Voyager, NASA’s Longest-Lived Mission, Logs 45 Years in Space

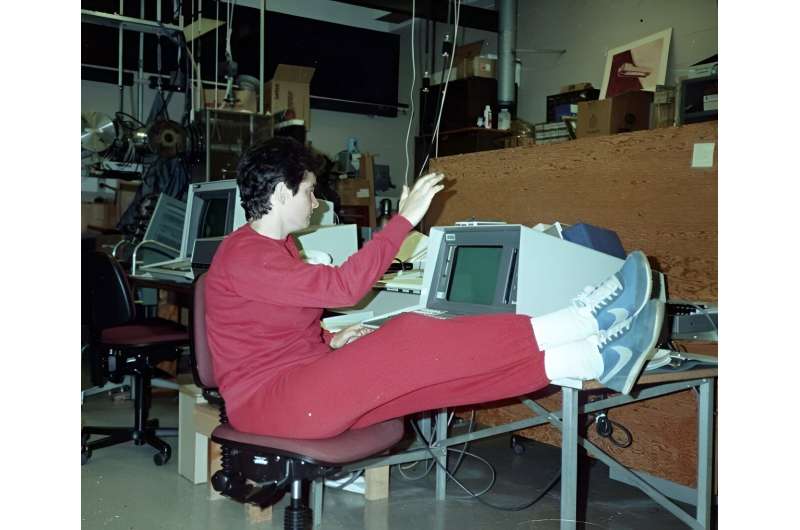
This archival image taken at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory on March 23, 1977, shows engineers preparing the Voyager 2 spacecraft ahead of its launch later that year.
Launched in 1977, the twin Voyager probes are NASA’s longest-operating mission and the only spacecraft ever to explore interstellar space.
NASA’s twin Voyager probes have become, in some ways, time capsules of their era: They each carry an eight-track tape player for recording data, they have about 3 million times less memory than modern cellphones, and they transmit data about 38,000 times slower than a 5G internet connection.
Yet the Voyagers remain on the cutting edge of space exploration. Managed and operated by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, they are the only probes to ever explore interstellar space – the galactic ocean that our Sun and its planets travel through.
The Sun and the planets reside in the heliosphere, a protective bubble created by the Sun’s magnetic field and the outward flow of solar wind (charged particles from the Sun). Researchers – some of them younger than the two distant spacecraft – are combining Voyager’s observations with data from newer missions to get a more complete picture of our Sun and how the heliosphere interacts with interstellar space.
NASA’s Solar System Interactive lets users see where the Voyagers are right now relative to the planets, the Sun, and other spacecraft. View it yourself here . Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
“The heliophysics mission fleet provides invaluable insights into our Sun, from understanding the corona or the outermost part of the Sun’s atmosphere, to examining the Sun’s impacts throughout the solar system, including here on Earth, in our atmosphere, and on into interstellar space,” said Nicola Fox, director of the Heliophysics Division at NASA Headquarters in Washington. “Over the last 45 years, the Voyager missions have been integral in providing this knowledge and have helped change our understanding of the Sun and its influence in ways no other spacecraft can.”
The Voyagers are also ambassadors, each carrying a golden record containing images of life on Earth, diagrams of basic scientific principles, and audio that includes sounds from nature, greetings in multiple languages, and music. The gold-coated records serve as a cosmic “message in a bottle” for anyone who might encounter the space probes. At the rate gold decays in space and is eroded by cosmic radiation, the records will last more than a billion years.

45 Years of Voyager I and II
Launched in 1977, NASA’s twin Voyager spacecraft inspired the world with pioneering visits to Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. Their journey continues 45 years later as both probes explore interstellar space, the region outside the protective heliosphere created by our Sun. Researchers – some younger than the spacecraft – are now using Voyager data to solve mysteries of our solar system and beyond.

This archival photo shows engineers working on vibration acoustics and pyro shock testing of NASA’s Voyager on Nov. 18, 1976. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech

NASA’s Voyager 1 acquired this image of a volcanic explosion on Io on March 4, 1979, about 11 hours before the spacecraft’s closest approach to the moon of Jupiter.

Neptune’s green-blue atmosphere was shown in greater detail than ever before in this image from NASA’s Voyager 2 as the spacecraft rapidly approached its encounter with the giant planet in August 1989.

This updated version of the iconic "Pale Blue Dot" image taken by the Voyager 1 spacecraft uses modern image-processing software and techniques to revisit the well-known Voyager view while attempting to respect the original data and intent of those who planned the images.

This illustrated graphic was made to mark Voyager 1’s entry into interstellar space in 2012. It puts solar system distances in perspective, with the scale bar in astronomical units and each set distance beyond 1 AU (the average distance between the Sun and Earth) representing 10 times the previous distance.

This graphic highlights some of the Voyager mission’s key accomplishments. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech Full image details

This graphic provides some of the mission’s key statistics from 2018, when NASA’s Voyager 2 probe exited the heliosphere. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech Full image details
Beyond Expectations
Voyager 2 launched on Aug. 20, 1977, quickly followed by Voyager 1 on Sept. 5. Both probes traveled to Jupiter and Saturn, with Voyager 1 moving faster and reaching them first. Together, the probes unveiled much about the solar system’s two largest planets and their moons. Voyager 2 also became the first and only spacecraft to fly close to Uranus (in 1986) and Neptune (in 1989), offering humanity remarkable views of – and insights into – these distant worlds.
While Voyager 2 was conducting these flybys, Voyager 1 headed toward the boundary of the heliosphere. Upon exiting it in 2012 , Voyager 1 discovered that the heliosphere blocks 70% of cosmic rays, or energetic particles created by exploding stars. Voyager 2, after completing its planetary explorations, continued to the heliosphere boundary, exiting in 2018 . The twin spacecraft’s combined data from this region has challenged previous theories about the exact shape of the heliosphere.

