NASA's Voyager 2 Probe Enters Interstellar Space

For the second time in history, a human-made object has reached the space between the stars.
For the second time in history, a human-made object has reached the space between the stars. NASA's Voyager 2 probe now has exited the heliosphere - the protective bubble of particles and magnetic fields created by the Sun.
Members of NASA's Voyager team will discuss the findings at a news conference at 11 a.m. EST (8 a.m. PST) today at the meeting of the American Geophysical Union (AGU) in Washington. The news conference will stream live on the agency's website .
Comparing data from different instruments aboard the trailblazing spacecraft, mission scientists determined the probe crossed the outer edge of the heliosphere on Nov. 5. This boundary, called the heliopause, is where the tenuous, hot solar wind meets the cold, dense interstellar medium. Its twin, Voyager 1 , crossed this boundary in 2012, but Voyager 2 carries a working instrument that will provide first-of-its-kind observations of the nature of this gateway into interstellar space.
Voyager 2 now is slightly more than 11 billion miles (18 billion kilometers) from Earth. Mission operators still can communicate with Voyager 2 as it enters this new phase of its journey, but information - moving at the speed of light - takes about 16.5 hours to travel from the spacecraft to Earth. By comparison, light traveling from the Sun takes about eight minutes to reach Earth.

The most compelling evidence of Voyager 2's exit from the heliosphere came from its onboard Plasma Science Experiment ( PLS ), an instrument that stopped working on Voyager 1 in 1980, long before that probe crossed the heliopause. Until recently, the space surrounding Voyager 2 was filled predominantly with plasma flowing out from our Sun. This outflow, called the solar wind, creates a bubble - the heliosphere - that envelopes the planets in our solar system. The PLS uses the electrical current of the plasma to detect the speed, density, temperature, pressure and flux of the solar wind. The PLS aboard Voyager 2 observed a steep decline in the speed of the solar wind particles on Nov. 5. Since that date, the plasma instrument has observed no solar wind flow in the environment around Voyager 2, which makes mission scientists confident the probe has left the heliosphere.

"Working on Voyager makes me feel like an explorer, because everything we're seeing is new," said John Richardson, principal investigator for the PLS instrument and a principal research scientist at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in Cambridge. "Even though Voyager 1 crossed the heliopause in 2012, it did so at a different place and a different time, and without the PLS data. So we're still seeing things that no one has seen before."
In addition to the plasma data, Voyager's science team members have seen evidence from three other onboard instruments - the cosmic ray subsystem, the low energy charged particle instrument and the magnetometer - that is consistent with the conclusion that Voyager 2 has crossed the heliopause. Voyager's team members are eager to continue to study the data from these other onboard instruments to get a clearer picture of the environment through which Voyager 2 is traveling.
"There is still a lot to learn about the region of interstellar space immediately beyond the heliopause," said Ed Stone, Voyager project scientist based at Caltech in Pasadena, California.
Together, the two Voyagers provide a detailed glimpse of how our heliosphere interacts with the constant interstellar wind flowing from beyond. Their observations complement data from NASA's Interstellar Boundary Explorer ( IBEX ), a mission that is remotely sensing that boundary. NASA also is preparing an additional mission - the upcoming Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe ( IMAP ), due to launch in 2024 - to capitalize on the Voyagers' observations.
"Voyager has a very special place for us in our heliophysics fleet," said Nicola Fox, director of the Heliophysics Division at NASA Headquarters. "Our studies start at the Sun and extend out to everything the solar wind touches. To have the Voyagers sending back information about the edge of the Sun's influence gives us an unprecedented glimpse of truly uncharted territory."
While the probes have left the heliosphere, Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 have not yet left the solar system, and won't be leaving anytime soon. The boundary of the solar system is considered to be beyond the outer edge of the Oort Cloud , a collection of small objects that are still under the influence of the Sun's gravity. The width of the Oort Cloud is not known precisely, but it is estimated to begin at about 1,000 astronomical units (AU) from the Sun and to extend to about 100,000 AU. One AU is the distance from the Sun to Earth. It will take about 300 years for Voyager 2 to reach the inner edge of the Oort Cloud and possibly 30,000 years to fly beyond it.
