The customer journey — definition, stages, and benefits

Businesses need to understand their customers to increase engagement, sales, and retention. But building an understanding with your customers isn’t easy.
The customer journey is the road a person takes to convert, but this journey isn’t always obvious to business owners. Understanding every step of that journey is key to business success. After reading this article, you’ll understand the customer journey better and how to use it to improve the customer experience while achieving your business goals.
This post will discuss:
- What a customer journey is

Customer journey stages
Benefits of knowing the customer journey.
- What a customer journey map is
How to create a customer journey map
Use the customer journey map to optimize the customer experience, what is a customer journey.
The customer journey is a series of steps — starting with brand awareness before a person is even a customer — that leads to a purchase and eventual customer loyalty. Businesses use the customer journey to better understand their customers’ experience, with the goal of optimizing that experience at every touchpoint.
Giving customers a positive customer experience is important for getting customers to trust a business, so optimizing the customer journey has never mattered more. By mastering the customer journey, you can design customer experiences that will lead to better customer relationships, loyalty, and long-term retention .
Customer journey vs. the buyer journey
The stages of the customer’s journey are different from the stages of the buyer’s journey. The buyer’s journey follows the customer experience from initial awareness of a brand to buying a product. The customer journey extends beyond the purchase and follows how customers interact with your product and how they share it with others.
Every lead goes through several stages to become a loyal customer. The better this experience is for customers at each stage, the more likely your leads are to stick around.
Ensure that your marketing, sales, and customer service teams optimize for these five stages of the customer journey:

1. Awareness
In the awareness phase, your target audience is just becoming aware of your brand and products. They need information or a solution to a problem, so they search for that information via social media and search engines.
For example, if someone searches on Google for pens for left-handed people, their customer journey begins when they’re first aware of your brand’s left-handed pen.
At this stage, potential customers learn about your business via web content, social media, influencers, and even their friends and family. However, this isn’t the time for hard sells. Customers are simply gathering information at this stage, so you should focus first on answering their questions and building trust.
2. Consideration
In the consideration phase, customers begin to consider your brand as a solution to their problem. They’re comparing your products to other businesses and alternative solutions, so you need to give these shoppers a reason to stick around.
Consideration-stage customers want to see product features that lean heavily toward solving problems and content that doesn’t necessarily push a sale. At this stage, businesses need to position their solution as a better alternative. For example, a nutrition coaching app might create content explaining the differences between using the app and working with an in-person nutritionist — while subtly promoting the benefits of choosing the app.
3. Purchase
The purchase stage is also called the decision stage because at this stage customers are ready to make a buying decision. Keep in mind that their decision might be to go with a competing solution, so purchase-stage buyers won’t always convert to your brand.
As a business, it’s your job to persuade shoppers at this stage to buy from you. Provide information on pricing, share comparison guides to showcase why you’re the superior option, and set up abandoned cart email sequences.
4. Retention
The customer journey doesn’t end once a shopper makes their first purchase. Once you’ve converted a customer, you need to focus on keeping them around and driving repeat business. Sourcing new customers is often more expensive than retaining existing clients, so this strategy can help you cut down on marketing costs and increase profits.
The key to the retention stage is to maintain positive, engaging relationships between your brand and its customers. Try strategies like regular email outreach, coupons and sales, or exclusive communities to encourage customer loyalty.
5. Advocacy
In the advocacy stage, customers are so delighted with your products and services that they spread the word to their friends and family. This goes a step beyond retention because the customer is actively encouraging other people to make purchases.
Customer journeys don’t have a distinct end because brands should always aim to please even their most loyal customers. In the advocacy stage of the customer journey, you can offer referral bonuses, loyalty programs, and special deals for your most active customers to encourage further advocacy.
Being aware of the customer journey helps shed more light on your target audience’s expectations and needs. In fact, 80% of companies compete primarily on customer experience. This means optimizing the customer journey will not only encourage your current customers to remain loyal but will also make you more competitive in acquiring new business.
More specifically, acknowledging the customer journey can help you:

- Understand customer behavior. Classifying every action your customers take will help you figure out why they do what they do. When you understand a shopper’s “why,” you’re better positioned to support their needs.
- Identify touchpoints to reach the customer. Many businesses invest in multichannel marketing, but not all of these touchpoints are valuable. By focusing on the customer journey, you’ll learn which of these channels are the most effective for generating sales. This helps businesses save time and money by focusing on only the most effective channels.
- Analyze the stumbling blocks in products or services. If leads frequently bail before buying, that could be a sign that something is wrong with your product or buying experience. Being conscious of the customer journey can help you fix issues with your products or services before they become a more expensive problem.
- Support your marketing efforts. Marketing requires a deep familiarity with your target audience. Documenting the customer journey makes it easier for your marketing team to meet shoppers’ expectations and solve their pain points.
- Increase customer engagement. Seeing the customer journey helps your business target the most relevant audience for your product or service. Plus, it improves the customer experience and increases engagement. In fact, 29.6% of customers will refuse to embrace branded digital channels if they have a poor experience, so increasing positive customer touchpoints has never been more important.
- Achieve more conversions. Mapping your customers’ journey can help you increase conversions by tailoring and personalizing your approach and messages to give your audience exactly what they want.
- Generate more ROI. You need to see a tangible return on your marketing efforts. Fortunately, investing in the customer journey improves ROI across the board. For example, brands with a good customer experience can increase revenue by 2–7% .
- Improve customer satisfaction and loyalty. Today, 94% of customers say a positive experience motivates them to make future purchases. Optimizing the customer journey helps you meet shopper expectations, which increases satisfaction and loyalty.

What is a customer journey map?
A customer journey map is a visual representation of every step your customer takes from being a lead to eventually becoming an advocate for your brand. The goal of customer journey mapping is to simplify the complex process of how customers interact with your brand at every stage of their journey.
Businesses shouldn’t use a rigid, one-size-fits-all customer journey map. Instead, they should plan flexible, individual types of customer journeys — whether they’re based on a certain demographic or on individual customer personas. To design the most effective customer journey map, your brand needs to understand a customer’s:
- Actions. Learn which actions your customer takes at every stage. Look for common patterns. For example, you might see that consideration-stage shoppers commonly look for reviews.
- Motivations. Customer intent matters. A person’s motivations change at every stage of the customer journey, and your map needs to account for that. Include visual representation of the shopper’s motivations at each stage. At the awareness stage, their motivation might be to gather information to solve their problem. At the purchase stage, it might be to get the lowest price possible.
- Questions. Brands can take customers’ common questions at every stage of the customer journey and reverse-engineer them into useful content. For example, shoppers at the consideration stage might ask, “What’s the difference between a DIY car wash and hiring a professional detailer?” You can offer content that answers their question while subtly promoting your car detailing business.
- Pain points. Everybody has a problem that they’re trying to solve, whether by just gathering intel or by purchasing products. Recognizing your leads’ pain points will help you craft proactive, helpful marketing campaigns that solve their biggest problems.
Customer journey touchpoints
Every stage of the customer journey should also include touchpoints. Customer touchpoints are the series of interactions with your brand — such as an ad on Facebook, an email, or a website chatbot — that occur at the various stages of the customer journey across multiple channels. A customer’s actions, motivations, questions, and pain points will differ at each stage and at each touchpoint.
For example, a customer searching for a fishing rod and reading posts about how they’re made will have very different motivations and questions from when later comparing specs and trying to stay within budget. Likewise, that same customer will have different pain points when calling customer service after buying a particular rod.

It might sound like more work, but mapping the entire customer journey helps businesses create a better customer experience throughout the entire lifecycle of a customer’s interaction with your brand.
Before jumping into the steps of how to create the customer journey map, first be clear that your customer journey map needs to illustrate the following:
- Customer journey stages. Ensure that your customer journey map includes every stage of the customer journey. Don’t just focus on the stages approaching the purchase — focus on the retention and advocacy stages as well.
- Touchpoints. Log the most common touchpoints customers have at every stage. For example, awareness-stage touchpoints might include your blog, social media, or search engines. Consideration-stage touchpoints could include reviews or demo videos on YouTube. You don’t need to list all potential touchpoints. Only list the most common or relevant touchpoints at each stage.
- The full customer experience. Customers’ actions, motivations, questions, and pain points will change at every stage — and every touchpoint — during the customer journey. Ensure your customer journey map touches on the full experience for each touchpoint.
- Your brand’s solutions. Finally, the customer journey map needs to include a branded solution for each stage and touchpoint. This doesn’t necessarily mean paid products. For example, awareness-stage buyers aren’t ready to make a purchase, so your brand’s solution at this stage might be a piece of gated content. With these necessary elements in mind, creating an effective customer journey map is a simple three-step process.
1. Create buyer personas
A buyer persona is a fictitious representation of your target audience. It’s a helpful internal tool that businesses use to better understand their audience’s background, assumptions, pain points, and needs. Each persona differs in terms of actions, motivations, questions, and pain points, which is why businesses need to create buyer personas before they map the customer journey.
To create a buyer persona, you will need to:
- Gather and analyze customer data. Collect information on your customers through analytics, surveys, and market research.
- Segment customers into specific buying groups. Categorize customers into buying groups based on shared characteristics — such as demographics or location. This will give you multiple customer segments to choose from.
- Build the personas. Select the segment you want to target and build a persona for that segment. At a minimum, the buyer persona needs to define the customers’ basic traits, such as their personal background, as well as their motivations and pain points.