Voyager 1 and 2 have accomplished a lot since they launched in 1977. This infographic highlights the mission’s major milestones, including visiting the four outer planets and exiting the heliosphere, or the protective bubble of magnetic fields and particles created by the Sun.
“Today, as both Voyagers explore interstellar space, they are providing humanity with observations of uncharted territory,” said Linda Spilker, Voyager’s deputy project scientist at JPL. “This is the first time we’ve been able to directly study how a star, our Sun, interacts with the particles and magnetic fields outside our heliosphere, helping scientists understand the local neighborhood between the stars, upending some of the theories about this region, and providing key information for future missions.”
The Long Journey
Over the years, the Voyager team has grown accustomed to surmounting challenges that come with operating such mature spacecraft, sometimes calling upon retired colleagues for their expertise or digging through documents written decades ago.
Each Voyager is powered by a radioisotope thermoelectric generator containing plutonium, which gives off heat that is converted to electricity. As the plutonium decays, the heat output decreases and the Voyagers lose electricity. To compensate , the team turned off all nonessential systems and some once considered essential, including heaters that protect the still-operating instruments from the frigid temperatures of space. All five of the instruments that have had their heaters turned off since 2019 are still working, despite being well below the lowest temperatures they were ever tested at.
Get the Latest JPL News
Recently, Voyager 1 began experiencing an issue that caused status information about one of its onboard systems to become garbled. Despite this, the system and spacecraft otherwise continue to operate normally, suggesting the problem is with the production of the status data, not the system itself. The probe is still sending back science observations while the engineering team tries to fix the problem or find a way to work around it.
“The Voyagers have continued to make amazing discoveries, inspiring a new generation of scientists and engineers,” said Suzanne Dodd, project manager for Voyager at JPL. “We don’t know how long the mission will continue, but we can be sure that the spacecraft will provide even more scientific surprises as they travel farther away from the Earth.”
More About the Mission
A division of Caltech in Pasadena, JPL built and operates the Voyager spacecraft. The Voyager missions are a part of the NASA Heliophysics System Observatory, sponsored by the Heliophysics Division of the Science Mission Directorate in Washington.
For more information about the Voyager spacecraft, visit:
https://www.nasa.gov/voyager
News Media Contact
Calla Cofield
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
626-808-2469
What Is on Voyager’s Golden Record?
From a whale song to a kiss, the time capsule sent into space in 1977 had some interesting contents
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/headshot/megan.png)
Megan Gambino
Senior Editor
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/Voyager-records-631.jpg)
“I thought it was a brilliant idea from the beginning,” says Timothy Ferris. Produce a phonograph record containing the sounds and images of humankind and fling it out into the solar system.
By the 1970s, astronomers Carl Sagan and Frank Drake already had some experience with sending messages out into space. They had created two gold-anodized aluminum plaques that were affixed to the Pioneer 10 and Pioneer 11 spacecraft. Linda Salzman Sagan, an artist and Carl’s wife, etched an illustration onto them of a nude man and woman with an indication of the time and location of our civilization.
The “Golden Record” would be an upgrade to Pioneer’s plaques. Mounted on Voyager 1 and Voyager 2, twin probes launched in 1977, the two copies of the record would serve as time capsules and transmit much more information about life on Earth should extraterrestrials find it.
NASA approved the idea. So then it became a question of what should be on the record. What are humanity’s greatest hits? Curating the record’s contents was a gargantuan task, and one that fell to a team including the Sagans, Drake, author Ann Druyan, artist Jon Lomberg and Ferris, an esteemed science writer who was a friend of Sagan’s and a contributing editor to Rolling Stone .
The exercise, says Ferris, involved a considerable number of presuppositions about what aliens want to know about us and how they might interpret our selections. “I found myself increasingly playing the role of extraterrestrial,” recounts Lomberg in Murmurs of Earth , a 1978 book on the making of the record. When considering photographs to include, the panel was careful to try to eliminate those that could be misconstrued. Though war is a reality of human existence, images of it might send an aggressive message when the record was intended as a friendly gesture. The team veered from politics and religion in its efforts to be as inclusive as possible given a limited amount of space.
Over the course of ten months, a solid outline emerged. The Golden Record consists of 115 analog-encoded photographs, greetings in 55 languages, a 12-minute montage of sounds on Earth and 90 minutes of music. As producer of the record, Ferris was involved in each of its sections in some way. But his largest role was in selecting the musical tracks. “There are a thousand worthy pieces of music in the world for every one that is on the record,” says Ferris. I imagine the same could be said for the photographs and snippets of sounds.
The following is a selection of items on the record:
Silhouette of a Male and a Pregnant Female
The team felt it was important to convey information about human anatomy and culled diagrams from the 1978 edition of The World Book Encyclopedia. To explain reproduction, NASA approved a drawing of the human sex organs and images chronicling conception to birth. Photographer Wayne F. Miller’s famous photograph of his son’s birth, featured in Edward Steichen’s 1955 “Family of Man” exhibition, was used to depict childbirth. But as Lomberg notes in Murmurs of Earth , NASA vetoed a nude photograph of “a man and a pregnant woman quite unerotically holding hands.” The Golden Record experts and NASA struck a compromise that was less compromising— silhouettes of the two figures and the fetus positioned within the woman’s womb.
DNA Structure
At the risk of providing extraterrestrials, whose genetic material might well also be stored in DNA, with information they already knew, the experts mapped out DNA’s complex structure in a series of illustrations.
Demonstration of Eating, Licking and Drinking
When producers had trouble locating a specific image in picture libraries maintained by the National Geographic Society, the United Nations, NASA and Sports Illustrated , they composed their own. To show a mouth’s functions, for instance, they staged an odd but informative photograph of a woman licking an ice-cream cone, a man taking a bite out of a sandwich and a man drinking water cascading from a jug.
Olympic Sprinters
Images were selected for the record based not on aesthetics but on the amount of information they conveyed and the clarity with which they did so. It might seem strange, given the constraints on space, that a photograph of Olympic sprinters racing on a track made the cut. But the photograph shows various races of humans, the musculature of the human leg and a form of both competition and entertainment.
Photographs of huts, houses and cityscapes give an overview of the types of buildings seen on Earth. The Taj Mahal was chosen as an example of the more impressive architecture. The majestic mausoleum prevailed over cathedrals, Mayan pyramids and other structures in part because Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan built it in honor of his late wife, Mumtaz Mahal, and not a god.
Golden Gate Bridge
Three-quarters of the record was devoted to music, so visual art was less of a priority. A couple of photographs by the legendary landscape photographer Ansel Adams were selected, however, for the details captured within their frames. One, of the Golden Gate Bridge from nearby Baker Beach, was thought to clearly show how a suspension bridge connected two pieces of land separated by water. The hum of an automobile was included in the record’s sound montage, but the producers were not able to overlay the sounds and images.
A Page from a Book
An excerpt from a book would give extraterrestrials a glimpse of our written language, but deciding on a book and then a single page within that book was a massive task. For inspiration, Lomberg perused rare books, including a first-folio Shakespeare, an elaborate edition of Chaucer from the Renaissance and a centuries-old copy of Euclid’s Elements (on geometry), at the Cornell University Library. Ultimately, he took MIT astrophysicist Philip Morrison’s suggestion: a page from Sir Isaac Newton’s System of the World , where the means of launching an object into orbit is described for the very first time.
Greeting from Nick Sagan
To keep with the spirit of the project, says Ferris, the wordings of the 55 greetings were left up to the speakers of the languages. In Burmese , the message was a simple, “Are you well?” In Indonesian , it was, “Good night ladies and gentlemen. Goodbye and see you next time.” A woman speaking the Chinese dialect of Amoy uttered a welcoming, “Friends of space, how are you all? Have you eaten yet? Come visit us if you have time.” It is interesting to note that the final greeting, in English , came from then-6-year-old Nick Sagan, son of Carl and Linda Salzman Sagan. He said, “Hello from the children of planet Earth.”
Whale Greeting
Biologist Roger Payne provided a whale song (“the most beautiful whale greeting,” he said, and “the one that should last forever”) captured with hydrophones off the coast of Bermuda in 1970. Thinking that perhaps the whale song might make more sense to aliens than to humans, Ferris wanted to include more than a slice and so mixed some of the song behind the greetings in different languages. “That strikes some people as hilarious, but from a bandwidth standpoint, it worked quite well,” says Ferris. “It doesn’t interfere with the greetings, and if you are interested in the whale song, you can extract it.”
Reportedly, the trickiest sound to record was a kiss . Some were too quiet, others too loud, and at least one was too disingenuous for the team’s liking. Music producer Jimmy Iovine kissed his arm. In the end, the kiss that landed on the record was actually one that Ferris planted on Ann Druyan’s cheek.
Druyan had the idea to record a person’s brain waves, so that should extraterrestrials millions of years into the future have the technology, they could decode the individual’s thoughts. She was the guinea pig. In an hour-long session hooked to an EEG at New York University Medical Center, Druyan meditated on a series of prepared thoughts. In Murmurs of Earth , she admits that “a couple of irrepressible facts of my own life” slipped in. She and Carl Sagan had gotten engaged just days before, so a love story may very well be documented in her neurological signs. Compressed into a minute-long segment, the brain waves sound, writes Druyan, like a “string of exploding firecrackers.”
