Conjugation verb travel
Model : cancel
Auxiliary : have , be
Other forms: travel oneself / not travel
Contractions
in the U.K. spelling we double up the 'l' in preterite and participle endings
The verb has several variants of conjugation, which may correspond to different meanings. Please use the menu to select one or all variants.
- he/she/it travels
- they travel
- I travelled/traveled
- you travelled/traveled
- he/she/it travelled/traveled
- we travelled/traveled
- they travelled/traveled
Present continuous
- I am travelling/traveling
- you are travelling/traveling
- he/she/it is travelling/traveling
- we are travelling/traveling
- they are travelling/traveling
Present perfect
- I have travelled/traveled
- you have travelled/traveled
- he/she/it has travelled/traveled
- we have travelled/traveled
- they have travelled/traveled
- I will travel
- you will travel
- he/she/it will travel
- we will travel
- they will travel
Future perfect
- I will have travelled/traveled
- you will have travelled/traveled
- he/she/it will have travelled/traveled
- we will have travelled/traveled
- they will have travelled/traveled
Past continous
- I was travelling/traveling
- you were travelling/traveling
- he/she/it was travelling/traveling
- we were travelling/traveling
- they were travelling/traveling
Past perfect
- I had travelled/traveled
- you had travelled/traveled
- he/she/it had travelled/traveled
- we had travelled/traveled
- they had travelled/traveled
Future continuous
- I will be travelling/traveling
- you will be travelling/traveling
- he/she/it will be travelling/traveling
- we will be travelling/traveling
- they will be travelling/traveling
Present perfect continuous
- I have been travelling/traveling
- you have been travelling/traveling
- he/she/it has been travelling/traveling
- we have been travelling/traveling
- they have been travelling/traveling
Past perfect continuous
- I had been travelling/traveling
- you had been travelling/traveling
- he/she/it had been travelling/traveling
- we had been travelling/traveling
- they had been travelling/traveling
Future perfect continuous
- I will have been travelling/traveling
- you will have been travelling/traveling
- he/she/it will have been travelling/traveling
- we will have been travelling/traveling
- they will have been travelling/traveling
- let's travel
- travelling/traveling
- travelled/traveled

Perfect participle
- having travelled/traveled
Helping millions of people and large organizations communicate more efficiently and precisely in all languages.
Online Language Dictionaries
Perfect tenses, continuous (progressive) and emphatic tenses, compound continuous (progressive) tenses, conditional, subjunctive.
*Blue letters in conjugations are irregular forms. ( example ) *Red letters in conjugations are exceptions to the model. ( example )
Report a problem.

Past Tense of Travel: Traveling Back in Time
By: Author Oliver
Posted on Last updated: August 12, 2023
Sharing is caring!
Welcome to our article on the past tense of travel! If you’re learning English grammar, you know that understanding verb tenses is an essential part of the language. The past tense is particularly important, as it allows us to talk about events and experiences that have already happened. In this article, we’ll explore the basics of English tenses, give an overview of the past tense, and focus specifically on how to use the past tense when talking about travel.
Travel is one of the most common topics of conversation, and being able to talk about past trips is a great way to connect with others and share experiences. However, using the past tense correctly can be tricky, especially when it comes to irregular verbs and complex sentence structures. In this article, we’ll provide plenty of examples and exercises to help you master the past tense of travel. We’ll also cover some common mistakes to avoid and provide additional resources for further learning.
So whether you’re planning your next trip or just want to improve your English skills, read on to learn everything you need to know about the past tense of travel!
Key Takeaways
- The past tense is essential for talking about past events and experiences, past tense of ‘travel’ is ‘traveled’
- By practicing with examples and exercises, you can improve your use of the past tense of travel and avoid common mistakes.

Past Tense of Travel
Travel is a verb that is commonly used in the past tense. In this section, we will cover the formation and usage examples of the past tense of travel.
To form the past tense of travel, we add “-ed” to the base form of the verb. For example:
- I traveled to Europe last summer.
- She traveled to Asia for business.
- We traveled to South America for vacation.
Simple Past
The simple past is used to describe a completed action in the past. Regular verbs like travel are formed by adding -ed to the base form. For example:
- I traveled to Paris last year.
Past Continuous
The past continuous is used to describe an action that was in progress at a specific point in the past. It is formed by using the past tense of “to be” (was/were) and the present participle (-ing) of the main verb. Here are some examples:
- I was traveling to Paris when I got a call from my boss.
Usage Examples
The past tense of travel is used to talk about a completed action in the past. Here are some examples:
- I traveled to Japan last year and had an amazing time.
- She traveled to Italy for her honeymoon and fell in love with the country.
- We traveled to Mexico for our anniversary and enjoyed the beautiful beaches.
We can also use the past tense of travel to talk about a past habit or routine. For example:
- When I was younger, I traveled to different countries every summer.
- She traveled for work every week and got used to living out of a suitcase.
- We traveled to visit our family every holiday season.
In conclusion, the past tense of travel is formed by adding “-ed” to the base form of the verb and is used to talk about completed actions or past habits. Practice using the past tense of travel in your own sentences to improve your English grammar skills.
Common Mistakes with Past Tense of Travel
If you are learning English, you might be struggling with the past tense of the verb “travel.” Here are some common mistakes people make and how to avoid them.
Mixing Past and Present Tenses
One of the most common mistakes is mixing past and present tenses. For example, saying “I travel to Paris last year” instead of “I traveled to Paris last year.” To avoid this mistake, remember to use the past tense of “travel” when referring to something that happened in the past.
Using the Present Participle
Another mistake is using the present participle instead of the past tense. For example, saying “I am traveling to London last week” instead of “I traveled to London last week.” To avoid this mistake, remember to use the past tense of “travel” when referring to something that happened in the past.
Using the Wrong Auxiliary Verb
Using the wrong auxiliary verb is also a common mistake. For example, saying “I was travel to Rome” instead of “I traveled to Rome.” To avoid this mistake, remember to use the correct auxiliary verb (in this case, “did”) when forming the past tense.
Example Sentences
Here are some example sentences to help you practice using the past tense of “travel” correctly:
- I traveled to Japan last summer.
- She visited her grandparents in Florida last month.
- They took a road trip across the United States.
- We flew to Paris for our honeymoon.
- He backpacked through Europe after college.
Remember, practice makes perfect! Keep practicing using the past tense of “travel” correctly, and soon it will become second nature.
Exercises to Practice Past Tense of Travel
Learning English grammar can be challenging, especially when it comes to mastering the past tense of travel. To help you improve your skills, we have compiled a list of exercises that you can use to practice and perfect your past tense of travel.
Interactive Exercises
Interactive exercises are a great way to practice the past tense of travel. They allow you to engage with the material and receive immediate feedback on your progress. Here are a few interactive exercises you can try:
- Fill in the Blank: In this exercise, you will be given a sentence with a blank space where the past tense verb should go. Your task is to fill in the blank with the correct past tense verb. For example, “I ___ to Paris last year.” The correct answer would be “went.”
- Matching: In this exercise, you will be given a list of past tense verbs and a list of travel-related words. Your task is to match the past tense verb with the correct travel-related word. For example, “flew” would match with “airplane.”
Written Exercises
Written exercises are another great way to practice the past tense of travel. They allow you to focus on the material and practice at your own pace. Here are a few written exercises you can try:
- Sentence Writing: In this exercise, you will be given a travel-related word, and your task is to write a sentence using the correct past tense verb. For example, “train” could be used in the sentence, “I ___ to New York on a train.”
- Paragraph Writing: In this exercise, you will be given a prompt related to travel, and your task is to write a paragraph using the correct past tense verbs. For example, “Write a paragraph about your last vacation.” You could write, “Last summer, I ___ to Hawaii with my family. We ___ on the beach, ___ in the ocean, and ___ at some amazing restaurants.”
By practicing these exercises, you will improve your understanding and mastery of the past tense of travel. Keep practicing, and before you know it, you’ll be a pro at English grammar!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the past tense of travel?
The past tense of travel is “traveled” in American English and “travelled” in British English. Both spellings are correct, but American English tends to drop the second “l” in the past tense and past participle forms of the verb.
Is it spelled Travelled or traveled?
As mentioned above, both spellings are correct. The difference in spelling is due to the variation in American and British English.
Which is correct travel or travelling?
Both “travel” and “travelling” are correct, but “traveling” is the preferred spelling in American English, while “travelling” is the preferred spelling in British English.
What’s the difference between travel and Travelled?
“Travel” is the present tense of the verb, while “travelled” is the past tense. The difference between the two is the time frame in which the action occurs.
What is the V2 form of travel?
The V2 form of travel is “traveled” in American English and “travelled” in British English.
What is the V3 form of travel?
The V3 form of travel is “traveled” in American English and “travelled” in British English.
In summary, the past tense of travel is “traveled” in American English and “travelled” in British English. Both spellings are correct, and the difference in spelling is due to the variation in American and British English. Additionally, “traveling” is the preferred spelling in American English, while “travelling” is the preferred spelling in British English.
The past tense of travel is \"traveled\" in American English and \"travelled\" in British English. Both spellings are correct, but American English tends to drop the second \"l\" in the past tense and past participle forms of the verb.
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"Is it spelled Travelled or traveled?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"Which is correct travel or travelling?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
Both \"travel\" and \"travelling\" are correct, but \"traveling\" is the preferred spelling in American English, while \"travelling\" is the preferred spelling in British English.
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What's the difference between travel and Travelled?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
\"Travel\" is the present tense of the verb, while \"traveled\" is the past tense. The difference between the two is the time frame in which the action occurs.
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What is the V2 form of travel?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
The V2 form of travel is \"traveled\" in American English and \"travelled\" in British English.
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What is the V3 form of travel?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
The V3 form of travel is \"traveled\" in American English and \"travelled\" in British English.
In summary, the past tense of travel is \"traveled\" in American English and \"travelled\" in British English. Both spellings are correct, and the difference in spelling is due to the variation in American and British English. Additionally, \"traveling\" is the preferred spelling in American English, while \"travelling\" is the preferred spelling in British English.
- Recent Posts
- Plural of Safe: What It Is and How to Use It Correctly - October 3, 2023
- Purple Color Names: Different Hues of Purple - October 2, 2023
- Addition Transition Words for Clear and Cohesive Writing - September 30, 2023
Related posts:
- Past Tense of Buy: How to Use them Correctly in English Grammar
- Mastering English Grammar: The Definitive Guide to Understanding the Past Tense of Cost
- Past Tense of Drag: Dragged Through Time
- Hoped or Hoped For? Mastering the Past Tense of Hope with Ease
- Slovenščina
- FAQ Technical Questions
- Text Translation
- Vocabulary Trainer
- Online Dictionary
- Login
- Online dictionary
- Products & Shop
- Conjugation
- Vocabulary trainer
- Dictionary API
- Add to home screen
- Browse the dictionaries
- Terms and conditions of use
- Supply chain
- Data Protection Declaration
- Legal notice
- Privacy Settings
- EN');"> English
- FR');"> French
- DE');"> German
- LA');"> Latin
- ES');"> Spanish
Verb Table for travel
- Simple tenses
- Continuous tenses
Conditional
Simple tenses • continuous tenses • conditional • imperative • impersonal, present perfect, past perfect, will -future, going to -future, future perfect, conditional past, past participle, browse the conjugations (verb tables), look up "travel" in other languages, links to further information.
You can suggest improvements to this PONS entry here:
We are using the following form field to detect spammers. Please do leave them untouched. Otherwise your message will be regarded as spam. We are sorry for the inconvenience.
My search history
- Most popular
- English ⇄ German
- English ⇄ Slovenian
- German ⇄ Spanish
- German ⇄ French
- German ⇄ Greek
- German ⇄ Polish
- Arabic ⇄ English
- Arabic ⇄ German
- Bulgarian ⇄ English
- Bulgarian ⇄ German
- Chinese ⇄ English
- Chinese ⇄ French
- Chinese ⇄ German
- Chinese ⇄ Spanish
- Croatian ⇄ German
- Czech ⇄ German
- Danish ⇄ German
- Dutch ⇄ German
- Elvish ⇄ German
- English ⇄ Arabic
- English ⇄ Bulgarian
- English ⇄ Chinese
- English ⇄ French
- English ⇄ Italian
- English ⇄ Polish
- English ⇄ Portuguese
- English ⇄ Russian
- English → Serbian
- English ⇄ Spanish
- Finnish ⇄ German
- French ⇄ Chinese
- French ⇄ English
- French ⇄ German
- French ⇄ Italian
- French ⇄ Polish
- French ⇄ Slovenian
- French ⇄ Spanish
- German ⇄ Arabic
- German ⇄ Bulgarian
- German ⇄ Chinese
- German ⇄ Croatian
- German ⇄ Czech
- German ⇄ Danish
- German ⇄ Dutch
- German ⇄ Elvish
- German ⇄ English
- German ⇄ Finnish
- German ⇄ Hungarian
- German → Icelandic
- German ⇄ Italian
- German ⇄ Japanese
- German ⇄ Latin
- German ⇄ Norwegian
- German ⇄ Persian
- German ⇄ Portuguese
- German ⇄ Romanian
- German ⇄ Russian
- German → Serbian
- German ⇄ Slovakian
- German ⇄ Slovenian
- German ⇄ Swedish
- German ⇄ Turkish
- Dictionary of German Spelling
- Greek ⇄ German
- Hungarian ⇄ German
- Italian ⇄ English
- Italian ⇄ French
- Italian ⇄ German
- Italian ⇄ Polish
- Italian ⇄ Slovenian
- Italian ⇄ Spanish
- Japanese ⇄ German
- Latin ⇄ German
- Norwegian ⇄ German
- Persian ⇄ German
- Polish ⇄ English
- Polish ⇄ French
- Polish ⇄ German
- Polish ⇄ Italian
- Polish ⇄ Russian
- Polish ⇄ Spanish
- Portuguese ⇄ English
- Portuguese ⇄ German
- Portuguese ⇄ Spanish
- Romanian ⇄ German
- Russian ⇄ English
- Russian ⇄ German
- Russian ⇄ Polish
- Slovakian ⇄ German
- Slovenian ⇄ English
- Slovenian ⇄ French
- Slovenian ⇄ German
- Slovenian ⇄ Italian
- Slovenian ⇄ Spanish
- Spanish ⇄ Chinese
- Spanish ⇄ English
- Spanish ⇄ French
- Spanish ⇄ German
- Spanish ⇄ Italian
- Spanish ⇄ Polish
- Spanish ⇄ Portuguese
- Spanish ⇄ Slovenian
- Swedish ⇄ German
- Turkish ⇄ German
Identified ad region: ALL Identified country code: RU -->