The Voyager probes are powered using heat from the decay of radioactive material, contained in a device called a radioisotope thermal generator ( RTG ). The power output of the RTGs diminishes by about four watts per year, which means that various parts of the Voyagers, including the cameras on both spacecraft, have been turned off over time to manage power.
"I think we're all happy and relieved that the Voyager probes have both operated long enough to make it past this milestone," said Suzanne Dodd, Voyager project manager at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, California. "This is what we've all been waiting for. Now we're looking forward to what we'll be able to learn from having both probes outside the heliopause."
Voyager 2 launched in 1977, 16 days before Voyager 1, and both have traveled well beyond their original destinations. The spacecraft were built to last five years and conduct close-up studies of Jupiter and Saturn. However, as the mission continued, additional flybys of the two outermost giant planets, Uranus and Neptune, proved possible. As the spacecraft flew across the solar system, remote-control reprogramming was used to endow the Voyagers with greater capabilities than they possessed when they left Earth. Their two-planet mission became a four-planet mission. Their five-year lifespans have stretched to 41 years, making Voyager 2 NASA's longest running mission.
The Voyager story has impacted not only generations of current and future scientists and engineers, but also Earth's culture, including film, art and music. Each spacecraft carries a Golden Record of Earth sounds, pictures and messages. Since the spacecraft could last billions of years, these circular time capsules could one day be the only traces of human civilization.
Voyager's mission controllers communicate with the probes using NASA's Deep Space Network ( DSN ), a global system for communicating with interplanetary spacecraft. The DSN consists of three clusters of antennas inGoldstone, California; Madrid, Spain; and Canberra, Australia.
