will show potential target audiences and their motivation, like working moms who want to make the most of their hours asleep.
Product advancements or service improvements
By mapping your customer’s journey, you’ll gain insights into what motivates them to make a purchase or prevents them from doing so. You’ll have clarity on when or why they return items and which items they buy next. With this information and more, you’ll be able to identify opportunities to upsell or cross-sell products.
A more enjoyable and efficient user experience
Customer journey mapping will show you where customers get stuck and bounce off your site. You can work your way through the map, fixing any friction points as you go. The end result will be a smoothly-running, logical website or app.
A customer-focused mindset
Instead of operating with the motivation of business success, a customer journey map can shift your focus to the customer. Instead of asking yourself, “how can I increase profits?” ask yourself, “what would better serve my customer?” The profits will come when you put your customer first.
At the end of the day, customer journey maps help you to improve your customer experience and boost sales. They’re a useful tool in your customer experience strategy .
How to create a customer journey map
There are many different ways to create a customer journey map. But, there are a few steps you’ll want to take regardless of how you go about mapping your customer’s journey.
Step 1. Set your focus
Are you looking to drive the adoption of a new product? Or perhaps you’ve noticed issues with your customer experience. Maybe you’re looking for new areas of opportunity for your business. Whatever it is, be sure to set your goals before you begin mapping the customer journey.
Step 2. Choose your buyer personas
To create a customer journey map, you’ll first need to identify your customers and understand their needs. To do this, you will want to access your buyer personas.
Buyer personas are caricatures or representations of someone who represents your target audience. These personas are created from real-world data and strategic goals.
If you don’t already have them, create your own buyer personas with our easy step-by-step guide and free template.
Choose one or two of your personas to be the focus of your customer journey map. You can always go back and create maps for your remaining personas.
Step 3. Perform user research
Interview prospective or past customers in your target market. You do not want to gamble your entire customer journey on assumptions you’ve made. Find out directly from the source what their pathways are like, where their pain points are, and what they love about your brand.
You can do this by sending out surveys, setting up interviews, and examining data from your business chatbot . Be sure to look at what the most frequently asked questions are. If you don’t have a FAQ chatbot like Heyday , that automates customer service and pulls data for you, you’re missing out!
Get a free Heyday demo
You will also want to speak with your sales team, your customer service team, and any other team member who may have insight into interacting with your customers.
Step 4. List customer touchpoints
Your next step is to track and list the customer’s interactions with the company, both online and offline.
A customer touchpoint means anywhere your customer interacts with your brand. This could be your social media posts , anywhere they might find themselves on your website, your brick-and-mortar store, ratings and reviews, or out-of-home advertising.
Write as many as you can down, then put on your customer shoes and go through the process yourself. Track the touchpoints, of course, but also write down how you felt at each juncture and why. This data will eventually serve as a guide for your map.
Step 5. Build your customer journey map
You’ve done your research and gathered as much information as possible, now it’s time for the fun stuff. Compile all of the information you’ve collected into one place. Then, start mapping out your customer journey! You can use the templates we’ve created below for an easy plug-and-play execution.
Step 6. Analyze your customer journey map
Once the customer journey has been mapped out, you will want to go through it yourself. You need to experience first-hand what your customers do to fully understand their experience.
As you journey through your sales funnel, look for ways to improve your customer experience. By analyzing your customer’s needs and pain points, you can see areas where they might bounce off your site or get frustrated with your app. Then, you can take action to improve it. List these out in your customer journey map as “Opportunities” and “Action plan items”.
Types of customer journey maps
There are many different types of customer journey maps. We’ll take you through four to get started: current state, future state, a day in the life, and empathy maps. We’ll break down each of them and explain what they can do for your business.
Current state
This customer journey map focuses on your business as it is today. With it, you will visualize the experience a customer has when attempting to accomplish their goal with your business or product. A current state customer journey uncovers and offers solutions for pain points.
Future state
This customer journey map focuses on how you want your business to be. This is an ideal future state. With it, you will visualize a customer’s best-case experience when attempting to accomplish their goal with your business or product.
Once you have your future state customer journey mapped out, you’ll be able to see where you want to go and how to get there.
Day-in-the-life
A day-in-the-life customer journey is a lot like the current state customer journey, but it aims to highlight aspects of a customer’s daily life outside of how they interact with your brand.
Day-in-the-life mapping looks at everything that the consumer does during their day. It shows what they think and feel within an area of focus with or without your company.
When you know how a consumer spends their day, you can more accurately strategize where your brand communication can meet them. Are they checking Instagram on their lunch break, feeling open and optimistic about finding new products? If so, you’ll want to target ads on that platform to them at that time.
Day-in-the-life customer journey examples can look vastly different depending on your target demographic.
Empathy maps
Empathy maps don’t follow a particular sequence of events along the user journey. Instead, these are divided into four sections and track what someone says about their experience with your product when it’s in use.
You should create empathy maps after user research and testing. You can think of them as an account of all that was observed during research or testing when you asked questions directly regarding how people feel while using products. Empathy maps can give you unexpected insights into your users’ needs and wants.
Customer journey map templates
Use these templates to inspire your own customer journey map creation.
Customer journey map template for the current state:
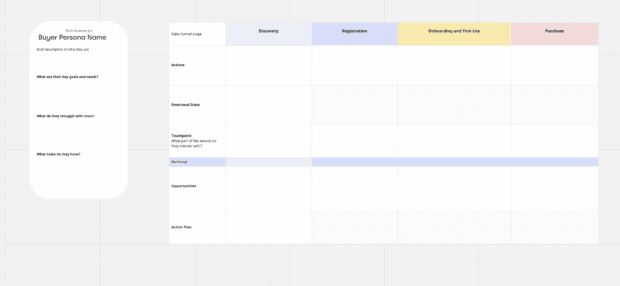
The future state customer journey mapping template:
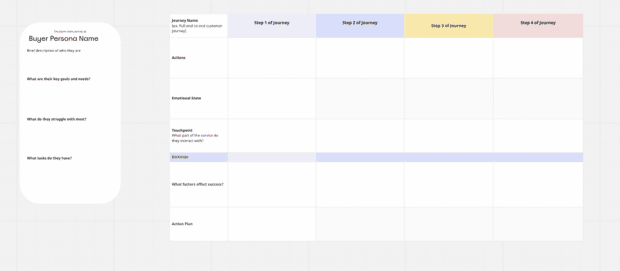
A day-in-the-life customer journey map template:

An empathy map template:
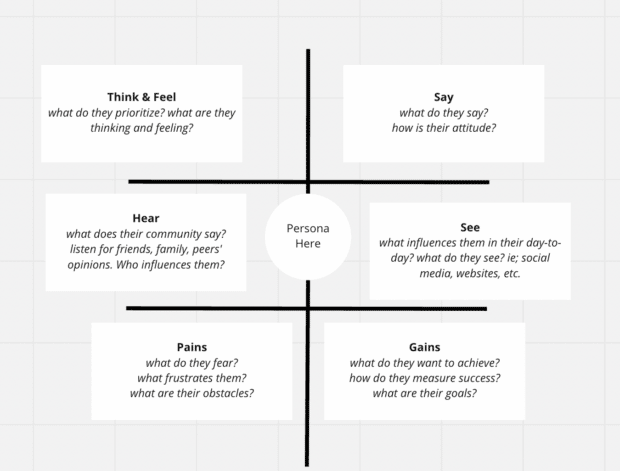
A customer journey map example
It can be helpful to see customer journey mapping examples. To give you some perspective on what these look like executed, we’ve created a customer journey mapping example of the current state.
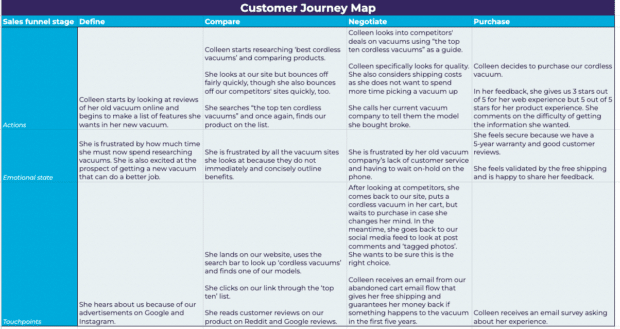
Buyer Persona:
Curious Colleen, a 32-year-old female, is in a double-income no-kids marriage. Colleen and her partner work for themselves; while they have research skills, they lack time. She is motivated by quality products and frustrated by having to sift through content to get the information she needs.
What are their key goals and needs? Colleen needs a new vacuum. Her key goal is to find one that will not break again.
What are their struggles?
She is frustrated that her old vacuum broke and that she has to spend time finding a new one. Colleen feels as though this problem occurred because the vacuum she bought previously was of poor quality.
What tasks do they have?
Colleen must research vacuums to find one that will not break. She must then purchase a vacuum and have it delivered to her house.
Opportunities:
Colleen wants to understand quickly and immediately the benefits our product offers; how can we make this easier? Colleen upholds social proof as a decision-making factor. How can we better show our happy customers? There is an opportunity here to restructure our website information hierarchy or implement customer service tools to give Colleen the information she needs faster. We can create comparison charts with competitors, have benefits immediately and clearly stated, and create social campaigns.
Action Plan:
- Implement a chatbot so customers like Colleen can get the answers they want quickly and easily.
- Create a comparison tool for competitors and us, showing benefits and costs.
- Implement benefit-forward statements on all landing pages.
- Create a social campaign dedicated to UGC to foster social proof.
- Send out surveys dedicated to gathering customer feedback. Pull out testimonial quotes from here when possible.
Now that you know what the customer journey mapping process is, you can take these tactics and apply them to your own business strategy. By tracking customer behavior and pinpointing areas where your customers experience pain points, you’ll be able to alleviate stress for customers and your team in no time.
Turn customer conversations and inquiries into sales with Heyday, our dedicated conversational AI chatbot for social commerce retailers. Deliver 5-star customer experiences — at scale.
Turn customer service conversations into sales with Heyday . Improve response times and sell more products. See it in action.
Become a better social marketer.
Get expert social media advice delivered straight to your inbox.
Colleen Christison is a freelance copywriter, copy editor, and brand communications specialist. She spent the first six years of her career in award-winning agencies like Major Tom, writing for social media and websites and developing branding campaigns. Following her agency career, Colleen built her own writing practice, working with brands like Mission Hill Winery, The Prevail Project, and AntiSocial Media.
Related Articles
FAQ Chatbot: The Best Way to Save Time on Customer Service
FAQ chatbots are bots designed to answer common questions people have about a product or service. They are used on websites or in customer service applications.

Customer Service Metrics: 2024 Guide + Free Template
Customers expect to get support wherever they look for and they expect it fast. To keep up, track the customer service metrics that matter.

Create a Customer Experience Strategy [FREE TEMPLATE]
This step-by-step template makes it easy to deliver a well-laid-out customer experience strategy that can give you planned, targeted growth.

Customer Experience Management Explained [11 Top Tips]
Turn that frown upside down! Keep your customers smiling with a strong customer experience management strategy.

- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
4 Strategies to Simplify the Customer Journey
- Richard L. Gruner

Making things easy is harder than you think.
While it may be tempting to offer your customers a never-ending array of products, customizations, and information, research shows that simplicity is almost always the best option for boosting both company value and customer loyalty. But what does it take to build a customer experience that’s smooth and simple from end to end? In this piece, the author offers four strategies to ensure simplicity is baked into every aspect of the customer’s journey: identify and communicate what simplicity means to your organization, look beyond product development to find ways to simplify throughout the customer journey, embrace internal complexity to achieve external simplicity, and remember that while simplicity is often necessary, it isn’t always the answer.
The modern consumer faces hundreds — if not thousands — of choices every day. What to read. Where to shop. What to buy. And each of those decisions takes a mental toll.
- RG Richard L. Gruner holds a PhD in marketing from the University of Melbourne and is Senior Lecturer (A/Prof) at the University of Western Australia. His work has been published in many top ranked peer-reviewed international journals, and he has a professional background in the media industry. One of his main research interests lies at the intersection of consumer psychology and digital tools. Find out more about Richard’s experience .
Partner Center
- Reviews / Why join our community?
- For companies
- Frequently asked questions
Customer Journey Maps
What are customer journey maps.
Customer journey maps are visual representations of customer experiences with an organization. They provide a 360-degree view of how customers engage with a brand over time and across all channels. Product teams use these maps to uncover customer needs and their routes to reach a product or service. Using this information, you can identify pain points and opportunities to enhance customer experience and boost customer retention.
“ Data often fails to communicate the frustrations and experiences of customers. A story can do that, and one of the best storytelling tools in business is the customer journey map.” — Paul Boag, UX designer, service design consultant & digital transformation expert
In this video, Frank Spillers, CEO of Experience Dynamics, explains how you can include journey maps in your design process.
- Transcript loading…
Customer Journey Maps – Tell Customer Stories Over Time
Customer journey maps are research-based tools. They show common customer experiences over time To help brands learn more about their target audience.
Maps are incredibly effective communication tools. See how maps simplify complex spaces and create shared understanding.
Unlike navigation maps, customer journey maps have an extra dimension—time. Design teams examine tasks and questions (e.g., what-ifs) regarding how a design meets or fails to meet customers’ needs over time when encountering a product or service.
Customer journey maps should have comprehensive timelines that show the most essential sub-tasks and events. Over this timeline framework, you add insights into customers' thoughts and feelings when proceeding along the timeline. The map should include:
A timescale - A defined journey period (e.g., one week). This timeframe should include the entire journey, from awareness to conversion to retention.
Scenarios - The context and sequence of events where a user/customer must achieve a goal. An example could be a user who wants to buy a ticket on the phone. Scenarios are events from the first actions (recognizing a problem) to the last activities (e.g., subscription renewal).
Channels – Where do they perform actions (e.g., Facebook)?
Touchpoints – How does the customer interact with the product or service? What actions do they perform?
Thoughts and feelings – The customer's thoughts and feelings at each touchpoint.
A customer journey map helps you understand how customer experience evolves over time. It allows you to identify possible problems and improve the design. This enables you to design products that are more likely to exceed customers’ expectations in the future state.