'travel' conjugation table in English
Past participle, present participle, present continuous, present perfect, present perfect continuous, past continuous, past perfect, past perfect continuous, future continuous, future perfect, future perfect continuous.
Quick word challenge
Quiz Review
Score: 0 / 5

All ENGLISH words that begin with 'T'
Verb "travel"
For the settings to take effect, you must restart the trainer Restart
Conjugation
Simple tense.
Present Simple
- he, she travels
- they travel
Past Simple
- I traveled ; travelled
- you traveled ; travelled
- he, she traveled ; travelled
- we traveled ; travelled
- they traveled ; travelled
Future Simple
- I will travel
- you will travel
- he, she will travel
- we will travel
- they will travel
Continuous Tense
Present Simple Continuous
- I am traveling ; travelling
- you are traveling ; travelling
- he, she is traveling ; travelling
- we are traveling ; travelling
- they are traveling ; travelling
Past Simple Continuous
- I was traveling ; travelling
- you were traveling ; travelling
- he, she was traveling ; travelling
- we were traveling ; travelling
- they were traveling ; travelling
Future Simple Continuous
- I will be traveling ; travelling
- you will be traveling ; travelling
- he, she will be traveling ; travelling
- we will be traveling ; travelling
- they will be traveling ; travelling
Perfect Tense
Present Perfect
- I have traveled ; travelled
- you have traveled ; travelled
- he, she has traveled ; travelled
- we have traveled ; travelled
- they have traveled ; travelled
Past Perfect
- I had traveled ; travelled
- you had traveled ; travelled
- he, she had traveled ; travelled
- we had traveled ; travelled
- they had traveled ; travelled
Future Perfect
- I will have traveled ; travelled
- you will have traveled ; travelled
- he, she will have traveled ; travelled
- we will have traveled ; travelled
- they will have traveled ; travelled
Perfect Continuous Tense
Present Perfect Continuous
- I have been traveling ; travelling
- you have been traveling ; travelling
- he, she has been traveling ; travelling
- we have been traveling ; travelling
- they have been traveling ; travelling
Past Perfect Continuous
- I had been traveling ; travelling
- you had been traveling ; travelling
- he, she had been traveling ; travelling
- we had been traveling ; travelling
- they had been traveling ; travelling
Future Perfect Continuous
- I will have been traveling ; travelling
- you will have been traveling ; travelling
- he, she will have been traveling ; travelling
- we will have been traveling ; travelling
- they will have been traveling ; travelling
Conditional
- I would travel
- you would travel
- he, she would travel
- we would travel
- they would travel
- I would have traveled ; travelled
- you would have traveled ; travelled
- he, she would have traveled ; travelled
- we would have traveled ; travelled
- they would have traveled ; travelled
Present Continuous
- I would be traveling ; travelling
- you would be traveling ; travelling
- he, she would be traveling ; travelling
- we would be traveling ; travelling
- they would be traveling ; travelling
Perfect Continuous
- I would have been traveling ; travelling
- you would have been traveling ; travelling
- he, she would have been traveling ; travelling
- we would have been traveling ; travelling
- they would have been traveling ; travelling
- we Let's travel
Other verbs
Be the first to comment.
Add comment
Conjugation English verb to travel
Simple present, present progressive/continuous, simple past, past progressive/continuous, present perfect simple, present perfect progressive/continuous, past perfect, past perfect progressive/continuous, future progressive/continuous, future perfect, future perfect continuous, conditional, progressive, perfect progressive, translation to travel.
Travel Past Tense: Verb Forms, Conjugate TRAVEL
- commonwealth travelled, us traveled
The past tense of travel is commonwealth travelled, us traveled
The Forms of Travel
Conjugate travel, travel in present simple (indefinite) tense, travel in present continuous (progressive) tense, travel in present perfect tense, travel in present perfect continuous tense, travel in past simple (indefinite) tense, travel in past continuous (progressive) tense, travel in past perfect tense, travel in past perfect continuous tense, travel in future simple (indefinite) tense, travel in future continuous (progressive) tense, travel in future perfect tense, travel in future perfect continuous tense, leave a comment cancel reply.
Conjugation of verb (past tense) travel
Past simple, traveled; travelled, past participle.
- ⭐Conjugation
- Podmínkové věty
- Frázová slovesa
- ⭐Conditional
- ⭐Subjunktiv
- ⭐Participle
Conjugation of the regular verb [travel]
Conjugation is the creation of derived forms of a verb from its principal parts by inflection (alteration of form according to rules of grammar). For instance, the verb "break" can be conjugated to form the words break, breaks, broke, broken and breaking.
The term conjugation is applied only to the inflection of verbs, and not of other parts of speech (inflection of nouns and adjectives is known as declension). Also it is often restricted to denoting the formation of finite forms of a verb – these may be referred to as conjugated forms, as opposed to non-finite forms, such as the infinitive or gerund, which tend not to be marked for most of the grammatical categories.
Conjugation is also the traditional name for a group of verbs that share a similar conjugation pattern in a particular language (a verb class). A verb that does not follow all of the standard conjugation patterns of the language is said to be an irregular verb .
Present Continuous
Past continuous, present perfect, present perfect continuous, past perfect, past perfect continuous, future continuous, future perfect, future perfect continuous, conditional of the regular verb [travel].
Causality (also referred to as causation or cause and effect ) is influence by which one event, process, state or object (a cause) contributes to the production of another event, process, state or object (an effect) where the cause is partly responsible for the effect, and the effect is partly dependent on the cause. In general, a process has many causes, which are also said to be causal factors for it, and all lie in its past. An effect can in turn be a cause of, or causal factor for, many other effects, which all lie in its future.
The conditional mood (abbreviated cond) is a grammatical mood used in conditional sentences to express a proposition whose validity is dependent on some condition, possibly counterfactual.
English does not have an inflective (morphological) conditional mood, except in as much as the modal verbs could, might, should and would may in some contexts be regarded as conditional forms of can, may, shall and will respectively. What is called the English conditional mood (or just the conditional) is formed periphrastically using the modal verb would in combination with the bare infinitive of the following verb. (Occasionally should is used in place of would with a first person subject – see shall and will. Also the aforementioned modal verbs could, might and should may replace would in order to express appropriate modality in addition to conditionality.)
Conditional present -->
Conditional present progressive -->, conditional perfect -->, conditional perfect progressive -->, subjunktiv of the regular verb [travel].
The subjunctive is a grammatical mood, a feature of the utterance that indicates the speaker's attitude toward it. Subjunctive forms of verbs are typically used to express various states of unreality such as: wish, emotion, possibility, judgement, opinion, obligation, or action that has not yet occurred; the precise situations in which they are used vary from language to language. The subjunctive is one of the irrealis moods, which refer to what is not necessarily real. It is often contrasted with the indicative, a realis mood which is used principally to indicate that something is a statement of fact.
Subjunctives occur most often, although not exclusively, in subordinate clauses, particularly that-clauses. Examples of the subjunctive in English are found in the sentences "I suggest that you be careful" and "It is important that she stay by your side."
The subjunctive mood in English is a clause type used in some contexts which describe non-actual possibilities, e.g. "It's crucial that you be here" and "It's crucial that he arrive early." In English, the subjunctive is syntactic rather than inflectional, since there is no specifically subjunctive verb form. Rather, subjunctive clauses recruit the bare form of the verb which is also used in a variety of other constructions.
Present subjunctive -->
Past subjunctive -->, past perfect subjunctive -->, imperativ of the regular verb [travel].
The imperative mood is a grammatical mood that forms a command or request.
An example of a verb used in the imperative mood is the English phrase "Go." Such imperatives imply a second-person subject (you), but some other languages also have first- and third-person imperatives, with the meaning of "let's (do something)" or "let them (do something)" (the forms may alternatively be called cohortative and jussive).
Imperativ -->
Participle of the regular verb [travel].
The past participle is one of the most important parts of English grammar. It’s used to express perfect tenses and to form the passive voice. It’s also a useful tool for writing sentences that describe actions that started in the past and are still happening today. The past participles of irregular verbs don’t follow a specific pattern and can have numerous endings.
Present participle -->
Past participle -->, recent articles.
- Differences: past simple and past continuous
- Past simple sentences
- Past continuous structure
- Adverbs of past continuous tense
- Past continuous verbs
Start with any verb and browse through irregular verbs in alphabetical order
Use the button "Random choice"
Looking for a specific irregular verb?
regular verbs & Irregular verbs
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Table of irregular verbs
Note that be has several irregular forms:
Present: ( I ) am , ( she, he, it ) is , ( you , we , they ) are
Past: ( I, she, he, it ) was , ( you , we , they ) were
-ed form: been

Word of the Day
a bitter pill (to swallow)
something that is very unpleasant but must be accepted

Sitting on the fence (Newspaper idioms)

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
Add ${headword} to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
Verb conjugation of "travel" in English
Travel Verb Forms: Past Tense and Past Participle (V1 V2 V3)
Meaning: to go from one place/city/country to another
Table of Contents
Travel Verb Forms V1 V2 V3 V4 V5
Travel past tense:.
Past Tense of Travel is Traveled .
Example: Sarah Traveled by Train.
Travel Past Participle:
Past Participle Form of Travel is Traveled .
Example: Sarah has Traveled by Train.
Travel Present Participle:
Present Participle Form of Travel is Travelling .
Example: Sarah is Travelling by Train.
Travel 3rd Person Singular:
3rd Person Singular of Travel is Travels .
Example: Sarah Travels by Train.
Travel Conjugation
Indefinite / simple present tense.
- I Travel by Train.
- We/You/They Travel by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam Travels by Train.
Present Continuous Tense
- I am Travelling by Train.
- We/You/They are Travelling by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam is Travelling by Train.
Present Perfect Tense
- I have Traveled by Train.
- We/You/They have Traveled by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam has Traveled by Train.
Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- I have been Travelling by Train.
- We/You/They have been Travelling by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam has been Travelling by Train.