For example, ClearVoice created a buyer persona called “John The Marketing Manager.” The in-depth persona details the target customer’s pain points, pet peeves, and potential reactions to help ClearVoice marketers create more customer-focused experiences.
2. List the touchpoints at each customer journey stage
Now that you’ve created your buyer personas, you need to sketch out each of the five stages of the customer journey and then list all of the potential touchpoints each buyer persona has with your brand at every one of these five stages. This includes listing the most common marketing channels where customers can interact with you. Remember, touchpoints differ by stage, so it’s critical to list which touchpoints happen at every stage so you can optimize your approach for every buyer persona.
Every customer’s experience is different, but these touchpoints most commonly line up with each stage of the customer journey:
- Awareness. Advertising, social media, company blog, referrals from friends and family, how-to videos, streaming ads, and brand activation events.
- Consideration. Email, sales calls, SMS, landing pages, and reviews.
- Purchase. Live chat, chatbots, cart abandonment emails, retargeting ads, and product print inserts.
- Retention. Thank you emails, product walkthroughs, sales follow-ups, and online communities.
- Advocacy. Surveys, loyalty programs, and in-person events.
Leave no stone unturned. Logging the most relevant touchpoints at each stage eliminates blind spots and ensures your brand is there for its customers, wherever they choose to connect with you.
3. Map the customer experience at each touchpoint
Now that you’ve defined each touchpoint at every stage of the customer journey, it’s time to detail the exact experience you need to create for each touchpoint. Every touchpoint needs to consider the customer’s:
- Actions. Describe how the customer got to this touchpoint and what they’re going to do now that they’re here.
- Motivations. Specify how the customer feels at this moment. Are they frustrated, confused, curious, or excited? Explain why they feel this way.
- Questions. Every customer has questions. Anticipate the questions someone at this stage and touchpoint would have — and how your brand can answer those questions.
- Pain points. Define the problem the customer has — and how you can solve that problem at this stage. For example, imagine you sell women’s dress shoes. You’re focusing on the buyer persona of a 36-year-old Canadian woman who works in human resources. Her touchpoints might include clicking on your Facebook ad, exploring your online shop, but then abandoning her cart. After receiving a coupon from you, she finally buys. Later, she decides to exchange the shoes for a different color. After the exchange, she leaves a review. Note how she acts at each of these touchpoints and detail her likely pain points, motivations, and questions, for each scenario. Note on the map where you intend to respond to the customer’s motivations and pain points with your brand’s solutions. If you can create custom-tailored solutions for every stage of the funnel, that’s even better.
A positive customer experience is the direct result of offering customers personalized, relevant, or meaningful content and other brand interactions. By mapping your customers’ motivations and pain points with your brand’s solutions, you’ll find opportunities to improve the customer experience. When you truly address their deepest needs, you’ll increase engagement and generate more positive reviews.
Follow these strategies to improve the customer experience with your customer journey map:
- Prioritize objectives. Identify the stages of the customer journey where your brand has the strongest presence and take advantage of those points. For example, if leads at the consideration stage frequently subscribe to your YouTube channel, that gives you more opportunities to connect with loyal followers.
- Use an omnichannel approach to engage customers. Omnichannel marketing allows businesses to gather information and create a more holistic view of the customer journey. This allows you to personalize the customer experience on another level entirely. Use an omnichannel analytics solution that allows you to capture and analyze the true cross-channel experience.
- Personalize interactions at every stage. The goal of mapping the customer journey is to create more personalized, helpful experiences for your audience at every stage and touchpoint. For example, with the right data you can personalize the retail shopping experience and customer’s website experience.
- Cultivate a mutually trusting relationship. When consumer trust is low, brands have to work even harder to earn their customers’ trust. Back up your marketing promises with good customer service, personalized incentives, and loyalty programs.
Getting started with customer journeys
Customer journeys are complicated in an omnichannel environment, but mapping these journeys can help businesses better understand their customers. Customer journey maps help you deliver the exact experience your customers expect from your business while increasing engagement and sales.
When you’re ready to get started, trace the interactions your customers have at each stage of their journey with your brand. Adobe Customer Journey Analytics — a service built on Adobe Experience Platform — can break down, filter, and query years’ worth of data and combine it from every channel into a single interface. Real-time, omnichannel analysis and visualization let companies make better decisions with a holistic view of their business and the context behind every customer action.
Learn more about Customer Journey Analytics by watching the overview video .
https://business.adobe.com/blog/perspectives/introducing-adobes-customer-journey-maturity-model
https://business.adobe.com/blog/how-to/create-customer-journey-maps
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/what-is-customer-journey-map
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Employee Exit Interviews
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Market Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- Customer Journey Mapping
- Customer Journey Stages
See how XM for Customer Frontlines works
The complete guide to customer journey stages.
12 min read If you want to turn a potential customer into a lifetime one, you’ll need to get to know every step of the entire customer journey. Here’s why the secret to customer retention lies in knowing how to fine-tune your sales funnel…
What is the customer journey?
What do we actually mean when we talk about the customer journey? Well, the simplest way to think about it is by comparing it to any other journey: a destination in mind, a starting point, and steps to take along the way.
In this case, the destination is not only to make a purchase but to have a great experience with your product or service – sometimes by interacting with aftersale customer support channels – and become a loyal customer who buys again.
And, just like how you can’t arrive at your vacation resort before you’ve done you’ve found out about it, the customer journey starts with steps to do with discovery, research, understanding, and comparison, before moving on to the buying process.
“Maximizing satisfaction with customer journeys has the potential not only to increase customer satisfaction by 20% but also lift revenue up by 15% while lowering the cost of serving customers by as much as 20%”
– McKinsey, The Three Cs of Customer Satisfaction
In short, the customer journey is the path taken by your target audience toward becoming loyal customers. So it’s really important to understand – both in terms of what each step entails and how you can improve each one to provide a maximally impressive and enjoyable experience.
Every customer journey will be different, after all, so getting to grips with the nuances of each customer journey stage is key to removing obstacles from in front of your potential and existing customers’ feet.
Free Course: Customer Journey Management & Improvement
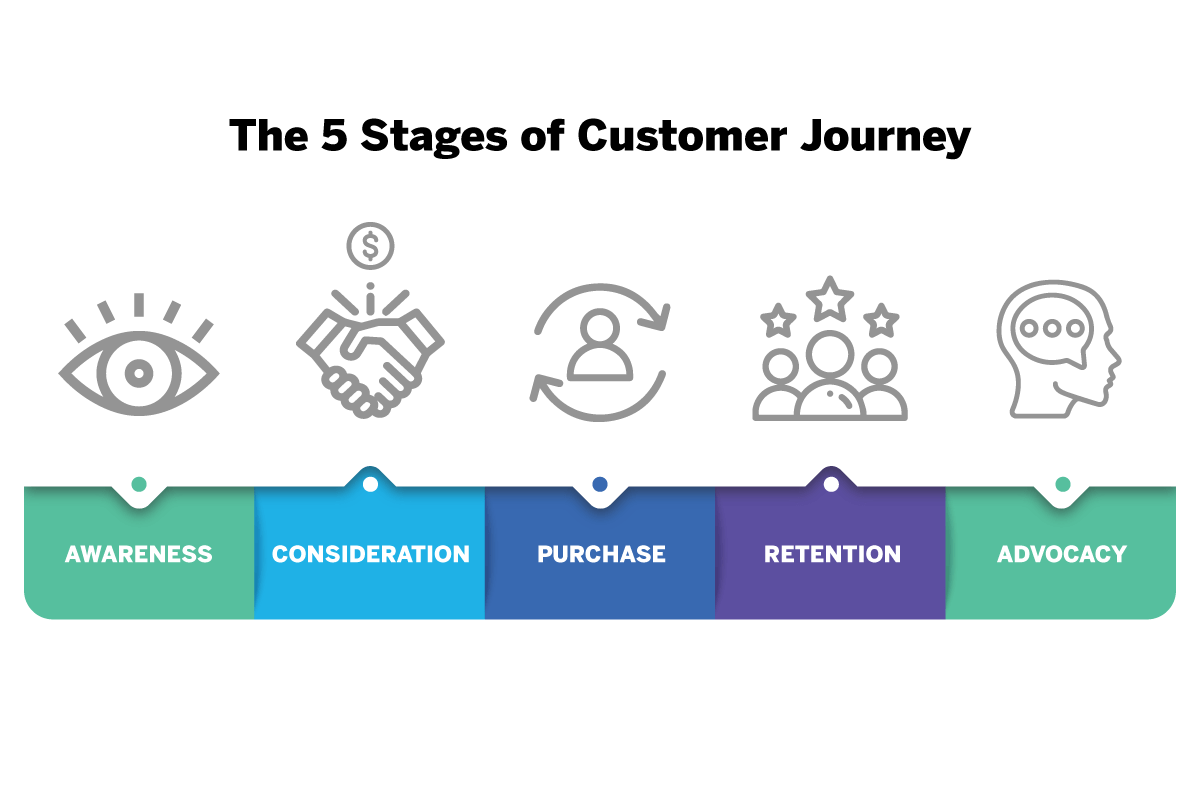
What are the essential customer journey stages?
While many companies will put their own spin on the exact naming of the customer journey stages, the most widely-recognized naming convention is as follows:
- Consideration
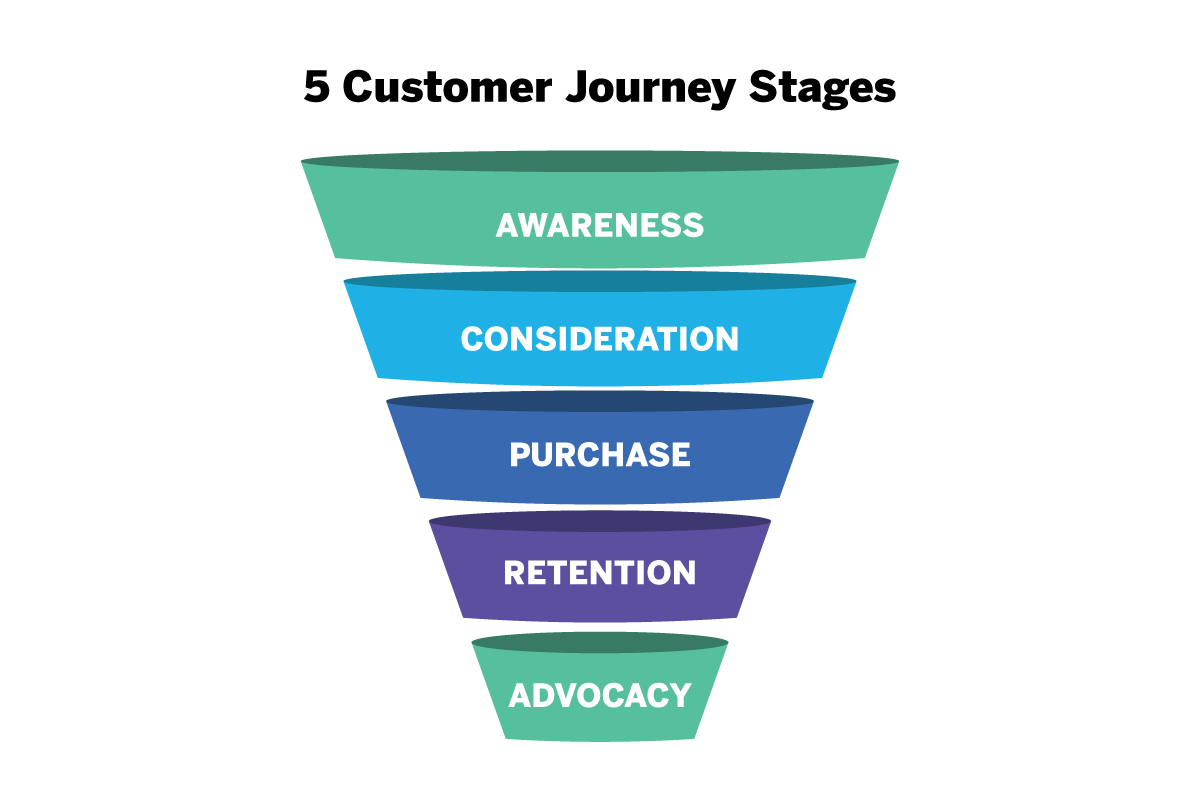
These steps are often then sub-categorized into three parts:
- Sale/Purchase
It’s important to understand every part of the puzzle, so let’s look at each sub-category and stage in turn, from the awareness and consideration stage, right through to advocacy:
Customer journey: Pre-sale
In the pre-sale phase, potential customers learn about products, evaluate their needs, make comparisons, and soak up information.
Awareness stage
In the awareness stage, your potential customer becomes aware of a company, product, or service. This might be passive – in that they’re served an ad online, on TV, or when out and about – or active in that they have a need and are searching for a solution. For example, if a customer needs car insurance, they’ll begin searching for providers.
Consideration stage
In the consideration stage, the customer has been made aware of several possible solutions for their particular need and starts doing research to compare them. That might mean looking at reviews or what others are saying on social media, as well as absorbing info on product specs and features on companies’ own channels. They’re receptive to information that can help them make the best decision.
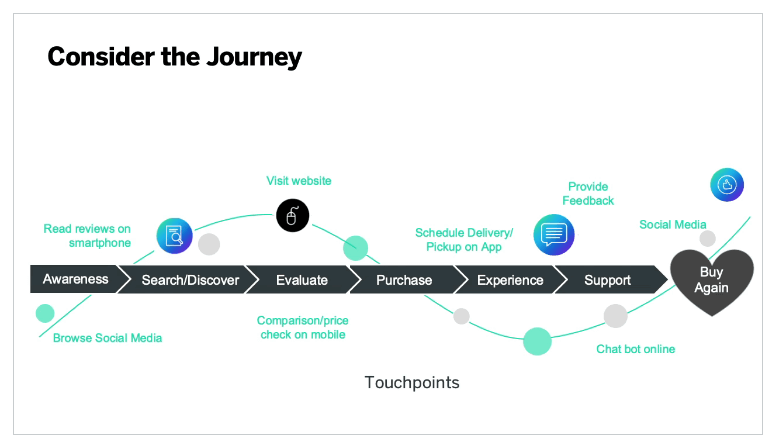
Customer journey: Sale
The sale phase is short but pivotal: it’s when the crucial decision on which option to go with has been made.
Decision stage
The customer has all the information they need on the various options available to them, and they make a purchase. This can be something that’s taken a long time to decide upon, like buying a new computer, or it can be as quick as quickly scouring the different kinds of bread available in the supermarket before picking the one they want.
Customer journey: Post-sale
Post-sale is a really important part of the puzzle because it’s where loyal customers , who come back time and again, are won or lost.
Retention stage
The retention stage of the customer journey is where you do whatever you can to help leave a lasting, positive impression on the customer, and entice them to purchase more. That means offering best-in-class customer support if they have any issues, but it also means being proactive with follow-up communications that offer personalized offers, information on new products, and rewards for loyalty.
Advocacy stage
If you nail the retention phase, you’ll have yourself a customer who not only wants to keep buying from you but will also advocate on your behalf. Here, the customer will become one of the most powerful tools in your arsenal, in that they’ll actively recommend you to their friends, family, followers, and colleagues.
What’s the difference between the customer journey and the buyer’s journey?
Great question; the two are similar, but not exactly the same. The buyer’s journey is a shorter, three-step process that describes the steps taken to make a purchase. So that’s awareness , consideration, and decision . That’s where things stop, however. The buyer’s journey doesn’t take into account the strategies you’ll use to keep the customer after a purchase has been made.
Why are the customer journey stages important?
The short answer? The customer journey is what shapes your entire business. It’s the method by which you attract and inform customers, how you convince them to purchase from you, and what you do to ensure they’re left feeling positive about every interaction.
Why this matters is that the journey is, in a way, cyclical. Customers who’ve had a smooth ride all the way through their individual journeys are more likely to stay with you, and that can have a massive effect on your operational metrics.
It’s up to five times more expensive to attract a new customer than it is to keep an existing customer, but even besides that: satisfied customers become loyal customers , and customer loyalty reduces churn at the same time as increasing profits .
So companies looking to really make an impact on the market need to think beyond simply attracting potential customers with impressive marketing, and more about the journey as a whole – where the retention and advocacy stages are equally important.
After all, 81% of US and UK consumers trust product advice from friends and family over brand messaging, and 59% of American consumers say that once they’re loyal to a brand, they’re loyal to it for life.
Importantly, to understand the customer journey as a whole is to understand its individual stages, recognize what works, and find things that could be improved to make it a more seamless experience. Because when you do that, you’ll be improving every part of your business proposition that matters.
How can you improve each customer journey stage?
Ok, so this whole customer journey thing is pretty important. Understanding the customer journey phases and how they relate to the overall customer experience is how you encourage customers to stick around and spread the news via word of mouth.
But how do you ensure every part of the journey is performing as it should? Here are some practical strategies to help each customer journey stage sing…
1. Perform customer journey mapping
A customer journey map takes all of the established customer journey stages and attempts to plot how actual target audience personas might travel along them. That means using a mix of data and intuition to map out a range of journeys that utilize a range of touch points along the way.
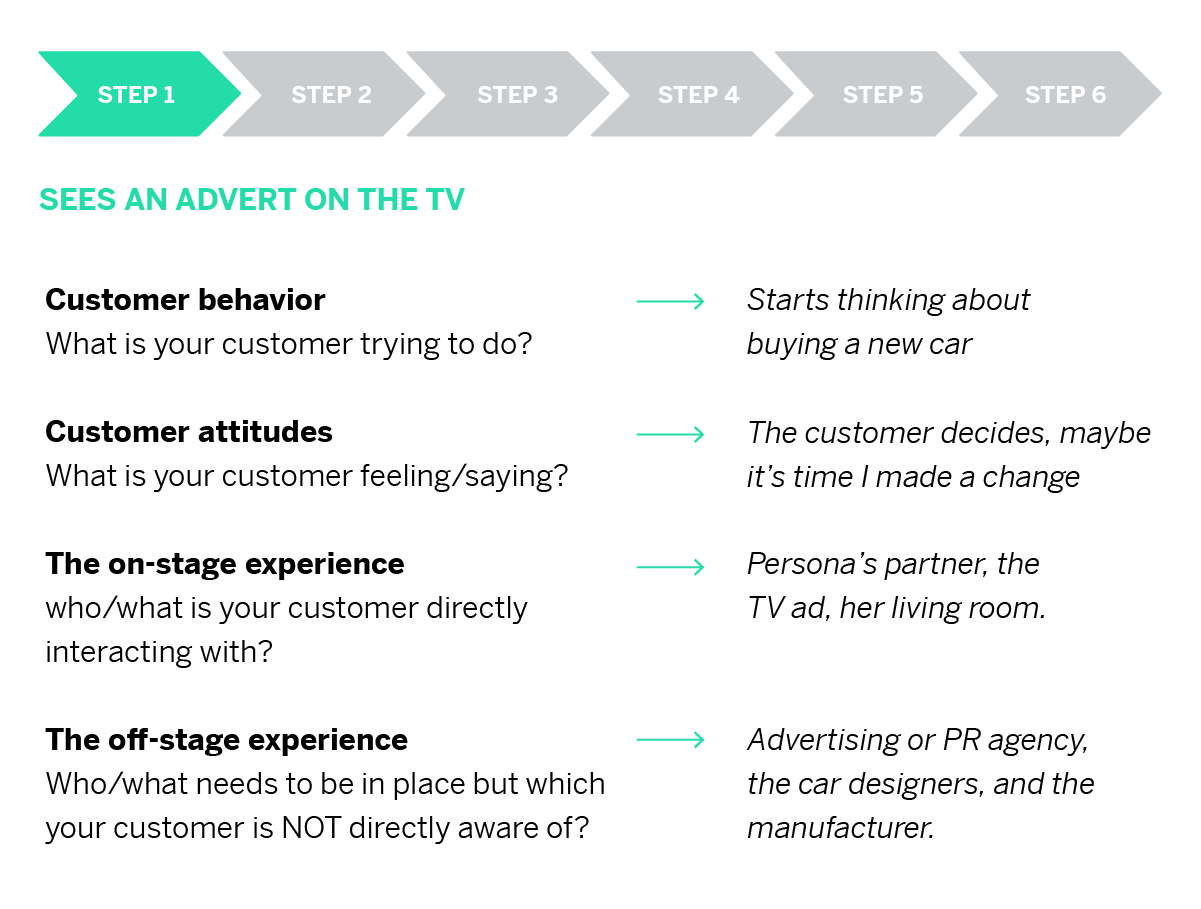
One customer journey map, for example, might start with a TV ad, then utilize social media and third-party review sites during the consideration stage, before purchasing online and then contacting customer support about you your delivery service. And then, finally, that customer may be served a discount code for a future purchase. That’s just one example.
Customer journey mapping is really about building a myriad of those journeys that are informed by everything you know about how customers interact with you – and then using those maps to discover weaker areas of the journey.
2. Listen like you mean it
The key to building better customer journeys is listening to what customers are saying. Getting feedbac k from every stage of the journey allows you to build a strong, all-encompassing view of what’s happening from those that are experiencing it.
Maybe there’s an issue with the customer sign-up experience, for example. Or maybe the number advertised to contact for a demo doesn’t work. Or maybe you have a customer service agent in need of coaching, who only makes the issue worse. By listening, you’ll understand your customers’ issues and be able to fix them at the source. That customer service agent, for example, may just feel disempowered and unsupported, and in need of the right tools to help them perform better. Fixing that will help to optimize a key stage in the customer journey.
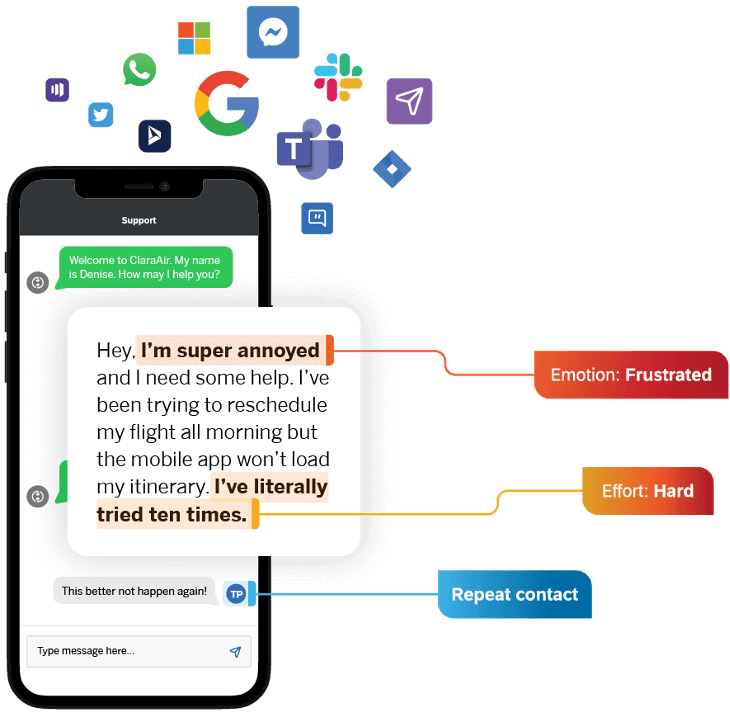
The key is to listen at every stage, and we can do that by employing the right technology at the right customer journey stages.
Customer surveys, for instance, can help you understand what went wrong from the people who’re willing to provide that feedback, but conversational analytics and AI solutions can automatically build insights out of all the structured and unstructured conversational data your customers are creating every time they reach out, or tweet, or leave a review on a third party website.
3. Get personal
The other side of the ‘listening’ equation is that it’s worth remembering that each and every customer’s journey is different – so treating them with a blanket approach won’t necessarily make anything better for them.
The trick instead is to use the tools available to you to build out a personalized view of every customer journey, customer journey stage, and customer engagemen t, and find common solutions.
Qualtrics Experience iD , for example, is an intelligent system that builds customer profiles that are unique to them and can identify through AI, natural language processing , and past interactions what’s not working – and what needs fixing.
On an individual basis, that will help turn each customer into an advocate. But as a whole, you’ll learn about experience gaps that are common to many journeys.
Listening to and understanding the customer experience at each customer journey stage is key to ensuring customers are satisfied and remain loyal on a huge scale.
It’s how you create 1:1 experiences, because, while an issue for one person might be an issue for many others, by fixing it quickly you can minimize the impact it might have on future customers who’re right at the start of their journey.
Free Course: Customer Journey Management Improvement
Related resources
Customer Journey
Buyer's Journey 16 min read
Customer journey analytics 13 min read, how to create a customer journey map 22 min read, b2b customer journey 13 min read, digital customer journey 13 min read, consumer decision journey 14 min read, customer journey orchestration 12 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
Learn / Guides / Customer journey mapping (CJM) guide
Back to guides
Customer journey mapping in 2 and 1/2 days
How to create a customer journey map that improves customer success.
Last updated
Reading time.
There’s a common saying that you can’t understand someone until you’ve walked a mile in their shoes—and that’s exactly what customer journey maps do: they help you put yourself in different customers’ shoes and understand your business from their point of view.
Why should you do it? How should you do it? Find the answers in this guide, which we wrote after interviewing 10+ customer journey experts who shared methodologies, dos and don’ts, and pro tips with us.
On this page:
What is a customer journey map?
How to create a customer journey map in 2 and ½ working days
4 benefits of customer journey mapping for your business
In later chapters, we dive deeper into customer journey analytics, workshops, and real-life examples.
Start mapping your customer journey
Hotjar lets you experience the customer journey through their eyes, so you can visualize what’s working and what needs improvement.
A customer journey map (CJM) is a visual representation of how customers interact with and experience your website, products, or business across multiple touchpoints.
By visualizing the actions, thoughts, and emotions your customers experience, a customer journey map helps you better understand them and identify the pain points they encounter. This is essential if you want to implement informed, customer-focused optimizations on your site.
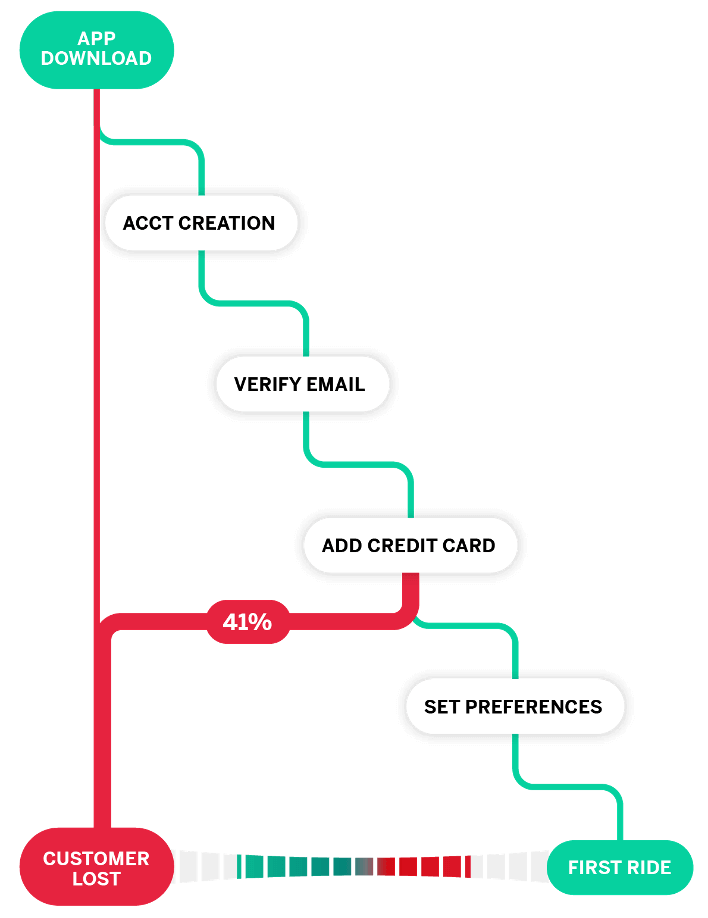
Mapping the customer journey: narrow vs. wide focus
A customer journey map can have a very narrow focus and only look at a few, specific steps of the customer experience or buyer’s journey (for example, a product-to-purchase flow on a website), or it can take into account all the touchpoints, online and offline, someone goes through before and after doing business with you.
Each type of customer journey map has its advantages:
A CJM with a narrow focus allows you to zero in on an issue and effectively problem-solve
A CJM with a wide focus gives you a broader, holistic understanding of how customers experience your business
Regardless of their focus, the best customer journey maps have one thing in common: they are created with real customer data that you collect and analyze . The insights are usually organized into a map (hence the name), diagram, or flowchart during a group workshop, which is later shared across the entire business so everyone gets a clear and comprehensive overview of a customer’s journey.
How to create your first customer journey map in 2 and ½ working days
The process of creating a customer journey map can be as long or short as you need. Depending on how many people and stakeholders you involve, how much data you collect and analyze, and how many touchpoints there are across the business, you could be looking at days or even weeks and months of work.
If you’re new to customer journey mapping, start from a narrower scope before moving on to mapping every single customer touchpoint .
Here’s our beginner customer journey mapping framework to help you create your first complete map in 2 and ½ working days:
Day 1: preliminary customer journey mapping work
Day 2: prep and run your customer journey mapping workshop.
Final ½ day: wrap up and share your results
Download your free customer journey map checklist (as seen below), to mark off your tasks as you complete them.
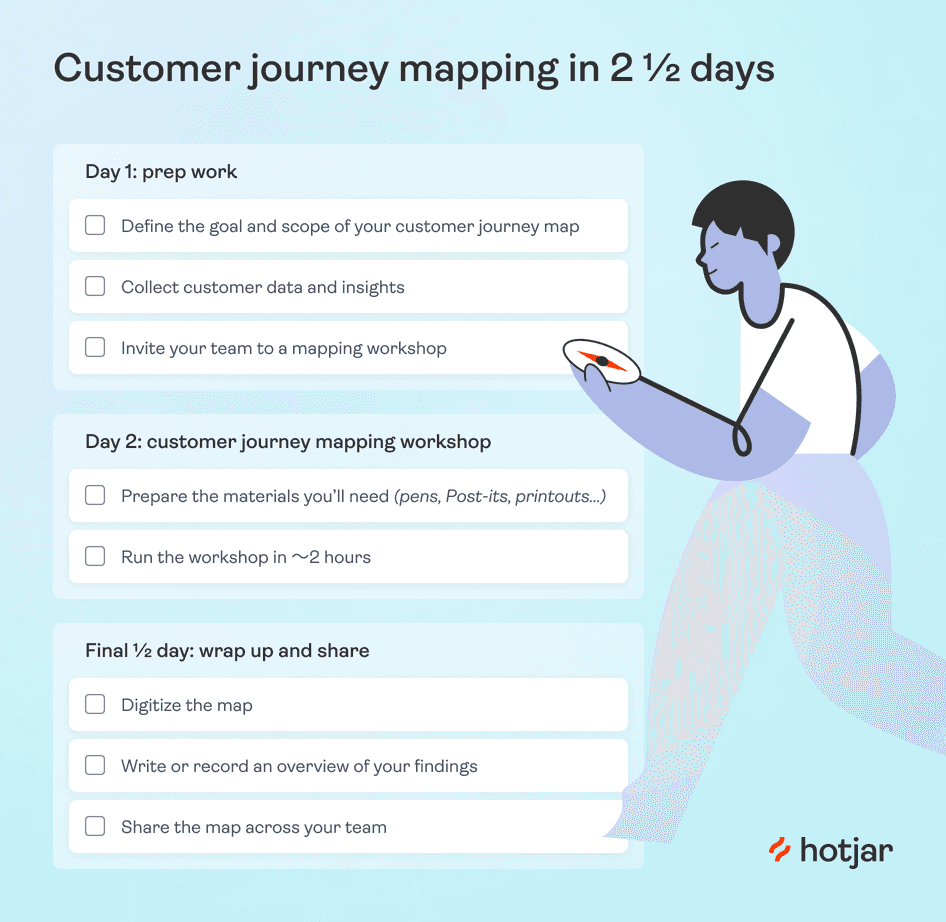
On your first day, you have three essential tasks:
Define the goal and scope of your CJM
Collect customer data and insights
Invite your team to a customer journey mapping workshop
Step 1: define the goal and scope of your CJM
Clarifying what part(s) of the journey you're looking at, and why, helps you stay focused throughout the mapping process.
If this is your first map, start from a known issue or problematic area of your website. Keep the scope small, and focus on anything you can break down into four or five steps. For example:
If you have a high drop-off on a pricing page with five calls-to-action, each of which takes users to a different page, that’s enough for a mappable journey
If your purchase flow is made of five self-contained pages, each of which loses you potential customers, that’s a good candidate for mapping
✅ The output: a one- or two-sentence description of what your map will cover, and why, you can use whenever you need to explain what the process is about. For example: this map looks at the purchase flow on our website, and helps us understand how customers go through each step and the issues or obstacles they encounter. The map starts after users click ‘proceed to checkout’ and ends when they reach the 'Thank You' page .
Step 2: collect customer data and insights
Once you identify your goal and scope, the bulk of your first day should be spent collecting data and insights you’ll analyze as part of your mapping process. Because your map is narrow in focus, don’t get distracted by wide-scale demographics or data points that are interesting and nice to know, but ultimately irrelevant.
Get your hands on as much of the following information as you can:
Metrics from traditional analytics tools (such as Google Analytics) that give you insight into what’s happening, across the pages and stages your customer journey map covers
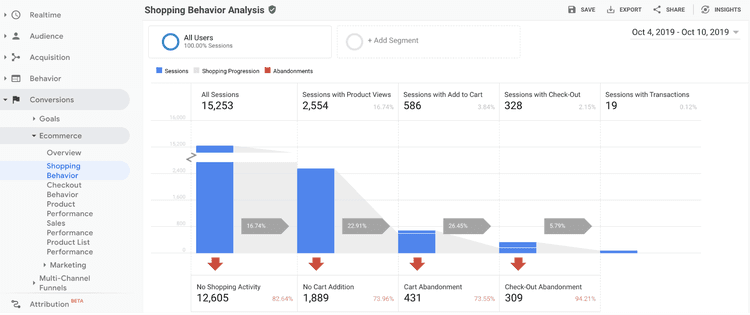
Data from analyzing your conversion ‘funnels’ , which record how many visitors end up at each stage of the user journey, so you can optimize those steps for potential customers and increase conversions
Behavior analytics data (from platforms like Hotjar) that show you how people interact with your site. For example, heatmaps give you an aggregate view of how users click, move and scroll on specific pages, and session recordings capture a user’s entire journey as they navigate your site
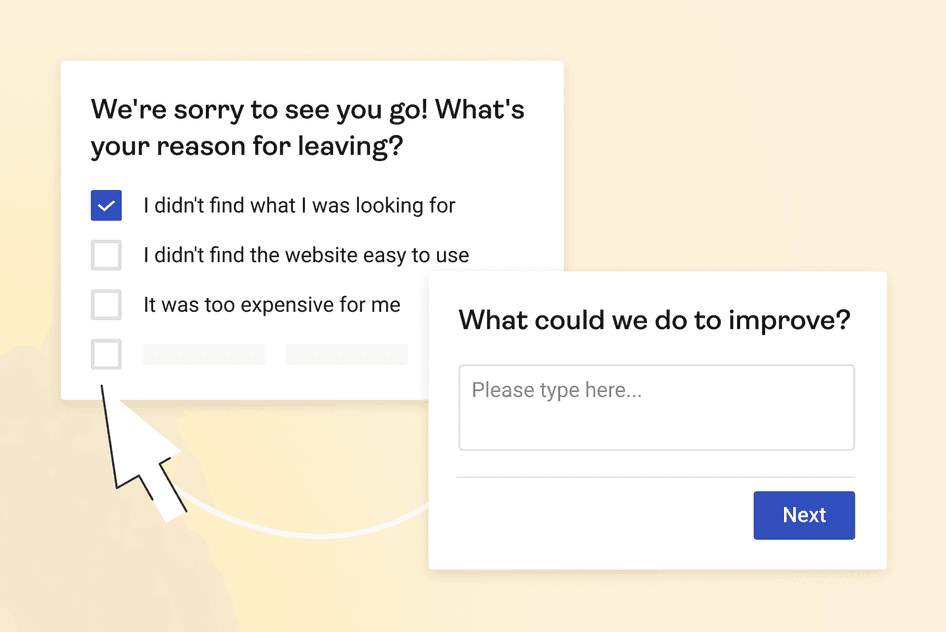
Quantitative and qualitative answers to on-site surveys relevant to the pages you’re going to investigate, as customer feedback will ultimately guide your roadmap of changes to make to improve the journey
Any demographic information about existing user and customer personas that helps you map the journey from the perspective of a real type of customer, rather than that of any hypothetical visitor, ensuring the journey makes sense for your target audience
Any relevant data from customer service chat logs, emails, or even anecdotal information from support, success, and sales teams about the issues customers usually experience
✅ The output: quantitative and qualitative data about your customers' interactions and their experiences across various touchpoints. For example, you’ll know how many people drop off at each individual stage, which page elements they interact with or ignore, and what stops them from converting.
💡Pro tip: as you read this guide, you may not yet have most of this data, particularly when it comes to heatmaps, recordings, and survey results. That’s ok.
Unless you’re running your CJM workshop in the next 12 hours, you have enough time to set up Hotjar on your website and start collecting insights right now. The platform helps you:
Learn where and why users drop off with Funnels
Visualize interactions on key pages with Heatmaps
Capture visitor sessions across your website with Recordings
Run on-site polls with Surveys
When the time comes for you to start your customer journey mapping process, this data will be invaluable.
Step 3: invite your team to a customer journey mapping workshop
In our experience, the most effective way to get buy-in is not to try and convince people after things are done—include them in the process from the start. So while you can easily create a customer journey map on your own, it won’t be nearly as powerful as one you create with team members from different areas of expertise .
For example, if you’re looking at the purchase flow, you need to work with:
Someone from the UX team, who knows about the usability of the flow and can advocate for design changes
Someone from dev or engineering, who knows how things work in the back end, and will be able to push forward any changes that result from the map
Someone from success or support, who has first-hand experience talking to customers and resolving any issues they experience
✅ The output: you’ve set a date, booked a meeting space, and invited a group of four to six participants to your customer journey mapping workshop.
💡Pro tip: for your first map, stay small. Keep it limited to four to six people, and no main stakeholders . This may be unpopular advice, especially since many guides out there mention the importance of having stakeholders present from the start.
However, when you’re not yet very familiar with the process, including too many people early on can discourage them from re-investing their time into future CJM tasks. At this stage, it’s more helpful to brainstorm with a small team, get feedback on how to improve, and iterate a few times. Once you have a firm handle on the process, then start looping in your stakeholders.
On workshop day, you’ll spend half your time prepping and the other half running the actual session.
Step 1: prepare all your materials
To run a smooth workshop, ensure you do the following:
Bring stationery: for an interactive workshop, you’ll need basic materials such as pens, different colored Post-its, masking tape, and large sheets of paper to hang on the wall
Collect and print out the data: use the data you collected on Day 1. It’s good to have digital copies on a laptop or tablet for everybody to access, but print-outs could be the better alternative as people can take notes and scribble on them.
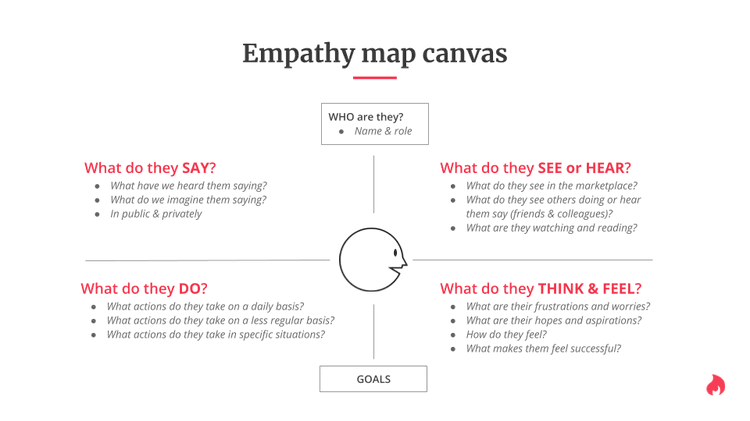
Print out an empathy map canvas for each participant: start the workshop with an empathy mapping exercise (more on this in Step 2). For this, hand each participant an empty empathy map canvas you can recreate from the template below.
Set up a customer journey map template on the wall: use a large sheet of paper to create a grid you'll stick to the wall and fill in as part of the workshop. On the horizontal axis, write the customer journey steps you identified during your Day 1 prep work; on the vertical axis, list the themes you want to analyze for each step. For example:
Actions your customers take
Questions they might have
Happy moments they experience
Pain points they experience
Tech limits they might encounter
Opportunities that arise
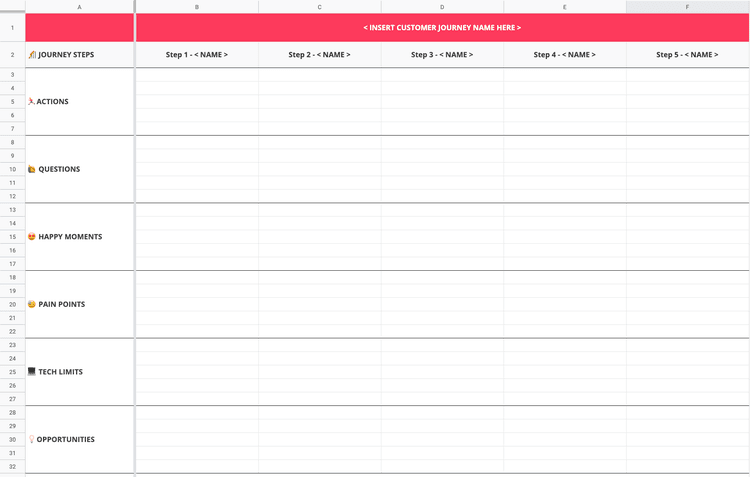
Step 2: run the workshop
This is the most interactive (and fun) part of the process. Follow the framework below to go from zero to a completed draft of a map in just under 2 hours .
Introduction [🕒 5–10 min]
Introduce yourself and your participants to one another
Using the one-two sentence description you defined on Day 1, explain the goal and scope of the workshop and the activities it will involve
Offer a quick summary of the customer persona you’ll be referring to throughout the session
Empathy mapping exercise [🕒 30 min]
Using the personas and data available, have each team member map their observations onto sticky notes and paste them on the relevant section of the empathy mapping canvas
Have all participants take turns presenting their empathy map
Facilitate group discussions where interesting points of agreement or disagreement appear
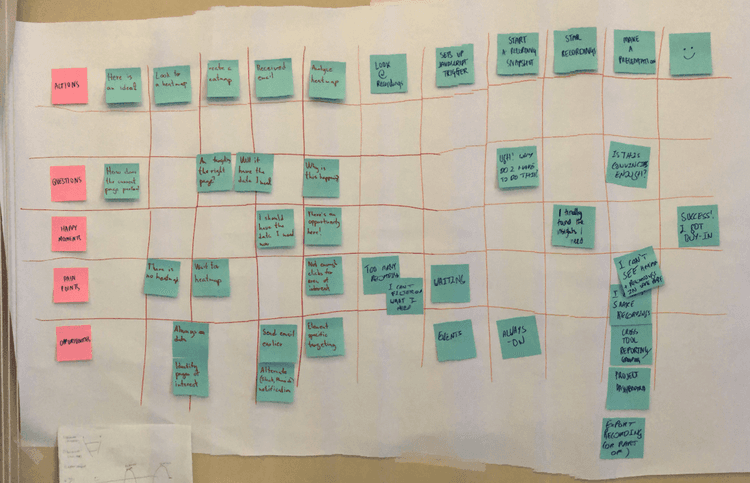
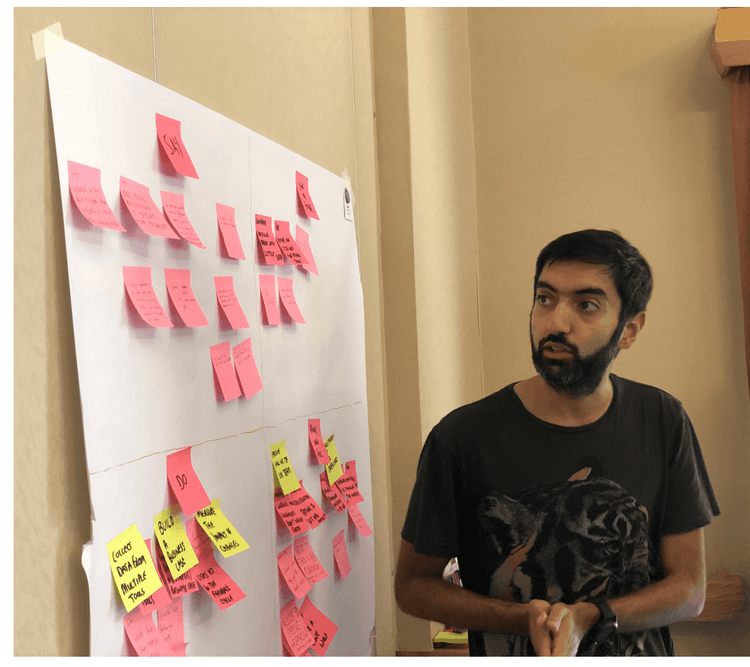
Customer journey mapping [🕒 60 min]
Using Post-its, ask each participant to fill in parts of the map grid with available information. Start by filling in the first row together, so everybody understands the process, then do each row individually (15–20 min). At the end of the process, you should have something like this:

Looking at the completed map, encourage your team to discuss and align on core observations (and take notes: they’ll come in handy on your final half day). At this point, customer pain points and opportunities should become evident for everybody involved. Having a cross-functional team means people will naturally start discussing what can, or cannot, immediately be done to address them (35–40 min).
Wrap up [🕒 5 min]
Congratulations! Your first customer journey map is complete. Finish the session by thanking your participants and letting them know the next steps.
Final half-day: wrap up and share
Once you’ve gone through the entire customer journey mapping workshop, the number one thing you want to avoid is for all this effort to go to waste. Instead of leaving the map hanging on the wall (or worse: taking it down, folding it, and forgetting about it), the final step is to wrap the process up and communicate the results to the larger team.
Digitize the map so you can easily update and share it with team members: it may be tempting to use dedicated software or invest time into a beautiful design, but for the first few iterations, it’s enough to add the map to your team’s existing workflows (for example, our team digitized our map and added it straight into Jira, where it’s easily accessible)
Offer a quick write-up or a 5-minute video introduction of the activity: re-use the description you came up with on Day 1, including who was involved and the top three outcomes
Clearly state the follow-up actions: if you’ve found obvious issues that need fixing, that’s a likely next step. If you’ve identified opportunities for change and improvement, you may want to validate these findings via customer interviews and usability testing.
4 benefits of customer journey mapping
In 2023, it’s almost a given that great customer experience (CX) provides any business or ecommerce site with a competitive advantage. But just how you’re supposed to deliver on the concept and create wow-worthy experiences is often left unsaid, implied, or glossed over.
Customer journey maps help you find answers to this ‘How?’ question, enabling you to:
Visualize customer pain points, motivations, and drivers
Create cross-team alignment around the business
Remove internal silos and clarify areas of ownership
Make improvements and convert more visitors into customers
We’ve done a lot of customer journey work here at Hotjar, so we know that the above is true—but don’t just take our word for it: all the people we interviewed for this guide confirmed the benefits of journey mapping. Let’s take a look at what they shared.
1. Visualize customer pain points, motivations, and drivers
It’s one thing to present your entire team with charts, graphs, and trends about your customers, and quite another to put the same team in front of ONE map that highlights what customers think, want, and do at each step of their journey.
I did my first customer journey map at MADE.COM within the first three months of joining the company. I was trying to map the journey to understand where the pain points were.
For example, people who want to buy a sofa from us will be coming back to the site 8+ times over several weeks before making a purchase. In that time, they may also visit a showroom. So now I look at that journey, at a customer’s motivation for going to the website versus a physical store, and I need to make sure that the experience in the showroom complements what they're doing on-site, and vice-versa, and that it all kind of comes together.
The map helps in seeing that journey progress right up to the time someone becomes a customer. And it also continues after: we see the next touchpoints and how we're looking to retain them as a customer, so that they come back and purchase again.
A customer journey map is particularly powerful when you incorporate empathy into it, bringing to light specific emotions that customers experience throughout the journey.

2. Create cross-team alignment around the business
The best, most effective customer journey maps are not the solo project of the user experience (UX) or marketing team (though they may originate there).
Customer journey maps are a quick, easy, and powerful way to help everybody in your business get a clearer understanding of how things work from a customers’ perspective and what the customers’ needs are—which is the first step in your quest towards creating a better experience for them.
Our first goal for preparing a customer journey map was to improve understanding customers across the company, so that every employee could understand the entire process our clients go through.
For example, people from the shipping department didn't know how the process works online; people from marketing didn't know how customers behave after filing a complaint. Everything seems obvious, but when we shared these details, we saw that a lot of people didn't know how the company itself works—this map made us realize that there were still gaps we needed to fill.

If we discover that customers have a pain point in a specific section of the map, different teams can look at the same section from several angles; customer support can communicate why something is not possible, and engineering can explain why it’s going to take X amount of effort to get it done. Especially in cross-functional teams where we all come from really different disciplines, I find these maps to be an incredible way for us all to speak the same language.
3. Remove internal silos and clarify areas of ownership
As a company grows in size and complexity, the lines of ownership occasionally become blurry. Without clarity, a customer might get bounced like a ping pong ball across Sales, Success, and Support departments—not great for the seamless and frictionless customer experience we all want to offer.
A central source of ‘truth’ in the form of a customer journey map that everybody can refer to helps clarify areas of ownership and handover points.
We were growing as a team, and we realized we needed to operationalize a lot of the processes that, before then, had just been manually communicated. We did it through a customer journey map. Our goal was to better understand where these hand-off points were and how to create a more seamless experience for our customers, because they were kind of being punted from team to team, from person to person—and often, it was really hard to keep tabs on exactly where the customer was in that entire journey.
4. Make improvements and convert more visitors into customers
A customer journey map will take your team from 'It appears that 30% of people leave the website at this stage' to 'Wow, people are leaving because the info is incomplete and the links are broken.' Once everyone is aligned on the roadblocks that need to be addressed, changes that have a positive impact on the customer experience and customer satisfaction will happen faster.
The customer journey map brings it all together: it doesn't matter who you've got in the room. If you’re doing a proper journey map, they always get enlightened in terms of ‘Oh, my word. I did not know the customer's actually experiencing this.’ And when I walk out of the session, we have often solved issues in the business. Accountability and responsibilities have been assigned, and I find that it just works well.