Georgian Chorus—“Tchakrulo”
The team discovered a beautiful recording of “Tchakrulo” by Radio Moscow and wanted to include it, particularly since Georgians are often credited with introducing polyphony, or music with two or more independent melodies, to the Western world. But before the team members signed off on the tune, they had the lyrics translated. “It was an old song, and for all we knew could have celebrated bear-baiting,” wrote Ferris in Murmurs of Earth . Sandro Baratheli, a Georgian speaker from Queens, came to the rescue. The word “tchakrulo” can mean either “bound up” or “hard” and “tough,” and the song’s narrative is about a peasant protest against a landowner.
Chuck Berry’s “Johnny B. Goode”
According to Ferris, Carl Sagan had to warm up to the idea of including Chuck Berry’s 1958 hit “Johnny B. Goode” on the record, but once he did, he defended it against others’ objections. Folklorist Alan Lomax was against it, arguing that rock music was adolescent. “And Carl’s brilliant response was, ‘There are a lot of adolescents on the planet,’” recalls Ferris.
On April 22, 1978, Saturday Night Live spoofed the Golden Record in a skit called “Next Week in Review.” Host Steve Martin played a psychic named Cocuwa, who predicted that Time magazine would reveal, on the following week’s cover, a four-word message from aliens. He held up a mock cover, which read, “Send More Chuck Berry.”
More than four decades later, Ferris has no regrets about what the team did or did not include on the record. “It means a lot to have had your hand in something that is going to last a billion years,” he says. “I recommend it to everybody. It is a healthy way of looking at the world.”
According to the writer, NASA approached him about producing another record but he declined. “I think we did a good job once, and it is better to let someone else take a shot,” he says.
So, what would you put on a record if one were being sent into space today?
Get the latest Science stories in your inbox.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/headshot/megan.png)
Megan Gambino | | READ MORE
Megan Gambino is a senior web editor for Smithsonian magazine.
- Become A Member
- Gift Membership
- Kids Membership
- Other Ways to Give
- Explore Worlds
- Defend Earth
How We Work
- Education & Public Outreach
- Space Policy & Advocacy
- Science & Technology
- Global Collaboration
Our Results
Learn how our members and community are changing the worlds.
Our citizen-funded spacecraft successfully demonstrated solar sailing for CubeSats.
Space Topics
- Planets & Other Worlds
- Space Missions
- Space Policy
- Planetary Radio
- Space Images
The Planetary Report
The eclipse issue.
Science and splendor under the shadow.
Get Involved
Membership programs for explorers of all ages.
Get updates and weekly tools to learn, share, and advocate for space exploration.
Volunteer as a space advocate.
Support Our Mission
- Renew Membership
- Society Projects
The Planetary Fund
Accelerate progress in our three core enterprises — Explore Worlds, Find Life, and Defend Earth. You can support the entire fund, or designate a core enterprise of your choice.
- Strategic Framework
- News & Press
The Planetary Society
Know the cosmos and our place within it.
Our Mission
Empowering the world's citizens to advance space science and exploration.
- Explore Space
- Take Action
- Member Community
- Account Center
- Eclipse 2024
- “Exploration is in our nature.” - Carl Sagan
The Voyager missions
Highlights Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 launched in 1977 and made a grand tour of the solar system's outer planets. They are the only functioning spacecraft in interstellar space, and they are still sending back measurements of the interstellar medium. Each spacecraft carries a copy of the golden record, a missive from Earth to any alien lifeforms that may find the probes in the future.
What are the Voyager missions?
The Voyager program consists of two spacecraft: Voyager 1 and Voyager 2. Voyager 2 was actually launched first, in August 1977, but Voyager 1 was sent on a faster trajectory when it launched about two weeks later. They are the only two functioning spacecraft currently in interstellar space, beyond the environment controlled by the sun.
Voyager 2’s path took it past Jupiter in 1979, Saturn in 1981, Uranus in 1985, and Neptune in 1989. It is the only spacecraft to have visited Uranus or Neptune, and has provided much of the information that we use to characterize them now.
Because of its higher speed and more direct trajectory, Voyager 1 overtook Voyager 2 just a few months after they launched. It visited Jupiter in 1979 and Saturn in 1980. It overtook Pioneer 10 — the only other spacecraft in interstellar space thus far — in 1998 and is now the most distant artificial object from Earth.
How the Voyagers work
The two spacecraft are identical, each with a radio dish 3.7 meters (12 feet) across to transmit data back to Earth and a set of 16 thrusters to control their orientations and point their dishes toward Earth. The thrusters run on hydrazine fuel, but the electronic components of each spacecraft are powered by thermoelectric generators that run on plutonium. Each carries 11 scientific instruments, about half of which were designed just for observing planets and have now been shut off. The instruments that are now off include several cameras and spectrometers to examine the planets, as well as two radio-based experiments. Voyager 2 now has five functioning instruments: a magnetometer, a spectrometer designed to investigate plasmas, an instrument to measure low-energy charged particles and one for cosmic rays, and one that measures plasma waves. Voyager 1 only has four of those, as its plasma spectrometer is broken.
Jupiter findings
Over the course of their grand tours of the solar system, the Voyagers took tens of thousands of images and measurements that significantly changed our understanding of the outer planets.
At Jupiter, they gave us our first detailed ideas of how the planet’s atmosphere moves and evolves, showing that the Great Red Spot was a counter-clockwise rotating storm that interacted with other, smaller storms. They were also the first missions to spot a faint, dusty ring around Jupiter. Finally, they observed some of Jupiter’s moons, discovering Io’s volcanism, finding the linear features on Europa that were among the first hints that it might have an ocean beneath its surface, and granting Ganymede the title of largest moon in the solar system, a superlative that was previously thought to belong to Saturn’s moon Titan.
Saturn findings
Next, each spacecraft flew past Saturn, where they measured the composition and structure of Saturn’s atmosphere , and Voyager 1 also peered into Titan’s thick haze. Its observations led to the idea that Titan might have liquid hydrocarbons on its surface, a hypothesis that has since been verified by other missions. When the two missions observed Saturn’s rings, they found the gaps and waves that are well-known today. Voyager 1 also spotted three previously-unknown moons orbiting Saturn: Atlas, Prometheus, and Pandora.
Uranus and Neptune findings
After this, Voyager 1 headed out of the solar system, while Voyager 2 headed toward Uranus . There, it found 11 previously-unknown moons and two previously-unknown rings. Many of the phenomena it observed on Uranus remained unexplained, such as its unusual magnetic field and an unexpected lack of major temperature changes at different latitudes.
Voyager 2’s final stop, 12 years after it left Earth, was Neptune. When it arrived , it continued its streak of finding new moons with another haul of 6 small satellites, as well as finding rings around Neptune. As it did at Uranus, it observed the planet’s composition and magnetic field. It also found volcanic vents on Neptune’s huge moon Triton before it joined Voyager 1 on the way to interstellar space.
Interstellar space
Interstellar space begins at the heliopause, where the solar wind – a flow of charged particles released by the sun – is too weak to continue pushing against the interstellar medium, and the pressure from the two balances out. Voyager 1 officially entered interstellar space in August 2012, and Voyager 2 joined it in November 2018.
These exits were instrumental in enabling astronomers to determine where exactly the edge of interstellar space is, something that’s difficult to measure from within the solar system. They showed that interstellar space begins just over 18 billion kilometers (about 11 billion miles) from the sun. The spacecraft continue to send back data on the structure of the interstellar medium.
After its planetary encounters, Voyager 1 took the iconic “Pale Blue Dot” image , showing Earth from about 6 billion kilometers (3.7 billion miles) away. As of 2021 , Voyager 1 is about 155 astronomical units (14.4 billion miles) from Earth, and Voyager 2 is nearly 129 astronomical units (12 billion miles) away.
The golden records
Each Voyager spacecraft has a golden phonograph record affixed to its side, intended as time capsules from Earth to any extraterrestrial life that might find the probes sometime in the distant future. They are inscribed with a message from Jimmy Carter, the U.S. President at the time of launch, which reads: “This is a present from a small, distant world, a token of our sounds, our science, our images, our music, our thoughts and our feelings. We are attempting to survive our time so we may live into yours.”
The covers of the records have several images inscribed, including visual instructions on how to play them, a map of our solar system’s location with respect to a set of 14 pulsars, and a drawing of a hydrogen atom. They are plated with uranium – its rate of decay will allow any future discoverers of either of the records to calculate when they were created.
The records’ contents were selected by a committee chaired by Carl Sagan. Each contains 115 images, including scientific diagrams of the solar system and its planets, the flora and fauna of Earth, and examples of human culture. There are natural sounds, including breaking surf and birdsong, spoken greetings in 55 languages, an hour of brainwave recordings, and an eclectic selection of music ranging from Beethoven to Chuck Berry to a variety of folk music.
Learn more Voyager Mission Status Bulletin Archives Experience A Message From Earth - Inspired by the Voyager Golden Record Neptune, planet of wind and ice
Support missions like Voyager 1 and 2
Whether it's advocating, teaching, inspiring, or learning, you can do something for space, right now. Let's get to work.
For full functionality of this site it is necessary to enable JavaScript. Here are instructions on how to enable JavaScript in your web browser .