How to Create a Customer Journey Map for Exceptional Experiences?
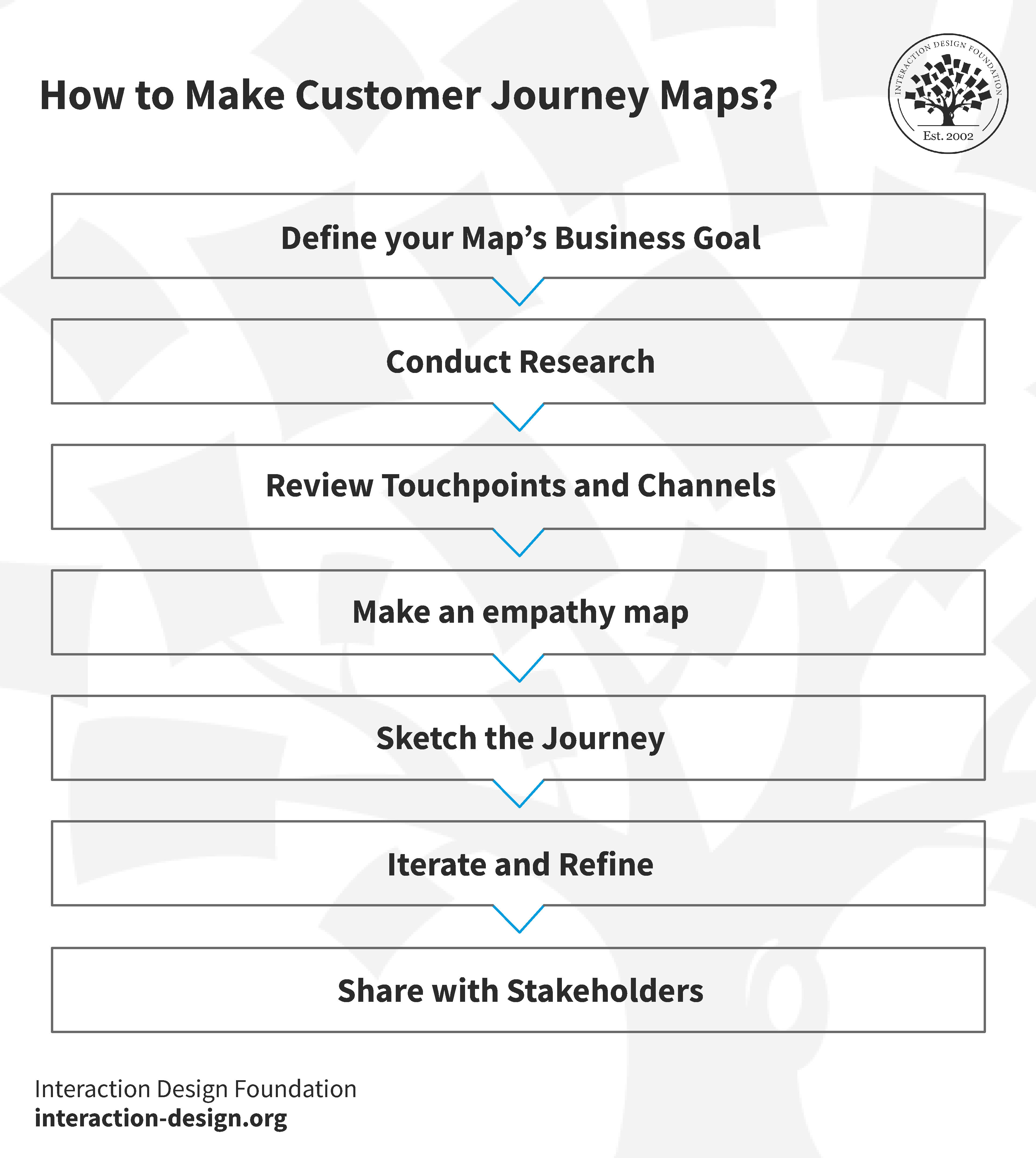
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0
Define Your Map’s Business Goal
Before creating a customer journey map, you must ask yourself why you're making one in the first place. Clarify who will use it and what user experience it will address.
Conduct Research
Use customer research to determine customer experiences at all touchpoints. Get analytical/statistical data and anecdotal evidence. Leverage customer interviews, surveys, social media listening, and competitive intelligence.
Watch user researcher Ditte Hvas Mortensen talk about how user research fits your design process and when you should do different studies.
- Copyright holder: Unsplash. Copyright terms and license: CCO Public Domain. Link: https://pixabay.com/en/clay-hands-sculpting-art-69...
- Copyright holder: Unsplash. Copyright terms and license: CCO Public Domain. Link: https://www.pexels.com/photo/man-in-black-shirt-an...
- Copyright holder: Indecent Proposer. Copyright terms and license: CC BY-NC 2.0 Link: https://www.flickr.com/photos/indecent_proposal/14...
- Copyright holder: Anna Langova. Copyright terms and license: CC0 1.0 Link: http://www.publicdomainpictures.net/view-image.php...
- Copyright holder: Conmongt. Copyright terms and license: CC0 Public Domain Link: https://pixabay.com/en/hourglass-time-time-lapse-clock-1623517/
Review Touchpoints and Channels
List customer touchpoints (e.g., paying a bill) and channels (e.g., online). Look for more touchpoints or channels to include.
Make an Empathy Map
Pinpoint what the customer does, thinks, feels, says, hears, etc., in a given situation. Then, determine their needs and how they feel throughout the experience. Focus on barriers and sources of annoyance.
Sketch the Journey
Piece everything—touchpoints, timescale, empathy map output, new ideas, etc.). Show a customer’s course of motion through touchpoints and channels across the timescale, including their feelings at every touchpoint.
Iterate and Refine
Revise and transform your sketch into the best-looking version of the ideal customer journey.
Share with Stakeholders
Ensure all stakeholders understand your map and appreciate how its use will benefit customers and the organization.

Buyer Journey vs User Journey vs Customer Journey: What's the Difference?
You must know the differences between buyer, user, and customer journeys to optimize customer experiences. A customer journey map is often synonymous with a user flow diagram or buyer journey map. However, each journey gives unique insights and needs different plans.
Customer Journey
The customer journey, or lifecycle, outlines the stages a customer goes through with a business. This journey can vary across organizations but includes five key steps:
1. Awareness : This is the first stage of the customer journey, where the customers realize they have a problem. The customer becomes aware of your brand or product at this stage, usually due to marketing efforts.
2. Consideration : Once customers know about your product or service, they start their research and compare brands.
3. Purchase : This is the stage where the customer has chosen a solution and is ready to buy your product or service.
4. Retention : After the purchase, it's about retaining that customer and nurturing a relationship. This is where good customer service comes in.
5. Advocacy : Also called the loyalty stage, this is when the customer not only continues to buy your product but also recommends it to others.
The journey doesn't end when the customer buys and recommends your solution to others. Customer journey strategies are cyclical and repetitive. After the advocacy stage, ideally, you continue to attract and retain the customers, keeping them in the cycle.
There is no standard format for a customer journey map. The key is to create one that works best for your team and product or service. Get started with customer journey mapping with our template:
This customer journey map template features three zones:
Top – persona and scenario.
Middle – thoughts, actions, and feelings.
Bottom – insights and progress barriers.
Buyer Journey
The buyer's journey involves the buyer's path towards purchasing. This includes some of the steps we saw in the customer journey but is specific to purchasing :
1. Awareness Stage : This is when a prospective buyer realizes they have a problem. However, they aren't yet fully aware of the solutions available to them.
2. Consideration Stage : After identifying their problem, the buyer researches and investigates different solutions with more intent. They compare different products, services, brands, or strategies here.
3. Decision Stage : The buyer then decides which solution will solve their problem at the right price. This is where the actual purchasing action takes place.
4. Post-Purchase Evaluation : Although not always included, this stage is critical. It's where the buyer assesses their satisfaction with the purchase. It includes customer service interactions, quality assessment, and attitudinal loyalty to the brand.
All these stages can involve many touchpoints, including online research, social media interactions, and even direct, in-person interactions. Different buyers may move through these stages at different speeds and through various channels, depending on a wide range of factors.
User Journey
The user journey focuses on people's experience with digital platforms like websites or software. Key stages include:
1. Discovery : In this stage, users become aware of your product, site, or service, often due to marketing efforts, word-of-mouth, or organic search. It also includes their initial reactions or first impressions.
2. Research/Consideration : Here, users dig deeper, exploring features, comparing with alternatives, and evaluating if your offering suits their needs and preferences.
3. Interaction/Use : Users actively engage with your product or service. They first-hand experience your solution's functionality, usability, and usefulness to achieve their goal.
4. Problem-solving : If they encounter any issues, how they seek help and resolve their issues fall into this stage. It covers user support, troubleshooting, and other assistance.
5. Retention/Loyalty : This stage involves how users stay engaged over time. Do they continue using your product, reduce usage, or stop altogether? It includes their repeated interactions, purchases, and long-term engagement over time.
6. Advocacy/Referral : This is when users are so satisfied they begin to advocate for your product, leaving positive reviews and referring others to your service.
Download this user journey map template featuring an example of a user’s routine.