Shaheema (right) working on a customer journey map
Collect the right data to create an effective customer journey map
The secret of getting value from customer journey mapping is not just building the map itself: it's taking action on your findings. Having a list of changes to prioritize means you can also measure their effect once implemented, and keep improving your customers' experience.
This all starts with collecting customer-centric data—the sooner you begin, the more information you’ll have when the time comes to make a decision.
Start mapping your customer journey today
Hotjar lets you experience your customer’s journey through their eyes, so you can visualize what’s working and what needs improvement.
FAQs about customer journey mapping
How do i create a customer journey map.
To create a useful customer journey map, you first need to define your objectives, buyer personas, and the goals of your customers (direct customer feedback and market research will help you here). Then, identify all the distinct touchpoints the customer has with your product or service in chronological order, and visualize the completion of these steps in a map format.
What are the benefits of customer journey mapping?
Customer journey mapping provides different teams in your company with a simple, easily understandable visualization that captures your customers’ perspective and needs, and the steps they’ll take to successfully use your product or service.
Consider customer journey mapping if you want to accomplish a specific objective (like testing a new product’s purchase flow) or work towards a much broader goal (like increasing overall customer retention or customer loyalty).
What is the difference between a customer journey map and an experience map?
The main difference between an experience map and a customer journey map is that customer journey maps are geared specifically toward business goals and the successful use of a product or service, while experience maps visualize an individual’s journey and experience through the completion of any task or goal that may not be related to business.
- Deutschland
- Asia, Australia & New Zealand
- Europe, Middle East & Africa
- United States & Canada
- Latinoamérica
Customer journey mapping: The path to loyalty
A version of this tutorial originally appeared in the free Primer app .
In an ideal world, the journey people take to become loyal customers would be a straight shot down a highway: See your product. Buy your product. Use your product. Repeat.
In reality, this journey is often more like a sightseeing tour with stops, exploration, and discussion along the way—all moments when you need to convince people to pick your brand and stick with it instead of switching to a competitor.
Staying on top of all of these moments might seem overwhelming, but mapping your customer’s journey can help. It can give you and your team a greater understanding of how your customers are currently interacting and engaging with your brand, and also help illustrate how your products and services fit into their lives, schedules, goals, and aspirations.
Let’s take a look at five steps your team can take to start journey mapping.
1. Find the sweet spot where your customers’ goals and your own align
Before you start journey mapping, nail down your business goals. Any marketing and communication you deliver during the customer journey should be focused on helping your brand reach those goals.
However, it’s important to acknowledge that your customers’ goals might be different from yours. For example, let’s say your goal is to sell more sunglasses with new, improved lenses that have a better profit margin. Meanwhile, your customers’ top concern might be getting sunglasses that match their personal style. Lens protection could be their second or even third priority.
Consider how your marketing and communication strategies can help your customers reach their goals while also getting you closer to yours.
2. Identify all of the communication touchpoints in your customer’s journey
When do you traditionally communicate or engage with customers? Make a list of these moments and group them based on when they happen during the journey: pre-purchase, purchase, and post-purchase.
Now find communication touchpoints you may have missed. Track what actions and interactions between your brand and your customers happen just before and after each of the pre-purchase, purchase, and post-purchase stages.
For example, you might decide that a major moment in your purchase stage is when your customers are guided through your website to buy an item in their shopping cart. But you might notice other communication touchpoints right before that purchase moment, like your website confirming to customers that an item has been added to their shopping cart, then suggesting related products.
Looking for all these touchpoints can quickly bog your team down in a lot of details and micro-interactions. To avoid that, prioritize the moments that get you closer to achieving your business goals.
3. Recognize pain points and moments of delight
How might your customers feel at the pre-purchase, purchase, and post-purchase stages as they attempt to achieve their goals? For example, could your customers be happy that your website makes browsing easy, but frustrated at how confusing it is to purchase a product?
Find the moments where your customers might have negative experiences. Who on your team is involved in those touchpoints? Your web designers? Your marketing team? Your copywriters? Are there other team members who could collaborate and improve the situation?
Say a customer likes how your online ad describes your product. But when they go to your store, salespeople present the product differently. That’s an opportunity for your copywriters and salespeople to better align their language and sales pitches.
4. Experience the customer journey yourself
Imagining how your customers might feel during their journey is valuable, but actually experiencing it for yourself can uncover much-needed insights.
If your business is run online, open a browser and experience what it’s like to be your customer. Similarly, if you have a brick-and-mortar store, go into a location that sells your product. Afterwards, ask yourself about the main communication touchpoints you encountered. Did they work well? Did they help you complete your journey? What was missing?
And don’t forget about the competition. Become one of their customers and experience the journey they’ve created. Then ask yourself all of the same questions.
5. Visualize your customer journey map
Go beyond just writing down your customer journey and communication touchpoints, and actually create a visual map of them. This doesn’t need to be a polished, heavily-designed visualization. Simply write each of your touchpoints down on individual sticky notes or papers, then pin them in order to a wall.
By doing this exercise, you’re helping your team take a bird’s eye view of the entire customer journey. You can organize your thoughts and collaboratively brainstorm new ideas for changing or adding to your communication at these touchpoints.
Make sure to create hypotheses around why new communication touchpoints will improve the customer journey, then implement and test them. If your hypotheses are wrong, go back to your journey map, reassess, tweak, and improve.
Yes, the journey mapping process can be fairly intensive, but it can have a big impact on your business. That’s why it shouldn’t be just a one-time event. Customer tastes can shift, new technology can become available, and your brand itself might evolve. So it’s important to do journey mapping at least once a year and evaluate what communication touchpoints are still working and what needs to be revisited.
Others are viewing
Marketers who view this are also viewing
Make it personal: Using marketing personas and empathy in your marketing
How to win travelers in the age of assistance, how hyundai changed course to improve the customer journey, how people decide what to buy lies in the ‘messy middle’ of the purchase journey, the ai handbook: resources and tools for marketers, better together: why integrating data strategy, teams, and technology leads to marketing success, stuart hogg.
Stuart Hogg is a marketing consultant who has worked with a number of Fortune 500 brands. He created “Journey Mapping: Connect the Customer Dots” for the Primer app.
Others are viewing Looking for something else?
Complete login.
To explore this content and receive communications from Google, please sign in with an existing Google account.
You're visiting our United States & Canada website.
Based on your location, we recommend you check out this version of the page instead:
← Back to Articles
Oct 5, 2020
How To Create A Customer Journey Map
- Digital Strategy
It goes without saying that a cohesive customer journey is absolutely critical for success. These marketers understand how a customer or user journey map can streamline processes and provide customers with a consistent experience with a brand. Ideally, a customer journey map transforms the online customer journey into a visually accessible method for digital marketers to use to their advantage.
To streamline your customer experience and be consistently available to consumers throughout their online experience, read on to uncover how you can create a best-in-class customer journey map for your own brand.
What Is a Customer Journey Map?
A customer journey map is a “visual representation of every experience your customers have with you.” Throughout their experience with your brand, a customer will most likely engage or be reminded of your brand on multiple platforms, in varying ways. A customer journey map helps your brand deliver a streamlined narrative of a customer’s experience throughout the online sales funnel.
Although it may seem that the journey from first interaction through to a sale is quite simple, it is anything but. A customer is bombarded with countless advertisements, newsletters, and competitive content on a daily basis. This makes their journey with your brand complicated, and a well-rounded customer journey map is your solution to making that experience easier.
Customers can interact with your brand in countless ways in the modern digital landscape. Some examples include :
- Reading a branded blog post
- Accessing your website from search engine platform
- Following your brand on varying social media channels
By creating a clear visualization of every possible way a customer can interact and contact your brand, a customer journey map can help you keep customers engaged while you increase conversions and revenue.
Why Create a Customer Journey Map?
With so much of the journey taking place digitally, it’s vital that digital marketers understand exactly where customers are interacting with your brand while providing accessible, high-quality content on a regular basis.
With an effective customer journey map, digital marketers will gain a better understanding of how their customers interact with their business while accessing helpful insight into what channels are most effective for converting leads into prospects, and prospects into loyal customers.
Gone are the days when products were traditionally marketed by boasting specific features. Modern buyers are interested in the brand as a whole, how they personally engage with them, and most importantly, how the offering can solve a problem they are facing. A streamlined customer journey map will help clarify how digital marketers can most effectively provide prospects with this information and keep them engaged and dedicated to completing a purchase.
Get Started with the Customer Journey Map
Now that you understand what a customer journey map is and how it can take your digital marketing efforts to the next level, let’s jump into how to map out the online journey. Your customer’s journey is complex, so the job of the map is to make it as focused and simple as possible.
Step 1: Use your sales funnel to define the buying process
Ideally, your brand will already have an online sales funnel developed that demonstrates how leads move through your content and marketing strategies to eventually complete a purchase. This information will provide you with a guideline as to how many potential touchpoints a customer has with your brand and content, and how each interaction feeds into the next.
Step 2: Think like a customer
Regardless of the massive increase in customer data, it’s tough to truly think like a customer. Each prospect is a unique human with different needs, emotions, personalities, responsibilities, and so on. So how can you, as a digital marketer, understand how your customers are making choices to eventually reach the end of your sales funnel and purchase your product or service?
Although you won’t be able to fully predict a prospect’s next steps, you can align their goals with varying stages of your sales funnel, while moving through the process yourself. Track these steps as you go through a variety of touchpoints and combinations of choices. If you come across a section of your buying journey that doesn’t feel like a natural next step, take note, and optimize this step to make the customer journey more logical and straightforward.
If you really want to optimize your customer journey, review transcripts of support calls and emails to track where a purchase process went wrong and work to fix these issues before moving onto the next step.
Step 3: Develop the touchpoints of customer interaction
Simply stated, a touchpoint is any digital place at which a customer can access information about your brand or engage with your website. In turn, each touchpoint is also critical for interaction and conversion on the business end of things.
Many of these touchpoints will have been tracked in the second step of this process. However, now is the time to plot these touchpoints logically. For example, a customer “liking” a social media post counts as one touchpoint, while clicking through to a link from that social media post is another. Group these touchpoints into logical areas, such as “social media touchpoints” and “web page touchpoints.”
Step 4: Implement your customer journey map and conduct research
First things first, though: create a visually-appealing customer journey map that is accessible for all necessary team members. A graphic designer can help compile your findings and touchpoints in a visual sequence that is understandable, logical, and beautiful.
Now that you’ve identified each possible touchpoint, grouped them into logical areas sequences, and developed an accessible customer journey map, it’s time to implement your new findings and see how they work digitally.
Platforms like Google Analytics will be of immense help if you’re looking to see where buyers are dropping out of the customer journey on a regular basis. If you notice patterns such as a lack of click-throughs from newsletters or customer abandonment just before the purchase is completed, analyze these touchpoints and make necessary improvements.
Targeted prospects want their journey to be as simple as possible, so including too many touchpoints in their buying process may not keep them engaged the entire way through. While reviewing your customer journey map, make sure that the journey is easy enough to keep them taking the ideal logical steps while providing the personalized and educational content they need to stay engaged.
Step 5: Regularly optimize your customer journey map
Like most aspects of a digital marketing strategy, your online customer journey will change frequently as technology develops and new digital platforms are introduced into the buying cycle. By taking the time to regularly review how your customers are moving through your buying cycle, you can identify gaps and develop processes to streamline the customer experience.
According to a 2016 report, the Aberdeen Group’s Customer Journey Mapping: Lead the Way to Advocacy , organizations experienced a 16.8% decrease in the size of the sales cycle when a user journey map is developed, implemented, and maintained successfully. Although the process of creating a customer journey map can be a timely endeavor for digital marketers, it provides unparalleled value for both your brand and your customers.
Offering prospects a streamlined and enjoyable online experience will help to keep them engaged while you drive sales forward. When you understand your customers’ needs and preferences, you can increase your own productivity by focusing your digital marketing developments on the touchpoints that need most help. Enable yourself to create consistent customer experiences that align your digital marketing strategies with the high-quality digital content that your customers have come to expect from your best-in-class organization.
- Why User Experience is Key to Digital Marketing Success
- 5 Customer Lifecycle Mistakes to Avoid at All Costs
- 3 Ways Little Data Trumps Big Data For a Superior User Experience
- Walkthrough: Google Analytics with Cathal Melinn
Related Free Video Lessons
- Digital Marketing Strategy Creative Strategy
- Social Customer Service Contributor Incentivizing
- Social Customer Service Social Customer Service Models
- Digital Marketing Strategy Setting Objectives
Related Content
Ebooks: ebook: the key social media platforms - a complete marketing guide, ebooks: ebook: a comprehensive guide to digital marketing strategy, webinars: webinar: how to maximize and promote webinars as part of your marketing plan, articles: 9 tips for excelling at international digital marketing, articles: how to choose the most qualified digital marketing agency, articles: implementing digital strategy: how to ensure it doesn’t fail.
- Categories:
Recommended For You
Webinars: webinar: 2024 trends in digital marketing, ebooks: the dmi guide to digital marketing for small business, toolkits: digital marketing strategy action plan template, articles: what are the best ai and marketing automation tools, articles: 5 inspiring covid-19 marketing campaigns, articles: 4 great examples of user-generated content (ugc), cpd points available.
This content is eligible for CPD points. Please sign in if you wish to track this in your account.
CPD Points Available
This content is eligible for CPD points. Please login if you wish to track this in your account.
- View Courses
- Change Password
Get the latest digital marketing data, insights and toolkits from DMI
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
4 Strategies to Simplify the Customer Journey
- Richard L. Gruner

Making things easy is harder than you think.
While it may be tempting to offer your customers a never-ending array of products, customizations, and information, research shows that simplicity is almost always the best option for boosting both company value and customer loyalty. But what does it take to build a customer experience that’s smooth and simple from end to end? In this piece, the author offers four strategies to ensure simplicity is baked into every aspect of the customer’s journey: identify and communicate what simplicity means to your organization, look beyond product development to find ways to simplify throughout the customer journey, embrace internal complexity to achieve external simplicity, and remember that while simplicity is often necessary, it isn’t always the answer.
The modern consumer faces hundreds — if not thousands — of choices every day. What to read. Where to shop. What to buy. And each of those decisions takes a mental toll.
- RG Richard L. Gruner holds a PhD in marketing from the University of Melbourne and is Senior Lecturer (A/Prof) at the University of Western Australia. His work has been published in many top ranked peer-reviewed international journals, and he has a professional background in the media industry. One of his main research interests lies at the intersection of consumer psychology and digital tools. Find out more about Richard’s experience .
Partner Center
Hey there! Free trials are available for Standard and Essentials plans. Start for free today.
Customer Journey
The customer journey consists of actions your customers take before and after they make a purchase. It should be part of your overall marketing strategy to improve lead generation and enable more effective marketing. By understanding the different actions your customers take before and after a conversion, you can start brainstorming new marketing tactics to improve the customer experience and keep them coming back for more.

Turn clustomers into customers with personalization
Discover ways to personalize messaging using Mailchimp segmentation and automation for customer differentiation and growth.
Think of a customer journey as a detailed map that shows the full experience a customer has with your business. It lets you see every interaction they have with your company, even before and after they engage. By first understanding the customer journey , it will be easier to define your goals and use our automation tool to create the overall marketing experience you want to provide.
What is a customer journey?
A customer journey outlines the different steps your customers take to become customers. Without the customer journey, your marketing funnel couldn’t exist. A marketing funnel helps you market your products and services to customers based on where they are in their customer journey. For example, someone researching products is at the top of the marketing funnel or at the very beginning stages of their journey.
Ultimately, a customer journey map tells a story about how customers interact with your brand, including how they first discovered your business to whether or not they’ll make a repeat purchase. The journey lays out different interactions someone could have with your brand, although not every customer needs to use all those touch points before converting.
While not all customer journeys are the same, you can use your website and marketing efforts to easily guide customers through the journey by taking them through different touchpoints.
What are the phases of a customer journey?
Knowing the customer journey definition is only the beginning; now you must learn the different stages involved. A customer journey is made up of phases , which are the distinct stages a customer passes through as they’re guided to take specific actions. The phases you include will depend on your business goals.
Do you want a user to adopt a new app you’ve released? Are you looking to get inactive newsletter subscribers to read your emails? Is your aim to turn occasional shoppers into regular, loyal customers? All these marketing paths require a strategy for getting your customers from point A to point B.

Most customer journeys will usually account for these phases:
This is how someone discovers your company, usually through a search engine or your paid advertising efforts. Let’s say your new future customer sees an ad for your latest line of ‘I Have the World’s Okayest Cat’ mugs, and they click through to your website to learn more about the brand and product. Now your business is stored in their memory.
Acquisition
Congrats! You can now call that new future customer an actual customer, because they loved the ‘I Have the World’s Okayest Cat’ mugs you released so much that they bought one. Not only that, they also signed up for your email list through a form on your site so they can be the first to learn about any new merchandise.
Now that you’ve acquired a new customer, you can send them a series of emails to make them feel welcome, showcase other stuff in your store they might be interested in, and help them understand when and how they might expect to hear from you in the future.
This refers to how you can get customers to regularly use your product or service, shop at your store, or read your content. Consider using email, social media, in-product messages, and personalization to make your customers’ experience more enjoyable.
Make your customers so happy that they’ll recommend your brand to others. This is probably one of the best ways to get new customers.
Once you’ve established the phases of a customer journey, you can plan the touchpoints you’ll use to connect with customers at the right moments.
Advantages of a customer journey map
Customer journey maps are useful marketing tools that can help you better understand your target audience and use that information to lead them down a path to conversion. All businesses can benefit from having a customer journey map, so whether you’re doing B2B marketing or building an e-commerce brand, it’s good to know how customers interact with your company.

A few other advantages of a customer journey map include:
- Understand consumer behavior . Understanding how users interact with your brand can help you comprehend their motivations.
- Identify touchpoints . Identifying the different interactions customers have with your brand before making a purchase can help you create more effective marketing campaigns.
- Support your marketing efforts . Learning as much as you can about your customers can improve marketing performance by allowing you to shorten the customer journey and increase conversions.
- Improve the customer experience . With customer data, you can improve customers' experiences with your brand, making them more likely to convert.
- Predict how customers will behave . Customer journey maps help you predict what customers will do next, allowing you to market to them no matter where they are in the funnel.
- Boost customer loyalty and engagement . By creating a path for your customers and providing great experiences, you can keep customers coming back for more. This makes customer journey mapping an essential customer retention strategy .
How to build a customer journey map
Building a customer journey map is easy, and it’s an effective way to learn more about your customers.
To build your own customer journey map, follow the steps below.
- Determine your business goals . You’ll need to determine your goals before establishing the touchpoints for your customer journey map. Goals can include converting more qualified leads into customers, increasing brand awareness, and so on.
- Understand your customers . Gather data on your customers to learn about their behavior and uncover new ways to market to them.
- List opportunities for communication . Consider all the different ways you can communicate with customers, including social media and email marketing.
- Test your customer journey . Pretend you’re the customer and test your journey to see how you can make it easy for customers to convert after their initial touchpoint with your business.
- Refine customer journey map if necessary . Refine your customer journey map when there are changes to your business. Breaking down the map into stages can help you meet your customers’ needs no matter where they are in their journeys.
How does marketing automation benefit the customer journey?
Marketing automation uses technologies that eliminate the need for you to send one-off emails or set up other marketing efforts every time you need to connect with customers. Basically, you set up an automation to execute your strategy the way you want, and it’ll do the marketing work for you.
Since automations are usually powered by if-then logic, they adapt to match the individual paths your customers take.
For example, before making a purchase people might read your website, consider what product they want, sleep on it, and eventually go back to buy. This wandering route is different for everyone. With automation, you can automatically send an email during the consideration stage of their journey, reminding them of the products they were interested in and encouraging them to finalize the purchase.

Here are a few ways automation can help you build lasting relationships by connecting with customers at each step of their journey with your business.
Connect with new fans
When someone expresses interest in what you have to offer and enters their email address in a subscriber pop-up form on your site, you can send them a welcome email to introduce yourself—and give them a reason to stick around. You can also provide information about how often they’ll receive marketing correspondence from your business.
Sell more stuff
When that contact starts to move toward a purchase, such as putting something in their cart without checking out, you can set it up so they receive an abandoned cart email from you.
Meanwhile, you can send occasional reminders to prospects that haven't interacted with you in a while. Retargeting ads and emails, for example, remind people about the great stuff they saw on your site. Chances are, at least some of them are still interested and will take action if you reach out.
Cultivates a trusting 2-way relationship
When you deliver relevant content to your customers , you show them that you care about them. The more you target your communications, the more they will trust you to keep providing high-quality products or services . You can even use automation to send coupons or other discounts to people that meet certain criteria for loyalty or spending.

Increase open and click rates
Build automated workflows to send relevant messages based on how your customers interact with your brand.
What is a Customer Journey in Mailchimp?
In Mailchimp, a Customer Journey is a marketing automation tool that lets you visually map dynamic, automated marketing paths for your customers. Depending on the phases you want customers to pass through—discovery, acquisition, retention, etc.—you can choose the starting points and other unique interactions to engage your customers every step of the way.
Any marketing or purchasing paths that you want to use your data to create can be mapped out with the Customer Journey Builder, which allows you to target specific users and focus on what will get them to move from one point to another.
To illustrate this, let's take a look at the welcome journey that people will enter when they sign up to receive your marketing. You’re probably familiar with welcome emails and have heard us talk about their value a bunch. The concept of a welcome journey is the same: greeting new contacts and introducing them to your brand.
A journey should include emails, but it also differs from an automated welcome email in 2 key ways:
- People don’t just trigger an email once they’ve met the criteria of your starting points. They’re added to and start a path that’s customized for them.
- You can plan what actions you want new customers to take throughout this journey and where you want them to end up.
Adding the right mix of rules and actions—including branching points and email—to a journey map can put new subscribers on the path to becoming loyal users and customers. Branching points help make the journeys you build for your customers more dynamic and adaptable, taking customers down If/Else paths based on specific behaviors.
You can also use a Customer Journey to tag new contacts based on insights that are important to your business. This will allow you to track customer interests and send more relevant marketing content later.
Ways to use automated Customer Journeys
Of course your needs for setting up automated Customer Journeys will vary based on how your business functions and scales, but there are a few key workflows that can help any small business build and maintain relationships with their customers.
Create Customer Journeys to:
Greet new customers & introduce your brand
First, you need to onboard new people who start following your brand. A great first impression is key to establishing a long-lasting relationship. Begin with an email that thanks people for signing up and provides the information they need to know. Show customers you care about getting to know them by sending a survey to discover what they’re interested in, so you can customize your marketing to fit their needs. You can also use this journey to measure how often your contacts want to hear from you and when they’re most likely to engage.
Reunite shoppers with their carts
Research shows that 69% of e-commerce shoppers abandon their carts before checking out. If you don’t have an abandoned cart automation setup, you’re missing out on a lot of easy sales. Shoppers who have left a cart have already expressed interest in your brand; they just need a nudge back to your store to finish buying. With a journey, not only can you set up an automated email to send when someone abandons a shopping cart, but you can use the flow to highlight other stuff you sell and keep customers coming back.
Re-engage customers who have lost interest
There are several ways you can win back inactive customers—it just depends on what type of engagement is most important for your business goals. You can set up a journey that customers will start when a specific amount of time has passed since they last bought something from your store, or you can target customers who haven’t opened any of your last 5 email campaigns. From there, you can decide what interactions will get these customers to fall in love with your brand again.
Ask for product reviews or feedback on your service
When someone buys a product, that’s the perfect time to reach out and make a connection. Get their thoughts on the order and shipping process. Check in on how they’re liking their purchase. And don’t forget to include a coupon for other stuff in your store they’re sure to love.
Organize your contacts based on their interests and levels of engagement
Use a Customer Journey to help manage your audience based on insights that are important to your business. Make behind-the-scenes changes—like adding and removing tags—that'll help you send relevant messages and create more meaningful interactions.
Find success with customer journeys
Customer journeys are an important marketing tool to communicate effectively with your customers and lead them down a path to conversion. The easier your customer journey is to follow, and the more touch points you take advantage of, the better experience you can provide. Even after your customers have converted, deliver ongoing support and communication to retain them and promote brand loyalty.
Visualizing your customer journey is simple with Mailchimp. Using our Customer Journey Builder , you can start to learn more about your customers’ behavior and write a sales email that converts no matter where they are in the buying process.
¿Qué es el customer journey? Definición y fases clave
Escrito por Daniella Terreros
Crea tu Customer Journey Map para ayudar a tus clientes en el proceso de compra.

Algo que es evidente es que a la hora de comprar todos solemos tener comportamientos similares: nos damos cuenta de que necesitamos un producto, buscamos opciones que respondan a esa necesidad, elegimos la mejor alternativa y realizamos la compra.
¿Alguna vez te has preguntado por qué llevamos a cabo este proceso? En esencia, a estos procesos se le conoce como recorridos de compra, o customer journeys, y son uno de los aspectos fundamentales que debe tener en cuenta tu empresa al momento de generar estrategias de marketing, campañas publicitarias y nuevos productos.
Plantillas gratuitas de Customer Journey Map
Cuéntanos un poco de ti para acceder a las plantillas.
Descubre qué son estos recorridos, cómo impactan en la forma en la que los consumidores adquieren productos y cuáles son las fases de compra para utilizarlas a tu favor y mejorar la experiencia de tus clientes.
¿Qué es el customer journey?
El customer journey es el proceso de compra que atraviesa un consumidor desde el instante en que se da cuenta de que necesita un producto hasta el momento en que lo adquiere y hace uso de él. Este proceso contempla todas las fases involucradas en la toma de decisión de una compra e impacta en la experiencia final que tiene el consumidor del producto.
5 razones para definir tu customer journey
1. incide en la optimización de tu canal de venta .
Hasta hace unas décadas el único canal de ventas disponible era por medio de tiendas físicas y locales comerciales. Debido a esto, y a pesar de las preferencias personales de los consumidores, la mayoría de los clientes llevaban a cabo un recorrido de compra similar. Con el surgimiento de las tecnologías de telecomunicación y del internet las dinámicas de consumo y venta se han transformado radicalmente.
Hoy en día cada vez un mayor número de empresas cuentan con más de un canal de venta. No obstante, en muchas ocasiones esto no tiene un impacto positivo en las finanzas de las empresas, por lo que es importante definir cuál es el mejor medio para concretar ventas.
Al conocer el customer journey de tus compradores será mucho más sencillo establecer el mejor medio para ofrecer tus productos. Si, por ejemplo, sabes que tu audiencia pertenece a un grupo joven será más sencillo restringir tu actividad exclusivamente a las ventas online, optimizando tu mejor canal de ventas y perfilando el público al que te diriges.
2. Facilita la adquisición de tus productos
Diseñar un buen recorrido de compra es esencial para ofrecer una buena experiencia de consumo. Debido a la competencia en el mercado es posible que los consumidores pasen demasiado tiempo comparando productos o ponderando las ventajas y desventajas de la solución que ofreces.
Al generar un customer journey puedes facilitar esta tarea para tus clientes. Para ello, incluye algunas listas comparativas de precios y características entre tus productos y los de las otras compañías u ofrece descuentos desde el primer momento. Sin duda esto hará más sencillo que tomen la decisión de adquirir tus mercancías .
Si conoces a tu público y estás familiarizado con sus hábitos de compra y sus preferencias e intereses, podrás diseñar una ruta preestablecida de venta hecha a la medida.
3. Tiene un impacto positivo en tus ganancias
Optimizar tu canal de venta y facilitar la adquisición de productos tiene un impacto positivo en tus finanzas. Esto se debe a que puedes disminuir de manera importante los costos operativos de tu empresa, pues habrás reducido los medios de venta y destinado esos recursos para optimizar tu mejor canal. Asimismo, al hacer más sencillo el proceso de compra puedes percibir mayores ingresos y hacerte de una cartera de clientes más amplia .
Ten en cuenta que definir un customer journey te permite, por ejemplo, ofrecer algunos otros productos de tu marca durante el proceso de venta o presentar las ventajas que conlleva la adquisición de complementos a la mercancía que tus clientes buscan. Al implementar estas estrategias de manera correcta puedes esperar un mayor ingreso por cada compra y potenciar la fidelidad de tus consumidores.
4. Ayuda a definir el perfil de tus consumidores
Conocer a tu buyer persona es igual de importante que definir el customer journey y, en mucho casos, ambos elementos se complementan.
El recorrido de compra puede darte información importante sobre las audiencias que están interesadas en adquirir tus productos, por lo que puedes utilizar esta información para delimitar el perfil de tus consumidores.
Si logras identificar que, dentro de sus customer journeys, los clientes suelen acercarse a tu empresa tras haber revisado los precios de la compañía líder es posible que busquen una solución más económica. Esto no es algo negativo y, en cambio, puede ser útil para dirigirte directamente a ese público y competir con las empresas más populares.
Además, si logras encauzar el customer journey de tus audiencias será más sencillo replicar este mismo modelo en poblaciones similares.
5. Promueve la cercanía con tus clientes
La fidelidad es un elemento clave para asegurar el éxito empresarial. Si bien algunas empresas buscan concretar ventas por única ocasión (en especial cuando ofrecen productos de lujo o de alto valor), la mayoría de los negocios requieren retener a sus clientes como consumidores frecuentes de las mercancías que ofrecen.
Ante este panorama es importante tener en en cuenta que el proceso de compra no acaba cuando los clientes adquieren los productos que buscan. En cambio, es un ciclo cuya prioridad es ofrecer una buena experiencia de uso al cliente con el fin de que vuelva a consumir las mercancías de la marca.
Si has delimitado de manera correcta el customer journey, es muy posible que puedas estimar la lealtad de los clientes y continuar ofreciéndoles sus productos favoritos y el mismo servicio y experiencia de compra. Para ayudarte en este proceso, HubSpot ofrece una guía diseñada para aumentar la lealtad de tus clientes .
5 fases del customer journey
- Fase de reconocimiento
- Fase de consideración
- Fase de compra
- Fase de uso
- Fase de valoración
1. Fase de reconocimiento
Cuando un consumidor se hace consciente de la necesidad de adquirir un producto es cuando estrictamente comienza un customer journey. Ya sea que reconozca su necesidad de compra de manera impulsiva o que un imprevisto le haga saber que requiere un producto para solucionar el problema, este momento es fundamental para el resto del recorrido de compra que el consumidor llevará a cabo.
En esta fase se hacen presentes las preferencias, intereses e historia particulares de cada individuo, pues el consumidor comenzará una búsqueda de los productos o marcas que conoce y que cree que pueden cubrir esta falta.
¿Cómo mejorar la experiencia en la fase de reconocimiento del customer journey?
La publicidad es el mejor aliado de las empresas para auxiliar a los consumidores durante esta primera parte del proceso. La simple presencia de una marca es suficiente para que el público sepa que existe una solución a su necesidad de compra.
Recuerda que la publicidad puede también ser el detonante de un interés por parte del consumidor en adquirir tu producto. Si has implementado una buena campaña publicitaria es posible que el customer journey sea muy breve y tu producto sea el que el cliente adquiera. Aprovecha el kit de planificación de HubSpot para crear mejores campañas de publicidad que retengan la atención de tus clientes.
2. Fase de consideración
En la mayoría de los casos los compradores llevan a cabo un proceso de deliberación sobre qué solución es la más adecuada a sus necesidades, ya sea porque quieren encontrar la opción más económica o porque requieren un producto que responda específicamente a sus intereses.
Durante esta fase el consumidor pondera los beneficios y desventajas de cada uno de los productos que tenga a su alcance e irá descartando aquellos que no satisfagan sus exigencias. Esta parte del proceso puede ser muy larga, sobre todo cuando la compra implica un pago elevado, o muy corta, como cuando queremos elegir una golosina mientras esperamos en la fila del supermercado.
¿Cómo mejorar la experiencia en la fase de consideración del customer journey?
Las herramientas de marketing son aquellas que deben acompañar a los consumidores durante esta fase. Si el cliente está llevando a cabo un proceso de valoración de las diferentes alternativas en el mercado, será deseable que tu marca comunique de manera clara y sencilla los beneficios que conlleva la adquisición de tus productos.
Sé sincero sobre las ventajas de tu producto y siempre busca diferenciarte de la competencia. De este modo, adquirirás un valor extra a los ojos de tus audiencias. Ten en mente que las buenas campañas de marketing inciden en la toma de decisión de un consumidor.
3. Fase de compra
Este es el momento que todos están esperando y, por ello, es una fase del customer journey que debe ser tratada con especial atención. En este punto el consumidor ya realizó la deliberación entre las opciones del mercado y ha tomado una decisión de compra.
Durante esta parte del proceso el cliente llevará a cabo la confirmación de la compra y el pago de la misma. La empresa debe estar preparada para ejecutar la transacción, estipular el proceso de posventa y, en caso de ser requerido, acordar plazos de entrega.
¿Cómo mejorar la experiencia en la fase de compra del customer journey?
Contar con un buen canal de venta es fundamental para mejorar la experiencia de un cliente. Si tu canal de ventas es online, es recomendable que mantengas un canal de comunicación abierto y que tu página sea lo más sencilla de usar. En cambio, si operas en tiendas físicas deberás contar con expertos gestores que atiendan a tus clientes y resuelvan todas sus dudas.
Además, deberás ofrecer una amplia gama de opciones de pago y confirmar la compra. Recuerda que la experiencia de compra es fundamental, pues es el punto mas álgido del customer journey.
4. Fase de uso
Es común afirmar que el customer journey acaba en el momento en que un cliente lleva a cabo la compra de un producto. Sin embargo, aunque la compra es el objetivo al que se dirige el consumidor y representa un punto relevante de su recorrido de compra, en realidad el proceso de consumo no acaba en este punto y existen fases posteriores a la venta que aún deben tomarse en cuenta.
La fase de uso es esencial para determinar el éxito de una operación comercial, pues incide en la reputación de una empresa y en la opinión que los clientes se hacen de ella. Durante esta etapa el comprador que ha adquirido un producto lo emplea para los fines que tenía estipulados.
Si el producto cumple con su función, la compra habrá sido exitosa y podemos confirmar que se ha cerrado el proceso del customer journey. En cambio, si el producto no cumple con lo esperado, el proceso continúa, pues se deberá buscar una nueva opción y, en caso de ser posible, llevar a cabo una devolución de la primera compra.
¿Cómo mejorar la experiencia en la fase de uso del customer journey?
Los canales de atención al cliente son, sin lugar a dudas, los medios indicados para mejorar la experiencia del cliente durante la fase de uso. Este servicio le permitirá solucionar sus dudas y resolver problemas que pueda estar experimentando con el producto.
Para potenciar la buena imagen de la marca, las empresas pueden ofrecer garantías en los productos que venden. Esto tendrá un efecto positivo en caso de que el producto adquirido tenga algún defecto, pues el cliente se sentirá acompañado por la compañía y asegurará que su customer journey ha valido la pena.
5. Fase de valoración
Como hemos revisado, la mayoría de los negocios necesitan que sus clientes se vuelvan consumidores recurrentes de los productos que ofrecen. Esto se debe a que las empresas con clientes leales tienen un mejor pronóstico de supervivencia en el mercado. Si bien la fase de valoración no forma parte de un único customer journey, sí es un elemento clave para comenzar un nuevo recorrido de compra .
Si los clientes se sienten satisfechos con la adquisición de un producto, en la siguiente ocasión seguramente volverán a elegir las mercancías de la misma marca. Este proceso de compra será más corto que el primero gracias a que la primera adquisición cumplió con sus expectativas. Por ello, la fase de valoración es esencial como puente entre diferentes operaciones comerciales.
¿Cómo mejorar la experiencia en la fase de valoración del customer journey?
Para aprovechar las ventajas de la fase de valoración y para mejorar la experiencia de los clientes durante este paso es fundamental abrir canales de comunicación con los consumidores, como sitios de reseñas y opiniones.
Si su experiencia de compra ha sido buena, los clientes darán una valoración positiva al producto y a tu negocio. Esto influirá positivamente en el proceso de compra de otros consumidores. Ten en cuenta que más del 90 % de los compradores han afirmado que sus hábitos de compra toman en consideración las reseñas de anteriores consumidores .
Si, por el contrario, su experiencia de compra no fue satisfactoria, los clientes podrán calificarte negativamente. Esta calificación te ayudará a mejorar tu servicio y la calidad de tus productos.
Como puedes ver, la escucha activa de las opiniones de tus clientes siempre tiene un efecto positivo si sabes aprovecharlas.