The remarkable twin Voyager spacecraft continue to explore the outer reaches of the solar system decades after they completed their surveys of the Outer Planets. Launched in 1977 (September 5 for Voyager 1 (V1) and August 20 for Voyager 2 (V2), whose trajectory took it past Jupiter after Voyager 1), the spacecraft pair made many fundamental discoveries as they flew past Jupiter (March 1979 for V1, July 1979 for V2) and Saturn (November 1980 for V1, August 1981 for V2). The path of Voyager 2 past Saturn was targeted so that it continued within the plane of the solar system, allowing it to become the first spacecraft to visit Uranus (January 1986) and Neptune (August 1989). Following the Neptune encounter, both spacecraft started a new phase of exploration under the intriguing title of the Voyager Interstellar Mission.

Five instruments continue to collect important measurements of magnetic fields, plasmas, and charged particles as both spacecraft explore different portions of the solar system beyond the orbits of the planets. Voyager 1 is now more than 118 astronomical units (one AU is equal to the average orbital distance of Earth from the Sun) distant from the sun, traveling at a speed (relative to the sun) of 17.1 kilometers per second (10.6 miles per second). Voyager 2 is now more than 96 AU from the sun, traveling at a speed of 15.5 kilometers per second (9.6 miles per second). Both spacecraft are moving considerably faster than Pioneers 10 and 11, two earlier spacecraft that became the first robotic visitors to fly past Jupiter and Saturn in the mid-70s.

This processed color image of Jupiter was produced in 1990 by the U.S. Geological Survey from a Voyager image captured in 1979. The colors have been enhanced to bring out detail. Zones of light-colored, ascending clouds alternate with bands of dark, descending clouds. The clouds travel around the planet in alternating eastward and westward belts at speeds of up to 540 kilometers per hour. Tremendous storms as big as Earthly continents surge around the planet. The Great Red Spot (oval shape toward the lower-left) is an enormous anticyclonic storm that drifts along its belt, eventually circling the entire planet.
As seen in the night sky at Earth, Voyager 1 is within the confines of the constellation Ophiuchus, only slightly above the celestial equator; no telescope can see it, but radio contact is expected to be maintained for at least the next ten years. Voyager 2 is within the bounds of the constellation Telescopium (which somehow sounds quite appropriate) in the far southern night sky.

Both spacecraft have already passed something called the Termination Shock † (December 2004 for V1, August 2007 for V2), where the solar wind slows as it starts to interact with the particles and fields present between the stars. It is expected that both spacecraft will encounter the Heliopause, where the solar wind ceases as true interstellar space begins, from 10 to 20 years after crossing the Termination Shock. Theories exist for what should be present in interstellar space, but the Voyagers will become the first man-made objects to go beyond the influences of the Sun, hopefully returning the first measurements of what it is like out there. Each spacecraft is carrying a metal record with encoded sounds and sights from Earth, along with the needle needed to read the recordings, and simplified instructions for where the spacecraft came from, in case they are eventually discovered by intelligent extra-terrestrials.

Keep track of the Voyager spacecraft on the official Voyager Interstellar Mission website or follow @NASAVoyager2 on Twitter. † The sun ejects a continuous stream of charged particles (electrons, protons, etc) that is collectively termed the solar wind. The particles are traveling extremely fast and are dense enough to form a very tenuous atmosphere; the heliosphere represents the volume of space where the effects of the solar wind dominate over those of particles in interstellar space. The solar wind particles are moving very much faster than the local speed of sound represented by their low volume density. When the particles begin to interact with interstellar particles and fields (the interaction can be either physically running into other particles or experiencing an electromagnetic force resulting from a charged particle moving within a magnetic field), then they start to slow down. The point at which they become subsonic (rather than their normal hypersonic speed) is the Termination Shock.
We rely on the generous support of donors, sponsors, members, and other benefactors to share the history and impact of aviation and spaceflight, educate the public, and inspire future generations. With your help, we can continue to preserve and safeguard the world’s most comprehensive collection of artifacts representing the great achievements of flight and space exploration.
- Get Involved
- Host an Event
Thank you. You have successfully signed up for our newsletter.
Error message, sorry, there was a problem. please ensure your details are valid and try again..
- Free Timed-Entry Passes Required
- Terms of Use
The Sun Spot
NASA Engineers Make Progress Toward Understanding Voyager 1 Issue

Since November 2023, NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft has been sending a steady radio signal to Earth, but the signal does not contain usable data. The source of the issue appears to be with one of three onboard computers, the flight data subsystem (FDS), which is responsible for packaging the science and engineering data before it’s sent to Earth by the telemetry modulation unit.
On March 3, the Voyager mission team saw activity from one section of the FDS that differed from the rest of the computer’s unreadable data stream. The new signal was still not in the format used by Voyager 1 when the FDS is working properly, so the team wasn’t initially sure what to make of it. But an engineer with the agency’s Deep Space Network, which operates the radio antennas that communicate with both Voyagers and other spacecraft traveling to the Moon and beyond, was able to decode the new signal and found that it contains a readout of the entire FDS memory.
The FDS memory includes its code, or instructions for what to do, as well as variables, or values used in the code that can change based on commands or the spacecraft’s status. It also contains science or engineering data for downlink. The team will compare this readout to the one that came down before the issue arose and look for discrepancies in the code and the variables to potentially find the source of the ongoing issue.
This new signal resulted from a command sent to Voyager 1 on March 1. Called a “poke” by the team, the command is meant to gently prompt the FDS to try different sequences in its software package in case the issue could be resolved by going around a corrupted section.
Because Voyager 1 is more than 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) from Earth, it takes 22.5 hours for a radio signal to reach the spacecraft and another 22.5 hours for the probe’s response to reach antennas on the ground. So the team received the results of the command on March 3. On March 7, engineers began working to decode the data, and on March 10, they determined that it contains a memory readout.
The team is analyzing the readout. Using that information to devise a potential solution and attempt to put it into action will take time.
News Media Contact Calla Cofield Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. 626-808-2469 calla.e. cofield @jpl.nasa.gov
share this!
March 18, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
As Voyager 1's mission draws to a close, one planetary scientist reflects on its legacy
by Daniel Strain, University of Colorado at Boulder
For nearly 50 years, NASA's Voyager 1 mission has competed for the title of deep space's little engine that could. Launched in 1977 along with its twin, Voyager 2, the spacecraft is now soaring more than 15 billion miles from Earth.
On their journeys through the solar system , the Voyager spacecraft beamed startling images back to Earth—of Jupiter and Saturn, then Uranus and Neptune and their moons. Voyager 1's most famous shot may be what famed astronomer Carl Sagan called the "pale blue dot," a lonely image of Earth taken from 6 billion miles away in 1990.
But Voyager 1's trek could now be drawing to a close. Since December, the spacecraft--which weighs less than most cars--has been sending nonsensical messages back to Earth, and engineers are struggling to fix the problem. Voyager 2 remains operational.
Fran Bagenal is a planetary scientist at the Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics (LASP) at CU Boulder. She started working on the Voyager mission during a summer student job in the late 1970s and has followed the two spacecraft closely since.
To celebrate Voyager 1, Bagenal reflects on the mission's legacy—and which planet she wants to visit again.
Many are impressed that the spacecraft has kept going for this long. Do you agree?
Voyager 1's computer was put together in the 1970s, and there are very few people around who still use those computing languages. The communication rate is 40 bits per second. Not megabits. Not kilobits. Forty bits per second. Moreover, the round-trip communication time is 45 hours. It's amazing that they're still communicating with it at all.
What was it like working on Voyager during the mission's early days?
At the very beginning, we used computer punch cards. The data was on magnetic tapes, and we would print out line-plots on reels of paper. It was very primitive.
But planet by planet, with each flyby, the technology got a lot more sophisticated. By the time we got to Neptune in 1989, we were doing our science on much more efficient computers, and NASA presented its results live across the globe over an early version of the internet.
Think about it—going from punch cards to the internet in 12 years.
How did the Voyager spacecraft shape our understanding of the solar system?
First of all, the pictures were jaw-dropping. They were the first high-quality, close-up pictures of the four gas giant planets and their moons. The Voyagers really revolutionized our thinking by going from one planet to the other and comparing them.
Jupiter and Saturn's ammonia white and orange clouds, for example, were violently swept around by strong winds, while Uranus and Neptune's milder weather systems were hidden and colored blue by atmospheric methane. But the most dramatic discoveries were the multiple distinct worlds of the different moons, from Jupiter's cratered Callisto and volcanic Io to Saturn's cloudy Titan to plumes erupting on Triton, a moon of Neptune.
The Jupiter and Saturn systems have since been explored in greater detail by orbiting missions—Galileo and Juno at Jupiter, Cassini at Saturn.