The Voyager Interstellar Mission is a part of NASA's Heliophysics System Observatory, sponsored by the Heliophysics Division of NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington. JPL built and operates the twin Voyager spacecraft. NASA's DSN, managed by JPL, is an international network of antennas that supports interplanetary spacecraft missions and radio and radar astronomy observations for the exploration of the solar system and the universe. The network also supports selected Earth-orbiting missions. The Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation, Australia's national science agency, operates both the Canberra Deep Space Communication Complex, part of the DSN, and the Parkes Observatory, which NASA has been using to downlink data from Voyager 2 since Nov. 8.
For more information about the Voyager mission, visit:
https://voyager.jpl.nasa.gov/
https://www.nasa.gov/voyager
More information about NASA's Heliophysics missions is available online at:
https://www.nasa.gov/sunearth

News Media Contact
Calla Cofield
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
626-808-2469
Dwayne Brown / Karen Fox
202-358-1726 / 301-286-6284
[email protected] / [email protected]

- April 11, 2024 | Webb Telescope Uncovers Neutron Star Hidden in Supernova Debris
- April 11, 2024 | How Our Brains Work: Connecting Lab-Grown Brain Cells Yields New Insights
- April 11, 2024 | Double Trouble: Decoding the Pain-Depression Feedback Loop
- April 11, 2024 | Elemental Surprise: Physicists Discover a New Quantum State
- April 11, 2024 | A Real Life Eye of Sauron? New Technology To Detect Airborne Threats Instantly
NASA’s Longest-Lived Mission: Voyager Probes Log 45 Years in Space
By Jet Propulsion Laboratory August 19, 2022
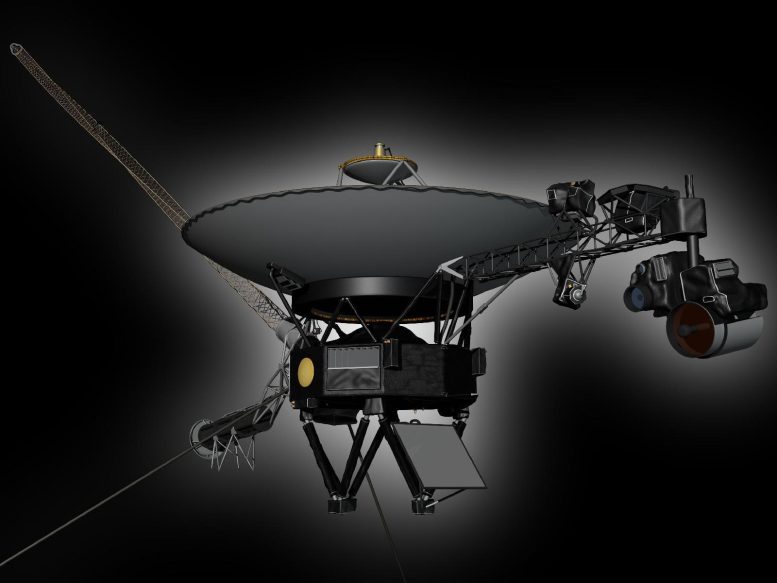

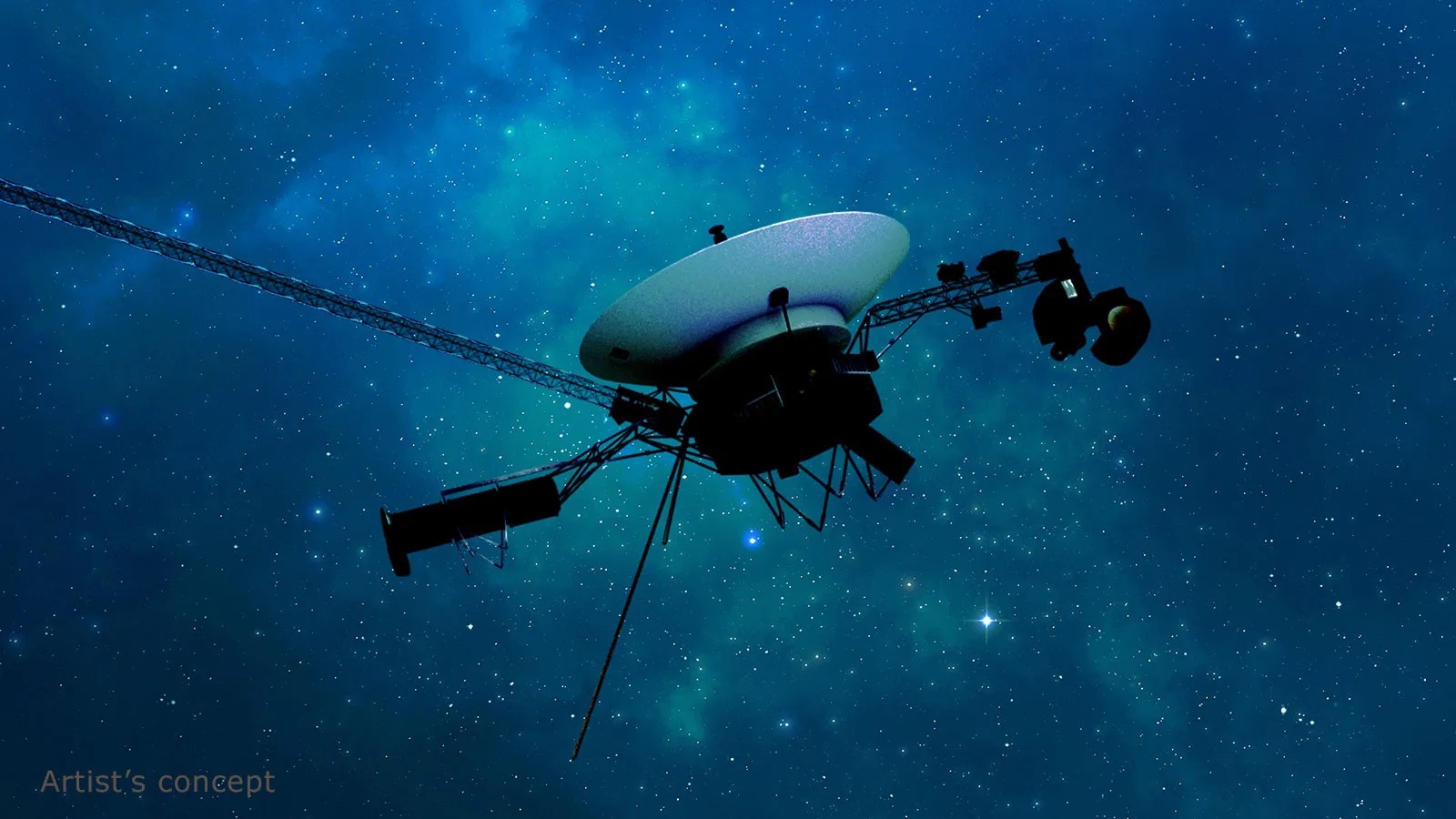
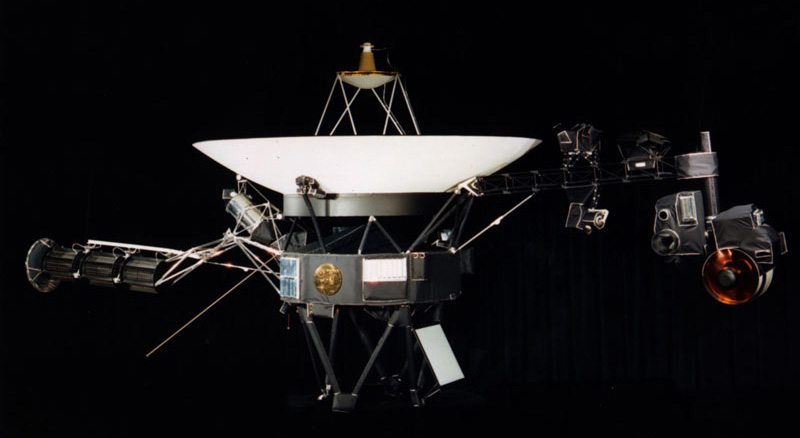