Publicado originalmente el 29 de marzo de 2022, actualizado el 14 de diciembre de 2023
Únete a la conversación, te invitamos a compartir este artículo.
Artículos relacionados.

Pirámide de Maslow: qué es, ejemplos y cómo usarla

Los 10 factores que afectan el comportamiento de tus consumidores

Teoría del consumidor: qué es, para qué sirve y ejemplos
Expandir Contenido
Narrativa Visual para Expertos en Marketing
Download for Later
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Soluciones Soluciones Muestra Online Comunidades Online Encuestas Offline Repositorio de Insights Quizzes y sondeos Licencia Académica Herramientas Net Promoter Score NPS+ Análisis Conjoint MaxDiff Closed-Loop Van Westendorp
- Recursos Blog eBooks Webinarios Plantillas para encuestas Estudios de caso Centro de ayuda
- Características
Inicio CX Experiencia del Cliente
Customer Journey: Qué es y cómo funciona

Antes de comenzar a ofrecer un producto o servicio a los consumidores, necesitas entender qué es Customer Journey o recorrido del cliente y comenzar a planearlo mejor. Solamente así lograrás satisfacer sus necesidades.
Los detalles y los giros de este viaje dependen de tu mercado, pero para atraer y retener a los clientes leales, debes incluir algunos puntos de contacto universales en tu recorrido.
Cuando un cliente decide comprar un producto o servicio, ya ha tomado medidas para buscar soluciones y sopesar sus opciones. Para generar una mejor experiencia al cliente , necesitas un plan que te mantenga relevante y con la mente en alto en cada punto del viaje.
En este artículo aprenderás qué es Customer Journey, cómo crearlo, y obtendrás los mejores consejos para fomentar la confianza, el compromiso y la lealtad del cliente.
¿Qué es Customer Journey?
El Customer Journey o trayecto del cliente son los pasos que realiza el consumidor durante el proceso de buscar una solución a su problema, deseo o necesidad.
Normalmente, estos viajes siguen pasos similares en todas las industrias, pero no siempre son lineales.
El propósito u objetivo del Customer Journey es, por un lado, medir y evaluar cómo estás sirviendo a tu cliente y mejorar tus servicios.
Por otro lado, averiguar qué ha cambiado en la vida de tus clientes (potenciales, actuales y ex), por qué visitan a tus competidores y no a ti, y aportar ideas para nuevos servicios.
Si un posible consumidor no está satisfecho con sus opciones en cualquier momento del viaje, puede ir hacia atrás en busca de algo más convincente.
Al obligar a los consumidores a comprometerse con tu marca, creas un punto de contacto con acciones y activos que los impresionan.
Encuentra aquí la diferencia entre customer journey y customer experience .
Ventajas de comprender el customer journey
Identificar el customer journey nos permite comprender mejor cómo compran para satisfacer sus necesidades y expectativas y qué papel desempeña una empresa concreta en este proceso.
Además, ser conscientes de todas sus interacciones (touchpoints) a través de cualquier canal, como el correo electrónico o las redes sociales, permite mejorar la experiencia de compra al tiempo que se transmite un mensaje coherente en todos los canales de comunicación.
A continuación, te explicamos los beneficios de implementar una estrategia de customer journey en tu negocio.
Tienes una mejor comprensión de las emociones del cliente:
La creación de un framework del journey te sitúa directamente en la mente del consumidor. Comprender por qué un cliente toma una decisión concreta prepara a tu empresa para el éxito.
Saber cómo se sienten los clientes te anima a mejorar el funcionamiento de la organización porque te permite identificar los puntos de fricción con el cliente a lo largo de su recorrido, lo que facilita su solución.
Analizar los puntos de fricción en los productos/servicios:
Trazar el journey del cliente da a la organización información sobre los puntos en los que la comunicación con el cliente es deficiente.
Por ejemplo, si el personal de atención al cliente no tiene personal suficiente, los clientes no reciben ayuda cuando la necesitan. Los clientes se enfadan porque esperan respuestas rápidas. Resuelves el problema contratando a otro miembro del equipo de asistencia para que atienda más preguntas de los clientes.
La creación de customer journey map ofrece el punto de vista de los clientes sobre una empresa. El mapa es una representación visual de las transacciones y emociones que conduce a través de cada punto de contacto con los clientes que ayuda a identificar los puntos débiles.
Mejorar la satisfacción de empleados y clientes:
A medida que se resuelven los problemas, aumentan los niveles de confianza tanto de los clientes como de los empleados. Se anima a los empleados a seguir haciendo un gran trabajo, lo que aumenta la satisfacción general de los clientes.
Crear un equipo unido:
Para desarrollar experiencias de cliente únicas, los equipos de tu organización deben estar en sintonía. Marketing, desarrollo de productos, ventas y atención al cliente deben trabajar juntos para mejorar los procesos dentro de la organización. A medida que los equipos trabajan juntos, aumenta la eficiencia y la eficacia de cada uno de ellos.
Importancia de tener un Customer Journey
Saber qué es Customer Journey te permite entender que cada consumidor es diferente. Son personas, como tú y como yo. No es necesario que pongas estos puntos del mapa en piedra. Es vital revisarlos regularmente y comparar tu estrategia con los resultados de la vida real. Sobre todo, escucha a tus clientes.
Conocer el Customer Journey te permite ver tu marca desde la perspectiva de los clientes para que pueda diseñar un UX que genere confianza y aumente la conversión.
Te ayuda a entender las necesidades de cada segmento de la audiencia en las diferentes etapas del ciclo de vida del cliente o del embudo de ventas, y así definir cuál es el mensaje de marketing y el proceso de ventas para ofrecer la experiencia de marca deseada.
Aprende también sobre la importancia del customer journey digital .
Fases del Customer Journey
Ahora que sabes lo que es Customer Journey, es momento de mirar más de cerca lo que puedes hacer para comprometerte con los consumidores potenciales y nuevos en cada paso del journey. Estas son las fases del customer journey que debes considerar:
1.- Concientización
Durante la fase de concientización o etapa de awareness del journey, los consumidores buscan soluciones y se encuentran con múltiples marcas y productos. Este es el momento de brillar si quieres provocar una primera buena impresión.
- Lo que los consumidores están haciendo: Durante este paso, los consumidores probablemente están llevando a cabo una investigación. Esto puede incluir la búsqueda de soluciones en línea a problemas con palabras clave, la lectura de entradas de blog y artículos de noticias, navegar en foros en línea y el primer encuentro con marcas.
- Lo que las marcas pueden hacer: Se podría pensar que los consumidores están haciendo todo el trabajo pesado en esta etapa porque están haciendo preguntas y navegando por el contenido. Sin embargo, no quieres acercarte a la conciencia de marca de forma pasiva. Captar las consultas de búsqueda entrantes con una fuerte estrategia de SEO. Construye tu presencia en los medios sociales. Comienza un blog o asóciate con los creadores de contenido para abordar las preocupaciones críticas del mercado objetivo. Los consumidores acudirán a ti cuando les proporciones activos atractivos e informativos sobre lo que les importa.
2.- Consideración
Una vez que has captado la atención de un prospecto, ya sea con tu contenido o a través de otras fuentes, necesitas aferrarte a él. En este punto, pasan de buscar respuestas sobre soluciones potenciales a buscar tus respuestas a esas soluciones.
Lo más probable es que tu marca sea considerada junto con otras, así que asegúrate de que cada impresión que des sea fuerte. En este punto, los consumidores están interactuando directamente con tu marca, y quieres que se queden para el siguiente paso en el Customer Journey.
- Lo que los consumidores están haciendo: Investigar marcas y productos específicos, comparar competidores y evaluar tus prioridades. Esto podría incluir una mirada más cercana a las especificaciones de tu producto y servicio, examinar las políticas de atención al cliente y recurrir a revisiones de comparación directa. La fase de consideración varía porque los medios de comunicación centrados en el consumidor se presentan de muchas formas.
- Lo que las marcas pueden hacer: Valora la importancia de la experiencia del usuario . Optimizar continuamente la experiencia (UX) en todos sus puntos de contacto, incluyendo las páginas de descripción y de transacciones de comercio electrónico. Aprende de los datos de usuario que obtienes cada día para mejorar los futuros encuentros con tu marca. Pequeñas cosas como asegurarse de que las descripciones y los procesos sean claros y que todos los botones funcionen correctamente marca una gran diferencia cuando alguien te considera frente a un competidor.
3.- Decisión
Es tu momento de hacer o deshacer durante el Customer Journey. Una vez que los clientes potenciales están satisfechos con la investigación y comparación de sus opciones, eventualmente tomarán una decisión.
A veces se dan cuenta de que ninguna de las marcas que han estado considerando ofrece lo que están buscando. Sí toman una decisión positiva, quieren facilitar el proceso eligiendo sus productos de confianza.
Lo que los consumidores están haciendo: Están considerando factores como el precio frente al valor, la capacidad de respuesta del servicio al cliente, los valores de la empresa y las políticas. En el momento en que están en la fase de decisión, no se trata sólo de las especificaciones del producto o la experiencia de compra . Los consumidores quieren apoyar a una marca en la que puedan confiar para ofrecer una solución de calidad a sus problemas.
Lo que las marcas pueden hacer: Para anticiparse a este paso, debes ir más allá. Esto podría incluir estrategias de marketing donde ofrezcas incentivos a los clientes potenciales que ya han visitado tu sitio web o se han comprometido con tu empresa. Asegúrate de que sus políticas de devolución y reembolso sean fáciles de encontrar, y entrena a tu equipo de atención al cliente para que responda a las preguntas clave para la toma de decisiones.
Aprende también sobre el consumer decision journey .
En este punto del Customer Journey tienes un nuevo cliente. ¡Felicidades! Toda esa planificación y creación de activos está dando frutos cuando llegan a la fase de acción. El consumidor ha decidido hacer su compra contigo, pero no asumas que es un trato hecho.
Necesitan ser capaces de completar la transacción y empezar a utilizar su oferta. Como todos los demás pasos del Customer Journey, este momento debe ser fácil e intuitivo para el usuario, así como agradable o atractivo.
Lo que los consumidores están haciendo: Dependiendo de tu modelo de negocio, los clientes están aprovechando este momento para comprar sus productos en línea, con un minorista físico o están reservando un servicio que planean experimentar pronto. Una vez que tengan el producto o servicio, comenzarán a poner en práctica su compra y si atraviesan la fase con éxito, te ganarás la lealtad del cliente .
Lo que las marcas pueden hacer: Optimizar la experiencia de transacción en el Customer Journey. Garantizar la calidad de su propio sitio de e-commerce o tienda física, y ver regularmente cómo la competencia está optimizando la experiencia de los consumidores que toman medidas en uno de los puntos de contacto.
Una vez completada la transacción, haz un seguimiento de tu nuevo cliente con la información que puedas necesitar para atender su compra y mantenga el contacto con tu equipo.
5.- Fidelización
Guiar a los clientes potenciales a través del Customer Journey requiere mucho trabajo y una planificación cuidadosa. Una vez que se ha establecido una relación, hay que alimentarla para construir la fidelización de clientes y ampliar tu alcance.
Los clientes entusiastas son más propensos a recomendar tu marca y productos a un amigo, lo que para muchos puede ser un factor decisivo. Cuando los mantienes contentos y superas sus expectativas con innovación y un excelente servicio al cliente, el Customer Journey es más corto y los costos por transacción son menores.
Lo que hacen los consumidores : En este punto, los clientes están usando tus ofertas para solucionar sus necesidades. Cuanto mejores sean los resultados y la experiencia que obtengan con tu producto, más probable será que vuelvan a comprar y te recomienden. También pueden comenzar a involucrarse con tu marca de manera más casual en las redes sociales y planear su próxima compra.
Lo que las marcas pueden hacer: Tomar la iniciativa de contactar con los clientes de una manera amistosa y solidaria. Una breve encuesta de experiencia del cliente es una buena manera de hacerles saber que te preocupas por sus comentarios.
Considera la posibilidad de iniciar un programa lealtad para referencias y futuras transacciones. Esta es también una excelente oportunidad para hacer que los consumidores vuelvan a algunos de los activos relevantes que creas para construir el conocimiento de la marca. Esto podría incluir el contenido de un blog con consejos para enriquecer su experiencia con el producto, un boletín de noticias con actualizaciones y promociones, oportunidades ocasionales para proporcionar más retroalimentación.
Elementos del Customer Journey
Existen diversos elementos que son esenciales al crear tu Customer Journey y que te ayudarán a tener un mejor análisis del cliente .
Cada uno de estos elementos te ayudarán a identificar los puntos que debes mejorar en tu recorrido:
Buyer persona
Los personajes de los compradores son representaciones icónicas de su cliente ideal. Se basan en investigaciones, en datos, hechos y entrevistas reales con compradores recientes (e incluso pueden incluir perspectivas de personas que aplazaron una decisión de compra o compraron una solución competitiva).
Al crear un buyer persona de forma correcta, los responsables de marketing podrán segmentar mejor sus mensajes, dirigiéndose a diferentes personas con el contenido y las ofertas más adecuadas; desarrollar nuevos productos/servicios basados en las necesidades y deseos de sus clientes clave; y llegar a las personas adecuadas, precalificando así a los clientes potenciales mediante la atracción de los mismos.
Recordemos que Customer Journey es la historia de la experiencia de un cliente, te ayuda a explicar lo que sucede en el camino, a quién y cómo sucede, por lo tanto, es necesario saber quién hace el viaje para contar la historia. El buyer persona representa a los clientes cuyo viaje estas mapeando.
Puntos de contacto o touchpoints
¿Dónde se encuentran los puntos de contacto con el cliente ? Los puntos de contacto abarcan todas las interacciones entre una marca y un cliente en cualquier punto del viaje del cliente.
Estos puntos de contacto individuales pueden influir en la forma en que un cliente percibe la experiencia general de tu marca; cada punto de contacto representa una oportunidad para guiar y deleitar al cliente .
Los touchpoints pueden ocurrir a través de canales web y fuera de línea, y pueden estar controlados por la marca o no.
Estos son algunos canales que puedes utilizar para estar en contacto durante el Customer Journey:
- En el lugar
- Vía telefónica
- Correo electrónico
- Redes sociales
- Recomendaciones boca a boca
- Sitios de evaluación
El número de puntos de contacto con el cliente y el tiempo que se tarda en completar cada paso puede variar dependiendo de múltiples factores, incluyendo:
- Las preferencias del cliente (es decir, su modo preferido de búsqueda, compra, apoyo, etc.).
- Relevancia e importancia del objetivo (por ejemplo, comprar un coche en comparación con comprar comida para su perro)
- Los canales elegidos por las empresas para interactuar con sus clientes
Indicadores de rendimiento
Una función clave es identificar las áreas de oportunidad críticas basándose en la comprensión de las percepciones de sus clientes sobre los experiencias.
Puedes utilizar indicadores comunes que indican positivo/neutral/negativo o que supera/satisface/no satisface las expectativas. Este enfoque generalizado de los indicadores de rendimiento puede utilizarse eficazmente para identificar y evaluar las áreas de oportunidad.
Dado que la investigación cualitativa suele realizarse con muestras de menor tamaño, la investigación cuantitativa con una muestra de gran tamaño puede reforzar la confianza en los conocimientos cualitativos. La investigación cuantitativa proporciona una oportunidad de capturar métricas de experiencia del cliente para etapas del viaje o puntos de contacto específicos. Al integrar las métricas en el mapa del viaje de los clientes, se convierten en una herramienta útil para medir las iniciativas de customer experience a lo largo del tiempo.
Algunas métricas útiles que puede incluir son:
- Net Promoter Score (NPS) u otras medidas de lealtad del cliente
- Métricas de satisfacción del cliente
- Evaluaciones cuantitativas de las emociones primarias que los clientes están experimentando en etapas específicas o puntos de contacto en su viaje
- Métricas de esfuerzo
- Medidas de importancia, utilidad, etc. de un punto de contacto específico
Las métricas que se recogen e incluyen en el Customer Journey te ayudarán a medir la salud de la experiencia del cliente, ahora y en el futuro. Y al hacerlo, debe existir un compromiso de tomar decisiones de valor basadas en el desempeño de la experiencia del cliente.
Mapa de la experiencia del cliente
El mapa de la experiencia del cliente te ayuda a enumerar los siguientes elementos que ayudarán a satisfacer a los usuarios y los obligará a seguir adelante. Considera estos ejemplos:
- Actividades y preguntas del consumidor
- Puntos de contacto como sitios web, foros y anuncios
- Activos como los medios de comunicación de pago, entradas de blog, vídeos y seminarios web (algunos activos son puntos de contacto con el cliente)
- Estrategias como SEO, redes sociales, gestionar comunidades virtuales , y crear programas de referencia
- Herramientas como informes de compromiso y encuestas en línea .
Canvas de Customer Journey
Te compartimos una plantilla de customer journey que te puede servir de ejemplo para que comiences a crear tu propio customer journey map e identifiques los puntos a mejorar en cada punto de contacto con el cliente.
Descarga el canvas de customer journey aquí :
¿Qué es el customer journey mapping?
Un Customer Journey Map (CJM), cuenta la historia de las experiencias de tus clientes con tu marca a través de cada punto de contacto, todo en el mismo lugar, o es una herramienta clave para mejorar la experiencia del cliente. Dependiendo del objetivo del CJM, puede ser más o menos complejo.
Lo que el cliente siente, ve y oye cuando interactúa con tu empresa constituye la base de su experiencia. Comprender estas experiencias te permite trazar y controlar con precisión el recorrido del cliente.
Ejemplo de customer journey map
Starbucks, por ejemplo, domina el concepto de intimidad del cliente para controlar la experiencia. El recorrido se calcula desde el momento en que el cliente entra por la puerta.
Imagínate un recorrido a un Starbucks local. Al entrar, percibes el aroma de los granos de café tostados. El encargado te saluda con una sonrisa. A medida que el murmullo de la charla desaparece en la tranquila música de fondo, sientes la calidez que te rodea. Cuando recibes tu café, ves tu nombre escrito a mano por uno de los simpáticos camareros. Si eres un cliente habitual, el personal te conoce por tu nombre y puede hacer tu pedido de memoria.
El gigante del café no sólo vende un producto. Vende lo que la gente recuerda mejor: la experiencia. La empresa fideliza a sus clientes combinando el producto con una experiencia inolvidable. Además, puede cobrar hasta 10 veces más que sus competidores. Starbucks entiende claramente
Conoce también el customer journey de Volkswagen .
El recorrido de tu cliente puede durar unas horas o más de varias semanas. La forma más sencilla de empezar es crear una línea de tiempo. A partir del conocimiento que tengas del cliente, completa lo que le ocurre en cada etapa de la línea de tiempo.
El marco del customer journey map incluye lo siguiente junto a la línea de tiempo:
- Acciones : ¿Qué hace el cliente? ¿Cuáles son las acciones clave que realiza un cliente para pasar a la siguiente etapa? ¿Qué acciones realiza una persona cuando no avanza?
- Motivaciones: ¿Qué impulsa al cliente a pasar a la siguiente fase? ¿Cuál es el objetivo? ¿Intenta resolver un problema? ¿Qué siente?
- Preguntas : ¿Cuáles son las incertidumbres del cliente? ¿Busca algo concreto? ¿Están confusos? Identifica en qué fase los clientes tienen más preguntas y resuélvelas rápidamente.
- Paint Points : ¿Qué obstáculos impiden a tus clientes pasar a la siguiente fase? ¿Es el proceso? ¿El precio?
Las opiniones directas de los clientes son la forma más eficaz de obtener respuestas. Envía encuestas o realiza entrevistas para conocer mejor a tus clientes y sus necesidades.
Consejos para realizar un customer journey mapping
Si has llegado hasta aquí, probablemente estarás de acuerdo en que conocer el recorrido de tu cliente es fundamental para crear una gran experiencia de cliente. Pero, ¿cómo sacarle el máximo partido?
Echemos un vistazo a algunos de los siguientes consejos para crear un Customer Journey Map eficaz:
Consejo nº 1: Crear un customer journey map es un trabajo de equipo
No es fácil reflejar en el Customer Journey Map todas las interacciones por las que pasa un cliente. La tarea puede complicarse aún más cuando las personas responsables de la interacción no se encuentran en los distintos departamentos.
Esto da por sentado las fases o interacciones por las que pasa el cliente con la empresa. Y lo que es peor, a veces lleva a trazar un customer journey map que hace más hincapié en los silos departamentales que en el recorrido general del cliente.
Recuerda que tu equipo no puede olvidar el objetivo. Trata de mapear la experiencia del cliente desde tu perspectiva. Esto se consigue con mayor eficacia cuando se reúnen los diferentes perfiles de la empresa. Sólo así el resultado final reflejará el conocimiento que cada uno tiene del cliente.
La idea es dedicar un espacio de trabajo con los diferentes profesionales, con y sin contacto con el cliente. Si esto es imposible, realizar al menos una validación con cada departamento es vital. Esto permitirá convertir tu customer journey map en una herramienta de responsabilidad compartida.
Consejo nº 2: Conoce a fondo a tu cliente
Comprender a tus clientes en cada intersección o punto de control de tu viaje es fundamental. Esto te permitirá desarrollar contenidos, productos y servicios que satisfagan sus necesidades. En lugar de recopilar datos ocasionales de los clientes, emplea encuestas continuas para recoger información.
Disfrutarás de la posibilidad de ajustar tu marketing o el desarrollo de productos en tiempo real para satisfacer las necesidades de los clientes a medida que cambia el mercado.
Consejo nº 3: Obtén una visión global
El customer journey comienza antes de que los clientes potenciales compren o se suscriban a los servicios. Los clientes potenciales comienzan su viaje cuando se enteran de las ofertas a través de tu sitio web, sitios de reseñas de clientes o anuncios. Tras las etapas de conocimiento y descubrimiento, los consumidores entran en el proceso de compra. Los clientes experimentan sus productos y servicios cuando se realiza una compra y, a continuación, se forman opiniones.
A lo largo de estas etapas, debes saber qué opinan los clientes sobre tu empresa y sus productos. Por ejemplo, ¿sabes qué factores hacen que los clientes te elijan frente a la competencia? ¿Cómo perciben los clientes a tu personal de ventas? ¿Qué les gusta a los clientes de tus productos? ¿Tu equipo de asistencia responde con precisión a las preguntas de los clientes?
¿Cómo crear un customer journey map?
Hay seis pasos principales para crear un customer journey map:
- Comprender el perfil del comprador objetivo : Una organización debe definir el perfil de tu comprador ideal antes de elaborar el mapa de recorrido del cliente.
- Reconocer la intención del público objetivo: ¿Qué espera conseguir un comprador al interactuar con una marca? ¿Cuáles son sus expectativas?
Responde a estas preguntas:
- Enviando encuestas online a todos los clientes
- Organizando grupos de discusión o entrevistas individuales.
A continuación, elabora planes de acción utilizando los resultados de su investigación para satisfacer las expectativas del comprador.
- Toma nota de los puntos de contacto: Traza un mapa de todos los puntos de contacto cada vez que un nuevo cliente visite tu sitio web o se ponga en contacto con un miembro del equipo de ventas. Incluye en tu mapa las interacciones antes, durante y después de la compra.
Tu organización debe comprender:
- Dónde obtienen los clientes información sobre tu sitio web: búsqueda en Google, redes sociales o anuncios de Google.
- ¿Qué páginas visitan la mayoría de los clientes? ¿Cuál es el tiempo promedio que pasan en cada una?
- ¿Disfrutaron los clientes comprando en la organización? ¿Han tenido alguna dificultad? ¿En qué medida les ha ayudado el equipo de atención al cliente?
- ¿Cumple mi organización todos los requisitos de mi público objetivo?
- ¿En qué fases suelen tener problemas los clientes?
- ¿Qué páginas del sitio web tienen tasas de rebote más altas de lo aceptable?
Si interactúas directamente con los clientes, asegúrate de preguntarles:
- ¿Cómo conoció nuestra organización?
- ¿Qué esperaba del sitio web de nuestra organización?
- ¿Se han cumplido sus expectativas?
- ¿Qué le llevó a comprar a nuestra organización?
- Haz una lista de prioridades: Puedes optimizar el customer journey map identificando las áreas que necesitan atención inmediata. Una vez que conozcas los problemas más comunes, podrás tomar medidas para limitar su impacto en la fidelidad del cliente.
Pon todas las ideas sobre el papel: La mayoría de los profesionales del marketing prefieren dibujar todo el mapa en una pizarra o utilizar herramientas de mapeo del viaje del cliente para crear un customer journey digital .