Voyager 2 is the only spacecraft that has visited Uranus and Neptune. Do we need to return?
My vote is to return to Uranus—the only planet in our solar system that's tipped on its side.
We didn't know before Voyager whether Uranus had a magnetic field. When we arrived, we found that Uranus has a magnetic field that's severely tilted with respect to the planet's rotation. That's a weird magnetic field.
Jupiter, Saturn and Neptune all emit a lot of heat from the inside. They glow in the infrared, emitting two and a half times more energy than they receive from the sun. These things are hot.
Uranus isn't the same. It doesn't have this internal heat source. So maybe, just maybe, at the end of the formation of the solar system billions of years ago, some big object hit Uranus, tipped it on its side, stirred it up and dissipated the heat. Perhaps, this led to an irregular magnetic field .
These are the sorts of questions that were raised by Voyager 30 years ago. Now we need to go back.
Culturally, Voyager 1's most lasting impact may be the 'pale blue dot.' Why?
I have huge respect for Carl Sagan. I met him when I was 16, a high school student in England, and I shook his hand.
He pointed to the Voyager image and said, "Here we are. We're leaving the solar system. We're looking back, and there's this pale blue dot. That's us. It's all our friends. It's all our relatives. It's where we live and die."
This was the time we were just beginning to say, "Wait a minute. What are we doing to our planet Earth?" He was awakening or reinforcing this need to think about what humans are doing to Earth. It also evoked why we need to go exploring space: to think about where we are and how we fit into the solar system.
How are you feeling now that Voyager 1's mission may be coming to an end?
It's amazing. No one thought they would go this far. But with just a few instruments working, how much longer can we keep going? I think it will soon be time to say, "Right, jolly good. Extraordinary job. Well done."
Provided by University of Colorado at Boulder
Explore further
Feedback to editors

Blind people can hear and feel April's total solar eclipse with new technology
2 hours ago

Mapping the best route for a spacecraft traveling beyond the sun's sphere of influence
Researchers outline new approach in search for dark matter through future DUNE research project

Researchers reveal evolutionary path of important proteins
Study identifies protein responsible for gas vesicle clustering in bacteria
Largest ice shelf in Antarctica lurches forward once or twice each day
3 hours ago
Researchers develop a thermoelectric material with optimal cost, efficiency and flexibility

Researchers find WWI and WWII bombs in the ground are becoming more volatile

Scientists discover a key quality-control mechanism in DNA replication
4 hours ago

Tiny orchid flowers pollinated by tiny flies
Relevant physicsforums posts, our beautiful universe - photos and videos.
6 hours ago
Where are the black holes?
Mar 28, 2024
Terminology for motion in the solar system, ecliptic maybe?
Atmospheric escape parametre statistics.
Mar 27, 2024
Stellar evolution path and Regression line
Mar 25, 2024
U.S. Solar Eclipses - Oct. 14, 2023 (Annular) & Apr. 08, 2024 (Total)
More from Astronomy and Astrophysics
Related Stories

NASA: let's say something to Voyager 1 on 40th anniversary of launch
Aug 15, 2017

Unwrapping Uranus and its icy secrets: What NASA would learn from a mission to a wild world
Nov 28, 2023

What does Uranus sound like?
Apr 2, 2019
Jupiter has at least three magnetosheath jets, finds Voyager 2 data study
Jan 11, 2024

Which planet has the most moons? Moons of Saturn, Venus and Jupiter explained
Aug 15, 2022

'Star Trek' actor Shatner sends message to Voyager
Sep 5, 2017
Recommended for you

Japan moon probe survives second lunar night


Astronomers conduct first search for forming planets with James Webb Space Telescope

Climate change is messing with how we measure time: Study

'Cosmic cannibals' expel jets into space at 40% speed of light
Let us know if there is a problem with our content.
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
Covering the business and politics of space
NASA optimistic about resolving Voyager 1 computer problem

- Click to share on X (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Clipboard (Opens in new window)

WASHINGTON — A NASA official says he is optimistic that a problem with the Voyager 1 spacecraft that has kept it from transmitting intelligible data for months can be resolved.
Speaking at a March 20 meeting of the National Academies’ Committee on Solar and Space Physics, Joseph Westlake, director of NASA’s heliophysics division, said it appeared possible to fix the computer problem on the nearly 50-year-old spacecraft that has disrupted operations since last November.
“I feel like we’re on a path now to resolution,” he said. “They’re on the right path and I think we’re going to get to a point where Voyager 1 is going to continue, alive and kicking in space.”
Spacecraft controllers first noticed a problem with the spacecraft in November, when the data transmitted by the spacecraft was unusable. Engineers concluded that the problem was with an onboard computer called the flight data system (FDS), which collects data from the spacecraft’s instruments and other spacecraft telemetry.
Several factors have hampered efforts to correct the problem. Voyager 1, launched in 1977, is now more than 24 billion kilometers from Earth, which means it takes 22.5 hours for signals to travel between Earth and the spacecraft. None of the people who developed the FDS in the early to mid 1970s are available to assist now, so the project has had to turn to documentation to help identify the problem.
NASA announced March 13 progress in fixing the FDS when a command called a “poke” was transmitted to Voyager, and the spacecraft responded by sending back a readout of its memory. The agency said at the time it will compare that readout to one transmitted before the problem to help identify the issue.
Westlake said at the committee meeting that the problem appears to be a corrupted memory unit on the spacecraft. “It’s a part failure on one of the memories and they’re looking for a way to move a couple hundred words of software from one region to another in the flight computer,” he said. A word is two bytes.
He did not estimate how long it would take to make those software changes. NASA, in its latest statement about the spacecraft, said that using the FDS memory readout “to devise a potential solution and attempt to put it into action will take time.”
Jeff Foust writes about space policy, commercial space, and related topics for SpaceNews. He earned a Ph.D. in planetary sciences from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and a bachelor’s degree with honors in geophysics and planetary science... More by Jeff Foust

Sign up for a SpaceNews newsletter
Get top stories, military space news and more delivered to your inbox.

Voyager 1's Communication Malfunctions May Show the Spacecraft's Age
A s it turns out, spacecraft aren't immune to age. In November 2023, NASA's 46-year-old Voyager 1 spacecraft started sending a stream of nonsense to Earth, spewing out signals without any morsel of meaning . Members of the Voyager 1 mission team are rushing to resolve the issue in the aging spacecraft and are relatively optimistic after receiving a more meaningful response from the spacecraft this month.
But the ongoing breakdown in communication casts doubts on the durability of the probe and about why its systems are so prone to problems - a product, it seems, of the passage of time.
Read More: The Best of Voyager: The Longest-Running Space Mission in History
What Went Wrong with Voyager 1?
Sent into space in 1977 as part of NASA's Voyager mission , the Voyager 1 spacecraft has traveled more than 15 billion miles through space. Throughout its travels, the spacecraft has collected information about its surroundings and its status while drifting deeper and deeper into the universe, compiling insights on the outer solar system and the space beyond the outer solar system alongside its twin, the Voyager 2 spacecraft .
The probe has had its fair share of bugs throughout the course of its trip, with one of its biggest blips beginning in November. Though the spacecraft continues to receive and respect the commands of the Voyager 1 mission team, its communication system started to fail at around that time, meaning the spacecraft cannot send meaningful signals of its own. Instead, it's stuck returning a repeating sequence of ones and zeros, rather than its typical output of important insights condensed in convenient bundles of binary code.
As of now, the problem seems to persist, interrupting Voyager 1's interstellar investigation. But this isn't the only problem that's troubled the probe. In fact, after almost fifty years of flight, Voyager 1 is increasingly showing signs of its age.
Read More: Voyager: The Man Behind the Mission
Why Is Voyager 1 Prone to Problems?
Initially intended to study Jupiter and Saturn , Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 were built to survive only five years of flight. But as their flybys of the two planets came to a close and as their trajectories forged further and further into space, it seemed a shame to cut their travels short. In time, their two-planet mission transformed into a four-planet mission, and their four-planet mission transformed into an interstellar mission, as the probes became the first spacecraft to shoot into the space between stars, in 2012 and 2018 respectively.
Since then, though, Voyager 1's smooth sailing has become bumpier and bumpier, possibly a product of age. In 2017, for instance, the probe's primary thrusters started to struggle, pushing the Voyager 1 team to switch to its secondary thrusters to maintain its ability to align itself for communication. And in 2022, Voyager 1's attitude articulation and control system (AACS) met with a malfunction of its own, reducing the spacecraft's messages to meaningless nonsense , a lot like the issue that started in November.
Aside from these issues, it's the diminishing power supplies of the aging spacecraft that pose the biggest problems: As their power diminishes, scientists are slowly switching off some of their scientific instruments in an attempt to save others. It's a strategic move, as mission team members attempt to get as much information out of the probes as possible, though issues, including the ongoing Voyager 1 glitch, only get in the way of that goal.
Read More: Voyager: What's Next for NASA's Interstellar Probes?
What Will Fix Voyager 1?
Identifying the issue in the spacecraft's computers, the Voyager 1 mission team concluded that the current conundrum arose from a " corrupted section " in the software of one of Voyager 1's communication systems, called the flight data subsystem (FDS). This subsystem bundles the information collected by the probe before it is beamed back to the mission team.
In December, the mission team restarted the FDS, though the restart failed to return the subsystem to its functional state. In the aftermath of the attempt, the team then decided to send a command called a " poke " to the probe on March 1. The poke was cautiously considered and planned to push the corrupted subsystem to work around its corruption.
A response was received on March 3, not nonsense, but still difficult to discern. The delay in the response was anticipated - it takes 22.5 hours for signals to reach the probe and another 22.5 hours for signals to reach the mission team - but the response was cryptic. It wasn't until March 10 that the mission team members determined the response carried a readout of the FDS memory, including its initial instructions as well as its altered code, whether altered by command or by the status of the spacecraft.
By comparing the readout to those received before the issue began, it is possible that the team will identify the source of the problem, as well as its solution. But that " will take time ," according to a NASA press release - a particularly precious resource for the aging probe.
Read More: 5 NASA Spacecraft That Are Leaving Our Solar System for Good
Article Sources
Our writers at Discovermagazine.com use peer-reviewed studies and high quality sources for our articles, and our editors review for scientific accuracy and editorial standards. Review the sources used below for this article:
NASA The Sun Spot. Engineers Working to Resolve Issue With Voyager 1 Computer
NASA. Voyager
NASA. Voyager 1
NASA. Voyager 2
NASA The Sun Spot. NASA Engineers Make Progress Toward Understanding Voyager 1 Issue
NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Voyager - Fact Sheet
NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Voyager - The Interstellar Mission
NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Voyager 1 Fires Up Thrusters After 37 Years
NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Engineers Investigating NASA's Voyager 1 Telemetry Data
NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory. NASA's Voyager Will Do More Science With New Power Strategy