This artist’s rendering shows NASA’s Voyager spacecraft. On the boom to the right, the Cosmic Ray Science instrument, Low Energy Charged Particle detector, the Infrared Spectrometer and Radiometer, Ultraviolet Spectrometer, Photopolarimeter and Wide and Narrow Angle Cameras are visible. The bright gray square is an optical calibration plate for the instruments. The Golden Record, containing images and sounds from Earth, is the yellow circle on the main spacecraft body. The dish is the spacecraft’s high-gain antenna for communications with Earth. The magnetometer boom stretches out to the upper left. The radio isotope thermoelectric generators, Voyager’s power source, are visible to the lower left. The two long thin rods extending out to the left are antennas used by the Plasma Wave instrument. The Planetary Radio instrument also used these antennas when it was turned on. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Launched in 1977, the twin Voyager probes are NASA ’s longest-operating mission and the only spacecraft ever to explore interstellar space.
Launched in 1977, NASA’s twin Voyager spacecraft inspired the world with pioneering visits to Jupiter , Saturn , Uranus , and Neptune . Their journey continues 45 years later as both probes explore interstellar space, the region outside the protective heliosphere created by our Sun. Researchers – some younger than the spacecraft – are now using Voyager data to solve mysteries of our solar system and beyond.
NASA’s twin Voyager probes have become, in many ways, time capsules of their era: They each carry an eight-track tape player for recording data, they transmit data about 38,000 times slower than a 5G internet connection, and they have about 3 million times less memory than modern cellphones.
Despite this, the Voyagers remain on the cutting edge of space exploration. Managed and operated by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory ( JPL ) in Southern California, they are the only probes to ever explore interstellar space – the galactic ocean that our Sun and its planets travel through.