Análisis del customer journey
Entender la organización desde el punto de vista del cliente aporta nuevas ideas y opiniones. El análisis del customer journey hace precisamente eso: analiza los puntos de vista de los clientes sobre los productos para que puedas realizar los cambios oportunos para mantener a los clientes fieles a tu marca. Utiliza los datos de los clientes para aplicar estrategias de marketing mejoradas.
El análisis consta de tres etapas: recopilación de información precisa, desarrollo de customer personas y análisis de las interacciones de los clientes.
A continuación se explica cómo el análisis del customer journey es beneficioso para recopilar información:
- Define claramente todos los puntos de interacción con el cliente .
- Evalúa cómo progresa el viaje de principio a fin.
- Analiza el impacto en la fidelidad del cliente y la compartibilidad de la marca en función de los puntos de interacción con el cliente.
- Destaca las áreas que hacen perder el tiempo al cliente para mejorar la eficiencia.
- Generaliza el recorrido de públicos similares para introducir mejoras y mantener satisfechos a los clientes.
Conoce cómo hacer un seguimiento de la trayectoria del cliente .
Canales de comunicación del customer journey
Tu mapa es una visión de 360 grados de los comentarios de los clientes desde cada paso de su viaje. El mapa es un modelo probado para comprender cómo, cuándo y dónde experimentan tus clientes tu marca.
Para empezar, aquí algunos lugares para medir la experiencia de forma continua:
- In situ: Capta las opiniones de los clientes en el momento en que visitan las empresas con ubicaciones físicas. Por ejemplo, supongamos que tienes un restaurante. Entrega a los comensales una breve encuesta que deberán llenar junto con la cuenta al final de la comida.
- Correo electrónico : Enviar correos electrónicos es una de las formas más sencillas de obtener opiniones de los clientes. Configura tu sistema de ventas para que envíe un correo electrónico después de que un cliente complete una compra.
- Call Center : Después de cada interacción con el cliente, puedes recopilar comentarios por correo electrónico o encuesta telefónica.
- En la App : Para los desarrolladores de aplicaciones, lo ideal es recopilar respuestas sin salir de la aplicación. Una encuesta dentro de la aplicación permite a los usuarios seguir disfrutando de la aplicación al tiempo que te proporcionan sus comentarios.
- Sitio web: Tus clientes potenciales navegan por tu sitio web para considerar la posibilidad de convertirse en clientes. Una vez que son clientes, siguen visitando para obtener asistencia y acceso a la cuenta. Recopilar opiniones sobre tu sitio web es esencial para un enfoque holístico de la experiencia del cliente.
Conoce más del customer journey de una tienda .
Cómo definir un customer journey de manera efectiva
Después de aprender qué es Customer Journey y los elementos que la conforman, es momento de construir un customer journey map que convierte a los prospectos en clientes leales y crear la mejor estrategia.
Te invitamos a conocer la opinión Antonio Linares, experto en estudios de Customer Experience.
Sigue estos 5 pasos para asegurarte de que tus clientes obtengan los productos necesarios para sus necesidades y disfruten de una experiencia al cliente que los hará regresar a tu negocio.
1.- Comprende lo que tienes que ofrecer y quién se beneficia de ello
Cada miembro de tu equipo debe saber cómo comunicar los beneficios de tus productos y servicios. ¡No puedes compartir algo cuando no sabes lo que es! De la misma manera, necesitas saber quién es tu cliente ideal.
Pregúntate, «¿Quién necesita más esta solución?» Esta es una buena oportunidad para aprovechar las encuestas online , que te permiten identificar a tu público objetivo, sus necesidades primarias relacionadas con tus ofertas, y cualquier otra consideración que necesite hacer para atraerlos.
2.- Crea a tu cliente ideal
Una vez que tengas una idea general de quién es tu público objetivo, crea unos cuantos perfiles para darles un nombre y una cara. Cuando tengas un sentido bien desarrollado de a quién incluir en tu segmentación demográfica, tendrás una comprensión clara de las variaciones en los viajes de sus clientes.
Por ejemplo, puedes descubrir que tus botellas de agua reutilizables resolverán los problemas de los atletas de todas las edades, de los millennials conscientes de la sostenibilidad y de los adultos con movilidad limitada. Evita ampliar demasiado tu mercado, porque eso puede desenfocarte y restarle eficiencia a tus estrategias de mercado.
Cree un arquetipo de cliente para cada uno de estos grupos dentro de tu público objetivo, teniendo en cuenta estas variables imaginarias pero realistas:
- Situación económica/intervalo de ingresos
- Intereses y aficiones
- Principales fuentes para comunicarse y obtener información
- Hábitos
- Puntos de contacto consistentes
- Marcas y productos favoritos
- Hábitos de consumo
3.- Identifica cualquier detalle específico de tu industria
La siguiente estrategia para crear un Customer Journey efectivo, consiste en obtener detalles de tu industria.
Generalmente, las paradas de los clientes durante su trayecto serán similares, sin embargo
sus necesidades específicas deben influir en sus propuestas de valor y en los activos que crees para comercializar tu producto.
4. Optimiza tus propuestas de valor
El Customer Journey es personal y tus propuestas de valor deben ser consistentes en cada encuentro con los consumidores.
A medida que te familiarices con tu mercado objetivo, pule tus propuestas de valor para que sean inclusivas, comunicativas y con aspiraciones. Utiliza estas declaraciones como una guía en el mapa de viaje de tus clientes y en los activos de marketing de tu empresa.
Es hora de poner en práctica tu mapa de la experiencia del cliente. Considera lo que cada uno de tus cliente necesitaría y hazlo a lo largo de todo el proceso mientras asignan estos elementos a cada fase del customer journey map.
5. Construye activos para cada punto de contacto en el Customer Journey
Al trazar el recorrido del cliente , tendrás una idea más clara de lo que te pedirán los consumidores ideales, las marcas que podrían estar considerando y los tipos de contenido que probablemente consumirán para pasar de una fase a la siguiente.
Dependiendo de tu industria, el contenido de los puntos de contacto con el cliente puede incluir los siguientes tipos de activos:
- Entradas al blog
- Contenido asociado o influyente
- Boletines impresos o por correo electrónico
- Infografías
- Información en redes sociales
- Videos (anuncios, tutoriales, seminarios web)
- Volantes promocionales
- Kits de muestra o demostraciones
Conoce las dimensiones del Customer Journey con este artículo.
Estrategias de Customer Journey
El journey es la clave para la fidelidad del cliente. Una mejor estrategia de customer journey no sólo conduce a clientes más fieles, sino que también a mayores márgenes de beneficio.
Estas son algunas estrategias de customer journey que puedes implementar:
- Personalizar la experiencia
El servicio personalizado ya no es una opción, es esencial.
Más de la mitad de los clientes esperan que las marcas se anticipen a sus necesidades y el 63% espera un servicio personalizado.
Dos de cada cinco clientes se quejan de que las marcas no cumplen sus expectativas de personalización. El 37% de los clientes afirma que no comprará productos de marcas que no personalicen la experiencia.
Una forma fácil de personalizar es ofrecer descuentos basados en el comportamiento del consumidor . También se pueden ofrecer recomendaciones personalizadas.
Prueba a utilizar la inteligencia artificial (IA) para generar recomendaciones de marca basadas en el comportamiento de compra de tus clientes, o utiliza un cuestionario para evaluar sus necesidades.
Aquí cómo personalizar la experiencia del cliente .
- Mejorar la navegación de la interfaz de usuario (UI)
Si tu sitio web es difícil de navegar, a los clientes les costará llegar a su objetivo final.
Una mala experiencia de usuario hace que los clientes se frustren y abandonen tu sitio web o aplicación. Tu sitio web debe describir el recorrido que deben hacer los visitantes para alcanzar los objetivos finales. Utiliza botones claros (CTA) y menús de navegación fáciles de encontrar y dispuestos de forma lógica.
- Optimizar tu sitio web para móviles
La mayor parte del tráfico web procede de dispositivos móviles. Según agencias de diseño web, la principal razón por la que los visitantes abandonan los sitios web es que no se adaptan a los dispositivos móviles.
Para optimizar el diseño de tu sitio debes reducir su tamaño para que se cargue rápidamente. Además, hay que asegurarse de que responda a las diferentes pantallas de los distintos dispositivos. También se aconseja reducir la cantidad de información en la pantalla y aumentar el tamaño de ciertos elementos para causar mayor impacto en el usuario.
- Utilizar chatbots
La mayoría de los agentes de atención al cliente coinciden en que los clientes tienen cada vez más expectativas de servicio. Así que otra de las estrategias de customer journey es hacer uso de chatbots, los cuales pueden ayudar a aliviar algunas de las cargas gestionando las consultas de las necesidades de los clientes utilizando la Inteligencia Artificial.
Los chatbots son excelentes agentes de atención al cliente, ya que pueden aprender hasta el 92% de las preguntas de los visitantes en solo cinco meses. Pueden proporcionar un servicio inmediato y de alta calidad sin que el cliente tenga que esperar días para que un agente de atención al cliente responda.
Puedes entrenar a tu chatbot para que proporcione primero recomendaciones a tus clientes u ofrezcan promociones personalizadas en función de sus consultas, esto ayuda a aumentar las posibilidades de que los clientes compren.
Conoce también más información a cerca del buyer journey .
- Realizar pruebas A/B
Una de las mejores formas de averiguar qué mejora la estrategia del customer journey es recopilar datos en tiempo real a través de encuestas.
Una gran cantidad de empresas afirman que el seguimiento de los datos de los usuarios tiene un impacto en las decisiones de diseño.
Las pruebas A/B son una forma de determinar qué versión de tu sitio web lleva a tus clientes a realizar los comportamientos que quieres que hagan y te muestra qué estrategia de customer journey es la más exitosa.
Te recomendamos revisar estas herramientas para monitorear el customer journey .
- Ofrecer opciones de autoservicio
Los clientes no siempre quieren contactar con un agente de atención. En su lugar, a menudo quieren buscar información por sí mismos. Por lo tanto, es esencial tener un centro de ayuda donde puedan buscar y encontrar respuestas a sus preguntas.
El 65% de las marcas no tienen una base de conocimientos en la que el cliente pueda buscar.
Estos son algunos ejemplos de tipos de autoservicio que puedes ofrecer.
- Optimizar tu experiencia omnicanal
Las marcas de alto rendimiento ofrecen un soporte omnicanal que da al customer journey una sensación de amplitud y les hace sentir que son conocidos y recordados por las marcas en todas las plataformas.
Los consumidores admiten que se sienten más cerca de la marca cuando ésta reconoce que son la misma persona a través de múltiples puntos de contacto. Los clientes se sienten frustrados cuando las marcas no pueden ofrecer una experiencia coherente cuando pasan de una plataforma a otra.
Descubre cómo crear tu propia estrategia omnicanal .
- Facilitar las transacciones
Muchas marcas dificultan el pago a los clientes más de lo que deberían. Esto hace que los clientes abandonen justo en el momento decisivo.
Los consumidores afirman que son más propensos a comprar en marcas donde las transacciones son rápidas y fáciles.
El proceso debe ser sencillo y ofrecer varios métodos de pago para que los clientes puedan elegir el que les resulte más fácil. Hay que ir más allá de las tarjetas de crédito y de PayPal e incluso considerar otras formas de pago como el Bitcoin.
- Seguimiento del abandono
El abandono de carritos de compra es muy común. Muchos compradores acumulan sus carros y sólo el 40% completa la compra.
El seguimiento del abandono con un correo electrónico puede hacer que el cliente vuelva al ciclo de compra.
Los mensajes de correo electrónico sobre el abandono del carrito tienen un éxito sorprendente a la hora de convencer a los consumidores de que compren.
- Controla los análisis de tus clientes
Si quieres impulsar a tus clientes a completar su journey, necesitas analizar los datos. Esto te ayudará a entender qué elementos impulsan a los clientes al éxito y cuáles impulsan la pérdida de clientes . Si no recopilas y analizsa los datos, no sabrá qué está obstaculizando tu estrategia de customer journey.
¿Sabes por qué los clientes dejan de utilizar tus servicios? Supervisa el comportamiento y recopila datos de los clientes.
Es esencial determinar qué indicadores clave de rendimiento (KPI) vas a medir y cuándo. Esto ayuda a tomar decisiones futuras y orienta tu estrategia.
¿Cómo utilizar el customer journey para mejorar la experiencia del cliente?
Los clientes esperan que cada intercambio con una marca sea fluido desde el principio. Comprender las interacciones en cada punto de contacto te ayuda a satisfacer las necesidades del cliente y mejora la eficiencia de tu negocio.
« Las empresas centradas en el cliente son un 60% más rentables que las que no lo están «. – Deloitte y Touche
Para trazar con precisión el journey, considera cada etapa de la compra de un producto. En cada etapa, anota lo que siente el cliente y las acciones que debe realizar para seguir adelante.
Examina las emociones en cada punto de contacto y valore las experiencias. ¿Es positiva o negativa?
Empieza a atar cabos e identifica qué lagunas no están a la altura de las expectativas de tus clientes. Este ejercicio te ayudará a formular y descifrar dónde puedes tener un impacto más significativo en la mejora de la experiencia.
Recopila información sobre la satisfacción del cliente para obtener resultados más precisos
Incluye las puntuaciones de satisfacción de tus clientes al trazar su plantilla de customer journey. Esta información adicional ayuda a validar las lagunas o suposiciones que haces a partir del mapeo.
Por ejemplo, tu cliente califica una puntuación CSAT de 3 en tu punto de compra y da una puntuación de 8 después de la compra. Sabrás inmediatamente que tu punto de venta requiere atención.
Examina varias puntuaciones de satisfacción del cliente para encontrar los puntos más críticos. Si hay un punto de contacto que obtiene una mala puntuación para la mayoría de los clientes, comienza tus mejoras por ahí.Comienza a seguir el customer journey. QuestionPro ofrece algunas de las herramientas de experiencia del cliente más avanzadas, como el customer journey mapping software .
El Customer Journey es una excelente herramienta pues te informa de las prioridades de desarrollo y ayuda a centrar tu presupuesto de marketing en puntos de contacto que pueden optimizar los resultados de los usuarios y aumentar los ingresos de tu negocio.
Tres cuartas partes de los profesionales coinciden en que la experiencia del cliente tiene un impacto significativo en la fidelidad. Si los clientes se sienten frustrados al interactuar con tu marca, lo más probable es que no vuelvan.
Como parte de la experiencia del cliente, el viaje debe ser una experiencia fácil y agradable, esto significa procesos simples y un servicio al cliente de primera categoría.
Ahora que sabes qué es Customer Journey y cómo crear tu propia estrategia, comienza a evaluar tu mapa del recorrido del cliente. En QuestionPro contamos con una herramienta especializada en la gestión de la experiencia del cliente: QuestionPro CX y también con la plataforma ideal para crear tu propio customer journey y tener visibilidad de cada paso del cliente: SuiteCX . Solicita una demostración y conoce cómo puedes dar seguimiento a lo que sucede en cada punto del contacto con tus clientes.
MAS COMO ESTO

Modelos predictivo: de los datos a la toma de decisiones inteligente
Mar 18, 2024

Análisis de impacto al negocio: ¿Qué es y cómo realizarlo?
Mar 15, 2024

Los 10 mejores software de gestión de suscripciones para tu empresa
Mar 14, 2024

Ponderación RIM: ¿Qué es, beneficios y cómo calcularla?
Mar 13, 2024
Otras categorías
- Beneficios para empleados
- Capacitación
- Compromiso con el cliente
- Compromiso de los empleados
- Comunidades
- Comunidades en línea
- Conocimiento de la marca
- Entrenamiento
- Estrategia de marketing
- Estudios de casos
- Experiencia del Cliente
- Fuerza de Trabajo
- Funciones mejoradas
- Herramientas y aplicaciones de investigación
- InsightsHub
- Interceptar
- Investigación académica
- Investigación de Consumidores
- Investigación de mercado
- Lealtad del cliente
- Mejores Practicas
- Mercadotecnia
- Productos de QuestionPro
- Productos QuestionPro
- Retención de empleados
- Satisfacción al cliente
- Sin categorizar
- Software para Encuestas
- Startup @es
- Toma de decisiones
- Marketing digital
Customer journey: qué es y cómo definirlo en tu estrategia
¿Has pensado alguna vez en que todas las compras que hacemos implican un proceso de compra previo al momento de la transacción? A este proceso le llamamos customer journey y engloba todas las fases por las que pasa una persona desde que identifica que tiene una necesidad hasta que adquiere un producto o servicio para solucionarla.
En este artículo definiré qué es el customer journey, qué fases tiene y cómo podemos definirlo en nuestra estrategia de marketing. ¡Sigue leyendo!
¿Qué es el customer journey? Definición y para qué sirve
El customer journey es el conjunto de interacciones que tiene un consumidor con una organización en el proceso de comprar o conseguir algo. La traducción literal del concepto customer journey en español sería algo parecido a “viaje del cliente”.
Por ejemplo, intenta imaginar el proceso de hacer un viaje en avión comprando los billetes por tu cuenta. Un posible escenario sería el siguiente ejemplo:
- Ves un anuncio en las redes sociales sobre un destino que está en oferta, pero al cabo de un rato sigues trabajando y te olvidas de ello.
- Después de unos días, recibes una newsletter por email con la misma oferta. Te acuerdas de que estabas planteando aprovechar la oferta.
- Entras en el sitio web de la aerolínea, introduces las fechas del viaje.
- Ves los precios y las condiciones, y decides comprar los billetes.
- Al cabo de un rato recibes un email de confirmación de la compra.
- Te descargas la aplicación de la aerolínea para tener los billetes en tu teléfono sin tener que imprimirlos.
- Unos días antes del viaje, recibes otro email recordándote la fecha y con instrucciones para prepararte para el vuelo.
- El día del viaje, acudes al aeropuerto y te diriges al quiosco electrónico de la aerolínea para hacer el check in.
- Interactúas con el personal del mostrador para entregar tu equipaje y te diriges a la puerta de embarque.
- Después del viaje, recibes una notificación en la aplicación de la aerolínea para que rellenes una encuesta de satisfacción.
- Todos estos pasos implican interacciones entre tú (el consumidor) y la aerolínea (la organización). Estas interacciones son lo que se conoce como puntos de contacto o touchpoints , y en conjunto forman este customer journey que acabamos de explicar.
- Fíjate cómo los puntos de contacto pueden darse en muchos canales, ya sean online o offline, en persona o por medios digitales, por teléfono, etc. Tenemos que ser conscientes de cada touchpoint por el que pasan nuestros consumidores para entender su customer journey.
Este ejemplo ilustra de manera práctica el concepto y la importancia de comprender el significado de customer journey para mejorar la experiencia de nuestros clientes.
El customer journey aplicado al inbound marketing
Cuando lo explicamos en el contexto del inbound marketing, el customer journey es el proceso por el que pasa una persona para comprar un producto o servicio en base a una necesidad que se le plantea, y toda la investigación y consideración de alternativas que hay entremedio. Es lo mismo que el proceso de compra del que hemos hablado otras veces en el blog y la página de InboundCycle. Encontrarás más información sobre el proceso de compra y sus fases en este contenido o en nuestra guía gratuita El ciclo de venta vs. el ciclo de compra . En el pasado se entendía que el ciclo o proceso de compra coincidía completamente con el ciclo de venta, pero actualmente el consumidor investiga y se informa antes de iniciar cualquier proceso comercial y tomar una decisión de compra . De hecho, un estudio de Corporate Executive Board (ahora parte de Gartner) de 2013 popularizó la idea de que el 57% de la decisión de compra B2B está tomada antes del primer contacto con ventas. Por supuesto, esta cifra es una gran generalización, pero sí es importante entender que el consumidor actual prefiere hacer una investigación previa por su cuenta y sin la influencia de un comercial.
Asimismo, definir y mapear este viaje del consumidor permite entender todo el proceso de compra, cuáles son las necesidades en todo momento del buyer persona, cómo investiga y qué tipo de información necesita en cada fase para poder avanzar .
Todo eso, en una estrategia de inbound marketing nos sirve para entender las temáticas de los contenidos que vamos a crear, también qué formatos de contenidos tenemos que crear y en qué canales tenemos que distribuirlo.
Por tanto, necesitamos tener muy bien definidos nuestros buyer personas antes de poder construir el customer journey . Como habrás leído, el buyer persona es el perfil de cliente ideal en el que nos basamos para crear una estrategia de inbound marketing, ya que todos los contenidos y acciones giran a su alrededor. Si quieres más información sobre el buyer persona, no te pierdas este post . También te recomiendo nuestra plantilla personalizable para crear buyer personas .

Además, la definición del customer journey también nos puede ayudar a conocer mejor nuestros buyer personas y a sacarles más partido. ¿Cómo?
Uno de los elementos centrales del buyer persona son los pain points, que pueden ser:
- Frustraciones
- Ineficiencias
Necesidades
- Motivaciones
- Oportunidades perdidas
- Costes excesivos
Puede que un buyer persona tenga un pain point determinado, que varios buyer personas lo tengan o que todo el mundo en la empresa los tenga.
Lo que empuja al buyer persona a empezar una investigación para obtener información son estos pain points. Por ejemplo, imagina que una persona joven está preocupada por su propia imagen y quiere mejorar en este aspecto. Puede iniciar una investigación y descubrir que una posible solución a su dolor es operarse de la vista para poder quitarse las gafas definitivamente. La investigación llega a mostrarle qué proveedores pueden ayudarle a resolver el pain point, y luego decide una solución y hace la compra final. ¡Más adelante te cuento más sobre este punto!

Fases del customer journey
Veamos qué fases tiene de forma genérica un customer journey aplicado a un proceso de compra. Uno de los temas que lleva a más confusión es cuál es la primera fase de este ciclo de compra.
Fase 0: awareness o concienciación
Pues bien, podemos decir que la fase 0 del customer journey es la fase de awareness o concienciación .
En esta fase el consumidor se da cuenta de que tiene un dolor latente , pero no sabe si debe hacer algo al respecto, qué lo está causando, cómo solucionarlo ni cómo definirlo. ¡También puede ser que el consumidor ni se dé cuenta de que tiene este pain point! El buyer persona que se encuentra en esta fase no está buscando aún soluciones ni haciendo ninguna investigación, hasta que llega un momento en el que empieza a buscar soluciones. Puede ser porque el dolor haya incrementado, por curiosidad, etc. Es importante mencionar que nos estamos refiriendo a los pain points como “dolor” pero evidentemente no tiene por qué ser un dolor físico, sino una necesidad, un problema o una motivación a satisfacer. ¡Recuérdalo! Las fases detalladas a continuación pueden corresponder a actividades de marketing o de ventas, y también hay una parte del customer journey que va más allá de la transacción, como la implementación de la solución elegida. Pero este no es el foco de este artículo, de modo que no lo trataremos en este post.
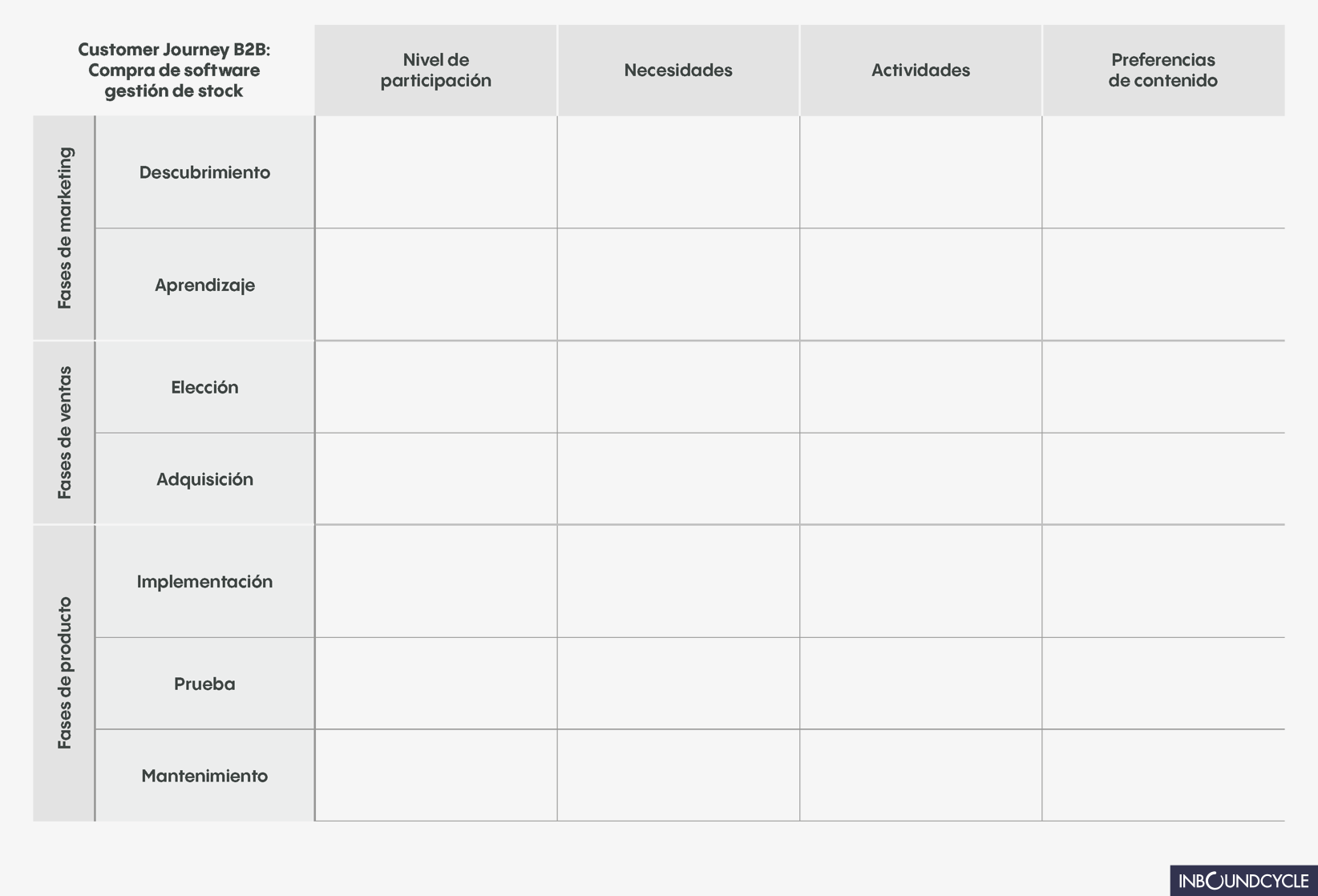
Fases de marketing
Justo después de la fase de concienciación vienen las fases del customer journey sobre las que pueden incidir nuestras acciones de marketing. Son las fases de discovering y learning . ¡Conócelas!
Fase 1: discovering o descubrimiento
En primer lugar, en la fase de discovering o descubrimiento el consumidor ya es consciente de que tiene una necesidad y busca informarse sobre el tema .
En esta investigación se define el problema, se entienden las causas y cómo otras personas lo han afrontado, y se aprenden buenas prácticas. Es, por lo tanto, una gran oportunidad para el departamento de marketing para presentar contenidos educativos que cubran esta necesidad y creen una urgencia para resolverla .
Fase 2: learning o aprendizaje
Y, en segundo lugar, encontramos la fase de learning o aprendizaje en la que el consumidor aprende qué soluciones existen a su pain point . Se tienen en cuenta las distintas opciones que hay y se empieza a crear una lista con ellas. Desde marketing podemos influir sobre esta fase con contenidos MOFU , enfocados a establecer un criterio de compra y a identificar necesidades de negocio y técnicas.
Fases de ventas
A continuación, encontramos las fases del proceso de compra en las que normalmente interviene el equipo de ventas. Son las fases de elección y adquisición.
Fase 3: choosing o elección
Inmediatamente después de la fase de aprendizaje tiene lugar la fase de choosing o elección , la cual requiere una implicación activa del equipo comercial. El consumidor reduce su lista de opciones y posibles soluciones al pain point a un pequeño grupo y empieza a hacer pruebas de productos y a evaluar proveedores , y finalmente toma una decisión final . La empresa tiene que demostrar que es el mejor proveedor gracias al contenido, el cual validará su experiencia en el campo y demostrará que la inversión va a ser rentable.
Fase 4: purchasing o adquisición
Y, finalmente, tenemos la fase de purchasing o adquisición , en la que el consumidor se prepara para poseer y mantener la solución. ¡Eso es todo! A partir de aquí, las fases posteriores ya corresponden a los departamentos de servicio de atención al cliente, operaciones, cuentas, etc., y se basan en mantener la satisfacción del cliente y a implementar la solución elegida con éxito . Es por esto que en este post no nos centraremos en estas fases ni las desarrollaremos.

Dimensiones de las fases del customer journey
Una vez tenemos las fases definidas, deberemos obtener información de cada una de las fases de nuestros compradores . Para hacerlo, necesitamos entender 4 dimensiones clave de cada una de las fases , lo cual nos va a permitir entender nuestros buyer personas y cómo avanzan en el customer journey.
Entender estas dimensiones nos da información sobre cómo informar e influenciar a los consumidores y elaborar mensajes para la persona adecuada en el momento adecuado. Estas dimensiones son las que veremos a continuación.
Nivel de participación
El nivel de participaciónace referencia al papel que juega el buyer persona dentro del círculo de decisión , ya sea dentro de la empresa en B2B o bien con amigos, familiares, pareja, etc., en el caso de B2C. Este nivel de participación puede ser:
- Drivers : dirigen el proceso en la fase actual.
- Participantes : toman parte en actividades en la fase actual.
- Gate-keepers : no participan en la fase actual, pero se necesita su aprobación para pasar de fase, por lo que tenemos que tener en cuenta sus necesidades.
- No implicados : no participan en la decisión.
Se refieren a qué necesita el consumidor para avanzar a la siguiente fase del customer journey. Puede ser información, aprobaciones de presupuesto, alineamiento con su equipo, etc.
Actividades
En el apartado de actividades hablamos de lo que hace el buyer persona en la fase actual del customer journey para avanzar. Pueden ser reuniones internas, recopilar información, reunirse con otros miembros del equipo, etc.
Preferencias de contenido
Qué tipo de contenido desea recibir el buyer persona en cada fase, incluyendo el nivel de profundidad del contenido, el formato, etc.
Como veíamos antes, la información del customer journey complementa perfectamente a los buyer personas . La descripción del buyer persona nos indica a quién nos dirigimos, cuáles son sus atributos, su psicología, su perfil, etc. Por otro lado, el customer journey nos indica qué camino sigue este buyer persona , cuál es la experiencia del cliente durante todo el ciclo de compra, por qué fases pasa antes de comprar un producto o contratar un servicio, qué necesita en todo momento, etc.
Si te fijas bien, los dos son elementos necesarios en una estrategia de marketing. Si solamente tenemos el buyer persona, nos falta mucha información para adaptar nuestro mensaje, nuestras comunicaciones, etc., y saber cómo adaptar los contenidos a cada caso. Evidentemente, el caso contrario tampoco es posible: mapear el customer journey sin entender los buyer personas evitará que podamos conocer cómo son los perfiles que pasan por aquellas fases. ¡Quédate con la idea!

Beneficios de mapear el customer journey
Si has llegado hasta aquí, probablemente estés pensando que el proceso de conocer el customer journey de tus consumidores es demasiado complicado. Implica bastante trabajo, reunir mucha información y consultar a muchas personas.
Seguramente te preguntes: ¿es necesario investigar este viaje del cliente si ya tengo mi buyer persona definido? La verdad es que sí, y es que son elementos estratégicos muy distintos. Mientras que el buyer persona es una visión estática del perfil del consumidor, el customer journey nos permite entender por qué fases y pasos va pasando, cómo se informa o cómo compra y esto es vital para diseñar las comunicaciones y acciones necesarias en un plan de inbound marketing.
Para convencerte totalmente, estos son algunos de los beneficios que obtendrás de conocer a la perfección el customer journey de tus clientes:
- Podrás conseguir que tus clientes te encuentren cuando necesiten tus productos o servicios. Como entenderás sus necesidades y qué proceso siguen para resolverlas, podrás anticiparte y crear campañas de marketing que atraigan compradores potenciales (en lugar de tener que ir a buscarlos).
- Te permitirá entender perfectamente tu buyer persona . Como hemos explicado anteriormente, el buyer persona tiene un aspecto comportamental que solo se entiende a través de la investigación del customer journey.
- Serás capaz de ofrecer una mejor experiencia a tus clientes . Tu negocio podrá ser proactivo porque conocerás los puntos de frustración del cliente y te anticiparás a sus necesidades.
- Toda la organización (incluyendo el equipo directivo) tendrá el foco puesto en el consumidor , y no en los productos o servicios.
Poniendo en práctica todo lo que te cuento en este post podrás crear y entregar contenido de calidad y bien segmentado a partir del mapa del customer journey que habremos generado.
En realidad, crear contenido relevante para las necesidades del comprador permite establecer confianza y destacar frente a nuestros competidores. ¿Y quién no lo quiere?
Además, conocer el customer journey también permite saber cómo impactar en la toma de decisiones de nuestros compradores gracias a este contenido de valor.
También conoceremos el pensamiento, las necesidades y las acciones de los compradores y podremos anticiparnos para ayudarles en su customer journey para, finalmente, demostrarles que somos la mejor solución para sus pain points.
Cómo crear un mapa del customer journey paso a paso
Ahora que ya hemos explicado qué es el customer journey y qué información necesitamos saber de cada fase para mapearlo correctamente, junto con los beneficios que nos puede ofrecer, veamos qué pasos tenemos que seguir para documentarlo correctamente.
El mapa del customer journey es una representación gráfica de este proceso que sigue el consumidor. Documentarlo de forma visual ayuda a los equipos de marketing y ventas (y otras personas de la organización) a entender qué interacciones tienen los consumidores con la empresa. Es importante que sea así ya que, normalmente, los procesos de compra no son lineales sino que acaban siendo bastante caóticos y con cambios de dirección constantes.
Paso 1: Entender la finalidad de mapear el customer journey
Antes de empezar a representar este viaje del cliente y sus puntos de contacto, reflexiona sobre el objetivo de este trabajo: ¿Necesitas mejorar la experiencia de usuario de tu sitio web? ¿Pretendes entender qué contenidos necesita el consumidor para avanzar en su decisión de compra? ¿Qué decisiones de compra necesitas optimizar o para qué productos necesitas mejorar la experiencia de compra?
Paso 2: Define tu buyer persona
Al principio del artículo ya hemos remarcado la importancia de conocer el buyer persona para diseñar el customer journey. Tal y como se explica en nuestras guías de creación de buyer personas, necesitarás recopilar datos y hacer entrevistas para conocer mejor sus motivaciones, necesidades y preferencias de compra.
Una vez hecho este trabajo, decide cuáles son los buyer personas clave para el viaje del cliente que estás mapeando (idealmente deberías trabajar 1 buyer persona pero también puedes usar 2).
Paso 3: Identifica los puntos de contacto del proceso
Crea una lista de todos los puntos de contacto o touchpoints que tiene tu buyer persona en su proceso, Es decir, las interacciones que tiene con tu organización en su proceso de compra. Estas interacciones entre la organización y el consumidor son oportunidades ideales para generar experiencias positivas.
Recuerda los ejemplos que hemos ido viendo a lo largo de este artículo y ten en cuenta que los puntos de contacto pueden ocurrir en muchos canales distintos, ya sean online o offline:
- Ubicación física como tienda, oficina, consulta, etc.
- Por teléfono.
- Redes sociales.
- Boca a boca.
- Aplicaciones móviles.
- Sitios de reseñas y opiniones.
Paso 4: Representa gráficamente y de forma ordenada los puntos de contacto
Ahora que ya tienes una lista de los touchpoints que ocurren en el viaje de tu consumidor, haz una representación visual de este proceso . A continuación te muestro un ejemplo para que te sirvan de inspiración:
Paso 5: Testear y optimizar el customer journey
Siempre es recomendable vivir en primera persona un proceso para entender sus debilidades y oportunidades de mejora. En este caso, también es buena idea empezar el proceso desde el principio, identificar los puntos de contacto a medida que vayan sucediendo (y tratando de averiguar si se te ha pasado alguno por alto) y seguir mejorando la experiencia.
Por ejemplo, siguiendo el journey de compra de billetes de avión, seguiríamos todo el proceso de reserva hasta después del viaje para poder vivir la experiencia y decidir cómo mejorarla.
También es importante recopilar datos y más información cuantitativa para saber qué puntos de contacto generan más problemas, quejas o frustración, identificando dónde hay más pérdida de clientes.
Tipos de mapas del customer journey
¿Te acuerdas de que el primer paso para mapear el customer journey era entender su objetivo? El resultado de este primer paso definirá cuál de los 4 tipos de customer journey acabarás creando.
No es lo mismo mapear el customer journey del proceso de compra en un ecommerce (el cual ocurre en un período de tiempo muy concreto) que el de la compra de una vivienda (mucho más largo) o de un producto que se use constantemente a lo largo del día (como una app que monitoree el ritmo cardíaco).
En función de si tienes que entender el día a día del consumidor o cómo consigue resolver una acción concreta, entre otras cosas, tendrás que usar uno de estos tipos de mapas del customer journey :
Estado actual
Intentan mostrar qué hace y piensa el consumidor en un momento muy concreto del tiempo. Son ideales para representar procesos concretos, como por ejemplo el proceso de registro en un sitio web, el unboxing de un producto o la visita a una oficina física de la empresa. Muestran la experiencia tal y como ocurre hoy en día.
Un día en mi vida
Son parecidos al tipo de mapa que ya hemos visto, en el sentido de que se fijan en el momento actual. Pero tienen una visión más amplia y muestran todo lo que ocurre en el día a día de la vida del consumidor, ya esté relacionado con tu empresa o no. Por ejemplo, a la hora de diseñar un producto pensado para cubrir necesidades no resueltas en el día a día del consumidor, o para diseñar un gadget o una app móvil que se usará a lo largo de todo el día.
Estado futuro
A diferencia de los dos anteriores, que muestran la realidad actual del consumidor, este tipo de mapas muestra situaciones futuras o ideales. Por lo tanto, pueden ofrecer más ideas innovadoras al no tener en cuenta las limitaciones actuales. ¿Cómo funcionará un producto o un servicio cuando se desarrolle una nueva tecnología? Este tipo de mapa es ideal para mostrarlo.
Plano del servicio
También llamados “service blueprints”, estos mapas representan todos los procesos, interacciones y tecnologías (ya sean percibidos o no por el consumidor) implicados en la creación de una experiencia para el consumidor. Por ejemplo, podría ser ideal para representar el proceso de reservar cita en una oficina bancaria para reunirse con un consultor e informarse sobre la contratación de una hipoteca (con todas las interacciones que ocurren).
Cómo reunir la información para mapear el customer journey
Después de entender los pasos para dibujar el customer journey, solamente nos falta saber cómo conseguir toda esta información. Una opción que hemos comentado ya en otras ocasiones para recopilar esta información es la de tener reuniones internas con otras personas de la organización que tengan contacto directo con nuestro buyer persona :
- Equipo comercial.
- Departamento de servicio de atención al cliente.
- Departamento de cuentas o de servicio de atención al cliente.
Evidentemente, cada equipo tendrá más conocimientos de las fases en las que intervienen, por ejemplo, el equipo comercial será experto en las fases de elección y adquisición. Por otro lado, una gran opción es entrevistar a nuestros clientes existentes . Tenemos que recordar que el buyer persona siempre va a ser nuestro cliente ideal, el cual no tiene por qué ser todos los clientes que tenemos actualmente. En caso de no estar alineados, deberemos intentar entrevistar a los clientes que sí coincidan con nuestro buyer persona para conocer el customer journey con precisión. Con un par de entrevistas por buyer persona tendremos suficiente para poder recopilar esta información. ¡Pruébalo!
Como hemos explicado anteriormente, también puedes recurrir a información más cuantitativa proporcionada por herramientas de analítica, como Google Analytics, información del CRM o encuestas de satisfacción.
Por supuesto, la investigación más empírica también puede ayudar a sacar algunas conclusiones importantes acerca del viaje del cliente. Por ejemplo, las redes sociales son extremadamente útiles como termómetro para saber qué piensan los clientes. Cuando una empresa genera experiencias muy positivas (y muy negativas) en sus clientes, éstos acostumbran a hacerlo público en las redes. Una simple búsqueda en redes sociales puede proporcionar mucha información del customer journey que las herramientas de analítica no te darán.
Con todo, en este momento tendremos ya nuestros buyer persona definidos, el customer journey mapeado con sus fases y las dimensiones de cada fase, y tendremos la información en cada una de estas últimas. Solamente nos quedará integrarlo todo y construir el mapa del customer journey con toda la información y empezar a usar esta poderosa herramienta para crear una mejor estrategia de contenidos para nuestra empresa.
2 ejemplos de customer journey
Veamos a continuación 2 ejemplos muy distintos para entender cómo aplica a distintos modelos de negocio el concepto de customer journey, las distintas fases que lo componen y los atributos de cada una de ellas.
Ejemplo de customer journey de empresa B2B
En primer lugar, nos centraremos en el caso imaginario de una empresa que vende una solución tecnológica que permite hacer previsiones de stock a negocios con tienda online. Uno de los buyer personas principales de esta empresa podría ser un responsable de operaciones que controla la logística del negocio, y que frecuentemente tiene roturas de stock.
Las distintas fases de su customer journey podrían ser:
1. Descubrimiento
La empresa de este consumidor lanza una campaña de Black Friday muy problemática porque muchos de los productos estrella se han quedado sin stock. La empresa podría haber tenido muchas más ventas, ya que la demanda era muy superior a la oferta, y este error es debido a una mala planificación de existencias.
Este jefe de operaciones es responsable del error y se da cuenta de que no puede volver a ocurrir, así que necesita alguna solución para no tener más roturas de stock en momentos de alta demanda. Empieza a investigar en Google sobre el tema, y consume blogs y contenidos sobre gestión de stock en grupos de LinkedIn y otras redes sociales.
2. Aprendizaje
Después de varias semanas informándose intensamente sobre cómo hacer mejor su trabajo, ha leído varias veces sobre los software de gestión de almacenes y de stock.
El negocio está en una fase bastante inicial y todo le parece muy sofisticado, pero se da cuenta de que sin soporte tecnológico no será capaz de escalar la empresa sin problemas. Aquí sigue investigando por su cuenta y reúne información sobre los principales software que existen para gestionar stock, contacta con varios proveedores y acude a varias demos de herramientas para entender cómo funcionan. Necesita información mucho más concreta del software.
3. Elección
Tras 2 meses reuniendo información y formando un criterio, este responsable de operaciones tiene que decidir entre 3 herramientas distintas que ha encontrado (después de descartar varias) y que cumplen con lo que está buscando. Será una inversión grande, así que implica directamente a la CEO de la empresa para tomar juntos la decisión.
Les preocupa el presupuesto, pero les preocupa más que sea una herramienta fácil de usar y con un buen soporte, pues no disponen de un equipo de IT propio. Necesitan informarse más sobre qué criterios son los más importantes a la hora de elegir un software de este tipo, y también busca opiniones de usuarios de las 3 herramientas para contrastar cómo son a la práctica.
4. Adquisición
Después de 1 mes adicional de evaluación, se acaban decantando por una de las herramientas. Él prefería la más cara, pero la CEO decidió quedarse con la segunda porque les encajaba en los presupuestos. Contactan con el proveedor y les piden una oferta final. Para ellos es muy importante poder negociar unas buenas condiciones de pago, ya que el flujo de caja es un reto en el negocio. No pueden asumir un pago anual por avanzado, así que intentarán negociar pago mensual o trimestral. Si todo sale bien, acaban contratando la solución y empieza la implementación.