Indefinite / Simple Past Tense
- I Traveled by Train.
- We/You/They Traveled by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam Traveled by Train.
Past Continuous Tense
- I was Travelling by Train.
- We/You/They were Travelling by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam was Travelling by Train.
Past Perfect Tense
- I had Traveled by Train.
- We/You/They had Traveled by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam had Traveled by Train.
Past Perfect Continuous Tense
- I had been Travelling by Train.
- We/You/They had been Travelling by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam had been Travelling by Train.
Indefinite / Simple Future Tense
- I will Travel by Train.
- We/You/They will Travel by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam will Travel by Train.
Future Continuous Tense
- I will be Travelling by Train.
- We/You/They will be Travelling by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam will be Travelling by Train.
Future Perfect Tense
- I will have Traveled by Train.
- We/You/They will have Traveled by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam will have Traveled by Train.
Future Perfect Continuous Tense
- I will have been Travelling by Train.
- We/You/They will have been Travelling by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam will have been Travelling by Train.
Past Tense of Travel Phrasal Verbs
Explore Other Verb Forms:
What is the Future Tense of Travel?
Future Tense of Travel is “ will Travel” .
What is the Present Tense of Travel?
Present Tense of Travel is “ Travel + s/es or ing” .
What is the Past Perfect Tense of Travel?
Past perfect tense of take is “ had Traveled ”.
Last updated on May 24th, 2023 at 02:22 am
Related Posts
Treat Verb Forms: Past Tense and Past Participle (V1 V2 V3)

Let Verb Forms: Past Tense and Past Participle (V1 V2 V3)
Forlese Verb Forms: Past Tense and Past Participle (V1 V2 V3)
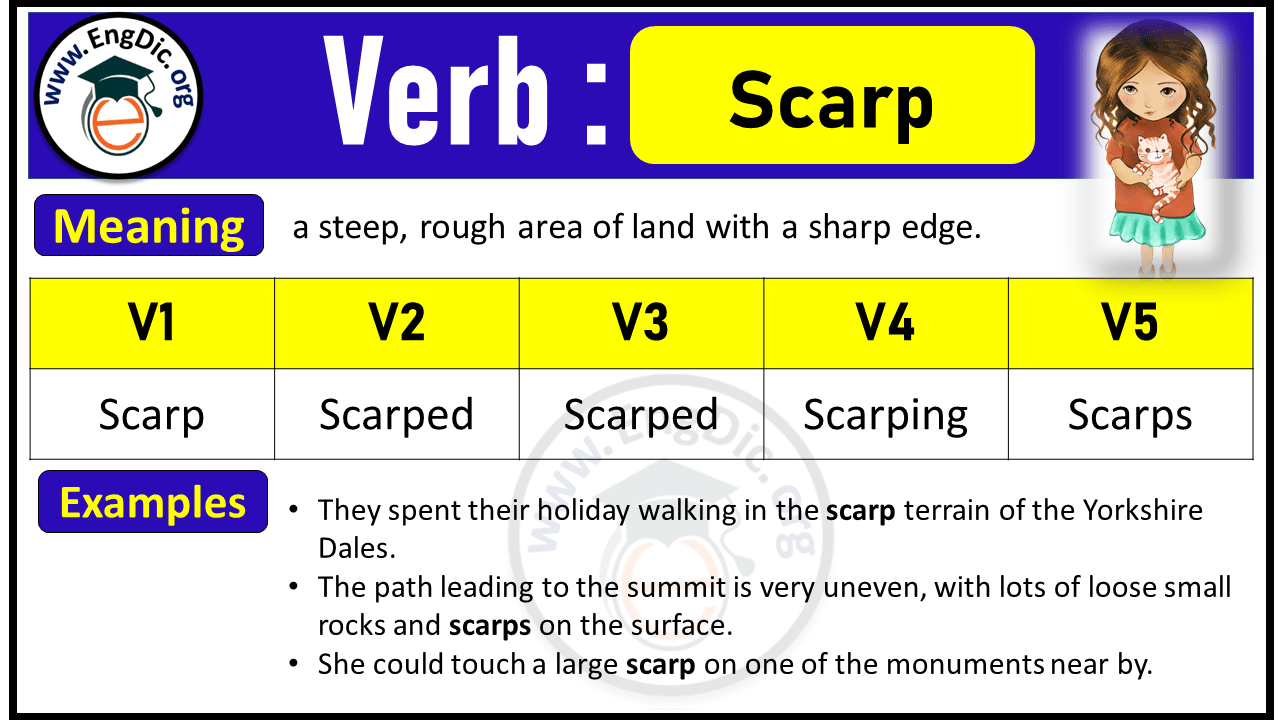
Scarp Verb Forms: Past Tense and Past Participle (V1 V2 V3)
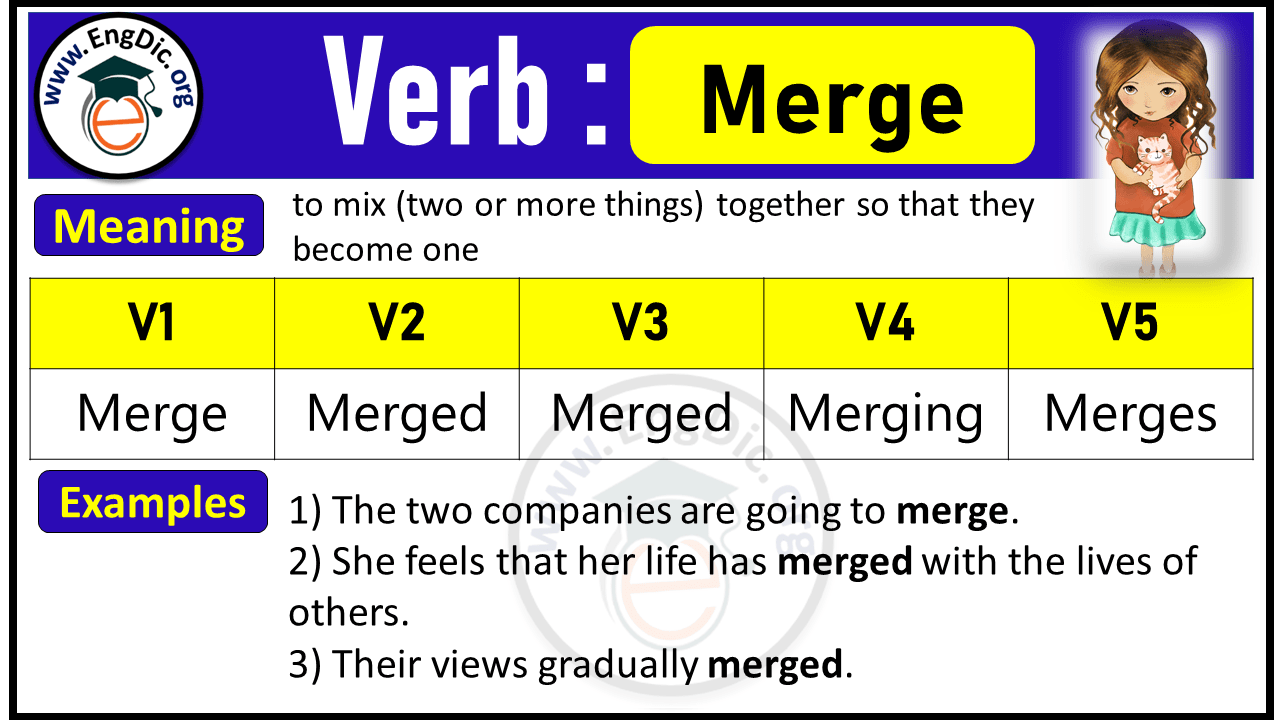
Merge Verb Forms: Past Tense and Past Participle (V1 V2 V3)
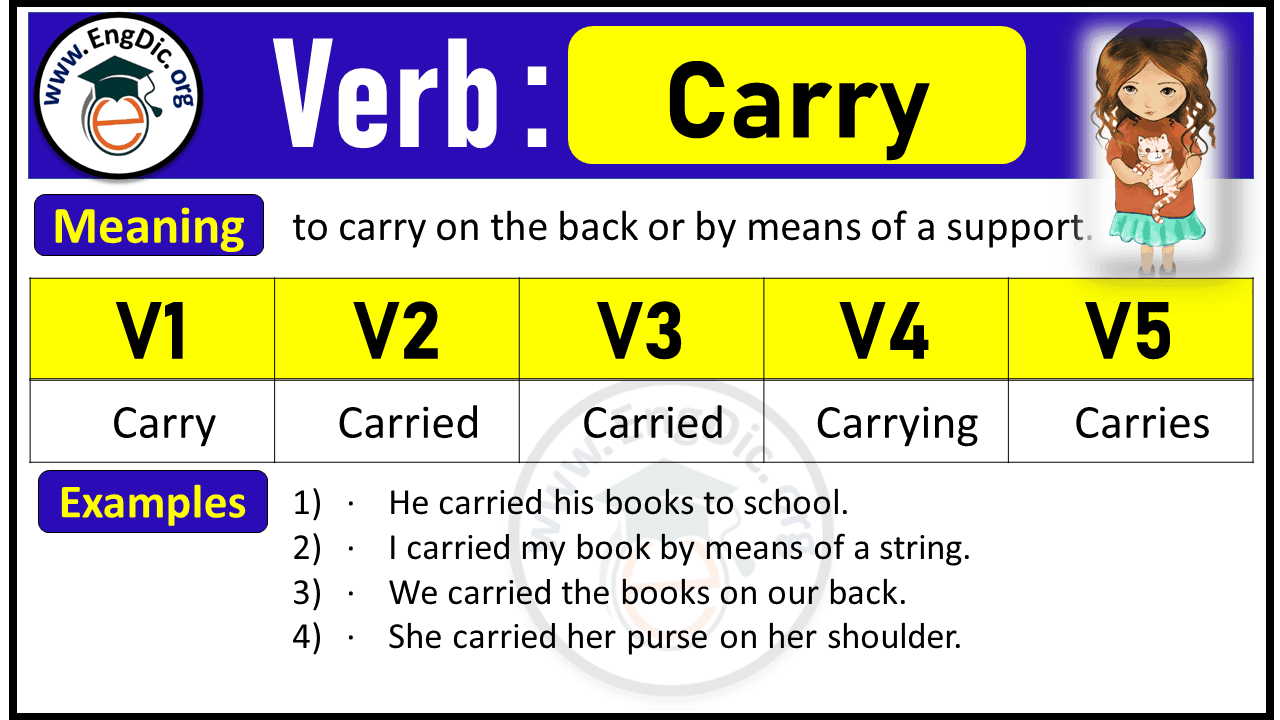
Carry Verb Forms: Past Tense and Past Participle (V1 V2 V3)
About the author.
Hi, I'm USMI, engdic.org's Author & Lifestyle Linguist. My decade-long journey in language and lifestyle curation fuels my passion for weaving words into everyday life. Join me in exploring the dynamic interplay between English and our diverse lifestyles. Dive into my latest insights, where language enriches every aspect of living.
Conjugación verbo travel - inglés
Modelo : cancel
Auxiliar : have , be
Otras formas: travel oneself / not travel
Contracciones
in the U.K. spelling we double up the 'l' in preterite and participle endings
La declinación de este verbo presenta algunas variantes ortográficas que podrían conllevar significados distintos. Seleccione una variante o todas en el menù.
- he/she/it travels
- they travel
- I travelled/traveled
- you travelled/traveled
- he/she/it travelled/traveled
- we travelled/traveled
- they travelled/traveled
Present continuous
- I am travelling/traveling
- you are travelling/traveling
- he/she/it is travelling/traveling
- we are travelling/traveling
- they are travelling/traveling
Present perfect
- I have travelled/traveled
- you have travelled/traveled
- he/she/it has travelled/traveled
- we have travelled/traveled
- they have travelled/traveled
- I will travel
- you will travel
- he/she/it will travel
- we will travel
- they will travel
Future perfect
- I will have travelled/traveled
- you will have travelled/traveled
- he/she/it will have travelled/traveled
- we will have travelled/traveled
- they will have travelled/traveled
Past continous
- I was travelling/traveling
- you were travelling/traveling
- he/she/it was travelling/traveling
- we were travelling/traveling
- they were travelling/traveling
Past perfect
- I had travelled/traveled
- you had travelled/traveled
- he/she/it had travelled/traveled
- we had travelled/traveled
- they had travelled/traveled
Future continuous
- I will be travelling/traveling
- you will be travelling/traveling
- he/she/it will be travelling/traveling
- we will be travelling/traveling
- they will be travelling/traveling
Present perfect continuous
- I have been travelling/traveling
- you have been travelling/traveling
- he/she/it has been travelling/traveling
- we have been travelling/traveling
- they have been travelling/traveling
Past perfect continuous
- I had been travelling/traveling
- you had been travelling/traveling
- he/she/it had been travelling/traveling
- we had been travelling/traveling
- they had been travelling/traveling
Future perfect continuous
- I will have been travelling/traveling
- you will have been travelling/traveling
- he/she/it will have been travelling/traveling
- we will have been travelling/traveling
- they will have been travelling/traveling
- let's travel
- travelling/traveling
- travelled/traveled
Perfect participle
- having travelled/traveled
Ayudando a millones de personas y grandes organizaciones a comunicar con más eficacia y precisión en todos los idiomas.
Past Tense of travel: Conjugations in Past and Present Participles