Understanding these stages can help optimize the user experience, providing value at each stage and making the journey seamless and enjoyable.
Always remember the journey is as important as the destination. Customer relationships start from the first website visit or interaction with marketing materials. These initial touchpoints can influence the ongoing relationship with your customers.
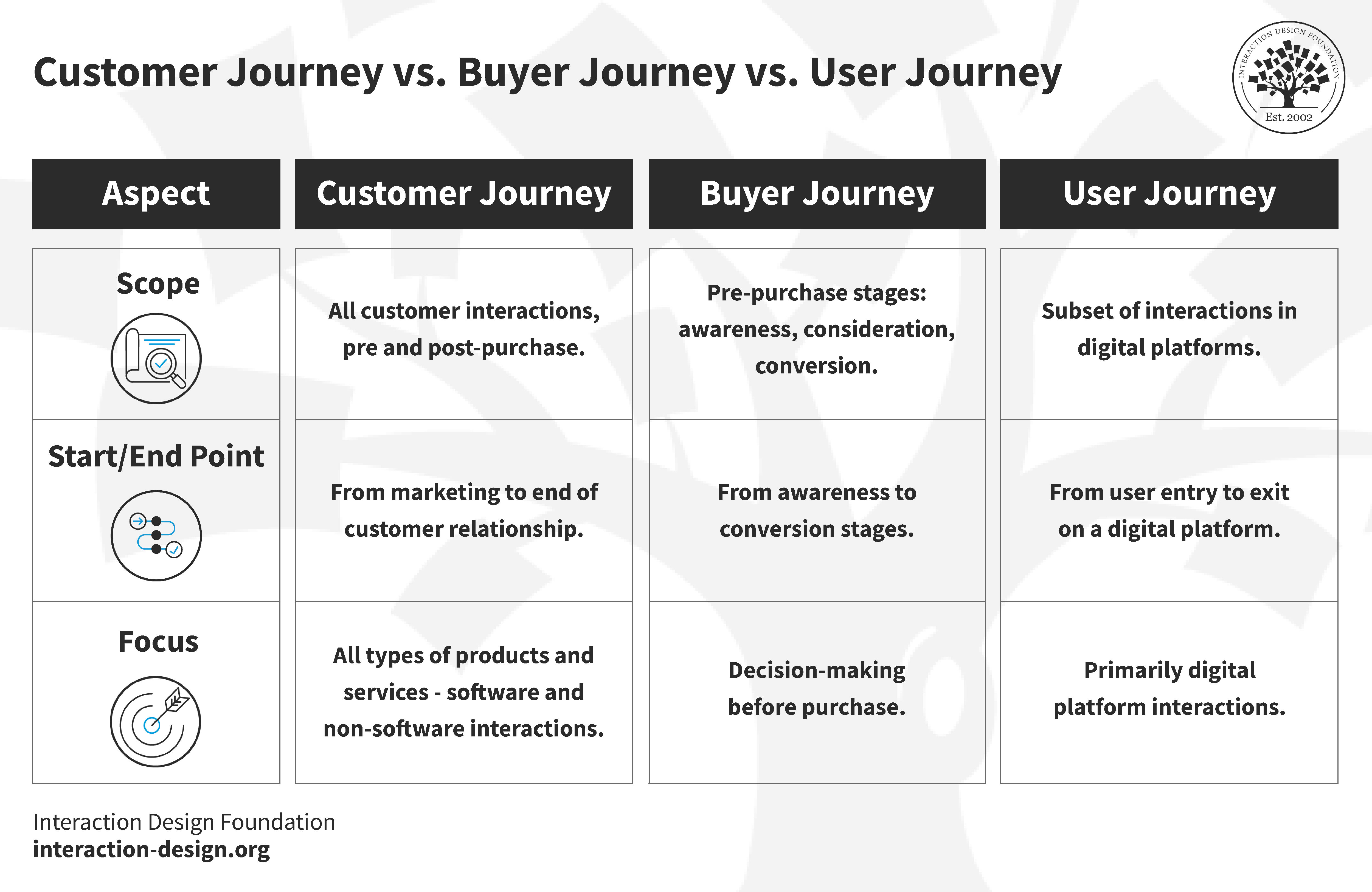
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 3.0
Drawbacks of Customer Journey Maps
Customer journey mapping is valuable yet has limitations and potential drawbacks. Recognize these challenges and create more practical and realistic journey maps.
Over-simplification of Customer Experiences
Customer journey maps often risk simplifying complex customer experiences . They may depict varied and unpredictable customer behaviors as straightforward and linear. This simplification can lead to misunderstandings about your customers' needs and wants. As a result, you might overlook customers' diverse and unique paths.
Always remember that real customer experiences are more complex than any map. When you recognize this, you steer clear of decisions based on simple models.
Resource Intensity
Creating detailed customer journey maps requires a lot of resources and time. You must gather extensive data and update the maps to keep them relevant. This process can strain small businesses or those with limited resources.
You need to balance the need for comprehensive mapping with available resources. Efficient resource management and prioritization are crucial to maintaining effective journey maps.
Risk of Bias
Creating customer journey maps carries the inherent risk of biases . These biases can arise from various sources. They can impact the accuracy and effectiveness of the maps.
Alan Dix, an expert in HCI, discusses bias in more detail in this video.
Common biases in customer journey mapping include:
Assumption Bias: When teams make decisions based on preconceived notions rather than customer data.
Selection Bias: When the data doesn’t represent the entire customer base..
Confirmation Bias : When you focus on information that supports existing beliefs and preferences. Simultaneously, you tend to ignore or dismiss data that contradicts those beliefs.
Anchoring Bias : Relying on the first information encountered (anchor) when making decisions.
Overconfidence Bias : Placing too much trust in the accuracy of the journey map. You may overlook its potential flaws.
These biases may misguide the team, and design decisions based on these maps might not be effective.
To address these biases, review and update journey maps with real user research data. Engage with different customer segments and gather a wide range of feedback to help create a more accurate and representative map. This approach ensures the journey map aligns with actual customer experiences and behaviors.
Evolving Customer Behaviors
Customer behaviors and preferences change with time. A journey map relevant today can become outdated. You need to update and adapt your maps to reflect these changes. This requires you to perform market research and stay updated with trends and customer feedback.
Getting fresh data ensures your journey map stays relevant and effective. You must adapt to evolving customer behaviors to maintain accurate and valuable customer journey maps.
Challenges in Capturing Emotions
Capturing emotions accurately in customer journey maps poses a significant challenge. Emotions influence customer decisions, yet you may find it difficult to quantify and represent them in maps. Most journey maps emphasize actions and touchpoints, often neglecting the emotional journey.
You must integrate emotional insights into these maps to understand customer experiences. This integration enhances the effectiveness of customer engagement strategies. You can include user quotes, symbols such as emojis, or even graphs to capture the ups and downs of the users’ emotions..
Misalignment with Customer Needs
Misalignments in customer journey maps can manifest in various ways. It can impact the effectiveness of your strategies. Common misalignments include:
Putting business aims first, not what customers need.
Not seeing or serving the varied needs of different customer types.
Not using customer feedback in the journey map.
Thinking every customer follows a simple, straight path.
Engage with your customers to understand their needs and preferences if you want to address these misalignments. Incorporate their direct feedback into the journey map. This approach leads to more effective customer engagement and satisfaction.
Over-Reliance on the Map
Relying too much on customer journey maps can lead to problems. These maps should serve as tools rather than definitive guides. Viewing them as perfect can restrict your responsiveness to customer feedback and market changes. Treat journey maps as evolving documents that complement direct customer interactions and feedback.
Make sure you get regular updates and maintain flexibility in your approach. Balance the insights from the map with ongoing customer engagement. This approach keeps your business agile and responsive to evolving customer needs.
Data Privacy Concerns
Collecting customer data for journey mapping poses significant privacy concerns. Thus, you need to create a balance. You must adhere to data protection laws and gather enough information for mapping.
You need a careful strategy to ensure customer data security. Stay vigilant to adapt to evolving privacy regulations and customer expectations. This vigilance helps maintain trust and compliance.
Learn More about Customer Journey Maps
Take our Journey Mapping course to gain insights into the how and why of journey mapping. Learn practical methods to create experience maps , customer journey maps, and service blueprints for immediate application.
Explore this eBook to discover customer journey mapping .
Find some additional insights in the Customer Journey Maps article.
Questions related to Customer Journey Maps
Creating a customer journey map requires visually representing the customer's experience with your product or company. Harness the strength of visual reasoning to understand and present this journey succinctly. Instead of detailing a lengthy narrative, like a book, a well-crafted map allows stakeholders, whether designers or not, to grasp the journey quickly. It's a democratized tool that disseminates information, unifies teams, and aids decision-making by illuminating previously unnoticed or misunderstood aspects of the customer's journey.
The customer journey encompasses five distinct stages that guide a customer's interaction with a brand or product:
Awareness: The customer becomes aware of a need or problem.
Consideration: They research potential solutions or products.
Purchase: The customer decides on a solution and makes a purchase.
Retention: Post-purchase, the customer uses the product and forms an opinion.
Advocacy: Satisfied customers become brand advocates, sharing their positive experiences.
For a comprehensive understanding of these stages and how they intertwine with customer touchpoints, refer to Interaction-Design.org's in-depth article .
A perspective grid workshop is a activity that brings together stakeholders from various departments, such as product design, marketing, growth, and customer support, to align on a shared understanding of the customer's journey. These stakeholders contribute unique insights about customer needs and how they interact with a product or service. The workshop entails:
Creating a matrix to identify customers' jobs and requirements, not initially linked to specific features.
Identifying the gaps, barriers, pains, and risks associated with unmet needs, and constructing a narrative for the journey.
Highlighting the resulting value when these needs are met.
Discuss the implied technical and non-technical capabilities required to deliver this value.
Brainstorming possible solutions and eventually narrowing down to specific features.
The ultimate aim is to foster alignment within the organization and produce a user journey map based on shared knowledge.
Learn more from this insightful video:
Customer journey mapping is vital as it harnesses our visual reasoning capabilities to articulate a customer's broad, intricate journey with a brand. Such a depiction would otherwise require extensive documentation, like a book. This tool offers a cost-effective method to convey information succinctly, ensuring understanding of whether one is a designer or lacks the time for extensive reading. It also helps the team to develop a shared vision and to encourage collaboration. Businesses can better comprehend and address interaction points by using a journey map, facilitating informed decision-making and revealing insights that might otherwise remain obscured. Learn more about the power of visualizing the customer journey in this video.
Pain points in a customer journey map represent customers' challenges or frustrations while interacting with a product or service. They can arise from unmet needs, gaps in service, or barriers faced during the user experience. Identifying these pain points is crucial as they highlight areas for improvement, allowing businesses to enhance the customer experience and meet their needs more effectively. Pain points can relate to various aspects, including product usability, communication gaps, or post-purchase concerns. Explore the detailed article on customer journey maps at Interaction Design Foundation for a deeper understanding and real-world examples.
Customer journey mapping offers several key benefits:
It provides a holistic view of the customer experience, highlighting areas for improvement. This ensures that products or services meet users' needs effectively.
The process fosters team alignment, ensuring everyone understands and prioritizes the customer's perspective.
It helps identify pain points, revealing opportunities to enhance user satisfaction and loyalty.
This visualization allows businesses to make informed decisions, ensuring resources target the most impactful areas.
To delve deeper into the advantages and insights on journey mapping, refer to Interaction Design Foundation's article on key takeaways from the IXDF journey mapping course .
In design thinking, a customer journey map visually represents a user's interactions with a product or service over time. It provides a detailed look at a user's experience, from initial contact to long-term engagement. Focusing on the user's perspective highlights their needs, emotions, pain points, and moments of delight. This tool aids in understanding and empathizing with users, a core principle of design thinking. When used effectively, it bridges gaps between design thinking and marketing, ensuring user-centric solutions align with business goals. For a comprehensive understanding of how it fits within design thinking and its relation to marketing, refer to Interaction Design Foundation's article on resolving conflicts between design thinking and marketing .
A customer journey map and a user journey map are tools to understand the experience of users or customers with a product or service.
A customer journey map is a broader view of the entire customer experience across multiple touchpoints and stages. It considers physical and digital channels, multiple user personas, and emotional and qualitative aspects.
A user journey map is a detailed view of the steps to complete a specific task or goal within a product or service. It only considers digital channels, one user persona, and functional and quantitative aspects.
Both are useful to understand and improve the experience of the users or customers with a product or service. However, they have different scopes, perspectives, and purposes. A customer journey map provides a holistic view of the entire customer experience across multiple channels and stages. A user journey map provides a detailed view of the steps to complete a specific task or goal within a product or service.
While user journeys might emphasize specific tasks or pain points, customer journeys encapsulate the entire experience, from research and comparison to purchasing and retention.
Customer journey maps and service blueprints are tools to understand and improve the experience of the users or customers with a product or service. A customer journey map shows the entire customer experience across multiple touchpoints and stages. It focuses on the front stage of the service, which is what the customers see and experience. It considers different user personas and emotional aspects.
A service blueprint shows how a service is delivered and operated by an organization. It focuses on the back stage of the service, which is what the customers do not see or experience. It considers one user persona and functional aspects. What are the steps that the customer takes to complete a specific task or goal within the service? What are the channels and devices that the customer interacts with at each step?
For an immersive dive into customer journey mapping, consider enrolling in the Interaction Design Foundation's specialized course . This course offers hands-on lessons, expert guidance, and actionable tools. Furthermore, to grasp the course's essence, the article “4 Takeaways from the IXDF Journey Mapping Course” sheds light on the core learnings, offering a snapshot of what to expect. These resources are tailored by industry leaders, ensuring you're equipped with the best knowledge to craft impactful customer journey maps.
Literature on Customer Journey Maps
Here’s the entire UX literature on Customer Journey Maps by the Interaction Design Foundation, collated in one place:
Learn more about Customer Journey Maps
Take a deep dive into Customer Journey Maps with our course Journey Mapping .
This course will show you how to use journey mapping to turn your own complex design challenges into simple, delightful user experiences . If you want to design a great shopping experience, an efficient signup flow or an app that brings users delight over time, journey mapping is a critical addition to your toolbox.
We will begin with a short introduction to mapping — why it is so powerful, and why it is so useful in UX. Then we will get familiar with the three most common types of journey map — experience maps, customer journey maps and service blueprints — and how to recognize, read and use each one. Then you will learn how to collect and analyze data as a part of a journey mapping process. Next you will learn how to create each type of journey map , and in the final lesson you will learn how to run a journey mapping workshop that will help to turn your journey mapping insights into actual products and services.
This course will provide you with practical methods that you can start using immediately in your own design projects, as well as downloadable templates that can give you a head start in your own journey mapping projects.
The “Build Your Portfolio: Journey Mapping Project” includes three practical exercises where you can practice the methods you learn, solidify your knowledge and if you choose, create a journey mapping case study that you can add to your portfolio to demonstrate your journey mapping skills to future employers, freelance customers and your peers.
Throughout the course you will learn from four industry experts.
Indi Young will provide wisdom on how to gather the right data as part of your journey mapping process. She has written two books, Practical Empathy and Mental Models . Currently she conducts live online advanced courses about the importance of pushing the boundaries of your perspective. She was a founder of Adaptive Path, the pioneering UX agency that was an early innovator in journey mapping.
Kai Wang will walk us through his very practical process for creating a service blueprint, and share how he makes journey mapping a critical part of an organization’s success. Kai is a talented UX pro who has designed complex experiences for companies such as CarMax and CapitalOne.
Matt Snyder will help us think about journey mapping as a powerful and cost-effective tool for building successful products. He will also teach you how to use a tool called a perspective grid that can help a data-rich journey mapping process go more smoothly. In 2020 Matt left his role as the Sr. Director of Product Design at Lucid Software to become Head of Product & Design at Hivewire.
Christian Briggs will be your tour guide for this course. He is a Senior Product Designer and Design Educator at the Interaction Design Foundation. He has been designing digital products for many years, and has been using methods like journey mapping for most of those years.
All open-source articles on Customer Journey Maps
14 ux deliverables: what will i be making as a ux designer.

- 1.2k shares
What are Customer Touchpoints & Why Do They Matter?
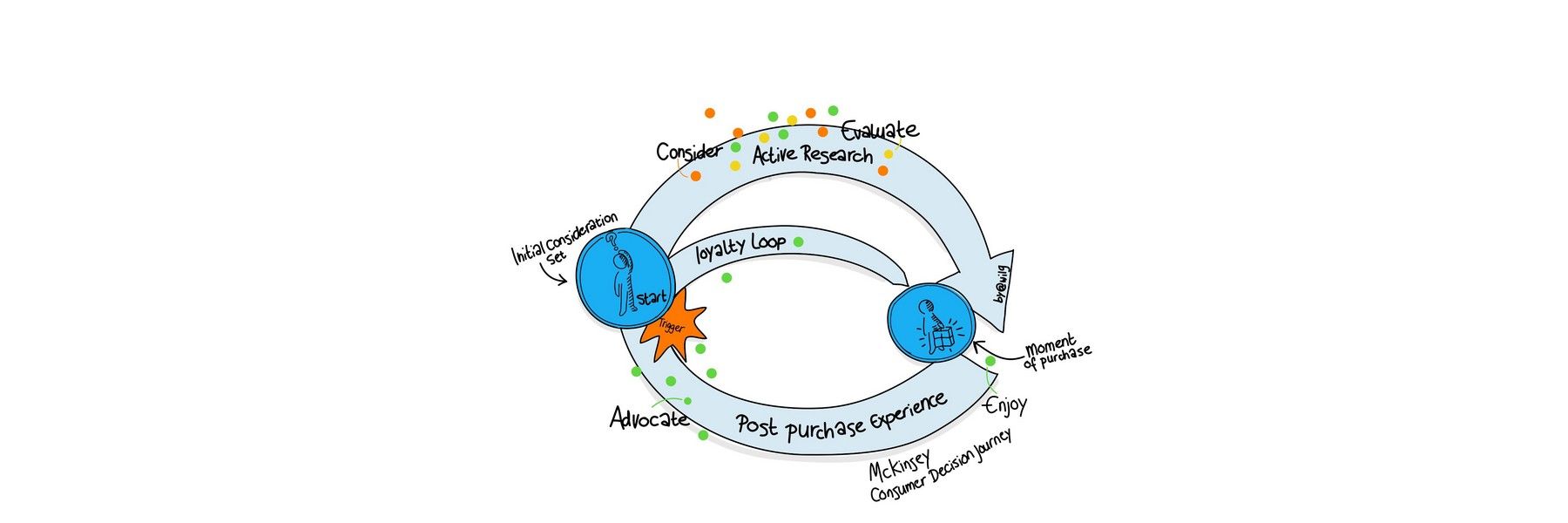
- 3 years ago
How to Visualize Your Qualitative User Research Results for Maximum Impact

- 2 years ago
How to Resolve Conflicts Between Design Thinking and Marketing

How to Create a Perspective Grid
- 10 mths ago
4 Takeaways from the IxDF Journey Mapping Course
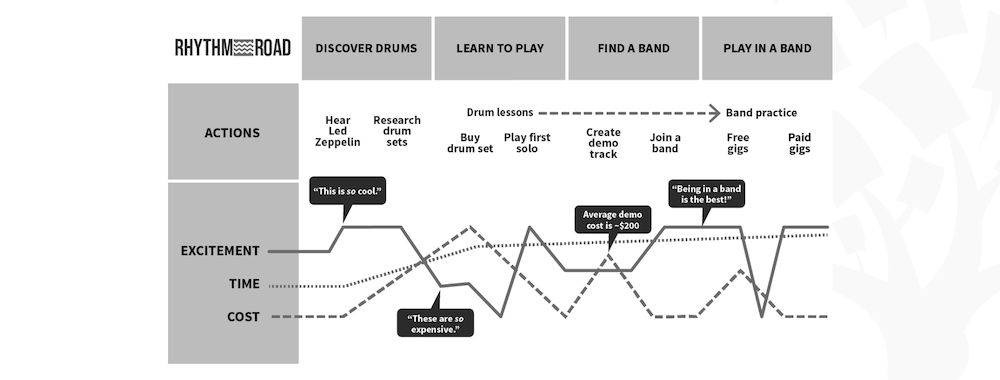
The Power of Mapping
User Story Mapping in Design
Open Access—Link to us!
We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge . Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change , cite this page , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge !
Privacy Settings
Our digital services use necessary tracking technologies, including third-party cookies, for security, functionality, and to uphold user rights. Optional cookies offer enhanced features, and analytics.
Experience the full potential of our site that remembers your preferences and supports secure sign-in.
Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Enhanced Functionality
Saves your settings and preferences, like your location, for a more personalized experience.
Referral Program
We use cookies to enable our referral program, giving you and your friends discounts.
Error Reporting
We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
Optimize your experience by allowing us to monitor site usage. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy.
Analytics Storage
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements.
Differentiates real visitors from automated bots, ensuring accurate usage data and improving your website experience.
Lets us tailor your digital ads to match your interests, making them more relevant and useful to you.
Advertising Storage
Stores information for better-targeted advertising, enhancing your online ad experience.
Personalization Storage
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience.
Advertising Personalization
Allows for content and ad personalization across Google services based on user behavior. This consent enhances user experiences.
Enables personalizing ads based on user data and interactions, allowing for more relevant advertising experiences across Google services.
Receive more relevant advertisements by sharing your interests and behavior with our trusted advertising partners.
Enables better ad targeting and measurement on Meta platforms, making ads you see more relevant.
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing.
LinkedIn Insights
Tracks conversions, retargeting, and web analytics for LinkedIn ad campaigns, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
LinkedIn CAPI
Enhances LinkedIn advertising through server-side event tracking, offering more accurate measurement and personalization.
Google Ads Tag
Tracks ad performance and user engagement, helping deliver ads that are most useful to you.
Share the knowledge!
Share this content on:
or copy link
Cite according to academic standards
Simply copy and paste the text below into your bibliographic reference list, onto your blog, or anywhere else. You can also just hyperlink to this page.
New to UX Design? We’re Giving You a Free ebook!

Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.
In 9 chapters, we’ll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!
Business growth
Marketing tips
Customer journey mapping 101 (+ free templates)

When I was a kid, I remember watching my parents switch between different credit cards to get the best rewards for a particular purchase. They almost always pulled out the American Express first because (as they explained to me) the base reward rate was higher than even the sector-specific perks offered by other cards. Twenty years later, when I decided to get a high-end credit card, Amex was the first one that came to mind.
Customer journey mapping is the process of planning out people's awareness of and relationship to your brand, starting with their very first impression—even if, as in my case, that impression is made a full decade before they can actually use your product.
Table of contents:
Customer journey map template
Parts of a journey map, stages of the customer journey, advanced customer journey mapping tips, types of journey maps, customer journey mapping example, what is a customer journey map.
A customer journey is the path a person takes to move from general awareness to prospective customer to (in the ideal scenario) brand loyalist . A customer journey map is a visual document that traces this path through all of the interactions, or touchpoints, a person will have with a brand.
Think back to any recent purchase of your own, and try to trace your own customer journey:
When and where was your first contact with the product or service?
How many channels of communication with the company did you have available?
How was the contact you had, if any? Was it personal or formulaic?
Were your problems, if any, solved? If so, were they solved in a timely manner?
What do you now know about the brand besides the product or service itself?
Of course, every customer is different. But you can't create a customer journey map for every individual—and you don't need to. Instead, you can segment your audience into customer personas and create a map for each.
The customer journey vs. the user journey vs. the buyer journey
What's the difference between the customer, user, and buyer journeys?
The customer journey is split up into two parts: the buyer journey and the user journey. The buyer journey covers everything up to the point of purchase. After that point, the customer becomes a user, and all of their experiences are part of the user journey.
Benefits of customer journey mapping
In a world where there are multiple high-quality options for just about every product on the market, brands need to foster long-term relationships with their customers to prevent them from being poached by competitors who offer a better customer experience .
Here are the main benefits of the customer journey mapping process:
Touchpoint optimization: With a clear understanding of what your touchpoints are and where they occur, you can track and adjust them based on how they perform.
Enhanced customer experience insights: Through customer profiling and a better overview of all the touchpoints that make a journey, you can acquire more precise and actionable customer experience insights.
Improved product development: Thoughtful and intentional journey planning creates more opportunities for meaningful customer feedback, which gives businesses better information to improve their product.
The customer journey map includes additional details within each phase (which I'll discuss in more detail later) to help you strategically plan your customers' touchpoints and move them closer to a purchase.
This customer journey map template is separated into five stages along the leftmost column, with guiding questions to help plan the customer's experience in each stage.
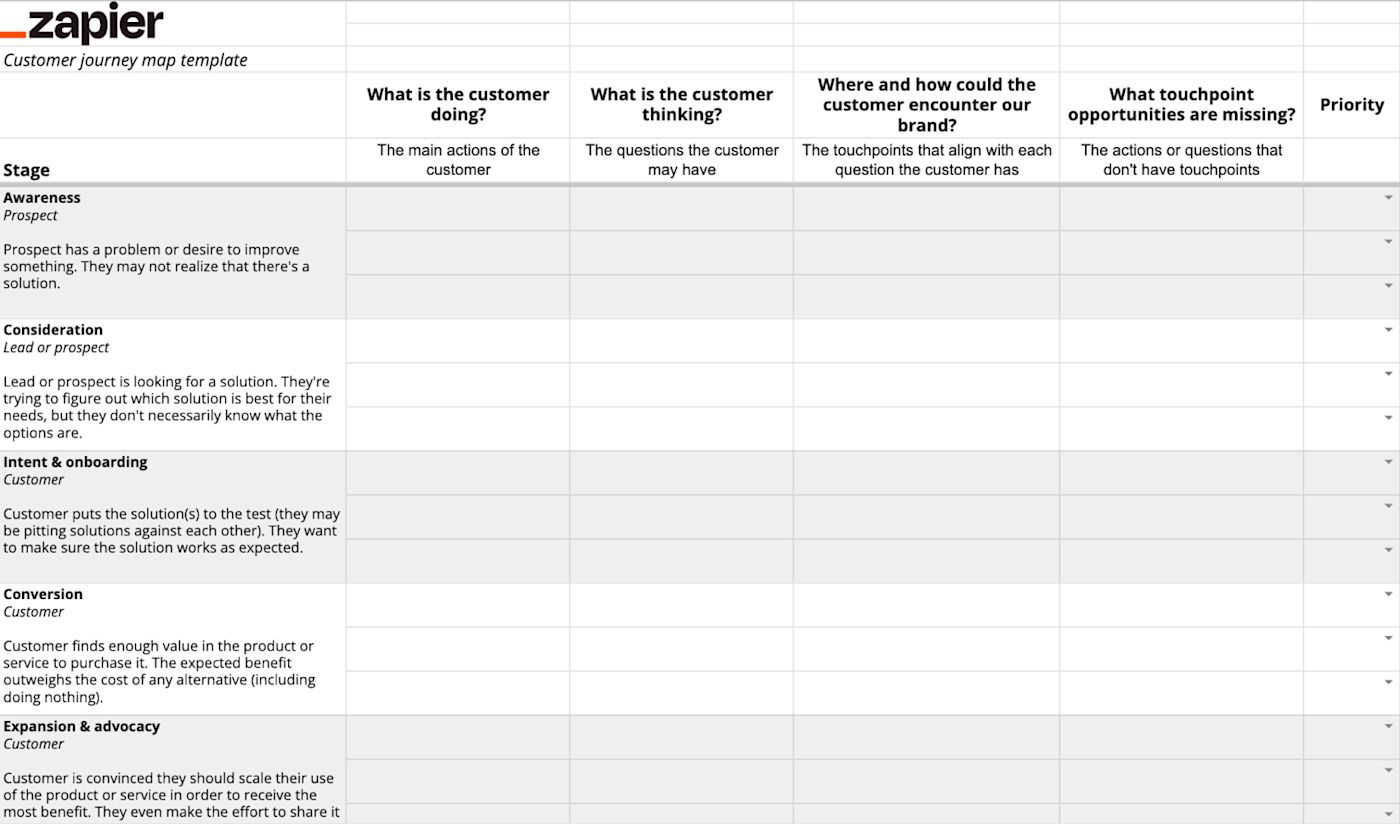
Below, we'll walk through each part of the customer journey map and how to use it.
If you're already familiar with journey mapping, you can start filling in the template right away. Otherwise, here's a quick walkthrough of what goes in each section.
What is the customer doing?
In this section, you'll jot down the main things that the prospect, lead, or customer is doing during this stage. For example, if you're a personal trainer, an awareness stage key step might include something like "Prospect wants to get in shape." Or if you offer an email newsletter app, an expansion and advocacy stage key step might be "Customer upgrades their plan."
Each stage will likely have more than one key step or milestone—that's good. You should be specific enough to be able to create touchpoints, content, and marketing campaigns geared toward each milestone.
What is the customer thinking?
Next, put yourself in the customer's shoes and think about what questions they might have at each stage. In the awareness stage, it might be things like "How can I do X better?" or "What is [your product name]?" In the consideration phase, questions like "Is this worth my time/money?" or "Will this help me solve my problem?" will come to the forefront.
Where and how could the customer encounter our brand?
After you've outlined what your customer is thinking at each stage, align each question with the relevant touchpoint that could address each concern.
Not all existing touchpoints will be a part of the planned customer journey . For example, I seriously doubt that American Express's customer journey map includes a milestone labeled "Customer gets a free ride because her friend has an Amex card and gets $15 in Uber cash each month." However, each question must have at least one touchpoint that directly and specifically addresses the customer's needs and questions at that point.
What touchpoint opportunities are missing?
When you have a question or milestone that doesn't have a corresponding touchpoint, you've found a gap in your customer journey. That means customers at this stage are going to be left with unmet needs and unanswered questions, and may look more seriously at competitor products as a result. It's essential to develop touchpoints to fill this gap and prevent losing potential customers at a key milestone.
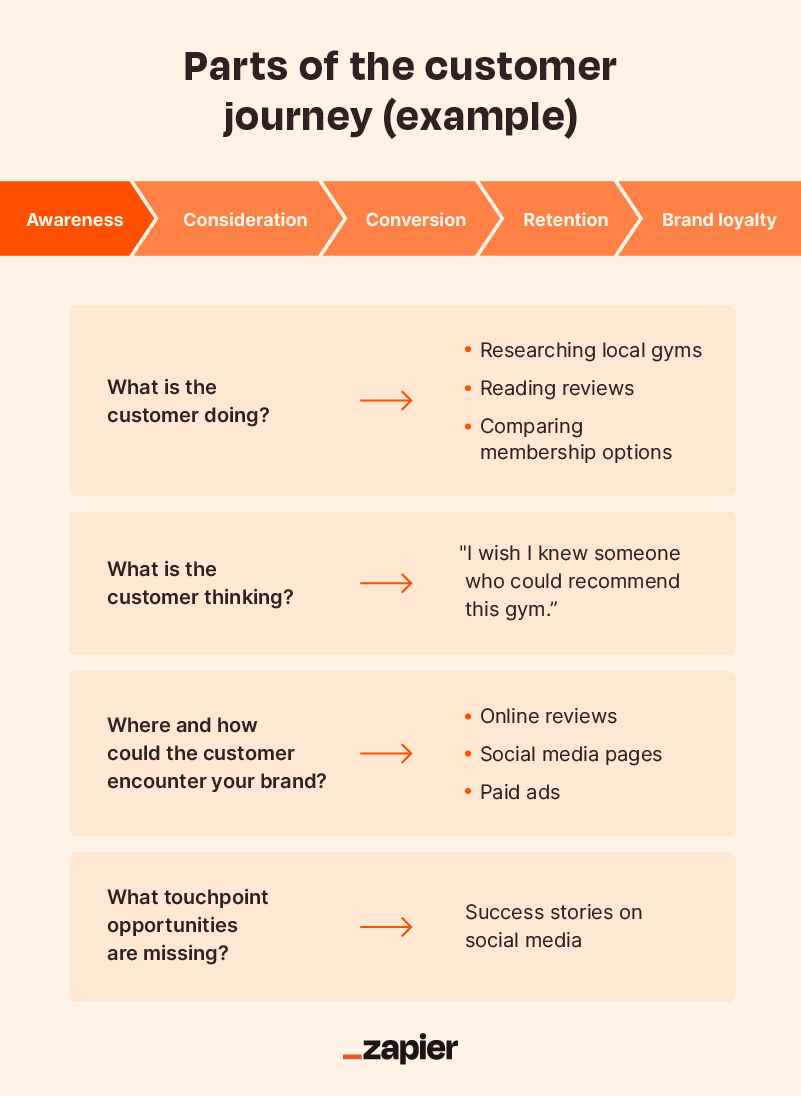
The customer journey map can be split into five phases: awareness, consideration, conversion, retention, and brand loyalty.
Customers can't decide whether or not they want your product if they don't know that it exists. In the earliest phase of the customer journey, a business's goal is to reach the individual and, ultimately, attract them to the brand.
For a small- to medium-sized business, the work of this stage involves reaching out directly to consumers via channels like advertising , SEO , and social media . For a household name like American Express, this stage is dedicated to ensuring the impression their brand makes is a positive one.
Consideration
Once potential customers are aware of your brand, the next phase they enter is called "consideration" or "research." This is when the customer's perspective shifts from simple awareness of your brand's existence to an understanding of the value that you have to offer them.
During this phase, the brand's goal is to design touchpoints that demonstrate to the user why their product can solve a problem or improve an experience that's specific to that person. This can be done using guides and how-tos, partnerships with other brands , and ads that portray a customer problem being solved.
Some businesses also include a mini-stage called "Intent" or "Onboarding," when the customer has decided they're interested in the product and is testing it out. The company's goal in this stage is simply to provide an exceptional user experience—they want to make sure the product works as intended and the customer's questions and requests are handled well.
A business can identify customers that are primed for conversion based on behavior in the consideration stage. Someone who signs up for a newsletter isn't a hot sales prospect quite yet, but when they start opening more emails and spending more time on the site, that's when brands know they're ready for a conversion push.
Types of conversions vary depending on the type of business and industry. Examples of conversion pushes include:
An abandoned cart email pushing a browsing shopper to complete a purchase
A physical mail offer pushing a potential customer to open an account
A seasonal campaign highlighting why a product is perfect for a particular holiday, celebration, or event
When a conversion is successful, a potential buyer becomes an actual customer. The goal in the retention stage is to demonstrate to the customer why they were right to make their purchase, and set them up to make more purchases or renew services in the future.
The retention stage is also where the user experience or user journey begins. The company's job in this phase, then, is to provide the best possible user experience. Easy installation, frictionless customer service, and—this part should be obvious—a product or service that works well and provides the user what they need are all key components to improved customer retention.
Brand loyalty
In the final customer journey phase, users go from run-of-the-mill satisfied customers to active advocates for your business.
You can encourage brand loyalty by offering exceptional customer service, referral programs, and loyalty discounts and exclusives.
Keep in mind: a customer doesn't need to be a zealot for your company to be an unintentional brand advocate. One of the biggest reasons I made the decision to apply for Amex's high-end card is because my best friend has it. She didn't specifically recommend it to me, but I became interested after experiencing a lot of the card benefits vicariously through her.
Everything we've covered up to this point will only get you as far as a basic customer journey map. That doesn't mean, however, that your customer journey map will be good . Once you have the basic journey mapping structure down, you'll want to take steps to continually improve your map's effectiveness.
Survey your customers and customer teams
When designing touchpoints and determining where and how customers interact with your business, don't guess—your existing customer base is a valuable resource you can tap for a firsthand customer perspective. You can i ncentivize customers to participate in surveys and fill out feedback forms by offering discounts and perks in exchange.
Talk to your customer-facing employees, too. The people who work directly with customers day-to-day will have more accurate information about how to interact with them.
Automate customer data collection
High-quality, premium experiences are defined by their high level of personalization, and that personalization is only possible if you have information about your customer. It's not possible to sit there and take notes on every person who interacts with your brand, but it is possible to automatically collect lead data from customer interactions and have them collated in your CRM tool .
Set up your contact management platform to automatically tag contacts with information like gender, age, products they've bought, events they've attended, what types of emails they open consistently and what emails they regularly ignore, whether their purchases indicate that they have pets or children, and so on. The more information you have, the better your customer experiences will be.
Tweak for B2B, B2C, and SaaS industries
The nature of the customer journey is different for SaaS, B2B, and B2C companies. A B2B company's interactions with prospects might include in-person conferences, while a SaaS company's touchpoints will be mostly digital. Companies that sell to consumers will need to think through individual people's experiences in a way that B2B companies don't. A company whose products are designed for emergencies will need to think through crisis scenarios instead of day-to-day customer experiences.
Tweak your customer journey categories to fit your company, product, and industry. Using a generalized or poorly-fitting customer journey map will result in vague and unhelpful interactions with your brand.
Create multiple maps for different journeys
When people refer to the customer journey, they're typically talking about the overarching journey from awareness to brand loyalty that we outlined above. However, you can map any part of the customer journey and experience.
Do you target college students? Replace the five stages with four academic quarters and map their experience over the course of a year.
Is your product designed to be used in the car? Map the customer journey through each hour of a long road trip.
Zooming in to create detailed maps of different aspects of the customer journey will help you create even more specifically tailored customer experiences.
The template above follows the standard stages of the customer journey, but it's not the only way to do your customer journey mapping.
Two other commonly-used journey maps are the "Day in a life" journey map and the customer support journey map. We've provided the key elements of both below, as well as customer journey map templates for each.
Day/week/month in the life map
The best way to map mini-journeys within the larger customer experience lifecycle is with a "Day in a Life" journey map . This map plots the same things as the general customer journey map—key milestones, questions, touchpoints, and gaps—but over a particular period of time instead of over the course of the entire relationship.
This map includes space for you to record the buyer persona's name, occupation, and motto, but these are really just shorthand for key persona characteristics. If you're selling baby diapers, for instance, your persona's occupation would be "parent," even if the person in question is also an accountant.
The "motto" should be a condensed version of your persona's primary mindset with regard to their wants, needs, and pain points. The motto for an expecting first-time parent might be, "I'm excited but nervous—I have to make sure I'm prepared for anything."
Use the column headers to set your time frame. If you're marketing to expecting parents, the time frame might be the nine months of a pregnancy, or you might map an expectant mother's experiences through a single day in her third trimester. At each stage, ask yourself the same questions:
Where and how could the customer encounter our brand? Alternatively: how could our brand provide value at each stage?
A day in the life customer journey map will not only help you zoom in to develop more tailored experiences, but it will also give you insights into what might be useful to add or improve in your product or service.
Support experience map
One of the most common, and most significant, customer/brand interactions is the customer support journey . A frustrating customer service experience can turn someone off of your brand and product entirely, while a particularly impressive experience can immediately convert a regular user into a brand advocate.
This journey map is a bit different in that it doesn't just map touchpoints; it maps functional interactions between the customer and customer service representatives as well as the behind-the-scenes activities necessary to support the customer-facing team.
This map starts when the support ticket is opened and ends when the customer's issue is resolved. The top row of the map is simple: what is the customer doing at each stage in the support process?
Next, you'll record the corresponding actions of your customer-facing, or "frontstage" team. This includes both employees' actions and the systems engaged in the support process. For example, if the first step of your customer support process is handled by a chatbot or automatic phone system, these will go in the technology row. If the customer moves forward to request to speak with a representative, then the second stage is where your "employee actions" row will come into play.
Finally, the bottom row is for behind-the-scenes activity performed by employees who don't interact with the customer at all. For example, if the customer representative needs to get information from another department to answer the customer's questions, the other department's involvement will be recorded in the "backstage actions" section of the map.
To put it all together, here's an example customer journey map for a gym.
Researches local gyms online
Reads reviews
Compares membership options
"I can't go up a flight of stairs without getting winded; I need to get my health and fitness on track."
"I wish I knew someone who could recommend this gym."
Encounters:
Online reviews
Social media pages
Missing touchpoint:
Success stories on social media in a front-and-center location, like a saved Instagram Stories collection or a pinned post
Views gym's social media
Visits gym's website
Views membership pricing page
"This gym looks clean and modern from the photos."
"I hate calling the gym, but I'd like to learn more about personal training or class options."
Contact form
Free trial request pop-up
A live chat box on the gym's website for prospective customers to ask questions about the facility or membership options before visiting
Visits the gym to take a tour
Meets with a membership consultant
Potentially signs up for free trial
"The staff was friendly and it was easy to sign up."
"I wish I could see what classes they offer and weekly schedules without having to visit the gym."
In-person visit
Facility tour
Consultation
Free trial sign-up
Orientation session
Gym access card
A mobile app where members can track their progress, access class schedules, book personal trainer sessions, and receive personalized workout recommendations
Visits the gym regularly
Participates in classes
Engages with personal trainers
Potentially pays for membership after free trial ends
"Maybe I should compare options again."
"I wish I knew someone who could work out with me."
Personal trainer consults
Email reminders about upcoming end to free trial
Personalized offer encouraging renewal
Follow-up call
Community-building events like workshops or challenges to foster a sense of community and support among members and staff
Refers friends and coworkers
Promotes the gym on social media
Regularly visits and attends classes
"My coworker would love this gym since it's so close to work."
"I love that teacher. I'm going to try some of her other classes."
Referral programs
Social media engagement
Reviews gym
Potentially provides a testimonial for gym
Missing touchpoints:
A loyalty rewards program for members' continued commitment and engagement that offers exclusive discounts, merchandise, or access to premium services
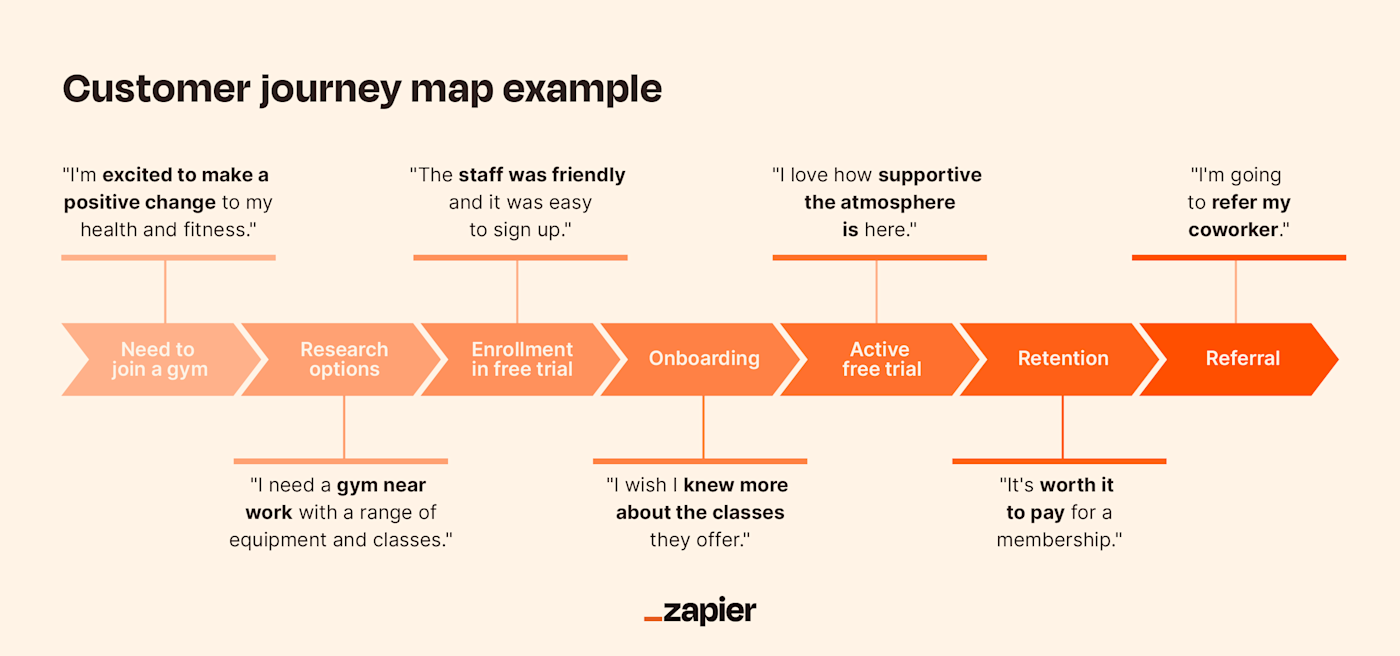
Your customers' spending habits, interests, challenges, and problems are always changing, and your customer journey maps should adapt along with them. But with so much data to track, it's a good idea to connect your insights to CRM software. Then you can automate your CRM to create specific, valuable experiences for your customers without breaking a sweat.
Related reading:
Beyond the sales pipeline: Using a CRM for customer success
A quick guide to contact management
B2B email marketing: Proven strategies + examples
4 tips for creating an inbound marketing strategy
This article was originally published in May 2021 by Nick Djurovic. The most recent update was in August 2023.
Get productivity tips delivered straight to your inbox
We’ll email you 1-3 times per week—and never share your information.