Ejemplo de customer journey de empresa B2C
Veamos ahora cómo el mismo concepto puede aplicarse perfectamente a negocios que vendan directamente al consumidor final. Este segundo ejemplo lo desarrollaremos sobre una empresa que ofrece servicios de intercambios en el extranjero para estudiantes universitarios. El buyer persona de esta segunda empresa es una chica que está terminando sus estudios universitarios (está en último año normalmente) y que busca poder vivir unos meses en otro país mientras termina su carrera. Las fases de su customer journey podrían ser algo como:
Nuestro buyer persona se encuentra en el penúltimo año de carrera. Ve que muchos de sus compañeros y compañeras están pensando en hacer intercambios en otros países durante el próximo curso, para terminar la carrera con un año muy diferente. No quiere ser menos y empieza a preguntar a sus compañeras de clase, a la vez que busca en Youtube experiencias similares de otras personas de su edad. Necesita saber si es algo para ella, si lo podrá aprovechar y cuál es la mejor forma de organizarlo. No sabe por dónde empezar.
Después de unos días investigando e informándose, ha encontrado mucho contenido de una empresa que se encarga de organizar estas experiencias para estudiantes, con tal de que no tengan que preocuparse por nada. Lo empieza a valorar como opción. Ve que organizarlo por su cuenta es algo complicado, no sabe cómo tramitar los visados, qué universidades le permiten convalidar sus asignaturas, qué países son más seguros… ¡tiene tantas dudas!
Empieza a descartar la opción de organizarlo por su cuenta, cuanto más lee en el blog de esta empresa que organiza los intercambios, más se da cuenta de las dificultades que implica.
Cuando ha pasado un mes desde que empezó a investigar, ya ha reunido suficiente información para saber qué necesita para prepararse. Está convencida de hacer la experiencia, pero tiene que valorar si finalmente organiza el intercambio por su cuenta directamente con la universidad, o lo hace con la empresa que encontró. Lo consulta con sus conocidos y familia. Cuando lo consulta con sus padres, le dicen que vale la pena pagar el precio extra para ir sobre seguro.
Finalmente, nuestro buyer persona se pone en contacto con la empresa organizadora de intercambios. Necesita saber un precio orientativo, porque tendrá que consultarlo con sus padres (que tomarán la decisión final). También necesita asegurarse de que la universidad que le propongan para el intercambio le convalide las asignaturas, con tal de no perder un curso entero de carrera. Una vez todo esto esté resuelto, estará preparada para contratar el intercambio.
Como ves, en este segundo ejemplo encontramos perfectamente los mismos elementos que forman un customer journey. Las 4 fases de marketing y ventas están presentes, y en cada una de ellas existen una serie de necesidades del buyer persona, actividades que realiza para satisfacerlas (con distintos roles en cada caso) y contenido que consume para formar un criterio de compra.
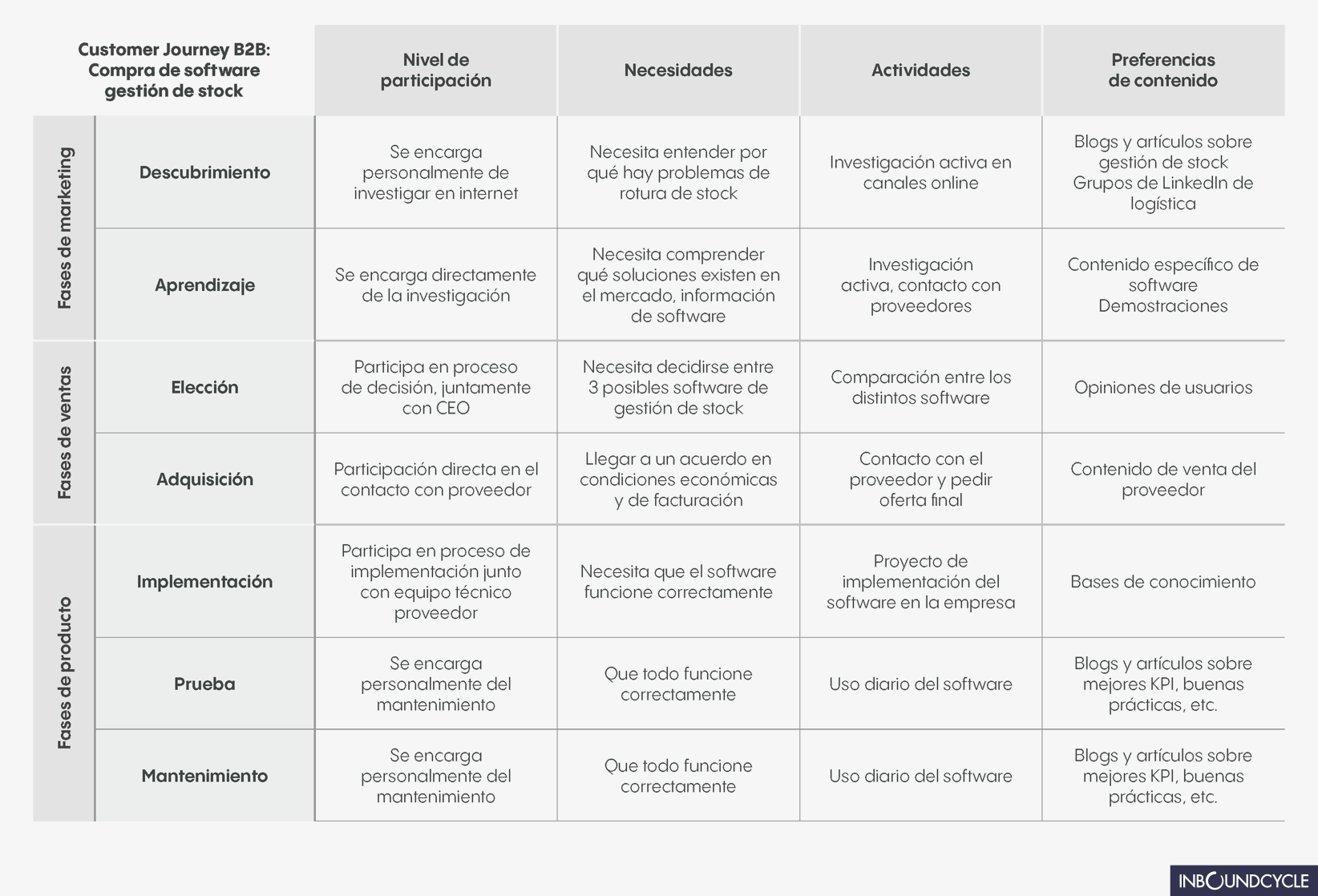
¿Estás a punto para identificar tu customer journey y planificar tu estrategia de marketing digital en base a los resultados obtenidos? Si todavía te quedan dudas o te apetece contarme tu experiencia, ¡sigo contigo en el área de comentarios!

Publicado originalmente el 10 de agosto de 2018, actualizado el 24 de marzo de 2022.
Revisado y validado por Susana Meijomil , Inbound Content Manager en InboundCycle.
Susana Meijomil
SEO & Content Manager de InboundCycle, responsable de la planificación, producción y publicación de contenido en nuestro blog, así como de la estrategia SEO. Además, ha sido directora del Curso Especializado Online en Inbound Marketing de IEBS Business School.
Think with Google - B2B's Digital Evolution
Bodine&Co. - The 4 Types of Customer Journey Maps
Mark Truelson - Mapping The Consumer Path Throughout The 5A’s
UXPressia - Create Service Blueprint in UXPressia
FAQs sobre el customer journey
¿dónde empieza el customer journey.
El customer journey generalmente empieza cuando el consumidor se da cuenta de que tiene una necesidad o problema a resolver. Este momento de concienciación es lo que desencadena una investigación para encontrar la mejor solución. En algunos casos podemos considerar que el viaje del cliente empieza cuando conocen una marca por primera vez, ya que algunas marcas son capaces de crear nuevas necesidades.
¿Cuál es la finalidad del customer journey?
Conocer el customer journey de tus clientes te permite entender mejor cómo compran para resolver sus necesidades y qué papel tiene tu negocio en este proceso. Ser consciente de todas las interacciones (puntos de contacto) que tienen a través de cualquier canal, como el email o las redes sociales, permite diseñar una mejor experiencia de compra y un mensaje consistente en todas las comunicaciones.
¿Cómo impacta el customer journey?
Conocer el customer journey de tus clientes tiene un alto impacto en el negocio, ya que permite tener conciencia de cómo y por qué te compran y qué obstáculos encuentran en el camino. Disponer de toda esta información es necesario para diseñar una mejor experiencia de compra a través de la optimización de los puntos de contacto.
¿Cómo tiene que ser un buen customer journey?
Diseñar un buen viaje del cliente es clave para dar la mejor experiencia de compra a tus clientes. Cada negocio es único, y las claves para conseguir esta buena experiencia pueden ser muy diferentes. Algunas recomendaciones son:
- Recoger mucho feedback de los clientes y analizarlo constantemente (puedes usar entrevistas o encuestas). Es decir, hacer muchas preguntas a tus clientes y por supuesto escuchar con atención sus respuestas.
- Usar este feedback para entender mejor a tus clientes, sus motivaciones y preferencias de compra.
- Centrarse en reducir la fricción en el proceso de compra.
- En definitiva, poner siempre el cliente en el centro de la estrategia del negocio.
¿Qué es un customer journey map, para qué sirve y cómo se hace?
El customer journey map es una representación visual del viaje del consumidor, es decir, los pasos que sigue una persona para acabar comprando o consiguiendo algo. Hacer esta representación del customer journey permite entender todas las interacciones que tiene el consumidor con el negocio, detectar puntos de fricción y optimizar la experiencia de compra. Para crear este mapa, necesitamos recopilar información del comprador y analizarla para luego representarla de forma esquemática, con el objetivo de alinear toda la organización.
¿Qué son las 5 A usadas al mapear el customer journey?
Se trata de 5 fases que a menudo se usan para explicar y estructurar el viaje del cliente. Las 5 A del customer journey son las siguientes:
- Aware: Descubrir una marca o recibir exposición a ella
- Appeal: Sentir atracción por esa marca o producto
- Ask: Pedir opiniones o consejo
- Act: Actuar, ya sea haciendo una compra, contratando un servicio, etc.
- Advocate: Seguir usando la marca y recomendarla a otros
Por ejemplo, imagina el proceso de compra de un vehículo. En tu día a día recibes mucha exposición a diferentes marcas (aware) pero es posible que algunas de ellas te llamen especialmente la atención y te gusten (appeal). Pides información a tus conocidos sobre esa marca y buscas opiniones y reseñas online (ask), finalmente te decides y acudes al concesionario para hacer la compra del vehículo (act). Pero el proceso no acaba aquí, porque después de varios meses conduciendo tu nueva adquisición, estás muy satisfecho con la compra y recomiendas esa marca a tus conocidos (advocate).
¿Qué son los pain points en el mapa del customer journey?
Los pain points (puntos de dolor) son retos o problemas concretos que crean fricción en el customer journey. A menudo son el desencadenante de ese proceso de compra, como por ejemplo la necesidad de contratar un seguro después de la adquisición de un vehículo. También pueden representar otros retos o molestias que encuentra el cliente a lo largo de su viaje, como los formularios poco amigables, un sistema de reservas que no funcione o una larga cola de espera al llamar a la empresa.
¿Qué son los puntos de contacto del consumidor?
Los puntos de contacto o touch points son cada una de las interacciones que tiene el consumidor con tu marca a lo largo de su customer journey. Estos puntos de contacto pueden ocurrir en diferentes canales, ya sean online o bien offline.
Algunos ejemplos de puntos de contacto son hacer una llamada para pedir cita a una consulta, recibir una newsletter, oír un anuncio en la radio o revisar el estado de un pedido en un chat.
¿Cuáles son las fases del proceso de compra?
El proceso de compra de un producto o servicio consta de las siguientes fases a nivel general: concienciación del problema o necesidad, investigación de soluciones, evaluación de las posibles soluciones, acción o compra y post-compra. Fíjate que tiene un gran paralelismo con las fases del customer journey, y es que podemos considerar el proceso de compra como un tipo de customer journey (aunque también hay customer journeys que no tienen la finalidad de acabar en una compra).
¿Qué es el recorrido del comprador?
El recorrido del comprador son cada una de las fases por las que pasa un consumidor antes de comprar un producto o contratar un servicio. Este proceso empieza por el momento de detectar una necesidad y termina con una compra que tiene el objetivo de resolverla. El concepto de recorrido del comprador es la traducción literal del concepto customer journey, así que lo podemos entender como sinónimo de proceso de compra.
También te pueden interesar...
¿Y tú qué opinas? ¡Déjanos aquí tus comentarios!
This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
Create a simple customer journey with email messaging
- 2 contributors
This article only applies to outbound marketing .
As you engage potential customers, they start by discovering your product, evaluate whether it meets their needs, look for a good offer, and finally make a purchase. We call this process the customer journey . Use customer journeys to create a model that helps you guide the members of a selected marketing segment through this process by using automated messaging, activity generation, interactive decision points, and more.
A simple customer journey can include just two steps: identifying the target segment and creating an activity that addresses the members of that segment. In the following procedure, you'll set up a simple customer journey that sends an email message to all the members of a target segment.
Before you start, you'll need:
- A segment containing the contacts you will send your email to. Your segment should include just one or two fictional contacts with valid email addresses that you can receive mail from, like the one you set up in Create a dynamic segment .
- A marketing email that is both valid and live. You should be able to use the message you designed and published in Create a marketing email and go live .
To create a customer journey that executes a one-time email blast:
Go to Outbound marketing > Marketing Execution > Customer Journeys . This takes you to a list of existing customer journeys. Select New on the command bar.

The New Customer Journey page opens with the Select a Customer Journey Template dialog box shown. Each template provides a starting point for designing a particular type of customer journey. The template dialog box provides tools for searching, browsing, and previewing your template collection. Select Skip to start creating the journey from scratch.

Now you are looking at the customer journey designer. Here, you will assemble a pipeline that defines each step of the journey. Like all journeys, this one starts with the participants, who in this case are the people you specify as part of a market segment.

Select Set audience (or, alternatively, select + ). The Audience properties pane will appear on the right side of the page. Leave the default settings there (for example, Segment selected as the audience source type). Select the segment that you want to target with your campaign in the segment lookup field.

After you select a segment, the first tile populates with the segment name and the Audience pane displays the segment properties.

When your customer journey is live, all contacts start at the Audience tile (the initial step). Contacts move forward depending on the tile rules, similar to a board game. Some tiles hold on to contacts for a while, while other tiles complete an action immediately and send the contact to the next tile in the pipeline. Other tiles can split the path based on contact information or interactions. When the journey is live, you'll be able to see how many contacts are waiting at each tile, along with a few key results associated with the tile.
In this example, you will add one more tile—an Email tile—which sends an email message to each contact who enters the tile.
Select + on the canvas, and then select Send an email from the contextual menu.

Select the email tile on the canvas and select the email message that you want to send. You can use the sample email message you created earlier in Create a marketing email and go live .

Once the email is selected, the Send an email tile populates with the email name and the Send an email properties pane displays the segment preview and properties.
All the segments and email messages that you reference in your customer journey must be live before you can go live with the customer journey itself.
Until now, you've been working in the Designer tab. Now go to the General tab, where you can name your journey and configure its run schedule.
Make the following settings in the General tab:
- Name : Enter a name for the customer journey that you can easily recognize later. This name is internal-only.
- Start date and time : Enter the time when the journey should begin processing contacts. When you select the field, a suggested default time is provided.
- End date and time : Enter the time at which the journey should stop processing contacts. All actions will stop at this time, even if some contacts are still in the middle of the journey. If you're just testing, allow a couple of weeks.
- Time zone : Select your local time zone (if needed). The other dates and times on the page will be displayed relative to this zone.
- Content settings : This should already be set to the default content settings record set for your instance. These settings affect the dynamic content of marketing emails sent by this journey (as mentioned in Create a marketing email and go live ).

While your journey is running, it will continue to process new contacts that join its segment, even if they join after the start date. This means that new contacts can join in at any time until the end date arrives.
On the command bar, select Save to save the work you've done so far.
To make sure your journey includes all required content and settings, select Check for errors in the command bar. Dynamics 365 Customer Insights - Journeys examines the customer journey and then displays results.
If errors were found, you'll see a message at the top of the window and various indicators to show where the problems are. For example, if one of your tiles is misconfigured, you'll see an error icon in the relevant tile, and you can read details about the error by selecting the tile and opening its Properties tab. If you followed this procedure and your email message is live, your journey should pass the error check. If it doesn't, read the error message, fix the reported issue, and try again until it passes.

Your journey is now ready to go. To start the journey, publish it by selecting Go live on the command bar.
Dynamics 365 Customer Insights - Journeys copies the journey to its email marketing service, which executes the journey by processing contacts, performing actions, and collecting results during the time it is set to run. The journey's Status Reason is updated to Live .

If you have sent test messages to yourself, it might take several minutes for your messages to send, so allow some time for them to arrive in your inbox. After they do, open them and load the images. Then you can go back to Dynamics 365 Customer Insights - Journeys and see how your journey is going. The Designer tab now shows information and results for each tile from your pipeline. Open the Insights tab to see detailed analytics.
Many entities in Dynamics 365 Customer Insights - Journeys provide an Insights tab for analyzing the results of your marketing initiatives. For example, try opening the email message you sent with this customer journey and check its Insights tab for even more information.
Additional resources
Sprinklr Service
Sprinklr Social
Works Best With
Sprinklr Insights
Sprinklr Marketing
Marketing Teams
Customer Service Teams
- Unified-CXM
- Company Our Story Leadership Newsroom Partners Careers Culture & Talent Investor Relations Security & Data Privacy
- Resources Learn Services Support CX-WISE Podcast Analyst Reports Product Demo Days eBooks & Reports Events & Webinars Blog Unified-CXM Guide Our Services Training For Agencies Help Center Release Notes Contact Us
- Platform & Technology
- Customer Service
- Marketing & Advertising
- Research & Insights
- Social Media Management
- Customer Stories
- Announcements
- Culture & Talent
How to Map Omnichannel Customer Journey [Steps + Best Practices]
March 18, 2024 • 7 min read
Share this Article
Sounds challenging, right?
Start with building an omnichannel customer journey map. It is the starting point to interpret customers’ digital behaviors and embrace a journey-centric design approach.
In this blog, you will learn a four-step process to craft omnichannel customer journeys with actionable insights and potential risks. Let’s dive in.
What is an omnichannel customer journey?
Omnichannel customer journey vs. single channel customer journey , key components of omnichannel customer journeys , how should you build an omnichannel customer journey map , step 1: internal investigation , step 2: assumption formulation, step 3: external research and validation , step 4: narrative visualization , craft memorable omnichannel customer journey with sprinklr .
An omnichannel customer journey refers to a seamless and integrated experience where customers interact with a company across multiple channels (e.g., website, mobile app, social media, in-store) to complete a task. It also implies maintaining consistency and continuity in interactions and data across all customer-brand interactions.
Defining customer journeys this way is more accurate because:
The landscape of devices and technologies has changed. Modern devices/technologies present brands with new opportunities to engage customers.
The sheer volume of interaction possibilities is endless. Customers can use one device to interact with brands in a myriad of ways, increasing the chances of failure.
Customer expectations have evolved. With expanding interaction possibilities, customers have the means to support enjoyable and cohesive customer journeys that are no longer confined to predetermined channels.
The goal is to ensure that no matter where your customers go to “meet” your business, you meet them right there, without introducing any friction or lag, with your agents being alerted automatically every time a customer switches channels, ensuring a great experience at every step of the way. It's like having a trapeze artist catching your customers mid-air. Micah Solomon CX Expert & Thought Leader
A customer journey map is the visualization of the process a customer undertakes to accomplish a task. An omnichannel customer journey map spans the process across all the interaction channels the customer uses to complete their task.
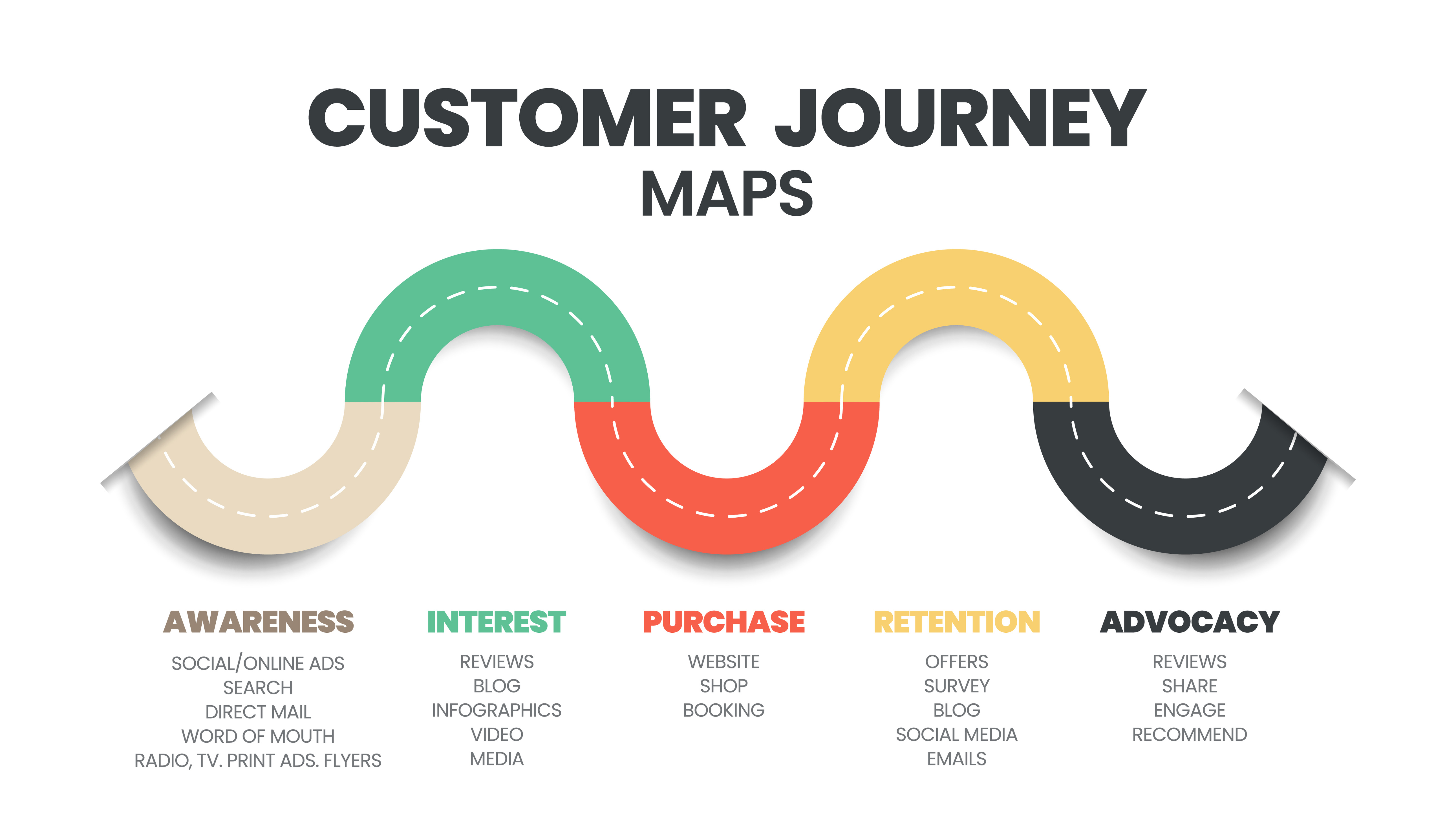
Interaction channels and touchpoints are integral to the concept of omnichannel customer journeys an its key components. Often used interchangeably, these two differ widely. Let’s see how.
An interaction channel is a medium where customers and brands interact, and they can be unidirectional or bidirectional.
Bidirectional interaction channels support instant two-way communication between customers and brands on traditional lines (such as physical stores and phone calls) and digital lines (email, website/app, live chat, texting apps, social media, etc.)
Unidirectional interaction channels are one-way initiated by customers or brands, including postal mail, TV advertisements, and print media. These channels are not real-time.
Interesting Article: Customer Service Channels – How to Pick the Right Ones for Your Business
Different industries patronize different channels in their omnichannel ecosystem. For instance, brick-and-mortar retailers give weightage to physical stores, while internet services may not own any physical channels at all. Companies can innovate channels to cater to their unique use cases. Amazon’s dash buttons are a prime example. These WiFi-enabled physical devices allow customers to reorder products with one long press and are a rare unidirectional channel that is channel-initiated.
Some channels are device-specific, while some are channel-neutral. Smartphone apps and mobile websites fall in the first category, while live chat and email belong to the second category. However, the interface of these channels may render differently on different devices.
Investment in channel integration yields growth in operating profitability . Channel integration is also a salient difference between multichannel and omnichannel ecosystems. Learn more .
Customer touchpoints are interaction instances. In a customer journey, a customer might interact multiple times with a business using different channels. Each interaction instance is termed a “customer touchpoint.” It includes three components:
The device used for interaction.
The interaction channel used for interaction.
The task being completed during interaction.
A customer journey is a series of customer touchpoints, each depicting details of that specific interaction (Refer to the figure below).
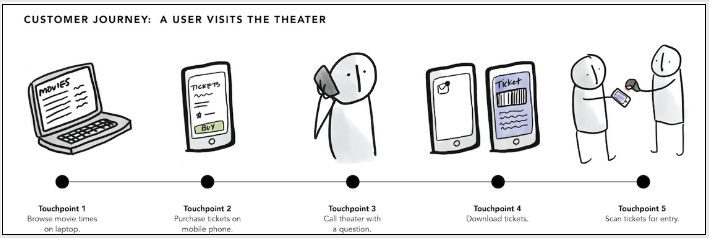
An omnichannel customer journey map is not a wishful depiction of what a customer journey should ideally look like. Rather, it is a truthful account of pain points that drive customers to your business and friction points that drive them away. By analyzing your journey maps, you should be able to pinpoint behavior patterns in specific customer segments and eventually predict their next move. This way, maps render a strong competitive advantage and boost customer retention and profitability.
Start with looking at relevant data within your organization. There is often existing (though disparate) information about the journey buried throughout various past internal efforts. This data - qualitative (e.g., data from past focus groups, customer-support call logs etc.) and quantitative (analytics, customer-satisfaction scores etc.) - can give you clues about how to focus the content of your research efforts.
Throughout a journey-mapping endeavor, you must bring stakeholders along. Without a doubt, journey mapping will reveal gaps and opportunities within the customer experience that, organizationally, are beyond the authority of the CX professional driving the mapping project. You must have buy-in and engagement from a cross-disciplinary team so that, when those issues and opportunities surface, stakeholders with decision-making authority are already convinced of the soundness of your method and able to understand the importance of resolving the problems it finds.
Establish a network of allies who are stakeholders from relevant departments (marketing, R&D, business analytics, etc.) who play a role in the customer journey and are impacted by it or can provide vital inputs for mapping.
Put your core team of allies to work. Together, generate a list of questions that you would like to answer, then send your allies back to their respective teams or departments to search for any available documentation or data that can help begin to answer those questions. Good places to start include:
Market-research surveys
Brand audits
Call center or customer support logs
Site surveys or VOC (voice of customer) feedback
Outputs from client advisory board (CAB) meetings
Customer journey analytics
By now, you will most likely have gathered enough insight to formulate a tentative hypothesis about how certain pieces of the customer journey look and what pain points exist. Start laying out that hypothesis in a draft framework called an assumption map or a hypothesis map .
Share the insights gained from internal research with all the concerned stakeholders and map the findings on a tentative journey map, which will be validated against external research in the next step.
You may be tempted to use existing stakeholder data as the basis for your journey map, but beware. While this data can give you a high-level understanding of customers’ general attitudes and levels of satisfaction for specific interactions, it does not help with understanding emotions, mindsets and motivations at the level required for effectively depicting the entire journey.
Then what?
Conduct external research on real customers using methods like:
⛔ Pitfall Alert: Basing Your Map on Assumptions
Research can be expensive and time-consuming, so what’s wrong with creating and using an “assumption map” based on stakeholder input and cutting out the research phase? While stakeholders do hold valuable knowledge about different areas of the customer journey, most of them do not have a broad enough perspective of the customer journey, nor a deep enough perspective of user needs at each stage, to be able to piece together a realistic, comprehensive view.
An assumption map carries two major risks :
It carries less weight and is more likely to be written off as “anecdotal” than seen as a compelling tool to drive change.
Decisions stemming from such inaccurate maps are faulty, altering the experience irreparably and leading to lost conversion opportunities.
Your takeaway? Base your maps on historical user data and primary research via interviews and customer surveys . Take a tour of Sprinklr’s omnichannel survey platform , or try it for free for a full 30 days by hitting the button below:
At this point, you need to create a visual narrative that will communicate the journey and all the critical moments, pain points, and high points within it. A good method is to have another workshop with your ally team. Having built context and common ground throughout your research process, bring them back together and evolve the hypothesis map based on your primary research findings.
Editor’s Choice: Customer Journey Management: Your A-Z Guide for 2024
The experience your customer has at individual customer touchpoints impacts their ongoing relationship with your brand. Take a look at your own omnichannel ecosystem.
What channels do you support? Across which devices? Ask yourself if there are important gaps to be filled in your channel solutions.
Sounds like a lot of work, right?
With Sprinklr, it isn’t.
Sprinklr’s unified customer experience management (Unified-CXM) platform takes the grunge work out of omnichannel journey mapping by:
Integrating data and insights across 30+ modern and traditional channels into one unified view.
Four interwoven tool suites for insights, marketing, sales and support for complete stakeholder buy-in and leak-proof journeys.
Granular journey analytics and reporting to highlight behavior trends and consumption patterns in real time.
If you want to partner with a brand that simplifies customer journey mapping and eliminates point-solution chaos for McDonald’s, Nike and Microsoft, jump aboard to Sprinklr. Explore the platform at your pace with a 30-day trial on the house:
Frequently Asked Questions
An omnichannel customer journey provides a seamless and integrated experience across multiple channels, ensuring consistency and continuity. In contrast, a multichannel approach involves utilizing various channels but may lack the same level of integration and cohesion.
Traditional customer surveys can gauge customer satisfaction levels and brand perceptions. However, to avoid human error, bias and skewed results, it’s advisable to use an AI-powered journey analytics tool like Sprinklr Service that generates granular metrics for all the interactions and touchpoints in a journey.
AI enhances the omnichannel customer journey by providing personalized recommendations, predictive analytics, chatbots for instant support, and data-driven insights, ensuring a seamless and efficient customer experience across channels.
Related Topics
Article Author