What is the past tense of “travel?” Most commonly, the past tense of the word “travel” is “travelled.” Although the word form will change based on its participle. And the sentence where it’s used. For example, referencing “travel” in the present participle form will change it to “travelling,” but in the infinitive form, will be “travel.”
What is the past tense of the word "travel"
The past tense (past participle) form of “travel” is “travelled.” The infinitive of the word form is “travel.” The present participle form is “travelling.” The past tense form is “travelled” and past participle form is “travelled.”
Understanding verb tenses
The general grammar rules that govern past tenses are as follows. The simple past tense form is created by adding a -ed or -d affix to the root word of the verb. Some verbs use a -t variation where they end in a -t. For example, when "dream" turns into "dreamt."
The past perfect tense is formed for regular verbs (ending in -ed, -d, or -t) by adding "had" followed by the verb. For example, "I had finished ."
The past continuous tense is formed by the verb "be" followed by the affix or ending of -ing. For example, " we were having dinner."
Lastly, the past perfect continuous tense is formed by adding "had been" followed by the affix or ending of -ing. For example, "I had been building a castle with my sister."
For more information on forming all past tenses, visit our " understanding verb tenses " resource.
Sentence examples for the past tense of the word "travel"
- Infinitive: I travel.
- Present participle: She is travelling.
- Past tense: I travelled.
- Past particle: I have travelled.
Verb forms of the word "travel"
Example sentences in all verb forms:
Indefinite present tense
Present continuous tense.
She/he/it is travelling.
Present perfect continuous tense
She/he/it has/had travelled.
Present perfect tense
She/he/it has/had been travelling.
Simple past tense
She/he/it travelled.
Past continuous tense
She/he/it were travelling.
Past perfect tense
Perfect continuous tense.
She/he/it will/shall travel.
Simple future tense
She/he/it will/shall be travelling.
Future perfect tense
She/he/it will/shall have travelled.
Future perfect continuous tense
She/he/it will/shall have been travelling.
Sentence examples in all forms
Sentence examples in all participles and parts of speech :
Fact checked: Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.

About the author
Dalia Y.: Dalia is an English Major and linguistics expert with an additional degree in Psychology. Dalia has featured articles on Forbes, Inc, Fast Company, Grammarly, and many more. She covers English, ESL, and all things grammar on GrammarBrain.
Core lessons
- Abstract Noun
- Accusative Case
- Active Sentence
- Alliteration
- Adjective Clause
- Adjective Phrase
- Adverbial Clause
- Appositive Phrase
- Body Paragraph
- Compound Adjective
- Complex Sentence
- Compound Words
- Compound Predicate
- Common Noun
- Comparative Adjective
- Comparative and Superlative
- Compound Noun
- Compound Subject
- Compound Sentence
- Copular Verb
- Collective Noun
- Colloquialism
- Conciseness
- Conditional
- Concrete Noun
- Conjunction
- Conjugation
- Conditional Sentence
- Comma Splice
- Correlative Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Coordinate Adjective
- Cumulative Adjective
- Dative Case
- Declarative Statement
- Direct Object Pronoun
- Direct Object
- Dangling Modifier
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Direct Characterization
- Definite Article
- Doublespeak
- Equivocation Fallacy
- Future Perfect Progressive
- Future Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect
- First Conditional
- Gerund Phrase
- Genitive Case
- Helping Verb
- Irregular Adjective
- Irregular Verb
- Imperative Sentence
- Indefinite Article
- Intransitive Verb
- Introductory Phrase
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Indirect Characterization
- Interrogative Sentence
- Intensive Pronoun
- Inanimate Object
- Indefinite Tense
- Infinitive Phrase
- Interjection
- Intensifier
- Indicative Mood
- Juxtaposition
- Linking Verb
- Misplaced Modifier
- Nominative Case
- Noun Adjective
- Object Pronoun
- Object Complement
- Order of Adjectives
- Parallelism
- Prepositional Phrase
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Personal Pronoun
- Personification
- Persuasive Writing
- Parallel Structure
- Phrasal Verb
- Predicate Adjective
- Predicate Nominative
- Phonetic Language
- Plural Noun
- Punctuation
- Punctuation Marks
- Preposition
- Preposition of Place
- Parts of Speech
- Possessive Adjective
- Possessive Determiner
- Possessive Case
- Possessive Noun
- Proper Adjective
- Proper Noun
- Present Participle
- Quotation Marks
- Relative Pronoun
- Reflexive Pronoun
- Reciprocal Pronoun
- Subordinating Conjunction
- Simple Future Tense
- Stative Verb
- Subjunctive
- Subject Complement
- Subject of a Sentence
- Sentence Variety
- Second Conditional
- Superlative Adjective
- Slash Symbol
- Topic Sentence
- Types of Nouns
- Types of Sentences
- Uncountable Noun
- Vowels and Consonants
Popular lessons

Stay awhile. Your weekly dose of grammar and English fun.

The world's best online resource for learning English. Understand words, phrases, slang terms, and all other variations of the English language.
- Abbreviations
- Editorial Policy
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
5 New Hotels Where the Past Meets the Present
Turrets, towers and tapestries greet guests at these evocative hotels in reimagined historic buildings in London, New York and beyond. (The food’s not bad, either.)