- 1 Understand
- 2.1 By plane
- 2.2 By train
- 3.1 By public transportation
- 4.1 Museums
- 4.2 Monuments
- 4.3 Religious Buildings
- 5.2 Theatres
- 5.4 Entertainment complexes
- 5.5 Water amusement parks
- 5.6 Aquarium
- 6.1 Bazaars
- 6.2 Shopping malls
- 7.1.1 Fast Food
- 7.2 Mid-range
- 7.3 Splurge
- 9.1.1 Hostels
- 9.1.2 Hotels
- 9.2 Mid-range
- 9.3 Splurge
- 10.1 Consulates
Krasnodar is the capital of Krasnodar Krai in southern Russia, with a popolulation in 2018 of just under 900,000. Its main industries are based on agriculture and food.
Understand [ edit ]
In the 18th century Russia expanded south under Catherine the Great, driving out Ottoman Turkey from control of the areas north of the Black Sea. The city that grew up here was called Yekaterinodar , Catherine's Gift, and became a diverse, entrepreneurial, attractive settlement. It was fought over in the Russian civil war, and since the Bolsheviks won, they got to rename it "Krasnodar", gift of the Reds. In 1942 / 43 it was occupied by the Nazis, with much destruction and death. However many of the old town buildings have been restored, though no-one could mistake the city's landmark hyperboloid tower for tsarist architecture.
Get in [ edit ]
By plane [ edit ].
From the airport, trolleybus 7 (1 hour) and minibuses 53 and 15 (40 minutes) operate service to main train station. Buses 1 and 1A operate service to the city centre. A taxi from the airport to the city centre should cost RUB500.
By train [ edit ]
Several trains per day operate between Krasnodar and the Black Sea port city of Novorossiysk (RUB650, 3 hours), Rostov-on-Don (RUB600, 3-4 hours), and Volgograd (RUB900, 14-16 hours).
By bus [ edit ]
Buses operate approximately every 3 hours between Krasnodar and the Black Sea port city of Novorossiysk (RUB350, 3.5 hours). Buses operate hourly to the Russian resort town of Anapa (RUB350, 3.5 hours). There are 6 buses per day to/from Rostov-on-Don (RUB400, 4-6 hours). There is also a daily bus to Sochi (6 hours).
Get around [ edit ]