Bhavna Gupta
Guest Contributor
Related Articles
Discover how Sprinklr Service Advanced streamlines operations, monitors sentiment, automates workflows and provides actionable insights through real-world case studies.
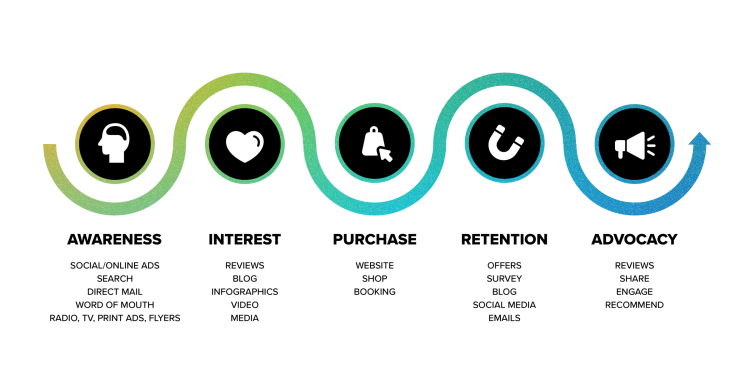
How to Create a Customer Journey Map from Scratch
Learn the definition of service level agreement (SLA), its role in customer service and a 5-step implementation guide. Discover top examples with FAQs.
Aksheeta Tyagi March 18, 2024 • 8 min read
![customer journey en marketing Top Customer Service Statistics to Know in 2024 [Latest Data]](https://images.ctfassets.net/ukazlt65o6hl/6VqZLpgxJXEvXLE9HLoMJb/58d85c1e604259a84c440b16dc1b7812/Feature_image.jpg?w=750&h=295&fl=progressive&q=70&fm=jpg)
Top Customer Service Statistics to Know in 2024 [Latest Data]
Stay ahead with the top customer service statistics for 2024: Key data, trends and insights to refine your service strategy and improve customer satisfaction.

- Custom Audiences
- Automotive Shoppers
- In-Market Shoppers
- Online Audiences
- Email Marketing
- Direct Mail
- Connected TV Advertising
- Social Media Advertising
- Full-Service Solutions
- Media Network
- Customer Marketing Platform
- Data Hygiene
- Porch Insights
- Mover Segments
- Marketing Resources
- Home Factors
- Home Services
- Furniture Retail
- Telecom/Utilities
- Restaurants & Hospitality
- Agencies/Intermediaries
- Movers & Shakers Podcast
- Case Studies
- Knowledge Center
- Executive Team
- News & Press Releases
- Client Login

- Restaurants & Hospitality
- Movers & Shakers Podcast
Segmentation Strategies for Every Stage of the Customer Journey (with Examples)
Understanding and catering to the diverse needs of consumers is crucial to succeed in today’s competitive environment. One effective way to achieve this is through segmentation strategies that align with every stage of the customer journey.
By tailoring your marketing efforts to address the unique preferences and behaviors of different segments, you can enhance engagement, drive conversions, and foster long-term loyalty.
What is the Customer Journey?
The customer journey refers to the series of steps or stages that a customer goes through when interacting with a brand, from initial awareness to post-purchase engagement and advocacy.
The customer journey is not linear; it can be complex and nonlinear, with customers moving back and forth between stages and touchpoints depending on their needs, preferences, and behaviors.
It can be influenced by various factors, including marketing efforts, customer service interactions, word-of-mouth recommendations, and personal experiences.
Segmentation Strategies for the Awareness Stage
At the awareness stage, your goal is to capture the attention of potential customers and introduce them to your brand. Segmentation at this stage can focus on demographics, interests, and online behavior.
Consider creating targeted content and ads that resonate with specific audience segments, ensuring relevance and capturing interest from the outset.
Segmentation Tips
Use Demographic Segmentation: Segment your audience based on demographics such as age, location, and income to create targeted messaging that resonates with specific groups. Example: A restaurant chain segments its audience based on location and sends out promotional emails. For subscribers in warmer climates, they highlight outdoor patio dining, refreshing cocktails, and beach-inspired dishes. Meanwhile, for subscribers in colder climates, they focus on cozy indoor dining, comfort food, and seasonal specials.
Interest-Based Segmentation: Identify audience segments with similar interests or preferences and tailor your content and ads to appeal to these specific interests. Example: An outdoor adventure company segments its audience based on interests and sends targeted Facebook ads promoting hiking and camping gear to subscribers who have shown interest in outdoor activities.
Leverage Behavioral Data: Analyze online behavior such as website visits, content engagement, and social media interactions to understand what types of content or products are most appealing to different segments. Example: A beauty brand analyzes website behavior and sends personalized email recommendations for skincare products based on specific skin concerns, such as acne or aging, to subscribers who have browsed relevant product pages.
Segmentation Strategies for the Consideration Stage
As customers move into the consideration stage, they’re evaluating their options and researching solutions to their needs. Segment your audience based on their engagement level and intent signals.
Tailor your messaging to address the pain points and preferences of each segment, providing valuable information and guiding them toward the next steps in their journey.
Segment by Engagement Level: Identify high-engagement segments who have interacted with your brand multiple times but haven’t yet made a purchase. Personalize your messaging to address any lingering concerns or objections they may have. Example: An online education platform segments its audience based on engagement level such as email opens, and sends personalized emails featuring success stories and testimonials from satisfied students to subscribers who have interacted with course content but haven’t enrolled yet.
Address Pain Points: Segment your audience based on common pain points or challenges they’re facing. Provide content and resources that offer solutions to these pain points and demonstrate how your product or service can help. Example: A software company segments its audience based on common pain points and sends targeted blog posts addressing specific challenges faced by different segments, such as productivity tips for small business owners or cybersecurity best practices for IT professionals.
Use Retargeting: Retarget website visitors who have shown interest in your products or services but haven’t converted yet. Serve them personalized ads or content to remind them of your offerings and encourage them to take the next step.
Example: An e-commerce retailer retargets website visitors who abandoned their carts with personalized Facebook ads featuring the products they added to their cart, along with a limited-time discount code to incentivize them to complete their purchase.
Segmentation Strategies for the Decision Stage
In the decision stage, customers are ready to make a purchase and are comparing products or services. Segment your audience based on purchase intent, past interactions, and preferred channels.
Offer personalized recommendations, discounts, or incentives to nudge them toward conversion. Provide clear and concise information to help them make informed decisions quickly and easily.
Segment by Purchase Intent: Identify segments that have demonstrated high purchase intent, such as adding items to their cart or visiting product pages multiple times. Offer personalized recommendations, discounts, or incentives to encourage them to complete their purchase. Example: A travel agency segments its audience based on purchase intent and sends targeted emails featuring vacation package deals to subscribers who have previously searched for flights or hotels on the website.
Simplify Decision Making: Segment by preferred communication channel where possible and deliver relevant information in a format that aligns with each segment’s preferences. For example, some customers may prefer to complete their purchase online, while others may prefer to speak with a sales representative over the phone. Customize your messaging and support options to accommodate each segment’s preferred channel, making it easier for them to complete their purchase. Example: To accommodate customers who prefer booking online, a travel company offers a user-friendly website interface with live chat support for instant assistance. For those who prefer personalized guidance, the company provides a dedicated toll-free number staffed by agents trained to assist with itinerary planning and booking arrangements.
Segmentation Strategies for the Post-Purchase Stage
The journey doesn’t end once a customer makes a purchase. Segmentation at this stage can focus on customer loyalty, satisfaction, and advocacy. Identify loyal customers and brand advocates, and nurture these relationships through targeted communications, exclusive offers, and loyalty programs.
Encourage satisfied customers to leave reviews, share their experiences, and become advocates for your brand.
Segment by Purchase History: Segment customers based on their past purchases to offer personalized recommendations for related products or complementary services. Example: An online retailer segments its audience based on past purchases and sends personalized email recommendations for complementary products or accessories based on previous purchases.
Reward Loyalty: Identify loyal customers and offer them exclusive rewards, discounts, or VIP perks to show appreciation for their continued support. Example: A coffee shop segments its audience based on loyalty status and offers exclusive discounts and rewards to repeat customers, such as a free coffee after every fifth purchase or early access to new menu items.
Segmentation Strategies for the Retention and Advocacy Stage
Retaining existing customers and turning them into brand advocates is crucial for long-term success. Segment your audience based on their engagement history, feedback, and advocacy level.
Provide ongoing value through personalized content, rewards, and VIP experiences. Encourage loyal customers to refer friends and family, participate in loyalty programs, and share user-generated content.
Identify Brand Advocates: Segment customers who have shown a high level of engagement and advocacy for your brand. Encourage them to become brand ambassadors by offering rewards for referrals or user-generated content. Example: A fitness brand identifies brand advocates among its customers who frequently share workout photos and testimonials on social media and invites them to join an exclusive ambassador program, offering perks such as free merchandise and VIP event invitations.
Provide Ongoing Value: Segment customers based on their interests or preferences and deliver personalized content, offers, or experiences that align with their needs. Example: A subscription box service segments its audience based on preferences and sends personalized product recommendations and content, such as recipe ideas or styling tips, tailored to each subscriber’s interests.
Foster Community: Create exclusive communities or loyalty programs for your most loyal customers. Encourage them to connect, share experiences, and advocate for your brand organically. Example: An online community platform segments its audience based on engagement level and encourages active members to participate in exclusive forums and events, fostering connections and encouraging user-generated content sharing.
Segmentation strategies tailored to each stage of the customer journey are essential for delivering relevant and personalized experiences that drive engagement, conversions, and advocacy.
Related Article – Customer Journey Mapping: A Step-By-Step Guide
By understanding the unique needs and preferences of your audience at each stage, you can create targeted campaigns that guide them seamlessly through the journey, fostering lasting relationships and maximizing the value of every interaction.

Related Posts

5 Audience Segmentation Pitfalls to Avoid (and How to Fix Them)

The Ultimate Audience Segmentation Guide

Top 10 Audience Segmentation FAQs
Get on the list.
Be the first to know when we share new content geared to help you attract your ideal customers!
Thank you! You’ll be the first to know when we post more great marketing content!
- Aftermarket
- Automotive Marketing
- Cookie Deprecation
- Customer Data Platform
- Homeowner Marketing
- Mover Marketing
- Movers & Shakers
- Social Media
- Uncategorized
Recent Posts
- Segmentation Strategies for Every Stage of the Customer Journey (with Examples) March 18, 2024
- 8 Data Enrichment Strategies to Power Your 2024 Campaigns March 13, 2024
- A Guide to Cookieless Advertising in 2024 March 11, 2024
Thank you! You'll be the first to know when we post more great marketing content!
- [eBook] 1st Party Data: Benefits & Best Practices for 2024 Get Your Free Copy
Brand Purpose: What It Is and Why It's Important
Updated: March 11, 2024
Published: October 15, 2023
Consumers support brands whose corporate purpose aligns with their own values. That’s the finding of a recent report by the World Economic Forum — and it makes sense. As consumers have become more aware in recent years of how businesses affect everything from society to the environment, many have begun to actively seek out businesses that have a strong track record of corporate social responsibility .
With this in mind, companies with a “big” brand purpose will find it easier to build trust and earn the business of like-minded consumers. And businesses not driven by purpose may miss the chance to attract them.
Table of contents:
What is brand purpose?
Why having a brand purpose is important, brand purpose examples, brand purpose statements.
A brand purpose is the reason behind a company’s operations. It’s what determines the products or services that a business offers, as well as how and why a business serves its target market. Further, it represents your brand’s identity .
In most cases, the company’s purpose is a sentence or paragraph that acts as a guiding light for all of its strategic decision-making.
A brand without a purpose is a ship without a compass. One year, it may rally behind a trendy cause, and the next year support a mission that contradicts its previous stance.
The issue: Customers will perceive that brand as disingenuous or unreliable. And many of today’s savvy consumers won’t buy from brands that lack a genuine purpose.
A Razorfish study shows 82% of consumers make purchases with purpose in mind. Another survey reveals that 44% of consumers are purpose-driven, meaning they exclusively support companies that align with their values.
This proves two key points:
- Brands must possess a clear purpose and communicate it to their target audience to foster trust and loyalty.
- Brands must take a stand, even if it means parting ways with some customers or partners along the journey.
The purpose driving your brand may not resonate with every customer, and that’s all right. The objective is to attract the right audience, not everyone. So, think carefully about the reason behind your brand and how it relates to your ideal customers.
Benefits of having a brand purpose
When you nail your brand’s purpose, it can bring a number of advantages that help you:
- Differentiate your brand from competitors: A brand purpose gives your company a unique stance to stand out in a crowded marketplace.
- Rally your teams around a cause: When everyone understands and embraces your brand’s purpose, it puts everyone on the same page and fosters unity and collaboration. Reports show that purpose-driven employers see 40% higher retention levels than those that aren’t.
- Build long-lasting customer loyalty: A clear brand purpose helps you connect with your target audience deeper, creating a strong emotional bond and fostering long-term customer loyalty.
- Drive innovation and creativity: A well-defined brand purpose inspires your teams to think outside the box and conceive innovative solutions, leading to new products, services, and experiences.
- Attract and retain top talent: A compelling brand purpose attracts like-minded individuals who are passionate about your mission, leading to a more engaged and motivated workforce. One survey shows 75% of leaders agree that a business strategy built around purpose leads to better talent attraction and retention.
- Enhance your brand’s reputation: A brand purpose that aligns with the values and aspirations of its target audience builds a positive brand reputation and fosters trust and credibility.
- Create meaningful impact: A brand purpose allows you to make a positive difference in society by addressing social or environmental issues, creating a sense of purpose and fulfillment for your brand and its stakeholders. Based on Razorfish’s research, buyers are 32% more likely to purchase from a brand with social advocacy than one offering a personal benefit.
- Increase customer advocacy: When customers resonate with your brand purpose, they become passionate advocates, spreading positive word of mouth and driving organic growth for your business.
- Adapt to changing market dynamics: A brand purpose serves as a compass, helping your company navigate challenges and adapt to changing market trends and consumer expectations.
There’s no one-size-fits-all approach to brand purpose. However, you want to ensure that yours ties to your overall vision and brand strategy .
Here’s a look at companies with powerful brand purposes that make a positive impact on the world and their revenue.
- Seventh Generation: Seventh Generation’s brand purpose is to “inspire a consumer revolution that nurtures the health of the next seven generations.” It acts out its purpose by creating products that are environmentally friendly and safe for people and the planet. Seventh Generation uses plant-based ingredients and avoids harmful chemicals in their formulas. Plus, it advocates for policies and practices that promote sustainability and reduce environmental impact.
- Toms: Toms’ brand purpose is to “improve lives through business.” It fulfills its brand purpose by following a “One for One” model: For every pair of shoes a customer purchases, Toms donates a pair to a child in need. They also fund medical treatments, clean water initiatives, and education programs in communities worldwide. Toms’ purpose-driven approach aims to improve lives and create positive social impact.
- Zoom: Zoom’s brand purpose is to “make video communications frictionless and secure, empowering people to accomplish more.” It lives out its brand purpose by providing a user-friendly and secure platform for videoconferencing and collaboration. Zoom focuses on making frictionless video communications so people can connect and collaborate from anywhere.
These examples show you can have a big-picture purpose that’s socially responsible or that simply makes lives easier for a specific group of people (like business professionals).
Your purpose statement communicates your brand’s core values and how they’ll impact customers’ lives.
Here’s a look at purpose statement examples for brands in different industries.
In the crowded retail space, you must have a distinct purpose from your competitors to stand out. One way to do this is to opt for sustainable practices.
Here’s an example of a one-line brand purpose statement for a retail company:
“To empower individuals to express their unique style and embrace their confidence through trendy and sustainable fashion choices.”
And how you could present this to shoppers:
“Picture this: You and your friends, together as a unified force, expressing your individual style and embracing your confidence through the latest, cutting-edge fashion choices. No more settling for mediocrity or conformity. With our trendy and sustainable clothing options, you can stand out from the crowd and make a statement that’s uniquely yours.”
Technology evolves rapidly, bringing forth new startups that seek to disrupt their relevant industries. Having a purpose is one way to keep your company relevant.
Here’s an example of a one-line brand purpose statement for a tech company:
“To simplify and enhance lives by providing innovative and user-friendly technology solutions that connect and empower individuals.”
And how you could present this to customers:
“Imagine a world where technology is not only advanced, but also intuitive and user-friendly. Our innovative solutions connect and empower individuals, making their lives simpler and more fulfilling. Say goodbye to frustration and hello to seamless integration. With our technology, you’ll wonder how you ever lived without it.”
Hospitality
Whether you own a hotel, hostel, or another business in the hospitality industry, having a purpose statement can help you attract the right guests.
Here’s an example one-line brand purpose statement for a hospitality company:
“To create unforgettable experiences and moments of relaxation for guests, offering a sanctuary of comfort and tranquility.”
And how you could present this to the public:
“Close your eyes and envision a place where every moment is filled with relaxation and tranquility. Our hospitality industry creates unforgettable experiences, offering a sanctuary of comfort for weary souls. Indulge in the luxury of pampering yourself and revel in the peacefulness that surrounds you. Welcome to a world of pure bliss.”
Food and Beverage
Today’s consumers are more health-conscious and picky about where they purchase their food. Showing how your brand cares for their well-being can lead to more people consuming your goods.
Here’s an example one-line brand purpose statement for a food and beverage company:
“To delight taste buds and nourish bodies with fresh, locally sourced ingredients, promoting a healthier and more sustainable food culture.”
And how you could present this to prospective buyers:
“Let your taste buds dance with delight as you savor the flavors of our food and beverage industry. We believe in using only the freshest, locally sourced ingredients to nourish your body and promote a healthier lifestyle. Join us in creating a sustainable food culture that not only satisfies your cravings, but also supports the environment.”
Your goal isn’t to generate big bucks for yourself, but you still need to earn revenue to sustain your operations and support your mission. If any business understands purpose, it’s a nonprofit.
Here’s an example one-line brand purpose statement for nonprofits:
“To make a positive impact on communities by empowering individuals to become change-makers and creating opportunities for growth and development.”
“Be the change you wish to see in the world. Our nonprofit industry empowers individuals to become change-makers and make a positive impact on their communities. Together, we can create opportunities for growth and development, helping those in need to thrive and succeed. Join us in making a difference and be the catalyst for change.”
Whatever direction you go in for your brand purpose, promote it throughout your organization to ensure alignment and consistency remain. A misaligned marketing campaign or PR statement could potentially unravel all your hard work overnight. Then once you’re aligned internally, share your purpose with the world.
hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(53, 'ad22bdd9-fd50-4b35-a4f5-7586f5a61a1e', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"});
What did you think of this article .
Give Feedback

Don't forget to share this post!
Outline your company's marketing strategy in one simple, coherent plan.
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform

Quantic India Witnesses the Success of 3rd Annual CX Excellence Awards 2024, the Cognitive Map to Customer's Mind: Connect, Converse and Coincide
BusinessWire India
New Delhi [India], March 19: The 3rd Annual CX Excellence Awards 2024 , hosted by Quantic India recently, was a groundbreaking event showcasing the pinnacle of customer experience innovation. With a reputation for pioneering solutions, Quantic India delivered a remarkable awards ceremony, drawing attendees from diverse industries to highlight the nation's best CX initiatives. The event featured insightful panel discussions led by industry experts, addressing crucial topics such as seamless Omni-channel experiences, real-time responsiveness, the role of Customer Data Platforms, social listening in crisis management, the future of OpenAI in CX, predictive analytics for customer retention, personalized rewards design, and customer privacy. Attendees had unparalleled opportunities to engage with over 25+ speakers, connect with award-winning organizations, and network with solution providers. It served as a platform to honor dynamic leaders across various sectors for their outstanding achievements.
Panel 1: Decoding the Diligent CX Map: Trends, Challenges, Innovation in the Industry
Expert Moderator for the Panel
- Vineet Rajan: Head of Marketing- SAP Customer Experience, SAP India
Esteemed Speakers on the Panel
- Vikram Singh : Head Customer Experience, PVRINOX Limited
- Krishna Gautam: Vice President Customer Experience, Urbanic
- Ankit Dixit: Head Of Customer Experience, BeatO
- Rahul Tandon: Chief Customer Service Officer, Ecom Express
- Writuparna Gupta Bakshi: Associate Vice President - Customer Experience and Operations, Junglee Games
- Apoorva Arora: Head - Process Excellence & Customer Service, Cashify
- Varun Sehgal: Director - Omni Channel, Limeroad.com
- Vamsi Yeluri: Strategic Advisor, Smartping
Panel 2: At Your Service 24x7: Power of Online Reputation & Social Listening
- Vibha Sarin Prabhakar: Chief Experience Officer, Shriram Automall
- Anamika Chatterjee: Heading Customer Service - Retail Finance, Hero FinCorp
- Kumar Chandan: Head- Customer Service- North& South, Panasonic
- C V Sai: Director- CX & Partner Experience, Urban Company
- Ambrash Kapoor: Head - Customer Service, ASICS Corporation
- Sunny Gulati: Head of Customer Experience, Bata India Limited
- Amit Ranjan : Head of Customer Happiness, Lenskart.com
- Kautuk Malviya: Head - Customer Experience Transformation, Nissan Motors India Private Limited
Panel 3: Fortifying Customer Loyalty to pave the way for Business Excellence
- Hemanth Purohit: Chief Executive Officer, Parahit
- Sandeep Singh Sachdeva: Head- Customer & Seller Experience, Snapdeal
- Pritiman Sarkar: Senior Vice President, SBI Cards and Payment Services Ltd
- Sweta Choudhary: Global customer experience
- Angad Wadia: VP- Operations & Customer Excellence and Head of Strategic Initiatives, Bajaj Capital Ltd
- Gagandeep Singh: SVP & Head - Customer Experience, Niva Bupa Health insurance
- Kanika Asija : AGM & Head of Group- Customer Experience Management, Tatapower-ddl
Following insightful panel discussions, Quantic India recognized CX domain experts and companies with awards for their long-term contributions.
Companies Who Won at the 3rd Annual CX Excellence Awards 2024
- Best Use of Net Promoter Score in Life Insurance: Canara HSBC Life Insurance
- Best Omni-channel Customer Experience Initiative in HealthTech: BeatO
- Best Use of Chat Support in Recommerce: Cashify
- Best In-App Customer Experience Initiative in Fashion Retail: Urbanic
- Best Use of Technology to Enhance Customer Experience in HFC: Wonder Home Finance Limited
- Best Integration of AI-Powered Chatbots in Consumer Durables: Sony India Pvt. Ltd.
- Best Omni-channel Customer Experience Initiative in Pre-owned Automobile Industry: Shriram Automall India Limited (SAMIL)
- Best Customer Journey Enhancement in Pharmaceutical: MANKIND PHARMA
- Best Customer Retention Initiative of the Year in FinTech: GroMo - Vitrak Technologies Private Limited.
- Best Customer Experience Initiative in Banking: Equitas Small Finance Bank
- Best Use of Technology to Enhance Customer Experience for Consumer Durables: Singer India
- Best Use of Technology to Enhance Customer Experience in InsureTech: InsuranceDekho
- Best Brand Building Campaign of the Year in E-commerce & Retail: Clovia
- Customer Centric Company of the Year in HealthTech: Tata 1mg
- Voice of Customer Impact Award in EdTech: LawSikho
- Best Customer - Centric Team of the Year in Healthcare: Pristyn Care
- Best Use of Chat Support in Financial Services: Clix Capital
- Best Contactless Service Experience in EdTech and Immigration: IELTSMaterial
- Best Use of Technology to Enhance Contact Centre Operations in Gaming: Junglee Games India Pvt. Ltd.
- Best Use of Data Analytics to Enhance CX in FinTech: OPL
- Best Education & Skill Development Campaign: CollegeDekho
- Best Customer Engagement Strategy in Fashion Services: Libas
- Best Omni-channel Customer Experience Initiative in Retail: Lenskart
- Best Customer-Centric Company of the Year in FMCG: Beejapuri Dairy Pvt. Ltd.
- Best Customer Experience Transformation Initiative in Retail: Bata
- Best Omni-channel Customer Experience Initiative in Electrical Construction Material: Panasonic Life Solution
- Best Use of Technology to Enhance Customer Experience in Electronic Payment Services: Euronet Services India Pvt. Ltd.
- Voice of Customer Impact Award in Power Distribution Sector: Tata Power Delhi Distribution Limited
- Best Use of WhatsApp Bot in CX in Logistics Service Provider: Rapido
- Rising Star in Digital Customer Engagement (D2C): MEENA BAZAAR
- Best Customer Retention Initiative of the Year in Insurance: HDFC ERGO GIC LTD.
- Best Digital Customer Experience Initiative in Financial Services: Dvara KGFS
- Best Customer Experience Excellence in Educational Solutions: Credenc
- Best Use of Data Analytics to Enhance CX in Online Job Portal: WorkIndia
- Voice of Customer Impact Award in FinTech: Stashfin
- Best Use of Technology to Enhance Customer Experience in Micro Mobility Platform: Yulu Bikes
- Best Customer-Centric Culture in Eyewear Retail: Cleardekho Eyewear
- Best Use of Gamification in Customer Engagement in Automobile: NISSAN MOTOR INDIA PVT. LTD.
- Best Digital Customer Experience Initiative in InsurTech: Symbo
- Strategic Excellence in Customer-Centric Leadership: PHYSICS WALLAH
- Best Customer Engagement Strategy in Beauty & Personal Care: Earth Rhythm
- Outstanding Customer Centric Initiative in Healthcare: Medanta
- Best Use of Technology to Enhance Contact Centre Operations in AgriTech: Ninjacart
- Customer-Centric Company of the Year in AgriTech: Otipy Internet Pvt. Ltd.
- Innovative Customer Engagement Campaign of the Year in FinTech: Upwards Fintech Pvt. Ltd.
- Best Customer Experience Initiative in Life Insurance: Pramerica Life Insurance Limited
- Best Use of Technology to Enhance Customer Experience in Healthcare: MeduLance Healthcare Pvt. Ltd.
- Best Use of Insights to Enhance Customer Experience in Telecom: Vodafone Idea Limited
- Best Use of Technology to Enhance Customer Experience in Financial Services: Hero Housing Finance
- Best Customer Engagement Strategy in NBFC: Ring
- Best Use of Technology to Enhance Customer Experience in E-commerce: Wakefit Innovations Pvt. Ltd.
- Best Customer Experience Initiative in Insurance: Bajaj Allianz General Insurance
- Best Digital Customer Experience Initiative in NBFC: Fedbank Financial Services Ltd.
- Best CX Initiative to Enhance Customer Satisfaction in Gaming: Zupee
- Best use of Real-time feedback in Healthcare & Diagnostics: Redcliffe Labs
- Innovative Customer Engagement Campaign of the Year in Real Estate: Magicbricks
- Excellence in Customer Support Automation: FuelBuddy
- Customer Centric Team of the Year in E-commerce Consumer Electronics: Noise
- Excellence in Customer Journey Optimization in Wealth Management: Bajaj Capital
- Best Integration of AI-Powered Chatbots in Gaming: PokerBaazi
- Best Omni-channel Customer Experience Initiative in Healthcare & Diagnostics: Redcliffe Labs
- Best Loyalty Program of the Year in Retail: Forever New
- Customer Centric Team of the Year in Travel Retail: Mumbai Duty Free
- Best Contact Centre of the Year in NBFC: SBI Cards and Payment Service Ltd.
- Best Contactless Service Experience in Health Insurance: Aditya Birla Health Insurance
- Best Use of Technology to Enhance Contact Centre Operations in Health Insurance: Niva Bupa Health Insurance
Individuals Who Won at the 3rd Annual CX Excellence Awards 2024
- CX Professional of the Year in Logistics: Rahul Tandon (Ecom Express Limited)
- Emerging Marketer of the Year in D2C: Abhishek Sinha (Sotbella Fashion)
- CX Professional of the Year in Consumer Services: Nirupam Srivastava (Hero Enterprise)
- CX Trailblazer Award in HealthTech: Tejasvi Singh Kushwah (Healthplix)
- Woman CX Trailblazer of the Year in Banking and Financial: Anamika Chatterjee (Hero Fincorp)
- Emerging CX Leader of the Year in EdTech: Sushant Gomber (Hero Vired)
- Emerging CX Leader of the Year in Healthcare: Shashi Ranjan (Dr. Lal Pathlabs Ltd.)
- Rising Star in Marketing Leadership in Financial Services: Abhishek Kumar (ICICI Securities)
- Emerging CX Leader of the Year in HealthTech: Linish Theodore (CNH Care)
Our Proud Sponsor Partners for the Event
- Presenting Partner: SAP Customer Experience
- Co- Presenting Partner: infobip
- Communication Partner: Smartping
- Powered By Partner: haptik
- AI Automation Partner: uniphore
- Co-Powered By Partner: parahit
- Exhibit Partners: LimeChat and Trooya by germin8
- Lanyard Partner: Radical Minds
- Media Partner: Quantic Connect
In today's rapidly changing business landscape, the demand for effective solutions is at an all-time high. At the recent event, leading solution providers highlighted their innovative approaches and shared success stories through case studies. Attendees had the chance to connect with industry peers and learn about leveraging modern technology to streamline business operations . Following an exploration of customer mind-set and diverse experiences across various sectors, Quantic India will soon delve further into the realm of customer experience with its upcoming edition - 4th Edition CX Excellence Awards on 21st June at Bengaluru .
(ADVERTORIAL DISCLAIMER: The above press release has been provided by BusinessWire India . ANI will not be responsible in any way for the content of the same)