By Stephanie Rosenbloom
When is a hotel more than a place to sleep? When it’s in a building with a storied past, allowing guests to go back in time to the Gilded Age or Edwardian era as easily as they go to the gym or spa.
Nowadays you can check into a 17th-century former soap factory on the French Riviera, or part of the Old War Office in London, or a Renaissance-palazzo-style building that was once a bank in New York. Here are five new hotels in historic spaces where you can experience the past and present, delighting in the architecture of vanished days even as you indulge in the latest luxuries.
Château de Théoule
Théoule-sur-mer, france.
This seaside respite on the Côte d’Azur was once a 17th-century soap factory yet looks like a castle thanks to a Scottish lord who, in the early 1900s, added turrets and crenelated ramparts. Near the Massif de l’Estérel mountain range, the property opened this month with 44 rooms and suites, some in the castle and others in villas. All have an airy feel, thanks to linen curtains, rattan light fixtures, hardwood floors and views of the Bay of Cannes.
While the building begs to be explored, soft sand and sunshine are the order of the day — and the hotel has its own beach, La Plage Blanche, with 90 sun beds. Château de Théoule is about 20 minutes from Cannes, though if you get hungry there’s no need to leave the sand. A beach restaurant and lounge has cocktails — like the Strambery Fields (elderberry-infused gin, vanilla syrup, strawberry purée, tonic and egg white) — and menu items that include salads, pissaladière (think focaccia with confit onions, anchovies and black olives), and grilled octopus with citrus fennel and chimichurri. If you can bear to leave your lounge chair, explore the area’s hiking trails, swim in the pool, or visit the hotel spa for a massage or body treatment.
As evening descends, head to Mareluna on the terrace of the castle overlooking the bay for Mediterranean food and wine with dishes like cuttlefish tagliatelle with avocado and smoked herring eggs. Prices from 360 euros, or about $390 in low season, and from €920 in high season (mid-June to mid-September). The hotel will close for the season in mid-November.
Raffles London at the OWO
The former workplace of government and military officials, including Winston Churchill , the Old War Office (known as the New War Office when it was built in the early 1900s) has long been a place of intrigue. Fans of James Bond may recognize its Edwardian Baroque - style exterior from some of the films, and indeed Ian Fleming , the creator of Bond and a former naval intelligence officer, is said to have visited the building. It’s now open to the public for the first time, with part of it reborn as the 120-room-and-suite Raffles London at the OWO, the first Raffles Hotels & Resorts property in Britain.
Inside the grand space, some of the offices of political and military leaders have become suites, including one named for Churchill. There are also corner suites that take their names from female spies and other women linked to the property’s history, including Viscountess Astor , the first woman to sit in the House of Commons, and World War II operatives such as Vera May Atkins , a spy who recruited British secret agents.
The hotel’s interior design is by Thierry Despont , the French architect and designer known for his work on the Ritz Paris and the centennial restoration of the Statue of Liberty, who died last year.
Strategic planning taking place nowadays involves when to book an appointment at the hotel’s spa, which spans four floors. Historic spaces have new purposes, like a former library that’s been transformed into a restaurant, Saison by Mauro Colagreco , with Mediterranean dishes from the chef, perhaps best known for his Michelin-starred restaurant, Mirazur , in France. At Mauro Colagreco , another of the chef’s restaurants at the hotel, tasting menus highlight seasonal British fruits and vegetables.
Visit the Drawing Room , a wood-paneled lounge with a Steinway piano, for afternoon tea or something stronger, which you can sip while overlooking the Horse Guards at Buckingham Palace. Or slip off for a drink in rooms formerly used by MI5 at the underground Spy Bar . Prices from 922 pounds, or about $1,162.
Hotel Casa Lucia
Buenos aires.
Once one of Latin America’s tallest buildings, the Edificio Mihanovich — commissioned in the 1920s by Nicolas Mihanovich, a shipping businessman — is now home to this new 142-room-and-suite hotel. Inspired by the shape of a lighthouse, the building was among the first things sailors could see when coming into port, according to Casa Lucia, and Mihanovich wanted it to be tall enough so that he could see his own ships.
These days, guests can benefit from his ambitions with bird’s-eye views from some of the soft-hued contemporary rooms and suites. Many have balconies with outdoor showers, and spots overlooking Buenos Aires and the Río de la Plata.
In addition to being near the river, you’re in the midst of all that the chic Recoleta neighborhood has to offer: French-inspired architecture, boutiques, galleries and tourist destinations such as the Recoleta Cemetery , where you can visit the tomb of the former first lady Eva Perón .
Back at the hotel, savor Argentine cuisine and, of course, wine at Cantina Restaurant , then go next door to Le Club Bacan , a moody cocktail bar with a large selection of Argentine wines. Later this spring, you should be able to drop by the completed fitness center or the spa, which will have a heated pool. Prices from $670.
The Fifth Avenue Hotel
Located in a building that’s more than a century old, as well as a new 24-story glass space called the Tower, this 153-room-and-suite hotel in Manhattan’s NoMad neighborhood harks back to the Gilded Age, when it was a home and carriage house. In the early 1900s the building was sold, eventually becoming the Second National Bank , a five-story Renaissance-palazzo-style structure designed by McKim, Mead & White, the architectural firm behind New York’s original Pennsylvania Station and the Brooklyn Museum .
Step inside today and you’ll see a shimmering lobby with chandeliers, walls paneled in antique mirrors, marble flooring and cabinets replete with curiosities. The interior design by Martin Brudnizki Design Studio is at once playful and sumptuous, featuring tapestries and walls saturated with colors and patterns. The guest rooms mix old and new with antiques, Murano glass chandeliers and wardrobes inspired by traditional Chinese cabinets.
Going out to eat in New York is a must. But the chef Andrew Carmellini , a James Beard Award winner known for restaurants like A Voce, Café Boulud and Locanda Verde, tempts guests to stay in. The hotel’s Café Carmellini is his take on modern Italian and French cooking, with a menu that includes dishes like black bass forestière and cannelloni of lobster and golden osetra. Afterward, drop by the art-filled, wood-paneled Portrait Bar , with an atmosphere inspired by Italian villas, for a drink by a fireplace. Prices from $895.
Charleston, S.C.
The 25 rooms, suites and residences in this stylish boutique hotel are spread across three buildings in downtown Charleston, including two from the Victorian era. And they are ideal if you want the amenities of a hotel and the flexibility of a vacation rental. All rooms have full kitchens, as well as washers and dryers. Some have French doors leading to private balconies and terraces. You’ll hardly want to hole up in your room, though. An outdoor terrace off the main lobby has a fireplace that invites you to pause after exploring the neighborhood’s romantic streets dotted with gas lamps, historic architecture, boutiques and restaurants.
Alternatively, wander over to the hotel’s Lequeux-Williams House, a Greek Revival-style building that the hotel says dates to 1834. Formerly a private residence, it has been repurposed into restaurants overseen by the chef Jason Stanhope , the winner of a James Beard Award for Charleston’s popular Fig restaurant. They include the Quinte , an oyster bar and cocktail spot (you can order seafood towers, soups, sandwiches and ice cream, too), named for a 1918 billiards hall that was in the same location. Or try Lowland , a tavern with inviting dining spaces spread over two floors, including an outdoor dining area on cobblestone that’s hundreds of years old. Wherever you sit, you can tuck into comfort food like a biscuit with farmer cheese and pepper jelly, or a burger and fries. Prices from $399.
Follow New York Times Travel on Instagram and sign up for our weekly Travel Dispatch newsletter to get expert tips on traveling smarter and inspiration for your next vacation. Dreaming up a future getaway or just armchair traveling? Check out our 52 Places to Go in 2024 .
Open Up Your World
Considering a trip, or just some armchair traveling here are some ideas..
Italy : Spend 36 hours in Florence , seeking out its lesser-known pockets.
Southern California : Skip the freeways to explore the back roads between Los Angeles and Los Olivos , a 100-mile route that meanders through mountains, canyons and star-studded enclaves.
Mongolia : Some young people, searching for less curated travel experiences, are flocking to the open spaces of this East Asian nation .
Romania : Timisoara may be the most noteworthy city you’ve probably never heard of , offering just enough for visitors to fill two or three days.
India: A writer fulfilled a lifelong dream of visiting Darjeeling, in the Himalayan foothills , taking in the tea gardens and riding a train through the hills.
52 Places: Why do we travel? For food, culture, adventure, natural beauty? Our 2024 list has all those elements, and more .
The Kim Mulkey way
The lsu coach holds grudges, battles everyone — and keeps winning. but at what cost.