Amanda Pell
Amanda is a writer and content strategist who built her career writing on campaigns for brands like Nature Valley, Disney, and the NFL. When she's not knee-deep in research, you'll likely find her hiking with her dog or with her nose in a good book.
- CRM (Customer Relationship Management)
- Sales & business development
- Small business
Related articles

8 essential tips for maximizing TikTok ads ROI
8 essential tips for maximizing TikTok ads...
The best marketing newsletters in 2024

11 Google Ads examples (and how to use their strategies)
11 Google Ads examples (and how to use their...
How will AI change SEO content production?
Improve your productivity automatically. Use Zapier to get your apps working together.


Salesforce is closed for new business in your area.
🔥 We just launched Topicfinder: the most a powerful content research tool! Try it Free Take The Tour!
The 9 Customer Journey Stages and Why They Are Important

In broad strokes, the customer journey is all the steps a person takes to become a customer. This path encompasses everything from realizing they have a problem that needs solving to buying and using your product to solve that problem.
Knowing this customer journey is vital because it allows you to focus your marketing efforts on different stages of that journey. It's similar to the sales funnel but more variable; everyone takes their unique path through your customer journey. Each step of the customer journey can be categorized within the sales funnel, but each customer has their way of making it through those stages.
Think about this: when you call a business, you must go through a phone tree to be directed to the right place. Or, you have to explain yourself to a receptionist, who has to figure out who to send you to. Or, you talk to a CS rep in a call center, get transferred up the chain three times, and still don't know if you'll ever get your issue solved.
If the business knew your stage in the journey, they could ensure that the people you contact the first time are the right people to talk to.
The Phases of the Customer Journey
When you define a customer journey, you'll find a bunch of guides and think pieces with different outlines for the customer journey. Some list four phases, some five, some six, and even more. What's going on?
The barest minimum customer journey has three stages: before the sale, during the sale, and after the sale. Sounds simple, right? It's a straightforward definition, but where do you draw the lines?

You can get quite granular with this. For example, here's a nine-stage example:
- Someone who isn't a customer and isn't even aware of your business yet discovers a problem they need to solve. This example can be anything from too much static in their laundry to a newfound dietary restriction to a business problem.
- The non-customer, aware that they have a problem, starts to look into possible solutions. Along the way, they discover you as one potential solution to their problem.
- This non-customer isn't sure they want to go with you to solve their problem. After all, if there's a company that might fix their issue, there's probably more than one. So, they carefully analyze your company to see your selling point and how well you can solve their problem.
- Still in the research phase, the non-customer looks at competitors and other potential solutions to their problem. They may not have even decided between buying an eCommerce product or rigging something DIY yet, but this is exploring their options. They may be signed up to your mailing list or become a fan on social media, but they are not yet a customer.
- The customer, through their research, has made two decisions. The first is to buy a competitor's solution, and the second is to buy your solution. They are now a customer.
- You don't take money, ship a product, and wash your hands of the transaction, do you? Of course not. In this stage, you engage with the customer – passively and actively – to onboard them into using your product. This process can involve anything from an instruction booklet in your product to a drip campaign offering usage tips.
- The usage stage is where the customer decides whether or not the investment was a good one. This time is also when they may reach out for support or leave a review. We've all had times when we make a purchase, but it takes weeks or months to get around to actually using it.
- This step is the ongoing relationship you have with an existing customer. Depending on your business, the relationship can be an ongoing subscription (or an increased service plan), or it can be a repeat purchase of a consumable, or it can be purchasing add-ons and extras (lenses and cases for a camera, for example.)
- Fully satisfied with both your product and your support, this customer is now loyal; they recommend you to their friends and strangers online, they advocate for you, and if you offer it and they're in the proper position, they may sign up to promote you via an affiliate program or referral system.
Several of these can be condensed, you may skip some, and some have dramatically more extended amounts of time a customer spends in them than others. That's what makes the customer journey so tricky, after all.
The Customer Journey in the Context of Content Marketing
All digital marketing is interconnected, but let's be honest; I'm not a PPC management agency or a technical SEO specialist; I'm a content marketer. I know enough to talk authoritatively about other forms of marketing, but I specialize in blogging and how blog content can engage potential customers. So, let's look at the customer journey stages in content marketing.
I've written before about why it's essential to know the user intent behind a keyword , so you know what type of content you should be writing. For example, if someone is searching for "red shoes," they're probably less interested in learning the history of how red shoes are viewed in various cultures and more interested in finding pages where they can buy red shoes.
Knowing the stage of the customer journey is similarly important. Giving visitors a user guide for a product they haven't even decided to buy will not work for you. Similarly, forwarding customers to a sales-focused landing page when they've already purchased your product is considered poor support.
Let's look at those nine journey stages and what content might be relevant to them.
1. Challenge
Challenge is the stage where a user learns they have a problem that may be solvable. This step is also a prime opportunity for content marketing .

Blog content written in this stage focuses on defining the user's pain point. It's about educating users on the issue, its challenges, the repercussions of not solving it, and how you may solve it. It uses keywords usually not used within the industry because a user might not know enough about the industry to use those terms.
To use content marketing as an example , I might produce content aimed at people who have no idea why a blog is helpful, explaining the basics of SEO and Google's algorithms and how content marketing interacts with them.
2. Discovery
At this point, the customer may have been on your blog before reading about their problem, or maybe they've only seen a reference to you on social media or elsewhere. The discovery stage is where they learn about your brand and that you aren't just educating them about the problem; you're offering a solution.

Content marketing here takes two forms. The first is landing pages. Landing pages aren't considered blog posts, but they can have some similarities, as they're both longer-form content. This content is still educational, but instead of educating the user on their problem, you're educating them about how your product can solve it.
You won't always get a sale from this content directly. Users may be too unaware of their options to pull the trigger, so they're likely to research alternatives.
3. Consideration
The consideration stage is where the user researches you in more detail. Blog posts don't necessarily come into play as much here, but technical writing, landing pages, features pages, pricing pages, reputation management, and other forms of marketing very much do.