By public transportation [ edit ]
Krasnodar has a dense network of trams, trolleybuses, city buses, taxis, the boat across the Kuban river and marshrutkas. Public transport fees are generally approximately RUB30.
See [ edit ]
Krasnaya (Red) Street is the main street of the city. Part of the street is closed to vehicles during evenings, when it becomes the center of nightlife.
Theater Square has largest splash fountain in Europe .
Museums [ edit ]
- 45.01759 38.9678 1 The Krasnodar Regional Art Museum Of Kovalenko , 13 Krasnaya St , ☏ +7 861 262-95-04 .
- 45.01759 38.9678 2 Krasnodar Regional Showroom of Fine Arts . Includes many famous works of Kuban and Russian and European artists from as early as 16th century.
- 45.019464 39.002994 3 Museum of Military Technologies Oruzhie Pobedy , v . Popular with kids that like to climb on the tanks.
Monuments [ edit ]
- Monument to Catherine the Great
- Sculpture of Walking Dogs - Mira 35 - Built in 2007, it was inspired by a famous Russian poet that commented on the number of dogs in Krasnodar.
- Monument to Shurik and Lida
- Monument of Cossacks writing a letter to the Turkish Sultan
- Monument to Kuban Cossacks
- Monument Avrora
- Monument A.S. Pushkin
- Obelisk In Honor Of The 200th Anniversary Of The Kuban Cossack Army
- I.E. Repin Monument
- Monument A.V. Suvorov
Religious Buildings [ edit ]
- St. Catherine's Cathedral
- Alexander Nevskiy Cathedral
- St. George's Church
- St. Elijah Church
- Holy Trinity Cathedral
- Chapel of Alexander Nevskiy
- Church of St. Nicholas
- Church of the Holy Libor
- St. Kazan Church
Do [ edit ]
- Climb the steel lattice hyperboloid tower built by Vladimir Grigorievich Shukhov in 1928. The tower likely wouldn't pass a safety inspection in most first world countries, but it is the best place to get a view of the city. The tower is near the circus.
- Watch football at Krasnodar Stadium. The home team is FC Krasnodar who play in the Russian Premier League, the top tier of Russian football. It was opened in 2016 with a capacity of 34,000. It's on the northeast edge of the city, 4 km from Krasnodar-1 main railway station (further out than the old "Kuban" Stadium). Take a bus to Vostochno-Kruglikovshaya Street.
Parks [ edit ]
- Rozhdestvenskiy Park of Culture and Leisure
- The Solnechny Ostrov (Sunny Island) Park
- Safari Park - Includes a zoo, but the animals are treated poorly
- Chistyakovskiy Grove Park
- Botanical Garden of Professor I. S. Kosenko
- City Botanical Garden
- Park of the 30th anniversary of the Victory
- City Park of Culture and Leisure
- Marshal Zhukov's Park
- Training Botanical Garden
- Park Druzhby
Theatres [ edit ]
Most are on Krasnaya Street
- Drama Theatre - Gorky , Ploshchad' Oktjabr'skoj Revoljucii, 2 .
- Children’s Puppet Theatre
- Philharmonic Hall
- Operetta Theatre
Cinema [ edit ]
- Avrora Kino , Krasnaya St 169 . Built in 1967. Two movie screens, including one with a capacity of 1,200. Also includes a cafe and pizzeria.
Entertainment complexes [ edit ]
Around 20 entertainment complexes are open 24 hours/day. These complexes usually include bowling alleys, shopping centers, video arcades, casinos, and restaurants.
Water amusement parks [ edit ]
Aquarium [ edit ].
- Ocean Park Aquarium , 161 Stasova St, inside Galaktika Mall . A 3,000 square meter aquarium. There are several tanks of fish to look at, including a tunnel-tank that patrons can walk under, allowing tiny sharks to swim over your head. It is best to visit during feeding time when the carnivorous fish make a gruesomely interesting scene. Be sire to feed the turtles in the koi pond -Use the RUB10 vending machine to purchase fish food. RUB400 .
Buy [ edit ]
Bazaars [ edit ].
- Vostochniy Rinok , 161 Stasova St . This outdoor assortment of booths offers the best in fresh produce and other domestic products. Be prepared to haggle/bargain, especially over non-produce items.
Shopping malls [ edit ]
- Galaktika , 182 Stasova St ( #10 tram north to the end of the line (Khladokombinat stop) ). A more Western-style shopping experience. Galaktika includes hundreds of clothing stores, sports stores, computer stores, and an "Okey" store (which is comparable to a Walmart). Galaktika also features an aquarium, a respectable food court, and other diversions.
Eat [ edit ]
Krasnodar has many restaurants, pubs, eateries, sushi bars, hookah bars, pizzerias, coffee/tea houses and fast food places. The predominant Krasnodar cuisine is a mix of south Russian, Georgian, Armenian and Greek flavors with emphasis on fresh local grown produce minimally spiced and mostly flavored by parsley, dill and cilantro.
Budget [ edit ]
- Lyubo-Dorogo . A popular local cafe chain. Appetizers: RUB90-280; Main courses: RUB150-350; Desserts: RUB70-110 .
Fast Food [ edit ]
There are several American fast food restaurants including Subway (5/2 Zipovskaya St, 149 Krasnaya St, 39 Krainyaya St, 38 Mira St), McDonald's (100 Dzerzhinsky St), and KFC (104 Uralskaya St)
Mid-range [ edit ]
- Borshberry , Krasnaya St 182 . A great place to have borsch and beer.
- Stan , Kubanskaya Naberezhnaya St 15 ( Along the river ), ☏ +7 918 330 1616 . Traditional food and atmosphere. Live traditional music. Food prepared on an open fire.
- Shanti , Ural'skaya St 79/1 ( SBS Megamoll ), ☏ +7 861 201-92-88 . The best place to have delicious food, fun and entertainment. Karaoke and night club.
Splurge [ edit ]
- Skotina , Suvorova St 64 , ☏ +7 861 299 9594 . Meat restaurant ans steakhouse with a great selection of wines and craft beers.
Drink [ edit ]
Many popular bars are clustered off the southern end of Krasnaya (Red) Street.
- Amsterdambar , Krasnoarmeyskaya ul. 64 , ☏ +7 861 251 1698 .
- Grey Bear Pub , Stavropolskaya St 133 . The slogan here is 'beer, beef, and sport'.
- Killfish , Krasnoarmeyskaya ul. 52 , ☏ +7 800 333 0977 .
- McKey Pub & Restaurant , Krasnykh Partizan 218 , ☏ +7 861 259 6635 . Irish pub with a great atmosphere and beer selection.
- Mr. Drunke Bar , Krasnoarmeyskaya ul. 58 , ☏ +7 861 299 9594 .
- Sgt. Pepper's Bar , ul. Chapaeva 94 , ☏ +7 861 944 1399 .
Sleep [ edit ]
Hostels [ edit ].
- Bla Bla Hostel , Rashpilevskaya ul. 106 ( In the centre of the city ), ☏ +7 861 221 2993 , [email protected] . Dorm bed: RUB500 .
- Like Hostel Krasnodar , Dlinnaya ul. 128 ( In the centre of the city ), ☏ +7 928 258 4777 . Dorm bed: RUB500 .
- Shukov Hostel , Kalinina 468 ( In the centre of the city ), ☏ +7 989 275 4288 , [email protected] . Modern and clean hostel. 24-hour front desk, free WiFi, trendy rooms with lockers and sockets. Orthopedic mattresses, linen and towels .
Connect [ edit ]
Consulates [ edit ], go next [ edit ].
- Novorossiysk - Black Sea port city
- Rostov-on-Don
- Has custom banner
- Has map markers
- Airport listing
- Has mapframe
- Do listing with no coordinates
- Buy listing with no coordinates
- Eat listing with no coordinates
- Sleep listing with no coordinates
- Usable cities
- Usable articles
- City articles
- Has Geo parameter
- Krasnodar Krai and Adygea
- All destination articles
- Pages with maps
Navigation menu

3-Day Krasnodar Itinerary
Navigate forward to interact with the calendar and select a date. Press the question mark key to get the keyboard shortcuts for changing dates.
Navigate backward to interact with the calendar and select a date. Press the question mark key to get the keyboard shortcuts for changing dates.
- Krasnodar in 3 days
- 1-Day Krasnodar Itinerary
- 2-Day Krasnodar Itinerary
- 4-Day Krasnodar Itinerary
- 5-Day Krasnodar Itinerary

Krasnodar Stadium

SBS Megamall
Safari park, chistyakovskaya roshcha, center goroda, krasnodarskiy akademicheskiy teatr dramy im. maksima gor'kogo, park kul'tury i otdykha imeni 30-letiya pobedy, where to eat, myasolove - steakhouse, restaurant "stan".
Track your travel spending and split costs with friends
Plan your trip. Keep your budget organized. Split the cost between tripmates. Wanderlog does it all.

Don’t forget to pack anything
Stay organized with a to-do list, packing list, shopping list, any kind of list.

All travel reservations in 1 place
Never dig through your emails again — access all your flights, lodging, and any reservations in 1 place.

Popular road trips from Krasnodar
What's the weather like in krasnodar.
It depends on when you visit! We've compiled data from NASA on what the weather is like in Krasnodar for each month of the year: see the links below for more information.
- Weather in Krasnodar in January
- Weather in Krasnodar in February
- Weather in Krasnodar in March
- Weather in Krasnodar in April
- Weather in Krasnodar in May
- Weather in Krasnodar in June
- Weather in Krasnodar in July
- Weather in Krasnodar in August
- Weather in Krasnodar in September
- Weather in Krasnodar in October
- Weather in Krasnodar in November
- Weather in Krasnodar in December
All road trips from Krasnodar
- Krasnodar to Berlin drive
- Krasnodar to Istanbul drive
- Krasnodar to Prague drive
- Krasnodar to Budapest drive
- Krasnodar to Moscow drive
- Krasnodar to Vienna drive
- Krasnodar to Sochi drive
- Krasnodar to Venice drive
- Krasnodar to St. Petersburg drive
- Krasnodar to Athens drive
- Krasnodar to Krakow drive
- Krasnodar to Copenhagen drive
- Krasnodar to Munich drive
- Krasnodar to Stockholm drive
- Krasnodar to Warsaw drive
- Krasnodar to Jerusalem drive
- Krasnodar to Dubrovnik drive
- Krasnodar to Tbilisi drive
- Krasnodar to Hamburg drive
- Krasnodar to Helsinki drive
- Krasnodar to Bucharest drive
- Krasnodar to Kyiv drive
- Krasnodar to Gelendzhik drive
- Krasnodar to Tallinn drive
- Krasnodar to Esto-Sadok drive
- Krasnodar to Salzburg drive
- Krasnodar to Verona drive
- Krasnodar to Paphos drive
- Krasnodar to Bologna drive
- Krasnodar to Riga drive
Explore nearby places
- Novaya Adygeya
- Slavyansk-na-Kubani
- Yablonovskiy
- Novotitarovskaya
- Plastunovskaya
- Goryachy Klyuch
- Ust-Labinsk
- Poltavskaya
- Belorechensk
- Vozrozhdeniye
- Khadyzhensk
- Arkhipo-Osipovka
- Praskoveyevka
- Novomikhailovskiy
All related maps of Krasnodar
- Map of Krasnodar
- Map of Labinsk
- Map of Novaya Adygeya
- Map of Krymsk
- Map of Slavyansk-na-Kubani
- Map of Tikhoretsk
- Map of Yablonovskiy
- Map of Novotitarovskaya
- Map of Dinskaya
- Map of Plastunovskaya
- Map of Goryachy Klyuch
- Map of Ust-Labinsk
- Map of Timashevsk
- Map of Poltavskaya
- Map of Gorskoye
- Map of Belorechensk
- Map of Pshada
- Map of Kubanskiy
- Map of Bzhid
- Map of Tenginka
- Map of Vozrozhdeniye
- Map of Vyselki
- Map of Khadyzhensk
- Map of Arkhipo-Osipovka
- Map of Dzhubga
- Map of Lermontovo
- Map of Shaumyan
- Map of Razdolnyy
- Map of Praskoveyevka
- Map of Novomikhailovskiy
- Map of Apsheronsk
Krasnodar throughout the year
- Krasnodar in January
- Krasnodar in February
- Krasnodar in March
- Krasnodar in April
- Krasnodar in May
- Krasnodar in June
- Krasnodar in July
- Krasnodar in August
- Krasnodar in September
- Krasnodar in October
- Krasnodar in November
- Krasnodar in December
Looking for other day-by-day itineraries in Krasnodar?
Check out our other curated itineraries that are also filled with jam-packed days:

- Itinerary + map in one view
- Live collaboration
- Auto-import hotels and reservations
- Optimize your route
- Offline access on mobile
- See time and distance between all your places

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The contents of the record were selected for NASA by a committee chaired by Carl Sagan of Cornell University, ... Once the Voyager spacecraft leave the solar system (by 1990, both will be beyond the orbit of Pluto), they will find themselves in empty space. It will be forty thousand years before they make a close approach to any other planetary ...
The Voyager Golden Record contains 116 images and a variety of sounds. The items for the record, which is carried on both the Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 spacecraft, were selected for NASA by a committee chaired by Carl Sagan of Cornell University.Included are natural sounds (including some made by animals), musical selections from different cultures and eras, spoken greetings in 59 languages ...
A poster of the planets and moons visited during the Voyager program. The Voyager program is an American scientific program that employs two interstellar probes, Voyager 1 and Voyager 2.They were launched in 1977 to take advantage of a favorable alignment of the two gas giants Jupiter and Saturn and the ice giants, Uranus and Neptune, to fly near them while collecting data for transmission ...
The Voyager message is carried by a phonograph record, a 12-inch gold-plated copper disk containing sounds and images selected to portray the diversity of life and culture on Earth. Launched in 1977, both Voyager spacecraft began a historic journey and each carried a unique 'time capsule' along with them.
Voyager 1 flew within 64,200 kilometers (40,000 miles) of the cloud tops, while Voyager 2 came within 41,000 kilometers (26,000 miles). Saturn is the second largest planet in the solar system. It takes 29.5 Earth years to complete one orbit of the Sun, and its day was clocked at 10 hours, 39 minutes.
Background. The Voyager 1 probe is currently the farthest human-made object from Earth.Both Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 have reached interstellar space, the region between stars where the galactic plasma is present. Like their predecessors Pioneer 10 and 11, which featured a simple plaque, both Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 were launched by NASA with a message aboard—a kind of time capsule, intended ...
Voyager 1 and its twin Voyager 2 are the only spacecraft ever to operate outside the heliosphere, the protective bubble of particles and magnetic fields generated by the Sun. Voyager 1 reached the interstellar boundary in 2012, while Voyager 2 (traveling slower and in a different direction than its twin) reached it in 2018. Mission Type.
Voyager 1 was the first spacecraft to cross the heliosphere, the boundary where the influences outside our solar system are stronger than those from our Sun. Voyager 1 is the first human-made object to venture into interstellar space. Voyager 1 discovered a thin ring around Jupiter and two new Jovian moons: Thebe and Metis.
Beyond Expectations. Voyager 2 launched on Aug. 20, 1977, quickly followed by Voyager 1 on Sept. 5. Both probes traveled to Jupiter and Saturn, with Voyager 1 moving faster and reaching them first. Together, the probes unveiled much about the solar system's two largest planets and their moons.
From a whale song to a kiss, the time capsule sent into space in 1977 had some interesting contents. ... Mounted on Voyager 1 and Voyager 2, twin probes launched in 1977, the two copies of the ...
Voyager Golden Record. December 4, 2017. Credit. NASA/JPL-Caltech. Language. english. Each Voyager spacecraft carries a copy of the Golden Record, which has been featured in several works of science fiction. The record's protective cover, with instructions for playing its contents, is shown at left.
The Voyager program consists of two spacecraft: Voyager 1 and Voyager 2. Voyager 2 was actually launched first, in August 1977, but Voyager 1 was sent on a faster trajectory when it launched about two weeks later. ... The records' contents were selected by a committee chaired by Carl Sagan. Each contains 115 images, including scientific ...
Since November 2023, NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft has been sending a steady radio signal to Earth, but the signal does not contain usable data. ... Voyagers and other spacecraft traveling to the Moon and beyond, was able to decode the new signal and found that it contains a readout of the entire FDS memory. The FDS memory includes its code, or ...
Voyager 2 is now more than 96 AU from the sun, traveling at a speed of 15.5 kilometers per second (9.6 miles per second). Both spacecraft are moving considerably faster than Pioneers 10 and 11, two earlier spacecraft that became the first robotic visitors to fly past Jupiter and Saturn in the mid-70s. This processed color image of Jupiter was ...
Mission Overview. The twin Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft are exploring where nothing from Earth has flown before. Continuing on their more-than-40-year journey since their 1977 launches, they each are much farther away from Earth and the sun than Pluto. In August 2012, Voyager 1 made the historic entry into interstellar space, the region between ...
The Voyager spacecraft were designed and constructed at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, California. The flight team, very much reduced in size more than 30 years after the launches, is also located at JPL. 3.1 . Voyager Interstellar Mission Description . The two Voyager spacecraft are continuing on long-term (1977-2025)
This new signal resulted from a command sent to Voyager 1 on March 1. Called a "poke" by the team, the command is meant to gently prompt the FDS to try different sequences in its software package in case the issue could be resolved by going around a corrupted section. Because Voyager 1 is more than 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers ...
For nearly 50 years, NASA's Voyager 1 mission has competed for the title of deep space's little engine that could. Launched in 1977 along with its twin, Voyager 2, the spacecraft is now soaring ...
Voyager 1, launched in 1977, is now more than 24 billion kilometers from Earth, which means it takes 22.5 hours for signals to travel between Earth and the spacecraft.
The Voyager spacecraft are the third and fourth human spacecraft to fly beyond all the planets in our solar system. Pioneers 10 and 11 preceded Voyager in outstripping the gravitational attraction of the Sun but on February 17, 1998, Voyager 1 passed Pioneer 10 to become the most distant human-made object in space. ... The contents of the ...
A s it turns out, spacecraft aren't immune to age. In November 2023, NASA's 46-year-old Voyager 1 spacecraft started sending a stream of nonsense to Earth, spewing out signals without any morsel ...
Meanwhile, Voyager 2 has traveled more than 12.6 billion miles (20.3 billion kilometers) from our planet. Both are in interstellar space and are the only spacecraft ever to operate beyond the ...
Hilton Garden Inn Krasnodar, 25/2 Krasnaya St ( 10-minute walk from Krasnodar city centre ), ☏ +7 861 210 2030. 4-star hotel. Free Wi-Fi, fantastic breakfast buffet, large rooms, free laundry room, work-out centre, free mini-bar, air conditioning, comfortable beds and modern bathrooms. RUB6,000. edit.
This is a real-time indicator of Voyager 1's distance from Earth in astronomical units (AU) and either miles (mi) or kilometers (km). Note: Because Earth moves around the sun faster than Voyager 1 is speeding away from the inner solar system, the distance between Earth and the spacecraft actually decreases at certain times of year.
Table of contents. Krasnodar in 3 days. Day 1: Most popular attractions; Day 2: South side of town; ... The mall has ample parking space available but the restrooms could be cleaner. It is highly recommended due to its spacious and modern design which includes an ice skating rink, bowling alley and movie theater making it a great place to shop ...
N. E. Zhukovsky and Yu. A. Gagarin" and was transformed into the Krasnodar Higher Military Aviation School of Pilots named after Hero of the Soviet Union A. K. Serov. Since 2011, the school began receiving Yak-130 aircraft for training cadets, and by the end of 2016, more than 70 combat training aircraft of this type had been received.
Krasnodar, kray (territory), southwestern Russia, extending northward from the crest line of the Caucasus Mountains across the plains east of the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov as far as the Gulf of Taganrog. The plains, crossed by the Kuban and other rivers flowing to the Sea of Azov, form two-thirds of the region. Their steppe-grass vegetation on rich soils has been almost entirely plowed under.
The identical Voyager spacecraft are three-axis stabilized systems that use celestial or gyro referenced attitude control to maintain pointing of the high-gain antennas toward Earth. ... (CCS) provides sequencing and control functions The CCS contains fixed routines such as command decoding and fault detection and corrective routines, antenna ...