TICKFAW, La. — In the two sisters’ minds, the old house remains as it was: a one-story brick ranch a hundred yards off the road, white fence under two ancient oaks, tin roof long before it all caved in.
Their father built on the farmland he had inherited. Dug a swimming pool, poured the concrete for a basketball court, carved two softball fields into pasture. His two girls, born less than a year apart, would grow up running and hiding and disappearing among the pines.
“I just miss the memories,” Tammy, the 60-year-old younger sister, says.
They’re in the backyard in her favorite, shooting baskets with Daddy by starlight. It feels so real, she says. So precious and warm.
“I wish I could have it all back,” she says.
FIFTY MILES SOUTH AND WEST , a massive crowd is here to watch the older sister, to wear sequins like her, to cheer on her team. Five decades have passed since Kim Mulkey’s father first bounced a basketball to his daughters, explaining the keys to victory.
Speed. Stamina. Grit.
The game itself hasn’t changed much, but everything else around Mulkey has. It’s a Sunday in early March, the same day Pete Maravich’s 54-year-old career scoring record will fall. More than 13,000 people are packed into the LSU arena named for Maravich, and Tigers alumnus and former NBA superstar Shaquille O’Neal is in the tunnel. He’s wearing a T-shirt with a picture of star LSU forward Angel Reese on the front and her nickname, “Bayou Barbie,” in hot pink letters on the back.
Reese strolls onto the floor. Fans chant “One more year!” pleading with her to stay in college. And because the value of her name, image and likeness (NIL) rights is estimated to be worth multiples more than the $240,000 WNBA maximum salary, she just might.
“Times are different,” Mulkey will say in a news conference following the game. “You can be beautiful. You can be talented. You can be tough. You can be you.”
Few live that last part more than Mulkey, who wears feathers almost as dramatically as she ruffles them. Her outfits during games are legendary, and during last year’s NCAA tournament , fans wanted to see Reese and her teammates tear through the bracket, sure. But they also wanted to see what their coach might wear, say or do next.
She explodes at officials and is suspicious of reporters. Mulkey declined repeated interview requests for this story, and after LSU received an email from The Washington Post seeking comment on various elements of this story, she used two NCAA tournament news conferences to take aim at The Post’s reporting , threatening legal action in the event of “a false story.” LSU declined to comment.
“Not many people are in a position to hold these kinds of journalists accountable,” she said. “But I am, and I’ll do it.”
It’s by no means her first or most high-profile controversy. In 2013, the NCAA suspended Mulkey for a tournament game after she criticized referees. She later publicly defended Baylor, her former employer, amid a sexual assault scandal in its football program. In November, she told reporters after a road game that they could blame her if they were sick at Thanksgiving.
“I ain’t a sissy,” she said , holding a tissue and choking back sniffles. “I’ve got some kind of cold. It might be covid, but I ain’t testing.”
She is also known to hold grudges and clash with players, including about their appearances and displays of their sexuality, according to interviews with former players and news reports . Mulkey and Brittney Griner, the coach’s biggest star at Baylor, have feuded for more than a decade. And while Griner’s 294-day detainment in a Russian prison eventually required White House intervention, it wasn’t enough to ease tension long after Griner first said Mulkey encouraged gay players to hide their sexuality and “keep your business behind closed doors,” Griner wrote in her memoir.
“Kim Mulkey is an amazing coach; the reason I went to Baylor is because of her,” says Kelli Griffin, who played for Mulkey from 2007 to 2010. But, Griffin says, “She made my life hell” by drawing attention to Griffin’s clothes and issuing a suspension that ultimately ended the player’s career. And she believes it started after Mulkey found out she was gay.
Mulkey’s attorneys, in letters to The Post, denied that Mulkey treated gay players “more harshly or differently.” They provided an affidavit from former Baylor player Morghan Medlock, who said that she was in a relationship with Griffin and that she never witnessed Mulkey mistreat Griffin or other gay athletes. Former Baylor and LSU player Alexis Morris put it more bluntly to ESPN: “Coach Mulkey is not homophobic.”
Mulkey, in a 2013 interview with OutSports , insisted that she didn’t care about players’ sexuality and wouldn’t ask them about it.
“I don’t think it’s anybody’s business,” she said then. “Whoever you are. I don’t care to know that.”
Her conflicts with star players are over other issues too, though, and they have continued at LSU, even as players’ leverage and celebrity swell. She benched Reese for four games this season for reasons the coach refused to explain, weeks after appearing to call out Reese for a poor shooting performance. (Reese did not respond to messages from The Post seeking comment.) Mulkey told a supporter last year that Reese had been left off an awards list because of her GPA, according to email obtained via public records request by The Post. In another email, Mulkey complained that Reese was one of several players who “stay on that social media crap.”
Mulkey is many things, among them a 5-foot-4 hoops whisperer, an exceptional teacher , a coach willing to dive deeply into players’ emotions to push them past their preconceived limits. She is also one of college basketball’s most colorful personalities, viewed by some as an almost cartoonishly ornery supervillain. Regardless, as the women’s game finally takes center stage, she is an essential part of the show. In last year’s national championship game, she wore a sequined, technicolor ensemble and unfurled the best game plan of her life.
LSU forced Iowa star Caitlin Clark to battle for every shot, every touch, every step. The Tigers shut off access to the lane, allowing Clark to be predictably lethal from long range but otherwise one-dimensional, enough for LSU’s blowout win and one achievement that eluded even Shaq and “Pistol Pete”: a national title.
It was Mulkey’s seventh as a player or coach, and even in victory she was sarcastic and prickly.
“Coaches are hollering, ‘Get off the court,’ ” Mulkey snapped after winning the 2023 tournament, her fourth title as a head coach. “And I said: ‘Don’t tell me what to do; I’m fixing to win another championship.’ ”
Coaches don’t win 723 games, reach five Final Fours and hang around this long by being cuddly. Mulkey isn’t your grandmother or your mascot, and while everyone else is fighting for women’s basketball, she’s fighting against something because it’s the fight that drives her. Even if you played for her, won for her, loved her.
“I’ll just say she doesn’t care about winning the popularity contest among coaches,” longtime Texas A&M coach Gary Blair says. “She wouldn’t want to.”
So, yes, all of this — the sold-out arenas, television ratings, attention — is well and good. A fire is finally rising in the women’s game.
Where have you been?
Because Mulkey is the fire, and she has been burning for 40 years, too busy laying waste to everything and everyone in her path to be impressed by Clark, Shaq or anyone else trying to soak in this storybook moment.
BACK WHEN THE FOOTAGE was grainy, if it existed at all, she was poetry in pigtails: whirling passes behind her back, between her legs, past opponents. Sonja Hogg knew Louisiana Tech would be getting speed and grit when she recruited Mulkey, but was it too much to hope for more?
“I thought maybe she’d grow a little bit,” Hogg says now.
No such luck, but in the early 1980s, women’s basketball teams took what they could get. There was no money for private jets or elaborate team dinners, so the Lady Techsters dined on fast food on bus rides to Texas and Oklahoma. And not even the nice bus. That one was reserved for the men’s team, leaving only the “Blue Goose,” such a rattletrap that the travel itinerary built in extra time for breakdowns.
Home games were social affairs, and everyone wanted to see the newest member of Hogg’s quintet. A point guard raining down 30 shots per game, as Clark sometimes does, would have been unseemly anywhere in 1982. But at Louisiana Tech, coaches just wouldn’t have allowed it. Mulkey’s job was to run the offense, distribute the ball, do things precisely Hogg’s way.
The right way.
Hogg (rhymes with “rogue”) was the visionary, the strategist, the program’s good cop. Assistant coach Leon Barmore was the hard-ass. Fit in, do right or go see the enforcer for a profanity-laced rant or a date with the arena stairs.
“Back in the day,” former Louisiana Tech player Mickie DeMoss says, “they didn’t have to explain why. You get there, or you’re going to run.”
Louisianans drove hours to watch the Lady Techsters, so named because the men’s mascot was the Bulldogs and, as Hogg once pointed out, “a lady dog is a bitch.” Hogg required her players to be ladylike, and little girls wore their hair braided like Mulkey’s as they squeezed into Memorial Gym. The arena could fit 5,200, but Hogg says if she greased the Ruston fire marshal with tickets, he would allow in a thousand more.
Because Hogg put on a show . Tennessee’s Pat Summitt wore pantsuits. Ohio State’s Tara VanDerveer donned sweaters. Cheyney’s C. Vivian Stringer occasionally wore a skirt. Hogg drove a white Cadillac, wore beaver skin or mink, styled her platinum hair into a towering meringue.
“I couldn’t be dragging around in some sweatsuit,” she says now. “I mean, I wore warmups during practice and tennis shoes and whatever, but gah -lee , you don’t do that on the sideline .”
Louisiana Tech smoked Tennessee in the 1982 Final Four , stirring whispers that Summitt was a fine coach but a choker in big games, and met Cheyney in the final. Hogg directed traffic in a dusty rose and light pink blouse, shell necklace and wool crepe pants as Stringer’s press initially put Louisiana Tech in a sleeper hold.
But Mulkey had the speed to break the press, crash the lane, lay it in. The smarts to recognize when a defender dropped into a zone before pulling up to drain one from deep. Hogg and Barmore freed Mulkey up to riff because she had the conditioning to let her ignore fatigue and continue punishing her opponents, choking them out, stomping the court and beaming as time expired. Tech won by 14, and Mulkey got hooked on winning NCAA championships after one taste.
“She looked like a cheerleader jumping,” Hogg recalls of Mulkey, who went 130-6 as a college player and reached the Final Four every year. “She wants perfection. That’s what she was always seeking.”
AS SOON AS LES MULKEY got out of the Marine Corps in 1963, he started clearing: strawberry vines, bushes, weeds and juvenile pines, even dairy cows from the playing surfaces he had been imagining for six years.
His father had given his two sons 25 acres to share off a highway in Tangipahoa Parish. Les’s younger brother planned to raise horses on his half. Les liked competition, one way to channel his overflowing energy, and if all went right, he would soon be hosting weekend softball tournaments and pickup basketball games.
Les signed Kim up to play youth baseball, then took the league to court when it refused to admit a girl, she later wrote. She made all-stars the next year. He took his daughters with him to play weeknight hoops, and if his team was a man down, he would draft Kim.
“ Her ?” an opponent once asked.
“You scared?” Les said.
A lifelong LSU fan, he hoped Kim would play college basketball for the Ben-Gals, as they were initially known. But when she picked Tech, he made the four-hour trip to Ruston for home games, slipping into the gym and fading into the crowd to watch his little girl.
“He was so proud of me,” Kim wrote, “and I was so proud that he was my dad.”
Some nights, though, there were no games. Les and Dru, Kim’s mom, went dancing sometimes. Other nights he would go drinking as he used to in the Corps, he says, ending up in another woman’s bed. With his daughters in college, Les left Dru and married another woman. She wasn’t much older than Tammy and Kim.
In 1987, the WNBA was a decade away. After playing at Tech, Mulkey moved down the bench as an assistant coach. And a few years after that, she wrote, her boyfriend and a colleague in the athletic department, Randy Robertson, presented her a jack-in-the-box with an engagement ring inside. He was popular and gregarious. She hated parties and crowds, had never taken a sip of alcohol. She said yes anyway, planning to toast with 7 Up at the wedding.
Les packed his tuxedo and made the familiar drive to Ruston. His new wife could attend, Kim advised, but only if she sat in the rear, away from the family. The way Kim saw it, sister Tammy says, her dad hadn’t just walked out on his family. He had quit on the people who depended on him, the worst thing a person can do.
Through her attorneys, Mulkey derided The Post for contacting family members, saying they did not “relate in any way to her career.” But Mulkey herself wrote about her dad’s infidelity and their estrangement in her 2007 autobiography, “Won’t Back Down.”
“His unfaithfulness to my mother devastated our entire family,” she wrote.
Still, Les figured, if he talked to her in person, Kim would come to her senses. But she wouldn’t budge. Neither would Les. His daughter walked down the aisle alone.
They haven’t spoken since.
CAN YOU IMAGINE KIM MULKEY begging? For anything? She says it happened in 2000, when she dropped to her knees before Louisiana Tech President Daniel Reneau.
Hogg was gone, but Barmore and Mulkey kept the Techsters machine humming: seven more Final Fours and the 1988 championship. Barmore was an unrelenting competitor, and by the end of the 1999-2000 season, he and Mulkey were butting heads more often. After he called her out in front of the team, she later wrote, Mulkey reached a breaking point. She requested a transfer to a different department as she searched for a new coaching job, and Barmore apologized and stepped down. He lobbied for Mulkey to get a shot.
Reneau was willing to consider it, but he offered only a three-year contract. Mulkey, then 37, wanted five. When they met in the president’s office, Mulkey wrote: “I got out of my chair, onto my knees, and begged that man for a five-year contract. Tears were flying everywhere.” (Reneau did not return calls and messages seeking comment.)
Few things are more important to Mulkey than loyalty, codified during the 1984 Olympics . Mulkey had broken her foot and expected to be sent home, but Summitt, the Tennessee legend, declared that Mulkey had earned her spot. Team USA won the gold medal, and Mulkey forever saw Summitt as a mentor and friend.
Reneau showed no such commitment.
“I just wanted Dan Reneau to say, ‘Hey, Kim, you know we’ll take care of you, you’re one of us,’ ” Mulkey wrote. “But the man was so cold.”
She took the job at Baylor, replacing Hogg, of all people. Mulkey said later that she never spoke to Reneau again.
AT BAYLOR’S FIRST CONDITIONING SESSION under its new coach, in the spring of 2000, forward Danielle Crockrom says, Mulkey approached and collected a fistful of the exhausted player’s jersey.
“Push past this point,” she says Mulkey told her, “and you’ll be an all-American.”
But team captain? Not now, maybe not ever, Crockrom recalls being told. Because, according to Crockrom’s telling, Mulkey knew the player had gotten burned out the previous season and stepped away for two weeks. She had quit. On her teammates, her coaches, herself. Then she had gone to Baylor’s athletic director to complain about Hogg and the team’s direction, Crockrom says now, leading to the staff shake-up.
Mulkey blew the whistle, ordering more sprints, reminding everyone, Crockrom says, that she had set the wheels of agony in motion by complaining.
“Be careful what you ask for,” Crockrom says. She wouldn’t fully understand the purpose until later. “This is what you need to be disrupted, to pull out the potential in you. I had potential in me that I hadn’t even begun to scratch.”
That season, Baylor won 21 games and reached the NCAA tournament for the first time. Crockrom was indeed named an all-American. The Bears lost in the first round, though, and Mulkey told players this was only the beginning. “We might have raised the bar too early,” Mulkey said with a chuckle after the loss.
There was more work to do, even if that meant Mulkey’s process wasn’t for everyone.
“The weeding-out process,” Crockrom says.
Mulkey handed out playbooks, Crockrom says, then yanked them away. She made the team run her plays again and again until calls resulted in a Pavlovian, muscle-memory response. Crockrom says Mulkey made post players keep pace with guards, using structured failure to push beyond physical and emotional barriers. She scheduled more and more conditioning sessions, one starting earlier than the last.
Because know who else was up and grinding? VanDerveer at Stanford. Geno Auriemma at Connecticut. Summitt at Tennessee. All were building perennial championship contenders as the women’s game competed for eyeballs on the increasingly crowded sports landscape. Lisa Leslie could dunk; Candace Parker could throw down against boys; Sue Bird and Diana Taurasi anchored a U-Conn. team that couldn’t lose.
Mulkey paid special attention to Summitt, whom coaching peers praised not just for doing things the proverbial right way but her way, establishing a standard and a recruiting pipeline and a juggernaut, all while raising a son.
Back when she was still an assistant, Mulkey had leaned on Summitt when she and Randy learned, in 1991, they were expecting a baby girl. She was running Louisiana Tech’s summer camp at the time, plus overseeing academics and acting as recruiting coordinator. She was “in a depression,” she would tell the Dallas Morning News in 2012 , and thought it would be impossible to add a daughter to the mix, especially when —
Summitt interjected.
You can , she told her. It’s possible to be a great coach and a great mother .
Mulkey believed Summitt, always her North Star, and took Makenzie on a recruiting trip when she was two weeks old. She breastfed Kramer, the couple’s infant son, before and after practices and games. Mulkey wrote that, by the time they moved to Waco, the kids had learned to give their mom space, especially after losses, and stop asking why she cussed so much.
She leaned into the things that made her at Louisiana Tech because those things won. Only she sometimes played the roles of Hogg and Barmore: approachable emissary while handing out stuffed bears at Waco bingo halls and nursing homes, a former Baylor colleague says, and ruthless taskmaster who, according to multiple former players, might single out anyone who seemed distracted or was having a tough day.
“If you’re having a hard time with something or you’re not performing at the level that she would like you to be, then get ready,” says Emily Niemann, a swing player who joined the team in 2003. “Because there’s no holding back.”
Niemann’s vertical jump was a mere 13 inches, and she says Mulkey brought it up constantly, instructing the team not to throw Niemann a lob pass because she wouldn’t catch it. Sometimes Mulkey’s comments felt like a joke, Niemann says; other times she felt humiliated.
In the 2004 NCAA tournament, fourth-seeded Baylor ran into Tennessee in the Sweet 16. The teams were tied as time expired, but officials huddled and determined that Baylor’s Jessika Stratton had fouled Tasha Butts. After Butts made two free throws, Summitt’s team advanced.
Mulkey never mentioned the loss again. The team nonetheless remembered, and the next season, Baylor crushed NCAA tournament opponents by an average of 15 points. Niemann made five three-pointers in a title-game beatdown of Michigan State.
“She’s so locked in and intense that it trickles down to everybody,” Niemann says. “And when you have a whole team of people where every loose ball matters, every deflection matters, every block-out, every trip down the floor — everything matters.
“It’s emotionally draining. On the other hand, it gets results.”