This step is also where the user may decide between different solutions, like a DIY option versus a product they can use versus a service they can hire. For example, someone who needs photography for an event might research the pros and cons of cell phone pictures versus buying a camera versus hiring a photographer.
4. Comparison
Similar to consideration (and often considered part of it), the comparison phase is where the user performs similar research into your competitors.
We create blog content that converts - not just for ourselves, but for our clients, too.
We pick blog topics like hedge funds pick stocks. Then, we create articles that are 10x better to earn the top spot.
Content marketing has two ingredients - content and marketing. We've earned our black belts in both.

This step is where comparison pages come into play. Blog posts can also do a lot of heavy lifting here. You can write lists of the top companies offering a service (with your position at the top), you can write about how to solve various problems authoritatively, and so on. You want a whole ecosystem of content that positions you as a reliable authority.
5. Purchase
The actual act of making the purchase doesn't have anything to do with content marketing.

The user decides, they go to your website to buy or sign up, and that's that. The purchase decision step is a critical stage to analyze, which is why it gets a unique entry, but that's more about the analytics and the KPIs you harvest than the content you produce.
6. Adoption
Once a user has made a purchase, you want to onboard them. Depending on the product you're selling , this can occur in various ways.
Content marketing involves creating usage guides, tips and tricks blog posts, drip campaigns offering resources, an internal knowledge base, and other content types. This step is also where customer support can come into play, with a staff that can help assist users with configuration, onboarding, setup, and so on.
Content marketing doesn't necessarily play a significant role in usage, but it can be relevant if you write content about how to use your product for specific purposes.

Your onboarding may cover primary uses, but you can cover more advanced or unusual benefits in other forms of content.
Support, again, isn't necessarily the realm of content marketing. However, it's usually a good idea for your support to have at least a self-help option, like a knowledge base or a blog category dedicated to solving issues and fixing problems.

That way, when the user has a problem, they can find resources on your site to use and have the option to contact you for more support if necessary. Being available for your customer's needs is critical for retention and a positive customer experience. This stage also involves listening closely to customer feedback and improving product functionality.
9. Advocacy
For customers that had a positive user experience, advocacy is a natural next stage. After all, we all have to navigate the world of commercialized everything around us, and recommendations from people we trust are among the most powerful ways to spread a product.

Through affiliate marketing and referral guides, customer loyalty programs, and more, content marketing can work here. However, some of this content marketing won't be yours, it will be the advocate's, so you may want to create style guides, brand reference guides, or media packs to help them out.
Customer Journey Glossary
You've likely heard some of these phases before, and others may be brand new to you.
Here are a few terms and phases we've left out from this list to define and demystify them:
- Retention stage: This is a common phase in a customer journey. Customer retention is along the lines of Phase #7, "Support"; after a customer has made a purchase, you provide support to ensure they're happy and remain a customer with your company.
- Decision stage: This is identical to Phase #5, "Purchase." When the customer decides to purchase, they are now a customer and have entered a new phase in the customer journey.
- First impression stage: This stage is identical to Phase #2, "Discovery." The visitor discovers your brand, product, or website for the first time and is aware of you.
- Awareness stage: The awareness stage of the journey is also identical to phase #2, "Discovery," just with a different name.
- Customer Journey Map: Also called a customer journey roadmap, this is an illustration of each of your customer journey phases. This chart can help train and educate the members of your team to help them understand how a new visitor becomes a customer and all of the steps in between.
- Touchpoints: Touchpoints are moments in time when visitors or customers might interact with your brand, and they can be from users who are at different stages of the customer journey. This may be a YouTube ad that they watched, an email they received, a word-of-mouth recommendation, or even a "Thank you for your order" email after deciding to purchase.
As you can see, there are a few different nicknames for some of these stages, but the definition remains the same.
Putting the Pieces Together
The stage of the user journey is just one aspect of content marketing. User intent, keywords, and the buyer persona are also relevant.
I always say that writing a blog post is just about the easiest part . A successful blog requires a ton of groundwork, both in one-time or annual research and in topic-specific, keyword-specific, and persona-specific definitions.
That's about all the help I can give you in generic terms. The trouble with this is that it heavily depends on your business, niche, and target audience. I have done a ton of research into my niche and industry, product, keywords, metrics, and all the rest, but it would only be helpful to my direct competitors if I shared it. Your job is to define all of it for yourself. Or, of course, hire me to handle your content marketing strategy for you and have me do it—your choice.
James Parsons is the founder and CEO of Content Powered, a premier content marketing agency that leverages nearly two decades of his experience in content marketing to drive business growth. Renowned for founding and scaling multi-million dollar eCommerce businesses through strategic content marketing, James has become a trusted voice in the industry, sharing his insights in Search Engine Watch, Search Engine Journal, Forbes, Entrepreneur, Inc, and other leading publications. His background encompasses key roles across various agencies, contributing to the content strategies of major brands like eBay and Expedia. James's expertise spans SEO, conversion rate optimization, and effective content strategies, making him a pivotal figure in the industry.
Join Thousands of Marketers and Get Free Tips Weekly!
Related Posts

Blog Sales Funnels: How Do They Work and Are They Worth It?

18 Methods to Find Buyer Intent Keywords For Your Business

How to Build an Effective SaaS Marketing Content Strategy
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Name (required)
Email (will not be published) (required)
Your Comment
Let’s Grow Your Business
Want some free consulting? Let’s hop on a call and talk about what we can do to help.
20 Customer Touchpoints That Will Optimize Your Customer Journey
Updated: June 15, 2021
Published: May 25, 2021
Have you ever made a model car, boat, or airplane? Or, built DIY furniture from IKEA? Or, maybe just played with Legos as a kid — or, like me, still do as an adult?

If you've tried any of these, you've encountered a set of instructions on how to build your product. Some are better than others, but all do the job of explaining the steps you need to take to achieve your goal.

Customer touch points (or touchpoints) work in a similar way. They represent important interactions that occur along the customer's journey. Grouping them chronologically paints a complete picture of an average customer experience with your business.
In this post, we'll explain what customer touch points are and the role they play on marketing and customer service teams. Then, we'll wrap up with a list of touch point examples and proven techniques to use them at your business.
Customer Touch Points
Touch points are interactions between businesses and customers that occur during the customer's journey. These moments significantly influence customer experience as well as brand perception. By outlining key touch points on a map, businesses can capitalize on timely opportunities to optimize their customer journey.
.webp)
Free Customer Journey Template
Outline your company's customer journey and experience with these 7 free templates.
- Buyer's Journey Template
- Future State Template
- Day-in-the-Life Template
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Customer touch points are typically recorded on a customer journey map . They're put together in chronological order to demonstrate what a typical customer's experience is like with a business.
This helps marketing and customer service teams identify touchpoints that cause friction so they can remove them and enhance the customer journey.
Here's an example of what a customer touchpoint looks like on HubSpot's customer journey map .
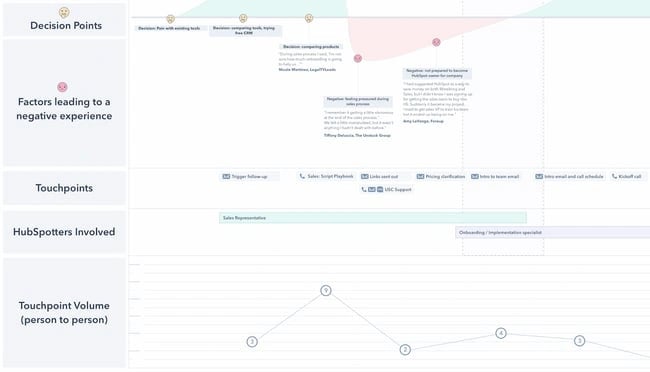
While this is only a small section of a much larger document, it gives us a good idea of how useful touchpoints are to marketing and customer service teams. In the original document, the green dots represent interactions that are positive, and the red ones represent points of friction. Yellow dots are moments when customers have to make decisions, which leads to either a green or red dot.
With this layout, we can look at an overall view of different touchpoints occurring within various stages of the customer journey. This makes it a lot easier to spot areas of your business that can be improved to increase customer delight .
Let's take a look at some examples of customer touchpoints below.
Customer Touch Points Examples
- Social Media
- Online Advertisement
- Digital Marketing Content
- Company Events
- Peer Referral
- Conversations With Company Representatives
- Product Catalogs
- Product Reviews
- Point of Sale
- Thank You Letters
- Product Feedback Surveys
- Upsell/Cross-Sell Emails
- Billing Actions
- Subscription Renewals
- Customer Support Channels
- Customer Success Programs
- Customer Onboarding
- Customer Loyalty Programs
- Self-Service Resources
We've segmented this list to cover touch points that occur before, during, and after a purchase. Additionally, we've also added a section that's specific to customer service teams.
Touch Points Before a Purchase
1. social media.
Social media could be included in every section of this list, but it's mostly used in customer acquisition . That's because social media is a cost-effective way of reaching a large portion of your target audience. You can use it to promote products, build relationships with clients, and enhance the overall reputation of your brand.
2. Online Advertisement
Have you ever noticed banner ads displayed at the top or sidebar of a webpage? Those are touch points that take prospects back to your website. For some brands, like Best Buy below, it's an effective way to draw traffic to their sites.
Image Source
3. Digital Marketing Content
Aside from ads, digital marketing content refers to any material that your company publishes online to promote its brand. These materials could be promotional videos, infographics, or engaging blog posts — like the one you're reading right now.
4. Company Events
If you're on a marketing or sales team, then you may have attended a conference this year where you stood in a booth to promote your company. These events are an excellent way to introduce your brand to customers who may not be aware of it.
One example is INBOUND , where companies from around the world meet to discuss marketing, sales, customer service, and other business topics. It's a great chance for business leaders to connect with new partners and discover strategies that can help their organizations grow.

5. Peer Referral
It's no secret that customers trust their peers over your advertisements. 83% of customers say that their friends and family are their most trusted sources of referrals. This makes it imperative for businesses to focus on word-of-mouth marketing if they want to be seen as trustworthy.
Touch Points During a Purchase
6. conversations with company representatives.
The most direct point of contact you have with customers is your in-person interactions. These conversations that take place in your stores have an immediate impact on the customer's purchase decision.
7. Product Catalogs
Whether they're online or a hard copy, catalogs are an excellent medium for showcasing your product line. An image of the product, coupled with an enticing description, gives the customer everything they need to know before making a purchase.
You can remove friction by adding a CTA on the page that adds the product to a shopping cart, like in the example below.