Experience Cloud Release Notes
- Release Notes
This page helps you locate the following self-help resources for Experience Cloud and Adobe enterprise applications:
- Release notes and product documentation
- Support knowledge base articles
- Upcoming events on Experience League
- Latest video tutorials
For the best self-help experience, sign in to Experience League and customize your search experience across Adobe’s free library of documentation , courses , events , community forums , and support .
To receive a monthly email notification about updates to this page, subscribe to the Adobe Priority Product Update .
Latest update: March 13, 2024
- Experience League events and updates
- Certification at Adobe
- Adobe System Status
- Adobe Experience Cloud - central interface and administration
- Adobe Experience Platform
- Adobe Real-Time Customer Data Platform
- Adobe Analytics
- Adobe Customer Journey Analytics
- Adobe Streaming Media Analytics
- Adobe Experience Manager
- Adobe Commerce
- Adobe Target
- Adobe Campaign
- Adobe Journey Optimizer
- Adobe Journey Orchestration
- Adobe Marketo Engage
- Adobe Workfront
- Adobe Mix Modeler
- Adobe Advertising
- Adobe Document Cloud
- Adobe Creative Cloud for enterprise
- Adobe Content Supply Chain Tutorials
- Customer Data Management - Voices
- Digital Experience Blueprints
- Adobe product security vulnerabilities
Experience League events and updates events
Learn about exciting events on Experience League. It’s a great place to learn, interact, and get answers from product experts at Adobe!
Events on Experience League
Updated March 2024
WORKFRONT | Customer workshop | Admin 101: Getting Workfront Data | New to Workfront? Join our “New Admin” monthly meetups to ask questions, get resources and recommendations, meet other new admins, and for this session, learn best practices for all things reporting in Workfront. | March 13 @ 8:00 AM PT | Register
EXPERIENCE MANAGER | AEM GEMS | Getting started with AEM Authoring and Edge Delivery Services | Join AEM GEMs webinar for getting started with AEM authoring with Edge Delivery Services. Learn how to create an AEM enabled project development alongside WYSIWYG authoring using AEM cloud service. | March 13 @ 9:00 AM PT | Register
EXPERIENCE MANAGER | Webinar | Espressos & Experience Manager: Why AEM is More Powerful in the Cloud | Join Adobe’s experts as they discuss how to ensure a smooth transition to the Cloud through content assessment and migration planning with tools like Best Practice Analyzer & Cloud Acceleration Manager. | March 14 @ 1:00 PM ET | Register
ADOBE SUMMIT | The Digital Experience Conference | Expand your skills, discover the latest trends, and explore the future of experience-led growth | Learn from leading brands, discover the future of generative AI, and get ready for experience-led growth. | March 25 - 28 @ Las Vegas and online | Register
ANALYTICS | Experience Makers: The Skill Exchange | Skill Exchange at Adobe Summit for Adobe Analytics | On March 28, 2024, we’ll be hosting the Adobe Analytics Skill Exchange at Summit in Las Vegas! Pre-register now to learn tips, tricks & best practices from Analytics customers & champions. | March 28 @ 9:00 AM PT | Register
EXPERIENCE MANAGER | Experience Makers: The Skill Exchange | Skill Exchange at Adobe Summit for AEM | On March 28, 2024, we’ll be hosting the AEM Skill Exchange at Summit in Las Vegas! Pre-register now to learn tips, tricks & best practices from AEM customers & Champions. | March 28 @ 9:00 AM PT | Register
EXPERIENCE MANAGER | Experience Makers: The Skill Exchange | Skill Exchange at Adobe Summit for Marketo Engage | On March 28, 2024, we’ll be hosting the Marketo Engage Skill Exchange at Summit in Las Vegas! Pre-register now to learn tips, tricks & best practices from Marketo Engage customers & Champions. | March 28 @ 9:00 AM PT | Register
WORKFRONT | Experience Makers: The Skill Exchange | Skill Exchange at Adobe Summit for Workfront | On March 28, 2024, we’ll be hosting the Adobe Workfront Skill Exchange at Summit in Las Vegas! Pre-register now to learn tips, tricks & best practices from Workfront customers. | March 28 @ 9:00 AM PT | Register
WORKFRONT | Community event | Connect: Admin Chat for Marketing & Creative | Are you a system admin for a marketing or creative team? This customer-driven session will connect you with other admins to discuss best practices as well as tips and tricks. | April 5 @ 9:00 AM PT | Register
View more upcoming events or browse event recordings on Experience League.
Adobe Content Supply Chain content-supply-chain
Learn about Content Supply Chain , Adobe’s an end-to-end solution to accelerate and simplify your content with generative AI and intelligent automation.
Certification certification
Attention all Adobe certification candidates! Visit the Experience Cloud Certification site on Experience League.
The Experience Cloud Certification site is your one-stop shop for all Experience Cloud certification-related content and is updated regularly with:
- Available certifications
- Certification renewals for Adobe applications
- Certification program updates
And more! Head over to Adobe Certification on Experience League and start your certification journey today!
Adobe System Status status
Learn about the latest features and updates in Adobe System Status.
Adobe System Status provides detailed information, status updates, and email notifications about Adobe products and services. Get notified about outages, disruptions, and maintenance events. Check it out at status.adobe.com .
For recent release notes, see:
- January 30, 2024
- October 2023
- August 2023
- January 2023
Experience Cloud - central interface and administration ecloud
Learn about Experience Cloud central interface components and administration. Manage products and users, configure profile settings and preferences, search Experience Cloud objects, and manage cookies.
Experience Platform Permissions
- You can now search for an API credential by name when viewing or modifying your credentials.
- User group membership information is now available for each role when viewing a user’s list of roles in the roles tab. The Remove Role option is disabled for users who have been assigned a role through a user group only.
For help on Experience Cloud central interface components, see the Experience Cloud Interface and Administration Guide (includes Customer Attributes, Experience Cloud Assets, and Audiences).
Experience Platform platform
Find latest release information and new documentation for Experience Platform and Mobile SDK. View new tutorials and Knowledge Base articles on Experience League.
Experience Platform release notes
Experience Platform Mobile SDK release notes
New Experience Platform tutorials and courses tutorials-aep
New videos, tutorials, or courses published for Adobe Experience Platform.
New Experience Platform support knowledge base kb-aep
New articles and updates to existing articles for Experience Platform.
Real-Time Customer Data Platform rtcdp
Find the latest tutorials for Real-Time Customer Data Platform on Experience League.
Video tutorials: Understanding Real-Time Customer Data Platform
Product documentation: Real-Time Customer Data Platform
Analytics analytics
Find the latest release information for Adobe Analytics and AppMeasurement. View new tutorials and courses on Experience League.
Analytics release date: March 13, 2024
Analytics release notes
Analytics product documentation and tutorials
AppMeasurement appm
Release version: 2.26.0
- AppMeasurement for JavaScript release notes
New Analytics tutorials and courses tutorials-analytics
New or updated videos, tutorials, or courses published for Adobe Analytics.
New Adobe Analytics support knowledge base kb-analytics
New articles and updates to existing articles for Analytics.
Customer Journey Analytics cja
Find the latest release information for Customer Journey Analytics. View new tutorials and courses on Experience League.
Customer Journey Analytics release date: March 13, 2024
Customer Journey Analytics release notes
Customer Journey Analytics product documentation and tutorials
New Customer Journey Analytics tutorials and courses tutorials-cja
New videos, tutorials, or courses published for Customer Journey Analytics.
Streaming Media Analytics sma
Find the latest release information for Streaming Media Analytics. View new tutorials and courses on Experience League.
Streaming Media Analytics release notes
Streaming Media Analytics product documentation and tutorials
Adobe Experience Manager aem
New features, fixes, and updates in Experience Manager. Adobe recommends customers with On-Premise deployments to deploy the latest patches to ensure higher stability, security, and performance.
Experience Manager roadmaps and release videos
Adobe recommends visiting the following resources to stay updated on release information:
- Experience Manager release updates and roadmaps - Learn about the Experience Manager release roadmap, previous release updates, and documentation updates.
- Experience Manager as a Cloud Service release updates - Watch feature video overviews of current and past releases of Experience Manager as a Cloud Service.
- Current Release Notes for Adobe Experience Manager (AEM) as a Cloud Service - Read the latest release notes for Experience Manager as a Cloud Service.
Latest Release Overview video
Watch the January 2024 Release Overview video for a summary of the features added in the 2024.01.0 (January 2024) release.
Experience Manager Sites as a Cloud Service
Extension Manager in AEM Sites
Explore the new Extension Manager in AEM Sites so you can personalize your AEM setup by configuring UI extensions.
The Extension Manager in AEM Sites enables developers and practitioners to access, manage, and customize UI extensions built with Adobe App Builder to enhance the functionality of AEM Sites.
With the Extension Manager, you can do the following:
- Enable or disable extensions on a per-instance basis;
- Configure extension parameters;
- Preview extensions and generate a shareable preview link;
- Discover UI extensibility features via interactive demos;
- Access Adobe’s experimental features through first-party extensions.
Adobe is actively seeking feedback and new use cases for UI extensions. If you would like to connect, send an email to [email protected] .
Experience Manager Assets as a Cloud Service
Admin view pre-release features
- Preview renditions for all supported video types – Experience Manager Assets now generates preview renditions of all supported video types by default without requiring a processing profile configuration
New features in Assets view
- Smart tags blocklist – Assets Essentials now lets you define a blocklist that is comprised of words that you do not want added as Smart Tags to assets when they are uploaded to the repository. This capability helps you to maintain brand compliance and reduces effort to moderate Smart Tags.
Experience Manager Forms as a Cloud Service
Early Adopter Program
For a chance to test some upcoming features, be a part of Adobe’s early adoption program.
Submit an Adaptive Form to Adobe Workfront Fusion Scenario – Forms as a Cloud Service offers out-of-the-box options to effortlessly connect an Adaptive Form with Adobe Workfront. This simplifies the process of submitting an Adaptive Form to an Adobe Workfront scenario, allowing you trigger a Workfront Fusion scenario on submission of an Adaptive Form.
Right to left languages support – Adaptive Forms built on Core Components can now be presented in a Right-to-Left (RTL) language like Arabic, Persian, and Urdu. The RTL languages are spoken by more than 2 billion people globally. Using a form in RTL language allows you to extend the reach of your adaptive forms to cater to these diverse audiences and select into RTL markets. In certain regions, it is also a legal mandate to provide forms in the local language. By accommodating local languages, you not only open doors to a broader audience but also ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
Protect your documents with DocAssurance APIs (Part of Communication APIs) – The DocAssurance APIs empower you to safeguard sensitive information by signing and encrypting the documents. Through encryption, the contents of a document are transformed into an unreadable format, ensuring that only authorized users can gain access. This fortified layer of protection not only shields valuable data from unauthorized eyes but also provides peace of mind. The Signature APIs let your organization protect the security and privacy of Adobe PDF documents that it distributes and receives. This service uses digital signatures and certification to ensure that only intended recipients can alter documents.
You can write to [email protected] from your official email ID to join the early adopter program and request access to the capability.
Experience Manager as a Cloud Service Foundation
Support for Dynatrace
- Dynatrace customers may monitor their AEM usage – Read how to request connectivity with your Dynatrace environment for application performance monitoring. The New Relic APM, which is available to all customers, stops collecting data if Dynatrace is enabled.
- RDE Support for Front-End Code using Site Themes and Site Templates – Rapid Development Environments (RDEs) now support front-end code based on site themes and site templates , for early adopters. With RDEs, this is done using a command-line directive, rather than a front-end pipeline . Send an email to [email protected] if you want to try it out and provide feedback.
Cloud Manager
New features
- Cloud Manager now validates the expiration dates not only for the main certificate , but for intermediate certificates as well.
- CDN logs are now returned in a compressed format.
For a chance to test some upcoming features, be a part of Adobe’s early adopter program.
Client-Side Collection by way of Real User Monitoring (RUM) – You can use the Real User Monitoring (RUM) Data Service to enable client-side collection for AEM as a Cloud Service.
Real User Monitoring (RUM) Data Service offers a more precise reflection of user interactions, ensuring a reliable measure of website engagement. It is a great opportunity to gain advanced insights into your page performance. This is beneficial for customers who use either Adobe-managed CDN or non-Adobe-managed CDN. For customers using a non-Adobe-managed CDN, automated traffic reporting can now be enabled for them, thus removing the need to share any traffic report with Adobe.
If you are interested in testing this new feature and sharing your feedback, send an email to [email protected] from the email address associated with your Adobe ID. Include the domain name for production, stage, and dev environments in your email. Availability of the early adopter program of this feature is limited.
Bring your own GitHub – If you use GitHub to manage your repositories, you can now validate code directly within your GitHub repositories through Cloud Manager . This integration eliminates the need to consistently sync code with the Adobe repository and allows you to verify pull requests before merging them into the main branches.
If you are interested in testing this new feature and sharing your feedback, send an email to [email protected] from your email address associated with your Adobe ID.
Self-Service Content Restore – A new self-service content restore feature now provides backup restoration for up to seven days and is available to early adopters for evaluation purposes featuring:
- Point-in-time backup restoration for the previous 24 hours
- Fixed time restorations for up to seven days
If you are interested in testing this new feature and sharing your feedback, send an email to [email protected] from your email associated with your Adobe ID.
- The early adopter program is limited to development environments only.
- Availability of the early adopter program of this feature is limited.
- This feature is for recovering accidentally deleted content and is not intended for disaster recovery.
Experience Audit Dashboard – The Cloud Manager Experience Audit dashboard includes a trended view of your page performance scores along with insights and recommendations to help you improve them. Experience Audit is included as a step in the Cloud Manager production pipeline.
The dashboard uses Google Lighthouse, an open-source, automated tool for improving the quality of your web apps. You can run it against any web page, public, or requiring authentication. It has audits for performance, accessibility, progressive web apps, SEO, and more.
Interested in test-driving the new dashboard? To get started, send an email to [email protected] from your email associated with your Adobe ID.
- An error was corrected where configuration pipelines would fail at the build step with an unclear error message if the location of the configuration files was not set properly. The error message is now clear and indicates that the user should check that the location of the configuration files is correct.
- When a build step finishes with status FAILED due to a BUILD_MAVEN_TRANSFER_ARTIFACT_ERROR , it is now properly described as an error due to merge conflicts with the destination branch.
Workfront for Experience Manager enhanced connector
The release date for the latest version 1.9.16 of Workfront for Experience Manager enhanced connector was January 19, 2024.
Release highlights
The latest version of the Workfront for Experience Manager enhanced connector includes the following bug fixes:
- The Workfront configuration in CRX DE currently does not store the project ID , causing errors when applying read-only permission. Learn more about how to configure permissions .
- No public documentation on how to add custom properties to the out-of-the-box index definition. Learn more about adding custom property .
- Deleting connection configurations on the enhanced connector significantly affects event subscriptions and other saved configurations, causing them to point to an old URL.
- Installing the forms add-on package does not install the Toggle Router , leading to the failure of the WFEC AMS environment Toggle feature.
- Enabling event subscriptions on EWC setup results in repeated API call failures with HTTP 400 error when setting up Workfront enhanced connector for the first time.
- Deleting comments on linked folder assets at Workfront fails to find the linked folder path on AEM.
- Insufficient support for large file assets in AEM results in a 4-byte size issue.
- No request time processing for critical flows in linked folder, document update, and note update.
Known issues
- While configuring project linked folders with AEM 6.4, Experience Manager does not save the values for sub-folders and Create linked folder in projects with portfolio fields. The value for the sub-folders field updates to undefined . The value for the Create linked folder in projects with portfolio field updates to Default Portfolio automatically after saving the configuration.
- When you use the classic Workfront experience, the Send to option available in the More drop-down list does not let you select the target destination within Experience Manager. The Send to option works correctly using the Document Actions drop-down list. The Send to option works correctly for More drop-down list and the Document Actions drop-down list available in the new Workfront experience.
Announcing the Complete AEM Sessions and Labs at Adobe Summit 2024 – Explore the comprehensive list of Adobe Summit 2024 AEM sessions and labs, your ultimate roadmap for a deeper AEM experience. See https://adobe.ly/3HD1mw3 .
AEM as a Cloud Service 2024.1.0 – Learn about the update at https://adobe.ly/3w2lhBL .
Lasted Blogs by AEM Community Users
- How to trigger Oak Index by way of AEM JMX to start the process of applying the changed index definitions
- How Not to Migrate Taxonomies to AEM Assets
- Exploring AEM’s Hidden Power: Unlocking OSGi Marvels
- AEM 6.5.5 Not Indexing Problem Fixed
Experience Manager release information
All Experience Manager release notes are maintained at the following pages:
- Experience Manager as a Cloud Service release information
- Experience Manager as a Cloud Service release updates
- Current Release Notes for Experience Manager as a Cloud Service
- Experience Manager Cloud Manager release notes
- Automated Forms Conversion Service release notes
- Experience Manager 6.5 Service Pack release notes
- Experience Manager 6.4 Cumulative Fix Pack release notes
- Experience Manager Assets Dynamic Media release notes
- Experience Manager Brand Portal release notes
- Experience Manager desktop app release notes
- Experience Manager Dispatcher release notes
- Adobe Primetime release notes
- Livefyre release notes
New Experience Manager tutorials and courses tutorials-aem
New videos, tutorials, or courses published for Experience Manager.
New Experience Manager support knowledge base kb-aem
New articles and updates to existing articles for Experience Manager.
Other Help resources for Experience Manager
- Dynamic Media Classic Help Home
- Experience Manager as a Cloud Service Guides
- Cloud Manager User Guide
- Experience Manager 6.5 Learn & Support Home
- Experience Manager 6.4 Learn & Support Home
- Experience Manager Documentation: Recent Updates
- Older Versions of Experience Manager Documentation
Adobe Commerce commerce
Get access to release notes, new tutorials, and Knowledge Base articles for Adobe Commerce on Experience League.
- See Release notes for Adobe Commerce and Magento Open Source to stay current.
- See Adobe Commerce Services Guides to see Commerce Services release information and documentation.
- See Product Availability to access individual product release notes and verify availability.
New tutorials for Adobe Commerce tutorials-commerce
New tutorials for Adobe Commerce on Experience League.
New Commerce support knowledge base kb-commerce
New articles and updates to existing articles for Adobe Commerce.
Target target
Get access to pre-release notes, current release notes, and new tutorials for Adobe Target.
- For pre-release information, see Adobe Target prerelease
- For current information, see Adobe Target release notes
Campaign ac
Get the latest updates for Adobe Campaign. Find new tutorials, courses, and Knowledge Base support articles on Experience League.
Latest Campaign product releases
Campaign Web Interface: What’s new | Product documentation
Campaign v8.6: Release notes | Product documentation
Campaign Standard v24.1 - Winter: Release notes
Campaign Classic v7.3.5: Release notes
Control Panel: Release notes
New Campaign tutorials and courses tutorials-campaign
New or updated videos tutorials published for Adobe Campaign.
New Campaign support knowledge base kb-campaign
New articles and updates to existing articles for Campaign.
Campaign help resources
- Campaign Web Interface: What’s new - Product documentation
- Campaign v8: Documentation - Release Notes - Implementation Guides
- Campaign Standard: Campaign Standard Documentation - Release Notes - How-to videos - Release Planning - Latest documentation updates
- Campaign Classic: Campaign Classic v7 Documentation - Release Notes - How-to videos - Latest documentation updates
- Campaign Control Panel: Documentation - Release Notes - How-to videos
Journey Optimizer journey-opt
Learn about the latest release information for Journey Optimizer. View the latest tutorials and Knowledge Base support articles on Experience League.
Latest Journey Optimizer product releases
Learn about the latest capabilities, improvements, and fixes in the Journey Optimizer Release Notes .
New Journey Optimizer tutorials tutorials-ajo
New videos, tutorials, or courses published for Adobe Journey Optimizer.
New Journey Optimizer support knowledge base
New articles and updates to existing articles for Journey Optimizer.
More resources for Journey Optimizer
- Journey Optimizer documentation - Release rotes - How-to videos
- Decision Management documentation - Release notes - How-to videos - Latest documentation updates
Journey Orchestration journey-orch
Access the latest release notes for Journey Orchestration on Experience League.
Latest Journey Orchestration product releases
Find out more about the latest capabilities, improvements, and fixes in the Journey Orchestration release notes .
More resources for Journey Orchestration
Journey Orchestration documentation
Release notes
How-to videos
Latest documentation updates
Marketo Engage marketo
Find out the latest release notes and release schedule for Marketo Engage.
Core Marketo Engage updates
- See March 2024 - current release notes for the latest information
- See Marketo Engage release schedule for the latest release schedule information and release notes.
New Marketo tutorials and courses tutorials-marketo
New videos, tutorials, or courses published for Adobe Marketo.
For the latest product documentation, see the Marketo product documentation home
Workfront workfront
Learn about the latest release notes for Adobe Workfront. Find new tutorials on Experience League.
New Adobe Workfront courses and tutorials tutorials-workfront
New Workfront tutorials on Experience League.
See the Workfront product releases page for a round-up of the latest information for all products.
Adobe Mix Modeler mix-modeler
See the following pages for the latest information:
- Mix Modeler release notes
- Mix Modeler product documentation
Adobe Advertising advertising
Release notes for Adobe Advertising.
New features in Advertising DSP advertising-dsp
See What’s New in Advertising DSP
New features in Advertising Search, Social, & Commerce advertising-search
See What’s New in Advertising Search, Social, & Commerce
Adobe Pass pass
Adobe Pass is a multi-screen TV platform that helps broadcasters, cable networks, and service providers create and monetize engaging, personalized viewing experiences.
See Adobe Pass Release Notes to find release-specific information, system requirements, limitations, fixed issues, and known issues.
Document Cloud doc-cloud
New tutorials and courses published for Document Cloud, including Acrobat Services and Acrobat Sign.
For Document Cloud tutorials, see:
- Adobe Acrobat
- Adobe Acrobat Sign
- Adobe Acrobat Services API tutorials
- Document Cloud Learn & Support
Creative Cloud for enterprise creative-cloud
New videos, tutorials, or courses published for applications in Adobe Creative Cloud for enterprise.
Updated February 2024
See Creative Cloud for enterprise tutorials for the latest tutorials.
Customer Data Management - Voices voices
Customer Data Management Voices is your destination as a customer data management technical and marketing practice leader and specialist. This collection of tutorials is your one-stop-shop to hear from your peers, get inspired, and learn about developments in MarTech. No registration required, simply click and watch.
Digital Experience Blueprints blueprints
Digital Experience Blueprints are repeatable implementations that let you address strategy and quickly solve established business problems. Each Blueprint provides a series of artifacts that explain the high-value business problem, architectures, implementation steps, technical considerations, and links to the relevant documentation.

Salesforce is closed for new business in your area.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
For example, at HubSpot, our customer's journey is divided into 3 stages — pre-purchase/sales, onboarding/migration, and normal use/renewal.. At each of these stages, HubSpot has a specific set of touchpoints to meet customers where they are. Like using blog posts to teach customers about marketing and sales, then nurturing them slowly toward a paid subscription.
The customer journey is a series of steps — starting with brand awareness before a person is even a customer — that leads to a purchase and eventual customer loyalty. ... Ensure that your marketing, sales, and customer service teams optimize for these five stages of the customer journey: 1. Awareness.
While marketing leaders have long understood the value of customer journey maps on customer satisfaction and loyalty, many still find it hard to incorporate them in their CX initiatives. To create value-driven customer journey maps that are aligned with the enterprise-wide CX initiatives, marketing leaders must master foundational elements such ...
Customer journey vs process flow. Understanding customer perspective, behavior, attitudes, and the on-stage and off-stage is essential to successfully create a customer journey map - otherwise, all you have is a process flow. If you just write down the touchpoints where the customer is interacting with your brand, you're typically missing up to 40% of the entire customer journey.
A customer journey map helps you gain a better understanding of your customers so you can spot and avoid potential concerns, make better business decisions and improve customer retention. The map ...
Discovery: Learn new things about the customer based on data and customer research. Ideation: Identify customer pain points and generate solutions. Activation: Include stakeholders in the project prioritization and selection. "Making an impact will require more than just a map," says Nordlund. "It's going to require a plan and it's ...
While many companies will put their own spin on the exact naming of the customer journey stages, the most widely-recognized naming convention is as follows: Awareness. Consideration. Decision. Retention. Advocacy. These steps are often then sub-categorized into three parts: Pre-sale. Sale/Purchase.
Here's our beginner customer journey mapping framework to help you create your first complete map in 2 and ½ working days: Day 1: preliminary customer journey mapping work. Day 2: prep and run your customer journey mapping workshop. Final ½ day: wrap up and share your results.
Let's take a look at five steps your team can take to start journey mapping. 1. Find the sweet spot where your customers' goals and your own align. Before you start journey mapping, nail down your business goals. Any marketing and communication you deliver during the customer journey should be focused on helping your brand reach those goals.
Step 4: Implement your customer journey map and conduct research. First things first, though: create a visually-appealing customer journey map that is accessible for all necessary team members. A graphic designer can help compile your findings and touchpoints in a visual sequence that is understandable, logical, and beautiful.
1. Generate awareness. Each customer journey starts with a question, generally revolving around where they can find the best product or service to meet a specific need. Being able to pinpoint when this question tends to arise and where customers are looking for answers can help guide your marketing efforts.
A customer journey is whatever interaction a consumer has with your company. Technically-referred as a sales funnel, it's often represented visually as a map, or an upside-down triangle. Today's customers are often aware of a brand, its products and services before they're ready click "buy". Every interaction a customer has with your company ...
But what does it take to build a customer experience that's smooth and simple from end to end? In this piece, the author offers four strategies to ensure simplicity is baked into every aspect of ...
Ask about Salesforce products, pricing, implementation, or anything else — our highly trained reps are standing by, ready to help. Contact us. OR CALL 1-800-664-9073. A customer journey map is a diagram of the touchpoints a customer has with your company, detailing how customers interact with your brand.
The customer journey consists of actions your customers take before and after they make a purchase. It should be part of your overall marketing strategy to improve lead generation and enable more effective marketing. By understanding the different actions your customers take before and after a conversion, you can start brainstorming new ...
A customer journey is a tool that helps marketers understand the series of connected experiences that customers desire and needs — whether that be completing a desired task or traversing the end-to-end journey from prospect to customer to loyal advocate. ... Gartner Marketing Symposium/Xpo™ Connect with the leading CMOs and marketing ...
3. Fase de compra. Este es el momento que todos están esperando y, por ello, es una fase del customer journey que debe ser tratada con especial atención. En este punto el consumidor ya realizó la deliberación entre las opciones del mercado y ha tomado una decisión de compra.
A customer journey map is a visual representation of experiences encountered by a customer, often depicted as a persona, in the buying process of a product or service. Brands and companies can leverage this to trace the potential thoughts and feelings of a customer at every point of interaction.
El propósito u objetivo del Customer Journey es, por un lado, medir y evaluar cómo estás sirviendo a tu cliente y mejorar tus servicios. Por otro lado, averiguar qué ha cambiado en la vida de tus clientes (potenciales, actuales y ex), por qué visitan a tus competidores y no a ti, y aportar ideas para nuevos servicios.
El customer journey aplicado al inbound marketing. Cuando lo explicamos en el contexto del inbound marketing, el customer journey es el proceso por el que pasa una persona para comprar un producto o servicio en base a una necesidad que se le plantea, y toda la investigación y consideración de alternativas que hay entremedio.
Here's a step-by-step approach to finding the right opportunities for automation. 1. Make a process map. The first step is to map each stage of the customer journey to the respective internal processes and workflows. For example, at the awareness stage, you'd have landing pages, contact forms, lead scoring, and so on.
To create a customer journey that executes a one-time email blast: Go to Outbound marketing > Marketing Execution > Customer Journeys. This takes you to a list of existing customer journeys. Select New on the command bar. The New Customer Journey page opens with the Select a Customer Journey Template dialog box shown. Each template provides a ...
A customer journey map is the visualization of the process a customer undertakes to accomplish a task. An omnichannel customer journey map spans the process across all the interaction channels the customer uses to complete their task. Omnichannel customer journey vs. Single channel customer journey
The customer journey is not linear; it can be complex and nonlinear, with customers moving back and forth between stages and touchpoints depending on their needs, preferences, and behaviors. It can be influenced by various factors, including marketing efforts, customer service interactions, word-of-mouth recommendations, and personal experiences.
Real-time Customer Insights & Engagement - An integrated profile fuses live data from all sources across customer touchpoints, including behavioral, transactional, financial, and operational data to optimize personal and contextual experiences for customers in their time.. Modern Omnichannel Orchestration & Execution - A single canvas on which to harmonize and optimize the customer journey ...
Brands must take a stand, even if it means parting ways with some customers or partners along the journey. The purpose driving your brand may not resonate with every customer, and that's all right. The objective is to attract the right audience, not everyone. So, think carefully about the reason behind your brand and how it relates to your ...
BusinessWire IndiaNew Delhi [India], March 19: The 3rd Annual CX Excellence Awards 2024, hosted by Quantic India recently, was a groundbreaking event showcasing the pinnacle of customer experience ...
parcelLab, a retail, e-commerce, and post-purchase customer experience platform, has announced the appointment of Noel Hamill as Global Chief Marketing Officer. According to a press release, Hamill will "define and execute parcelLab's global go-to-market strategy and vision, overseeing all marketing functions and helping to transform the ...
Customer Data Management - Voices voices Customer Data Management Voices is your destination as a customer data management technical and marketing practice leader and specialist. This collection of tutorials is your one-stop-shop to hear from your peers, get inspired, and learn about developments in MarTech.
A customer journey is whatever interaction a consumer has with your company. Technically-referred as a sales funnel, it's often represented visually as a map, or an upside-down triangle. Today's customers are often aware of a brand, its products and services before they're ready click "buy". Every interaction a customer has with your company ...