THREE MONTHS LATER, Niemann says, Mulkey summoned her to the coach’s office. The player had been seen around Waco with a woman, and people had begun murmuring about her sexuality.
“It’s not a good look,” Niemann says Mulkey told her. Baylor is the world’s largest Baptist university, and its policy still prohibits premarital sex and defines marriage as between a man and woman. Mulkey advised Niemann to be careful because the program would be watching.
For months, Niemann had struggled with questions about her identity, slowly coming to grips with being queer, she says. The product of a conservative home in Houston, a graduate of a Christian school and now a player at Baylor, she found many of her feelings were in conflict with her surroundings.
“I can’t talk to anyone,” she says now. “I couldn’t find a way to make things feel right.”
She was thinking of transferring, Niemann says, and met with Mulkey and her parents about it. Mulkey was flabbergasted, the coach wrote in her memoir, adding that among Niemann’s reasons for wanting to leave Baylor was that Mulkey was sometimes too hard on players.
“This is how I do what I do,” Niemann recalls the coach saying. “And if you can’t take it, maybe you should leave.”
Niemann left. Later, she wrote that she “did not leave Baylor because coach Mulkey is homophobic.” The coach, Niemann wrote, was only expressing opinions that were the “dominant belief system” on campus.
Mulkey wrote about Niemann in her memoir, suggesting that “unhappiness comes from within one’s soul” and that Niemann’s experience was an isolated case.
Other players point out that hard coaching is a key driver of Mulkey’s success, even as her peers go softer amid the shifting power dynamics of college sports. For Mulkey, players say, that often extends to comments about players’ hairstyles, tattoos and makeup.
“She hates my different hair colors,” former Bears guard DiDi Richards says. “ ‘Why is your hair purple?’ ‘Are you going to wear them two ponytails?’ If you would change the color, she’d go, ‘You and these damn colors.’ ” The comments came from a place of affection, Richards believes. They could get personal, too, though Richards says they show how Mulkey pushes players, physically and emotionally, in pursuit of wins.
Mulkey’s attorneys described the comments as “good-natured banter, as often happens on and around the court.”
A few months after Baylor’s first championship, Mulkey’s husband told her he felt neglected. They attended couples counseling, Mulkey would write, and she offered to leave coaching. Robertson nonetheless wanted to end their marriage. “I told Randy … that he better be sure,” Mulkey wrote, “because there was no turning back.” (Robertson did not respond to an email.)
By this point, those in Mulkey’s orbit had learned that disloyalty could result in harsh consequences. Les Mulkey sent notes to his daughter, pleading for reconciliation, but Mulkey wrote that she returned them unread. After Reneau, the former Louisiana Tech president, sent Mulkey a message congratulating her on the national championship, Mulkey would say later, it sat unopened on her desk for years.
“Talk to that man?” she told the Dallas Morning News in 2012. “That’s not who I am.”
AT BAYLOR, MULKEY IMPORTED a layer of trust by surrounding herself with past allies: Barmore, who came out of retirement to be an assistant coach; a longtime Louisiana Tech booster to oversee Baylor’s budget and travel; and a former Techsters team manager to handle recruiting.
Everything Mulkey did, at least as it related to basketball, worked: two Sweet 16s in five years and, in 2010, another Final Four. Texas kids dreamed of wearing the green and gold, and when Kelli Griffin was in seventh grade, she wrote a paper about someday leaving Houston to play for Kim Mulkey.
Griffin had come out in high school, but though she and Mulkey never explicitly discussed her sexuality while she was being recruited, Griffin says now that it was “obvious” and that she assumed Mulkey knew. She promised Griffin’s mother, Madine, that Baylor was a “family” and that she would protect Kelli.
Not long after Griffin arrived on campus, she says, Mulkey began asking why she dressed like a boy: baggy jeans, basketball shorts, sweats. A lady, Griffin says the coach told her, wears a dress. “Okay, this lady might not like gay people,” Griffin recalls thinking.
She considered transferring, but in 2008, one of Griffin’s friends and former AAU teammates committed to Baylor. Brittney Griner was a 6-foot-8 phenom and YouTube dunking sensation who, not long after reporting to campus, grabbed a rebound, glided the length of the court with the ball, then dunked it.
“Dang, Kim,” Barmore said in an interview. “I think we’ve got something here.”
Griner is gay, but she didn’t come out publicly until 2013, after her final game at Baylor. Still, whenever Mulkey sensed Griner was distracted or stressed, Mulkey blamed “girlfriend problems,” Griner later wrote, even if Griner wasn’t dating anyone. “She sounded like she was speaking a foreign language,” Griner wrote.
“Maybe she would have understood me better,” Griner wrote, “if I had shared more with her, but there was always a little bit of a disconnect with us, because I never really knew if Kim fully accepted me for who I am.”
Mulkey also called out players if they gained weight, instructing the team’s strength coach to conduct weigh-ins in front of the team, according to Griffin and another player. Players weren’t to bring non-basketball matters to Mulkey, they say, encouraged to confide in assistant coaches instead. And Niemann and multiple other former players say shame was a frequent tool in Mulkey’s coaching arsenal, whether during practice drills or in addresses to the team. Some of these former players spoke on the condition of anonymity because of fears of retaliation in the close-knit women’s basketball community.
Mulkey’s attorneys said the former players’ allegations were too vague to respond to.
Mulkey didn’t like the stars tattooed on Griner’s shoulders because, the player later wrote, they sent the “wrong message.” Griner pacified her coach by wearing a T-shirt under her jersey.
“It seemed like all she cared about was the image of the program as seen through the eyes of a very specific segment of the population,” Griner wrote. “Just once, I wanted her to stop worrying about what everyone else thought and stand by my side.”
In 2010, Griffin was the second-ranked Bears’ starting point guard. One night, Griffin says, an ex-girlfriend and Bears teammate showed up at Griffin’s home, and a fight broke out.
Griffin says she called Mulkey to report the incident, and the next morning, Mulkey announced that Griffin would be suspended indefinitely. The teammate, whom Griffin wouldn’t identify to The Post because, she said, the teammate had not come out as gay, wasn’t punished, according to Griffin. In a separate interview, Griffin’s mom, Madine, also recalled that the other player wasn’t suspended.
Griffin says she confronted Mulkey to ask why she was being penalized and that Mulkey told her she was owed no explanation.
“I thought I did everything I was supposed to,” she says.
After The Post asked Mulkey’s representatives about these events, they provided a statement from the former player, Morghan Medlock, who was in a relationship with Griffin at the time. Medlock claimed Griffin was actually suspended for using marijuana.
In a phone interview the next day, Medlock reiterated that Mulkey “never knew” there had been an altercation between Griffin and Medlock. Griffin just stopped coming to practice, Medlock said. Medlock said she did not remember how she learned the reason Griffin was suspended.
Medlock said she decided to give the statement after receiving a call this week from an individual who falsely claimed Griffin had identified Medlock to The Post.
“If my name never came up, I wouldn’t be on the phone with you right now,” she said. Medlock would not reveal who had contacted her and refused to say when she had last spoken with Mulkey.
“What difference does it make?” she said. “How I got the information, who I got it from, where I got it, that doesn’t matter.”
She then ended the call.
Griffin maintains that she was not suspended for drugs and that she didn’t use marijuana in college. The Baylor women’s basketball spokeswoman from 2010, who’s now retired, told The Post in a text message Wednesday that she was “not privy” to the reason for Griffin’s suspension. Baylor’s current spokesman declined to comment on this and other elements of this article.
Griffin says she told assistant coach Damion McKinney that she intended to transfer because, Griffin says, “I couldn’t play for Kim anymore.” (McKinney did not respond to messages seeking comment.)
But transferring wouldn’t be easy. Long before the NCAA, in 2021, introduced the transfer portal, allowing players to come and go among schools without penalty, players generally needed to be released by one school before pursuing a transfer to another.
Four days after appearing in an exhibition game, the Baylor program released a statement to the media. It didn’t say Griffin intended to transfer.
It said she “quit.”
YEARS PASSED, AND WITH KIM and Tammy grown and gone and their dad starting over, pine seedlings took root on the softball fields. The walls of the pool collapsed and got filled in. The basketball goal was cut down and hauled away. Trash collected on the concrete slab, once the site of late-night competitions; cans rusted; and discarded shoes became waterlogged, becoming moldy and deformed. Someone spray-painted KEEP OUT on a sheet of corrugated metal that replaced a wall, wood beams rotted, pipes sunk into the earth.
The pines matured and swallowed the fields, grass grew, and weeds sprouted, flowered and spread. After nearly four decades, the overgrowth had narrowed the property’s walking paths and obscured the driveway.
The woods had retaken their land, and any evidence that a family had ever been here was gone.
IN SPRING 2016, MULKEY’S SON , who’s now 29, convinced her it was time to go see Summitt . The legendary Tennessee coach, perhaps Mulkey’s dearest friend in coaching, had been diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease five years earlier.
Summitt was in a senior living facility in Knoxville, and Mulkey knew what visiting her meant. Kim kept saying “I love ya,” she would tell reporters later, and Pat kept saying it back. Four weeks later, Summitt was gone.
This was the same year that Baylor fired football coach Art Briles after a damning investigation of the football program’s coverup of at least 17 acts of sexual or domestic assault by 19 players. Mulkey went on the attack. She snapped at reporters who brought up the scandal, saying she was “tired of hearing” about it, then turned a postgame speech after her 500th career win into a pulpit.
“If somebody is around you and they ever say, ‘I will never send my daughter to Baylor,’ you knock them right in the face,” she said. Mulkey later apologized.
The school’s leaders, many of whom had been brought in to restore the school’s reputation, found themselves dealing with new headaches involving Mulkey. Even before Baylor announced plans to replace the old Ferrell Center with a new arena, Mulkey told peers that she expected the court to be named for her.
Baylor declined The Post’s requests to interview Athletic Director Mack Rhoades and school president Linda Livingstone.
Mulkey distanced herself further from players whose time at Baylor had ended abruptly or unexpectedly. When Niemann returned to campus for a celebration of Baylor’s 2005 championship, it was an important step in her process of healing, she says.
“I wanted to go back to the place,” Niemann says, “and step back into that gym and re-engage with that community and not have my head held down in shame. That’s what I needed to do: This is me; this is who I am. I did some awesome things, I made some poor decisions, and this is still a part of my life.”
Niemann found Mulkey and approached her. Niemann says she thanked her former coach for the impact she had made on her life and said she was sorry for the way things ended.
Niemann said Mulkey said nothing and walked away.
“There was just nothing there,” she says. “There was no warmth. There was no nothing.”
Three months after Mulkey contracted the coronavirus in 2021, forcing the cancellation of a home game against U-Conn., she urged the NCAA to “dump” testing for the virus . A few weeks later, Mulkey approached Baylor administrators to let them know she had an offer from LSU. She planned to accept unless Baylor gave her a better deal.
In a decision that rocked the industry, the school made no counteroffer.
ONE MONDAY MORNING IN 2022 , LSU players arrived at the basketball facility and were greeted with an unusual directive: Turn off your phones and put them in the other room.
Mulkey went ballistic. Days earlier, two LSU players had gotten into a fight. Teammates got between them, but the two kept at it, with spit flying and glass thrown. The scene had unfolded in front of a group of visiting recruits.
“My regret in this life,” one of the people present says, “I didn’t record this meeting.”
That was impossible, though, because at Baylor and now at LSU, former players say, staffers sometimes mitigated the risk of Mulkey’s tirades being recorded by barring phones from the room. (Mulkey’s attorneys did not address this incident in their responses to The Post.)
It had been a tense year already. Earlier in 2022, Griner, now starring for the Phoenix Mercury, was detained at an airport in Russia , where, like many WNBA players, she supplemented her earnings by playing overseas. Officials claimed she had vape cartridges containing hashish oil in her luggage.
WNBA players wore Griner’s No. 42 during the All-Star Game, and Seattle Storm player Sue Bird pleaded for Griner to be released. NBA star Stephen Curry spoke out in support of Griner, and President Biden signed an executive order threatening sanctions on any government that wrongfully detained Americans.
It was as if everyone was discussing Griner’s plight. Everyone, that is, except Griner’s college coach.
“And you won’t,” Mulkey shot back at a reporter who said he hadn’t seen her comment on the situation.
Whatever the root of their beef, it had intensified enough that Mulkey would rarely say Griner’s name. She made an exception in June 2022, when Mulkey appeared on the “Tiger Rag” radio show.
“I pray for Brittney,” Mulkey said. “I want her home safely. I think there’s lots of people speaking out on her behalf, and those of us who don’t necessarily speak publicly about it certainly are praying for her.”
Still, former LSU players say, those within the program had learned to avoid mentioning Griner or interacting with social media posts that supported the detained player.
Even in the tightknit coaching community, a frequent discussion topic was Mulkey’s unwillingness to look beyond a grudge.
“I really was hoping that Kim would make a statement. Really hoping she would,” says DeMoss, the former Louisiana Tech player and longtime coach who adds that she considers Mulkey a friend. “You’ve got a kid that’s stuck in Russia; I mean, that’s bigger than any feud that y’all had. No one knew how long they were going to detain her over there.
“We were all hoping [Mulkey] could just rise above it for that moment. Just get her back home. But she didn’t.”
Through her attorneys, Mulkey rebutted any suggestion that she failed to support Griner.
In December 2022, after nearly a year in prison, Griner was released and returned to the United States in a prisoner exchange. The basketball community expressed relief and joy, and reactions — not all supportive, considering the exchange freed a notorious Russian arms dealer — poured out from both sides of the political aisle. Mulkey issued a brief statement to ESPN: “God is good. Prayers are powerful. Brittney is on the way home where she belongs. Our prayers remain with her and her family as they recover and heal together.”
Three months later, after Mulkey reached her fifth Final Four, a reporter asked whether Mulkey had spoken with Griner. She hadn’t. Four days later, Mulkey, in a pink- and gold-sequined jacket, cut down the net and held up a newspaper with Reese pictured and CHAMPS! in massive letters.
Even among some of Mulkey’s ex-players, the enthusiasm was muted.
“As a head coach, you’re responsible for so many people; you’re taking on a role that leaves a very lasting impression,” a former Baylor player says. “You might be able to win us a championship, but are people going to want to come back and see you?”
EVERY ONCE IN A WHILE , Les Mulkey climbs into his work truck, drives past the old property, makes his way 50 miles south and west to Baton Rouge. He hasn’t spoken with his older daughter in 37 years, but same as he used to, he can slip into a gym, fade into the crowd and watch his little girl.
“I love my babies,” he says. “I ain’t ashamed.”
Kim has her daddy’s eyes, the same skeptical eyebrows, the same pride. “They’re just alike,” younger daughter Tammy says. Tammy said in early March that she doesn’t speak to her sister, either. There was some disagreement five or six years ago, Tammy says, but she won’t say what caused it. She believes they will reconnect eventually. “I’m sure we will,” she says. “One day. I hope.”
Les has no such delusions. Isn’t it odd, he says, to love a child so much that you leave them be? It’s how Kim wants it, he says, but he prays every night that, tomorrow, she will want something new. He is 86 now and lives alone, in a dilapidated trailer way out past the pines. It’s where he retreats after his drives to Baton Rouge. He has dozens of pictures, newspaper cutouts, mementos from Kim’s basketball career. Tammy calls it a shrine.
It’s all he has left of her, and with many of Les’s friends dying recently, he thinks about what’s next. He was cocky, he says. Stubborn. A little too proud, he says, so when his time comes, Les figures it will be when he’s alone, surrounded by achievements but not people, wasting away like the things he once built.
LONG AFTER ANOTHER LSU WIN , Mulkey takes a photo with a woman in a wheelchair. Then she points at a crowd assembled beyond the tunnel, lamenting that she’s about to walk into that .
“Kim!” a young fan yells.
“You’ve got to say Coach Mulkey,” an adult corrects.
Mulkey heads that way, drawing cheers, and encourages patience. She will get to everyone, she promises. As the arena empties, the coach signs autographs, raises her eyebrows at the Kim Mulkey bobblehead the school gave out, poses for selfies not far from the banner LSU hung for last year’s championship.
As afternoon turns to evening in Baton Rouge, Mulkey is still signing and chatting with fans. She’s an icon and a winner, one of the best motivators and teachers any sport has seen. But Mulkey is right: Times are different. Long after Summitt’s Tennessee teams slept on gymnasium floors because her program couldn’t afford hotel rooms, Mulkey now makes $3.26 million per year, most in the women’s game. Meanwhile, Louisiana Tech, once a women’s basketball dynasty, hasn’t made the NCAA tournament in a dozen years. Baylor is no longer among the sport’s upper tier, another structure abandoned and left to wither.
Along the LSU baseline, families wait for Mulkey to reach them. When they’ve gotten whatever they’ve been waiting for, they head toward the steps and a row of glass doors. As they walk, fathers tell their kids that was Kim Mulkey they just met, the coach who won all those championships, told it like it is, did it all her way.
Reporters fold their tripods and unplug their microphones from press row. Athletics staffers head toward the Pete Maravich Assembly Center exits. The crowd thins, and workers use a leaf blower to remove trash from empty rows.
“Miss Kim!” a voice calls, and it echoes through the arena. Mulkey walks across the hardwood, sequins glinting and heels clicking, to snap another picture. Then, when they all have what they wanted, the last of the friends, families and groups leave together, beneath a banner marking Mulkey’s latest achievement, and the coach heads back toward the tunnel, off into the evening alone.
Molly Hensley-Clancy in Washington contributed to this report.