8. Ecommerce
For many businesses, ecommerce is the most effective way to acquire customers and close deals. That's because websites can be accessed globally, making it possible for an SMB in one location to provide products and services to a customer on the other side of the world.
Understanding the various touch points within ecommerce can dramatically improve the customer experience for SaaS and other online companies.
9. Product Reviews
In today's digital age, product reviews are no longer a pre-purchase touch point. Now, customers have smart devices that can call up product reviews while they're shopping in your stores. Additionally, some online retailers include reviews on the listing page, so you can see what other customers think without navigating away from the page. You can see an example of this touch point in the image below.
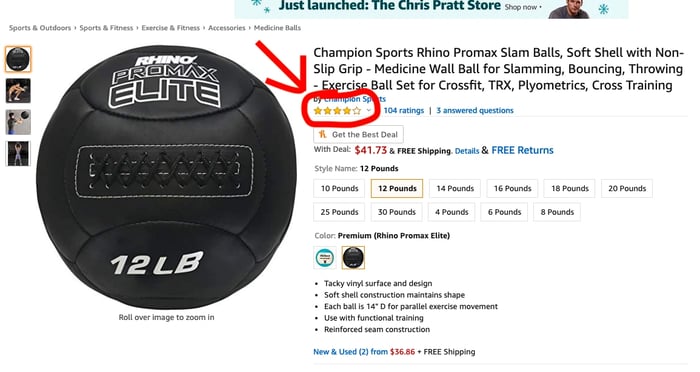
10. Point of Sale
This is the last touch point your customers will reach before making a purchase. That's because this is where your sales rep makes their case for why the customer needs your product. For many businesses, this is a momentous step in the customer journey.
Touch Points After a Purchase
11. thank you letters.
One effective way to build customer rapport is by following up with a thank you letter. This can be an email, or, if possible, a hand-written note that thanks customers for their business. It's a great way to show customers you care and develop a long-term relationship with them.
If you're not sure how to start sending customer thank you letters, check out our guide here .
12. Product Feedback Surveys
Product feedback surveys are sent after a purchase and they evaluate the customer's experience with your product or service. If the customer leaves a negative review, the company can reach out to learn more about the issue. They then relay this information to the product development team, who makes enhancements on the next version of the product.
13. Upselling/Cross-selling Emails
Customer needs don't go away after a purchase is made. In fact, some customers have additional needs once they start to use your product.
This presents an opportunity for you to upsell or cross-sell customers on additional or premium items in your store. We can see an example of this in the image below.
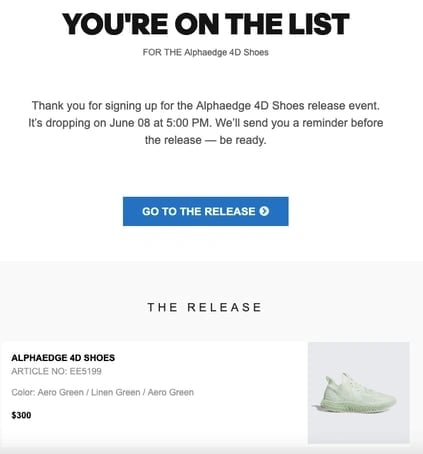
14. Billing Actions
Billing is often an overlooked touch point on this list. That's because it happens after a purchase occurs and has no direct influence on the customer's decision to buy your product. However, it's still a vital step in the customer's journey because a negative experience can result in an immediate instance of churn, if not addressed properly.
15. Subscription Renewals
If you're a subscription-based business, renewals are crucial to your revenue model. You need customers to renew their subscriptions to maintain steady growth for your business. This makes it important that you remove as much friction as possible from your renewal process. After all, it should be effortless for an existing customer to stay a customer after their contract is up.
Touch Points in Customer Service
16. customer support channels.
Customer support channels are any platforms that service agents use to communicate with customers. This includes chat, email, phone, social media, peer review sites, and more. Businesses need to invest in omni-channel support if they want to create a delightful experience for their customers.
17. Customer Success Program
Customer success programs have a variety of touch points found within them. When a customer success department recognizes a potential problem, they reach out to customers to notify them of the issue or offer a solution. This demonstrates a commitment to the customer's goals, which builds additional rapport over time.
18. Customer Onboarding
Customer onboarding is a popular touch point for service teams because many customers abandon products shortly after buying them. That's because they either don't know how to use it, or they don't have the time to learn how to use it. Both result in churn, making it essential for companies to invest in effective onboarding programs.
19. Customer Loyalty Programs
Loyalty programs are another important touch point that service teams should be aware of. These programs strengthen your relationship with a customer and turn them into lifelong advocates. By incentivizing people with exclusive rewards and discounts, they'll be more likely to share positive reviews about your business.
20. Self-Service Resources
When customers are in a hurry or only have a quick question for your support team, they don't want to spend 20 minutes waiting on hold for a rep. Instead, you can offer self-service resources that feature troubleshooting steps customers can take on their own. That way, they're not dependent on your service team for answers and can find solutions on their own time, making your product more convenient and easier-to-use.
All of these touch points are essential for creating a strong customer journey. But how do you use them in your business? Let’s walk through that below.
Using Customer Touchpoints in Your Business
By using customer touchpoints, you’ll exponentially improve the customer experience . But not all touch points will make sense for your company. For instance, if you’re a SaaS business, you might not have an online catalog. And if you’re running the business on your own, your customer likely won’t run into a sales team.
To create a custom customer touchpoint map, you’ll want to take the following steps.
1. Put yourself in your customers’ shoes.
First and foremost, put yourself in your customers’ shoes and envision the steps they take as they make a purchase decision. Where do they look first? How do they reach a purchase decision? And what do they do if they run into problems using the product?
Let’s take a look at an example customer journey below.
- The customer becomes aware of a problem and researches ways to solve their issue.
- After finding a solution, they search for a particular product. They look through product listings on Google, then explore offerings on retailer websites such as Amazon.
- They search for product reviews.
- After finding sufficient information, they purchase the product.
- They use the product, but run into trouble. They look for articles and resources on how to solve the issue on their own.
- They reach out to a customer service representative.
After, match each of these customer actions to a certain touchpoint. Here’s what that looks like:
- Touchpoint one : A robust blog that covers commonly-researched issues by your customers.
- Touchpoint two : A series of paid ads in Google’s and Amazon’s product pages.
- Touchpoint three : A collection of un-sponsored product reviews on your website.
- Touchpoint four : A customer portal that allows customers to easily check out and see their order status.
- Touchpoint five : Self-service options such as knowledge bases and product how-tos.
- Touch point six : An easy-to-find customer service portal or phone number that allows them to get in touch.
2. Decide what’s feasible based on your company size and budget.
Now that you have a rough idea of the resources and information your customer will need during their journey, it’s time to decide which ones are easiest to implement based on your company size and budget.
If you sell a complicated product but run a one-person business, investing in a full-scale service desk with knowledge bases and ticketing features might not be feasible. But you could start by adding free live chat .
The key here is to find an alternative that’s easy to adopt for you and your team and that’s scalable as your business grows. You don’t want to be boxed in after your customer touchpoint strategy yields positive results.
3. Establish touch point tasks.
Deciding on the touch points is one thing; translating them to actionable tasks is another. You’ve decided what’s feasible, and now it’s time to turn it into action.
Here’s what that can look like for the example referenced above.
First Touchpoint Tasks
- Create a strong cluster content strategy that solves for the customer.
- Decide on the first five posts, which will be published in four weeks.
- Hire four freelancers to write the content.
- Use the in-house marketing team to leverage buyer personas and current customer acquisition data.
Second Touchpoint Tasks
- Create a Google Merchant Center account and Amazon seller account .
- Write unique descriptions for each product using the services of two freelancers.
- Source product photos and general information such as specifications, country of origin, sustainability score, and so on.
- Add product listings to Google and Amazon.
Third Touchpoint Tasks
- Add product reviews to the site using a WordPress review plugin or another solution.
- Invite current customers to write reviews by offering a 10% discount on a future purchase.
- Respond to reviews as they come in so prospects can see the brand is active.
You’d continue down the touchpoints list, adding tasks until you have a comprehensive checklist that everyone on your team can reference.
4. Leverage software tools to automate touch point tasks.
Use marketing, sales, and service software to ensure touch point tasks run smoothly with minor intervention.
Let’s say that you’ve decided to invest in social media marketing as the first touch point, but you have a three-person marketing team, and you don’t know how to get started. You can consider a social media management tool such as HubSpot’s Social Inbox (included in Marketing Hub). And if your team is new to social media management, you can have everyone take a social media certification course.
If you’ve decided that one of your customers’ touch points is chatting with a salesperson, you’d invest in a CRM that helps your sales team keep track of all communication and automatically schedule follow-up calls.
If one of your touchpoints is a discount delivered over email, you’ll want to automatically send the message using email marketing software . No need for you to manually type each email out and send it to every customer.
And if one of your touchpoints is an easy-to-reach service desk, you’ll invest in customer service software that can take care of ticketing — and even resolve simple inquiries with a customer service bot.
These tools can help you streamline your customer touchpoint process so that it progresses with minimal intervention from your team. In that way, as you serve more and more customers, no touchpoint slips through the cracks.
Use Customer Touchpoints to Enhance the Customer Journey
By using customer touch points, you can play a role at every step of the customer journey. Nothing is left up to chance. Instead, you provide targeted information at just the right time. Whether you’re a one-person business or an enterprise-level team, you should use touchpoints to enhance the customer experience, empowering you to retain more customers and grow better.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in January 2020 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![different customer journey How AI Image Misuse Made a World of Miscommunication [Willy's Chocolate Experience]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/ai%20image%20misuse%20the%20willy%20wonka%20experience%20%281%29.png)
How AI Image Misuse Made a World of Miscommunication [Willy's Chocolate Experience]

7 Ways to Delight Your Customers This Holiday Season

14 Customer Experience Fails that Companies Can Learn From
![different customer journey How Customer Experience Has Evolved Over the Last Decade [+ 2024 Trends]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/future-of-customer-experience.png)
How Customer Experience Has Evolved Over the Last Decade [+ 2024 Trends]
![different customer journey Memorable Examples of AR in Customer Experience [+Tips for Implementing the Technology]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/augmented%20reality%20customer%20experience.png)
Memorable Examples of AR in Customer Experience [+Tips for Implementing the Technology]
![different customer journey How to Create an Effective Customer Journey Map [Examples + Template]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/customer-journey-map_13.webp)
How to Create an Effective Customer Journey Map [Examples + Template]

Digital Customer Experience: The Ultimate Guide for 2023
![different customer journey How to Implement a Hybrid Customer Service Strategy That Works [Expert Tips]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/hybrid%20customer%20service_featured.png)
How to Implement a Hybrid Customer Service Strategy That Works [Expert Tips]

User Flows: 8 Tips For Creating A Super Smooth User Experience

11 Best Practices for B2B Customer Experience
Outline your company's customer journey and experience with these 7 free customer journey map templates.
Service Hub provides everything you need to delight and retain customers while supporting the success of your whole front office
- 1-800-553-8159 Expand Menu
- Subscribe to Our Emails Expand Menu
- Chat with Sales Expand Menu
- Contact Us Expand Menu

9 Best Real-life Customer Journey Map Examples

April 4, 2024
The customer journey mapping process is a visual representation of the experiences and interactions customers have with a company, from initial awareness to post-purchase evaluation.
These maps utilize infographics to showcase touchpoints across the customer-brand relationship, revealing strategies for personalized experiences that enhance consumer success and engagement.
By aiding businesses in understanding the customer journey, identifying pain points, and enhancing overall experiences, journey mapping contributes to increased sales, loyalty, cost savings, and team alignment.
How Customer Journey Maps Impact Business Performance?
Customer journey maps serve as invaluable tools for enhancing business performance by facilitating a smoother path to customer satisfaction.
They provide insights into the customer experience, allowing businesses to empathize with customers, identify pain points, and address challenges they encounter along the way.
By pinpointing inconsistencies between touchpoints, such as communication gaps across platforms or departments, customer journey mapping aids in improving service quality and retention. Leveraging customer journey contact center data, these maps optimize genuine customer engagements across all communication channels.
Key Elements of a Customer Journey Map
Numerous customer journey mapping software options exist in the market, each offering unique features. Here are the key elements that characterize these customer journey map templates.
Customer Personas
To create a customer journey map, you first need to know who your potential customer is. This begins with developing customer personas, which are fictional representations of typical customers based on demographics, behaviors, and customer needs.
For instance, Uber has two primary personas: passengers seeking seamless rides from A to B, and drivers desiring flexibility and supplemental income.
Touchpoints
Touchpoints encompass every interaction a customer has with your brand throughout their buying journey. When creating a customer journey map, it's essential to outline these points of contact, information gathering, or interactions with your brand. Typical touchpoints include:
- Marketing emails and newsletters
- Phone calls, service and support lines, online chatbots
- Store staff, checkout registers, service points
- Website, apps, social media platforms
- Packaging, shipping, delivery
Customer Emotions
In this step, you map out the specific emotional experience of the customer at each touchpoint. What are they thinking? What actions do they take? How are they feeling?
Avoid guesswork by gathering real feedback from customers through surveys and, ideally, direct interactions with your customer support team.
Critical Moments
Critical moments are the touchpoints that significantly influence the overall customer experience, whether positively or negatively. These moments of truth provide opportunities for innovation and growth as they represent instances, such as pain points, where people are willing to invest in addressing their critical needs.
Channels and Platforms
Channels and platforms encompass the diverse mediums through which customers engage with your business. These may include traditional channels like in-person visits or phone calls, alongside digital channels such as websites, social media, or mobile apps. Understanding the preferred communication channels of different customer segments helps in effectively engaging with your customers throughout their journey.
From Concept to Reality: Creating Your Customer Journey Map
Customer journey maps are not one size fits all; however, there are fundamental steps that you can take to create your own.
Step 1: Define customer touchpoints
Identify all customer interactions, from ads to website visits, forming the core of your user journey map, illustrating the path from awareness to purchase and beyond.
Step 2: Create customer buyer personas
Develop fictional representations of your target audience, considering demographics and behaviors.
Step 3: Set goals
Establish goals for each touchpoint on your map, whether it's increasing brand awareness, driving sales, or fostering customer loyalty.
Step 4: Conduct user studies and surveys
Conduct user studies and surveys to understand how customers discover products, interact with your brand, and identify pain points or challenges they encounter.
Step 5: Analyze your customer journey map
Evaluate key metrics such as repeat purchases, sales, and customer satisfaction to assess the effectiveness of your customer’s journey map. Use the data to optimize touchpoints and enhance the overall digital customer experience .
Real-life Application: 9 Customer Journey Map Examples Across Industries
Example 1: consumer saas- spotify.
Spotify, a leading audio streaming service, utilized a customer journey map to enhance its music-sharing experience for users. The objective was to determine the optimal integration of music-sharing features within the customer journey.
The map detailed the user experience from opening Spotify on a mobile device to interacting with shared songs. By analyzing each stage and touchpoint, including user actions, thoughts, and emotions, Spotify identified pain points and implemented improvements for a smoother music-sharing experience.
This comprehensive journey map prioritized customer engagement, considered user behavior, and aimed to enhance overall user satisfaction, ultimately encouraging more frequent music sharing among users.
Example 2: Entertainment - Netflix
Similar to Spotify, Netflix's customer journey map incorporates stages, emotions, and thoughts, albeit with a different approach. In Netflix's map, each touchpoint is described in a more goal-oriented manner, focusing on addressing the goals through rows such as 'motivations', 'pain points', and notably, 'opportunities'.
Additionally, this customer journey map is tailored with a clear target persona in mind, likely detailed in their marketing materials, along with a predefined scenario. This approach makes Netflix's customer journey more actionable and focused on achieving its objectives.
Example 3: E-commerce - Amazon
Amazon, a global e-commerce giant, employs sophisticated technology and custom systems to guide customers through the sales journey. While its customer journey map is complex and extensive, it can be broken down into manageable parts for analysis.
For instance, Amazon's customer conversion funnel illustrates how its products facilitate the customer journey, driving engagement and maximizing sales. When conducting your customer journey mapping , remember to incorporate key metrics to monitor success and gain deeper insights into the overall customer experience.
Example 4: B2B - Hubspot
HubSpot opted for a linear design for their customer journey map, organizing common experiences along a timeline and using color coding to denote pain points or moments of delight. This format made the map easy to interpret and actionable for other teams.
Additionally, they incorporated testimonials from customers, categorized based on their position in the journey, to provide firsthand perspectives on interactions. These stories humanized the map, making the identified issues feel more relevant and pressing to employees.
Example 5: SaaS- Zendesk
This customer journey map example from Zendesk uniquely emphasizes customer churn and reconsideration. While it doesn't delve into the specifics of customer activities, thoughts, or emotions, it distinguishes itself by accounting for a range of outcomes, including churn and reevaluation.
For teams prioritizing these aspects, this format offers a valuable framework for gaining deeper insights into the customer's mindset at each stage of their journey.
Example 6: Toy- Lego
LEGO has innovatively crafted a Customer Journey Map using a tool called the "experience wheel." This wheel analyzes a flight to New York City in a simplified manner.
At its core are the persona's characteristics, surrounded by three levels of experience representing the journey's goal achievement. The outer circle details each step of the journey, marked with emoticons reflecting positive, neutral, or negative experiences. This straightforward format allows for easy creation, making it suitable for discussions and idea-generation sessions. It offers a quick way to view products or services from the customer's perspective.
Example 7: SaaS - TurboTax
TurboTax, a leading online tax preparation software, developed a customer journey map to launch its new product, Personal Pro.
The map, created through a blend of data research, customer surveys, and discussions with tax professionals, tracks the customer experience from website entry to tax filing completion. By identifying and addressing customer pain points, the map enables TurboTax to enhance the overall experience, ensuring smoother and more satisfactory interactions.
Example 8: Transport - Uber
Uber's customer journey map not only includes clearly defined stages, emotional waves, and thoughts at each touchpoint but also incorporates additional visuals from their app and descriptive elements.
For instance, the persona is well-defined, eliminating the need to reference external marketing documents for details. Moreover, the critical analysis for action section provides a clear assessment of both positives and areas for improvement at each step of the journey.
Example 9: Retail - Starbucks
Starbucks’ customer journey map, using a timeline style, highlights diverse touchpoints and aims to enhance customer experience. It gathers feedback from outlet visits and categorizes experiences into three components:
- Poached experience: Customers are asked about their overall impression of the outlet they visited, particularly during peak hours.
- Enhanced experience: Starbucks also assesses any negative experiences encountered by customers and seeks resolutions to prevent their recurrence.
- Touchpoints: This refers to the level and extent of interaction the consumer has experienced with the brand, whether in person, through the website, app, etc.
How to Implement Customer Journey Maps Using Five9
Implementing customer journey maps using Five9 is a simple process. With Five9, agents gain access to a unified view of customer history, including interactions from email, web chat, and phone calls.
By integrating all channels into a single interface, Five9 ensures that agents have a clear understanding of the customer journey, enabling them to respond effectively at every stage.
Discover how using Five9 customer journey mapping can boost customer service, helping agents understand and meet customer expectations, leading to increased satisfaction and loyalty.
Related Articles