COMMENTS
What is the past tense of "travel?". Most commonly, the past tense of the word "travel" is "traveled.". Although the word form will change based on its participle. And the sentence where it's used. For example, referencing "travel" in the present participle form will change it to "traveling," but in the infinitive form ...
Conjugate the English verb travel: indicative, past tense, participle, present perfect, gerund, conjugation models and irregular verbs. Translate travel in context, with examples of use and definition.
travel. 'travel' is the model of its conjugation. In British English, the final consonant is doubled before -ing and -ed. infinitive: present participle: past participle: (to) travel. trave ll ing. trave ll ed.
Conjugation of Travel. Simple / Indefinite Present Tense. He/She/It travels . I travel. You/We/They travel. Present Continuous Tense. He/She/It is Commonwealth travelling, US traveling. I am Commonwealth travelling, US traveling. You/We/They are Commonwealth travelling, US traveling.
Mixing Past and Present Tenses. One of the most common mistakes is mixing past and present tenses. For example, saying "I travel to Paris last year" instead of "I traveled to Paris last year." To avoid this mistake, remember to use the past tense of "travel" when referring to something that happened in the past. Using the Present ...
to do. to say. to love. to eat. to make. to like. to tell. to drive. 'to travel' conjugation - English verbs conjugated in all tenses with the bab.la verb conjugator.
Infinitive: to travel Gerund: travelling Past participle: travelled Simple past: travelled. Note. ... Present. I travel I travel: you travel you travel: he/she/it travels he/she/it travels: we travel we travel: they travel they travel: you travel you travel: I do not travel I don't travel: you do not travel you don't travel:
Conjugate the verb travel in all tenses: present, past, participle, present perfect, gerund, etc. English Deutsch български Ελληνικά English ... Verb Table for travel. Simple tenses; Continuous tenses; Conditional; Imperative; Impersonal; Simple tenses • Continuous tenses • Conditional • Imperative • Impersonal.
Present Continuous. I am travelling or traveling you are travelling or traveling he/she/it is travelling or traveling we are travelling or traveling you are travelling or traveling they are travelling or traveling.
Conjugation of the verb Travel in all tenses: future, present and past. 🎮 Conjugation trainer for memorizing forms.
Conjugation English verb to travel in several modes, tenses, voices, numbers, persons : indicative mode, subjunctive, imperative mood, conditional, participle form, gerund, present, past, future perfect, progressive. The-conjugation.com. Menu. Other languages available English ... I will/shall have been traveling you will have been traveling he ...
Travel in Past Continuous (Progressive) Tense. Singular. Plural. I was commonwealth travelling, us traveling. We were commonwealth travelling, us traveling. You were commonwealth travelling, us traveling. You were commonwealth travelling, us traveling. He/She/It was commonwealth travelling, us traveling. They were commonwealth travelling, us ...
Learn the three forms of the English verb 'travel'. the first form (V1) is 'travel' used in present simple and future simple tenses. the second form (V2) is 'travelled (BrE)', 'traveled (AmE)' used in past simple tense. the third form (V3) is 'travelled (BrE)', 'traveled (AmE)' used in present perfect and past perfect tenses.
Conjugation is the creation of derived forms of a verb from its principal parts by inflection (alteration of form according to rules of grammar). For instance, the verb "break" can be conjugated to form the words break, breaks, broke, broken and breaking. The term conjugation is applied only to the inflection of verbs, and not of other parts of speech (inflection of nouns and adjectives is ...
The Present Perfect Progressive (Continuous) is a form of the verb that shows the action or state started in the past and continued until the present. For example: Lisa has been dancing for 3 hours without stopping. Click here for the full info, rules, examples and exercises on the present perfect progressive and how to use it.
Table of irregular verbs - English Grammar Today - a reference to written and spoken English grammar and usage - Cambridge Dictionary
Learn how to conjugate travel in various tenses. Present: I travel, you travel, he travels ... Vocabulix. English Verbs. Verb Practice. Learn English. Vocabulary Builder. Learn english online ... Past he traveled we have traveled... Future will travel... Conditional would travel... Conjunctive... Verb drill 'travel'
Conjugate Travel in every English verb tense including present, past, and future.
Verb tense identifies when the action of a sentence takes place - the past, present, or future. The action in a sentence (also known as the time frame) has either happened, is happening, or will happen. Each verb tense has its own set of grammar rules. English verb tense forms also identify their aspect, which refers to the state of the action.
Travel Past Tense: Past Tense of Travel is Traveled.. Example: Sarah Traveled by Train. Travel Past Participle: Past Participle Form of Travel is Traveled.. Example: Sarah has Traveled by Train. Travel Present Participle: Present Participle Form of Travel is Travelling.. Example: Sarah is Travelling by Train. Travel 3rd Person Singular:
Conjugación verbo travel en inglés, ver modelos de conjugación inglés, verbos irregulares. Definición y traducción en contexto de travel. Traducción Context Corrector Sinónimos Conjugación. ... Conjugación verbo travel inglés: present, past tense, past perfect, present perfect, future. Ver la traducción en contexto para travel y su ...
To speak of Evelyn in the past is still hard, so Ms. Dieckhaus will sometimes linger on the present tense: she is kind, she gets her work done early, she has a spicy side.
What is the past tense of "travel?". Most commonly, the past tense of the word "travel" is "travelled.". Although the word form will change based on its participle. And the sentence where it's used. For example, referencing "travel" in the present participle form will change it to "travelling," but in the infinitive form ...
Turrets, towers and tapestries greet guests at these evocative hotels in reimagined historic buildings in London, New York and beyond. (The food's not bad, either.)
The game itself hasn't changed much, but everything else around Mulkey has. It's a Sunday in early March, the same day Pete Maravich's 54-year-old career scoring record will fall. More than ...