10 Essential Contact Center Metrics and KPIs to Measure in Healthcare

Four Healthcare Contact Center Trends in 2024

Step-by-step Guide to Creating the Perfect Customer Journey Map
Call 1-800-553-8159 to learn more about five9.
Get a Quote
- What is a digital customer journey?
Last updated
22 May 2023
Reviewed by
Jean Kaluza
Learn the definition of the digital customer journey and why it’s crucial for your product in this comprehensive guide.
The digital buyer or customer journey encompasses all of a customer’s interactions with your company, from discovery to purchase.
It consists of all the interactions across all online brand channels and touchpoints, including:
The company's website
Mobile applications
Social media channels
SMS messaging
These interactions influence their purchasing experience.
- Why analyze your digital customer journey?
Since a digital customer journey guides the customer to purchase, analyzing it will enable you to offer a seamless shopping experience.
You should also analyze your digital customer journey to:
Understand customer needs and expectations
Proactively detect friction points that are challenging a seamless customer experience
Gain insights into adjusting your marketing efforts for better results
- The different stages of the digital customer journey
The stages of a buyer's journey vary by business and customer. However, when a customer embarks on purchasing a product or service, they go through these five distinct phases:
Awareness: The discovery phase
Here, customers are at the start of the buyer lifecycle. This is where customers discover their problems and seek solutions to these pain points. They have a goal in mind and need to find a solution.
During this phase, customers become aware of your brand's existence and the products you sell. Brand awareness can span multiple channels, such as:
Word of mouth
Social media
Brand advocates
Email marketing
Search engine suggestions
Affiliate marketing
As a business, good branding and a solid social media presence are essential to capture the audience's attention.
With a digital customer journey, you have stronger control over your marketing campaigns than the traditional customer journey.
Consideration: The evaluation phase
This is the stage where customers have done enough research and are now evaluating the different brands and their offers. The customer is aware of your brand and may start evaluating whether you can solve their problem.
When a customer is dissatisfied with a brand’s offerings, they move on to one that delivers a seamless experience.
During the evaluation phase, customers:
Visit various company websites
Review platforms
Watch product videos to choose the best solution
Read in-depth case studies and reviews
Customers who are satisfied with your company will sign up for a free trial. A brand has a lot of control at this stage, so ensure that you demonstrate how you can solve their problem.
Decision: The selection phase
This is the final stage of the digital customer journey. The customer selects a brand they want to proceed with and make their purchase.
Some content to promote at this stage is free demos, consultations, and product promotions to demonstrate an advantage over your competitors.
Retention: Turning users into regulars
A common problem is ensuring stickiness to your product: Companies can achieve high logins and subscriptions but fail anyway. Preventing this requires learning what keeps their users from returning.
Meta used “Facebook friends” to retain users, which was instrumental in achieving its lofty goals. The company learned that a new Facebook user with five friends was much more likely to log in regularly.
Advocacy: The promoting phase
What could become the most vital stage to achieve is the advocacy phase. Here, a company can cultivate a more effortless marketing cycle.
During the advocacy stage, users become champions of your product without prompt or incentive, referring their friends and peers. This obviously saves valuable marketing dollars, organically shuffling in primed users to your discovery phase.
Amazon uses a version of the buyer’s phases known as The Product-Led Growth Flywheel , which it refers to as the virtuous cycle.
The Flywheel encapsulates existing metrics and structures from marketing and product to achieve organic growth exponentially by cultivating champions that do your marketing work for you.
- What is a digital customer journey map?
A digital customer journey map visually depicts a customer's interaction with a brand.
This visual representation gives a narrative of a customer's steps, from initial engagement with a brand to the last stage of purchasing a service or product.
It comprises:
Consumer data
Transaction information
Customer service interactions
Cross-device browsing history
A digital customer journey map provides insight into what motivates customers to purchase and their pain points when interacting with various touchpoints.
- What are the benefits of customer journey mapping?
Customer journey mapping involves developing a customer journey. The goal is to map out the customer's actions at each touchpoint.
Customer journey mapping has endless benefits, including:
A deeper understanding of your customers
Customer journey mapping gives you a holistic view of all customers interacting with your brand.
It allows you to understand their varying characteristics and purchasing behaviors. This enables a company to tailor its products.
With customer personas , your brand can better address their needs and wants.
Curating a unique customer experience
Journey mapping provides a perspective of the customer's experience, and you learn how to structure your processes to encourage more customer purchases.
Since customer demands are growing, digital journeys are becoming vital in how companies engage with customers. It allows companies to improve their customers' interactions over digital channels.
Growth of business revenue
Knowing your customers' pain points positions you to offer solutions to their problems, so you can boost sales and increase revenue in the long run.
Improving touchpoints will boost the customer onboarding process, building new revenue.
Reducing operational costs
When you know more about your customers, forming a strategy is clearer and cheaper. Understanding their demographics means you’re less likely to spend money everywhere. For example, knowing your customers aren’t on Facebook can save your ad campaign budget.
Sometimes customers have basic questions that bots can handle. Leveraging live chatbots can reduce the cost of hiring real agents to interact with your customers.
With personalized market campaigns, the marketing team knows what to communicate and when. This allows the company to optimize the return on market investments.
- Creating your digital customer journey map
Here is a brief guide to mapping your digital customer journey:
Step 1: Conduct customer research
You create a digital customer journey map using data from primary research . Collecting and analyzing target audience data is vital to making customer-centric decisions.
To ensure you have reliable information, conduct focus groups , in-person interviews , and brainstorming workshops .
Step 2: Design a buyer persona
With the collected research data, create buyer personas. A buyer persona is a profile of your ideal customer where you consider their characteristics and behaviors, such as demographics.
As you design a digital customer journey map, account for different customer needs and expectations for your personas. These personas allow you to understand your customers better, including their motivations, challenges, needs, and what they need you to solve.
Step 3: Leverage the power of personalization
Option overload is an issue as brands compete for consumers' attention.
Personalizing the customer experience allows you to stand out and tailor products to their needs. With personalization, you can display appropriate messages to target personas instead of wasting resources.
Step 4: Define the stages of a digital customer journey
The next step is to determine the actions that will lead your customers to conclude a purchase.
Consider the customer's perspective, thoughts, emotions, pain points, and goals for each stage. This will help you understand what each customer is struggling with and trying to accomplish.
Step 5: Outline all your touchpoints with the target audience
Touchpoints are where prospective customers interact with your brand.
They can include:
Social media profiles
YouTube videos
First, list all the touchpoints and evaluate how each fits your customer's journey. Remember that touchpoints differ from one buyer persona to another depending on their customer journey map.
Outlining the touchpoints allows you to assess which is most crucial in their purchasing process.
Next, optimize each touchpoint for customer onboarding and conversion.
If you’re unsure, use web analytics to identify traffic sources.
Step 6: Align your touchpoints to offer a seamless customer experience
Once you’ve defined the customer touchpoints and the main stages in a customer journey, put it all together.
Create a well-organized digital customer journey map to guide buyers from start to end.
Step 7: Update customer journey maps frequently
A customer journey map is an ongoing investment as changes often occur.
Once you’ve mapped out a digital customer journey, identify gaps and ways to improve customer satisfaction .
To achieve this, frequently collect customer feedback and use it as a foundation for improvements.
You can also experience the customer journey yourself: Walk through all the stages while noting any obstacles you encounter.
Here are some questions to get you started as you review your customer journey:
Was the purchasing process easy?
How easy was it to get in touch with customer care?
Was the agent helpful?
Is the whole exercise time-consuming?
Is the information at the different stages relevant?
How should you deliver a seamless customer experience?
- Digital customer journey examples
Here are two examples of digital customer journeys:
Example one: Repairing a broken car
During the awareness stage, the car owner knows the car is unfit for driving, so they must fix it.
They search for a mechanic and may look for customer testimonials from previous customers of nearby garages.
During the consideration stage, the client has various solutions and seeks the best option to solve their issue.
Next, the customer will compare garages offering specific repair services before identifying one with the best reviews or a successful track record.
Once the customer settles on a garage that offers repair services, they will interact with the mechanic and begin repair negotiations.
Example 2: Booking of an airplane ticket
In this example, the customer's journey begins when they realize they need to travel.
At the awareness stage, the customer will conduct online research on airlines and routes to their destinations. They may come across the airline via social media channels, advertisements, or even referrals from friends.
Once they list all the airline brands, the customer will consider the available flights and decide which best fits their needs.
On the other side, airlines try to upsell additional services to appeal to customers. Therefore, customers may consider airlines that upsell services such as priority onboarding or upgraded seats.
Depending on their spending limits or airlines with better offerings, customers will compare the flight options that best suit their budget. They abandon tickets outside their means.
The decision stage ends when the customers purchase a ticket and receive an onboarding pass, travel information, and guides via email.
Who is involved in a digital customer journey?
A digital customer journey is a process a user (potential customer) goes through when interacting with a brand.
What are the four types of digital users?
The four types of digital users are explorers, socializers, achievers, and listeners.
Which department is responsible for the customer journey?
Sales and marketing departments play a vital role in optimizing a customer journey map.
Get started today
Go from raw data to valuable insights with a flexible research platform
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 January 2023
Last updated: 20 March 2024
Last updated: 26 March 2024
Last updated: 24 June 2023
Last updated: 29 May 2023
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 14 November 2023
Last updated: 3 April 2024
Last updated: 21 June 2023
Last updated: 19 November 2023
Last updated: 6 April 2023
Last updated: 31 July 2023
Last updated: 16 March 2024
Last updated: 22 June 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, log in or sign up.
Get started for free

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A customer journey map helps you gain a better understanding of your customers so you can spot and avoid potential concerns, make better business decisions and improve customer retention. The map ...
Every customer journey will be different, after all, so getting to grips with the nuances of each customer journey stage is key to removing obstacles from in front of your potential and existing customers' feet. Free Course: Customer Journey Management & Improvement.
Customer Support Blueprint Template. Each of these templates can help organizations gain new insights on their customers and help make improvements to product, marketing, and customer support processes. Download them today to start working on your customer journey map. 2. B2B Customer Journey Map Example.
Breaking down the customer journey, phase by phase, aligning each step with a goal, and restructuring your touchpoints accordingly are essential steps for maximizing customer success. Here are a few more benefits to gain from customer journey mapping. 1. You can refocus your company with an inbound perspective.
The customer journey is a series of steps — starting with brand awareness before a person is even a customer — that leads to a purchase and eventual customer loyalty. ... Likewise, that same customer will have different pain points when calling customer service after buying a particular rod.
The customer journey has seven stages. Each one is linked to some type of contact between the customer and your touchpoints. Direct contact typically occurs before a customer makes a purchase, while the customer is making a purchase, and after the customer makes a purchase. Now that we've covered how customers are likely to come into contact ...
Best Practices for an Efficient Customer Journey Stages. 1. Establish a Good First Impression. The first impression is the most important one. That's why it's so important to establish a good one from the very start—especially in the awareness and consideration stages. 2.
This way, you double-check and confirm your findings for a more complete picture. A hands-on approach ensures your customer journey map reflects the real-world experience and equips you to take targeted actions to improve the overall customer journey. 7. Make changes and find solutions. So your map is complete.
1. Define your purpose. The first step to creating a successful customer journey map is to define your product's vision or purpose. Without a clear purpose, your actions will be misguided and you won't know what you want users to achieve during their journey on your website, product page, or web app.
What stands out about this journey map template is that it has a space for describing the specific stage of the customer, which you can also use to write associated actions. There's also a star rating row that can help sum up the customer experience at each stage. 6. Business Software Customer Journey Map Template.
Here's our beginner customer journey mapping framework to help you create your first complete map in 2 and ½ working days: Day 1: preliminary customer journey mapping work. Day 2: prep and run your customer journey mapping workshop. Final ½ day: wrap up and share your results.
It's important to remember that each customer journey is unique and people may go through the phases at different speeds. In B2B sales (business-to-business sales) in particular, the buying journey is also often non-linear, with customers dipping in and out of journey phases as they make a buying decision.
The customer journey is the sum of all the interactions a customer has with a brand before, during and after a purchase. A smooth, effortless customer journey can ensure a prospect converts into a customer in the quickest time possible. Brands need to factor in consumer needs and behavioral patterns when mapping out customer journeys to deliver ...
There are many different types of customer journey maps. We'll take you through four to get started: current state, future state, a day in the life, and empathy maps. We'll break down each of them and explain what they can do for your business. Current state. This customer journey map focuses on your business as it is today.
A customer journey is whatever interaction a consumer has with your company. Technically-referred as a sales funnel, it's often represented visually as a map, or an upside-down triangle. Today's customers are often aware of a brand, its products and services before they're ready click "buy". Every interaction a customer has with your company — be it online, over the phone, via social media ...
In this piece, the author offers four strategies to ensure simplicity is baked into every aspect of the customer's journey: identify and communicate what simplicity means to your organization ...
A customer journey map is often synonymous with a user flow diagram or buyer journey map. However, each journey gives unique insights and needs different plans. Customer Journey. The customer journey, or lifecycle, outlines the stages a customer goes through with a business. This journey can vary across organizations but includes five key steps: 1.
The nature of the customer journey is different for SaaS, B2B, and B2C companies. A B2B company's interactions with prospects might include in-person conferences, while a SaaS company's touchpoints will be mostly digital. Companies that sell to consumers will need to think through individual people's experiences in a way that B2B companies don't.
Customer journey mapping (also called user journey mapping) is the process of creating a customer journey map, a visual story of your customers' interactions with your brand. This exercise helps businesses step into their customer's shoes and see their business from the customer's perspective. It allows you to gain insights into common ...
Spotify. Audible. Apple Podcasts. Google Podcasts. Amazon Music. 4. Retention stage. Your customer's journey doesn't end with a sale, or at least it doesn't need to. The old marketing maxim suggests that it costs five times more to obtain a new customer than to retain an old one.
Awareness stage: The awareness stage of the journey is also identical to phase #2, "Discovery," just with a different name. Customer Journey Map: Also called a customer journey roadmap, this is an illustration of each of your customer journey phases. This chart can help train and educate the members of your team to help them understand how a ...
Touchpoint four: A customer portal that allows customers to easily check out and see their order status. Touchpoint five: Self-service options such as knowledge bases and product how-tos. Touch point six: An easy-to-find customer service portal or phone number that allows them to get in touch.
Step 1: Define customer touchpoints. Identify all customer interactions, from ads to website visits, forming the core of your user journey map, illustrating the path from awareness to purchase and beyond. Step 2: Create customer buyer personas. Develop fictional representations of your target audience, considering demographics and behaviors.
With a digital customer journey, you have stronger control over your marketing campaigns than the traditional customer journey. Consideration: The evaluation phase This is the stage where customers have done enough research and are now evaluating the different brands and their offers.