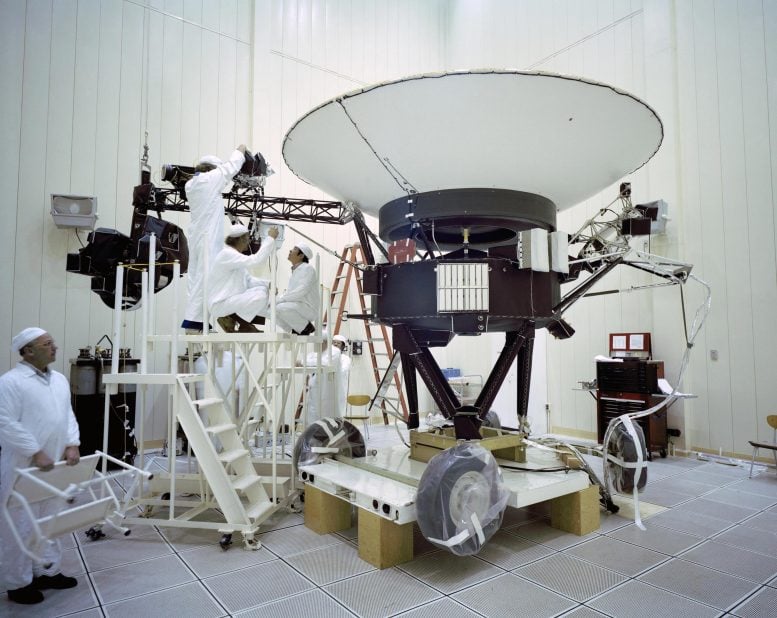

This archival image taken at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory on March 23, 1977, shows engineers preparing the Voyager 2 spacecraft ahead of its launch later that year. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
The Sun and the planets reside in the heliosphere, a protective bubble created by the Sun’s magnetic field and the outward flow of solar wind (charged particles from the Sun). Scientists – some of them younger than the two distant spacecraft – are combining Voyager’s observations with data from newer missions to get a more complete picture of our Sun and how the heliosphere interacts with interstellar space.
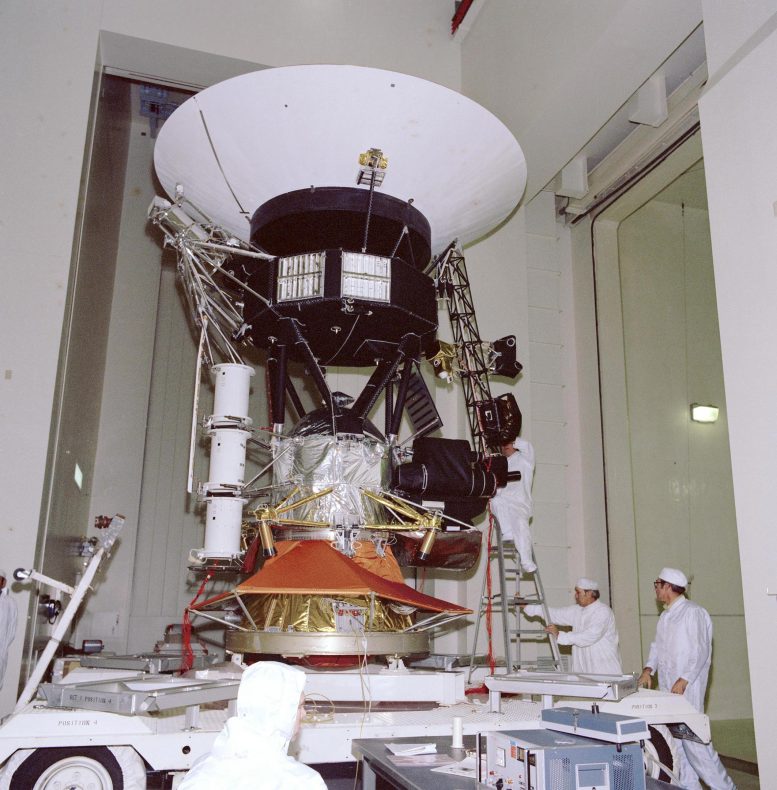

This archival photo shows engineers working on vibration acoustics and pyro shock testing of NASA’s Voyager on November 18, 1976. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
“The heliophysics mission fleet provides invaluable insights into our Sun, from understanding the corona or the outermost part of the Sun’s atmosphere, to examining the Sun’s impacts throughout the solar system, including here on Earth, in our atmosphere, and on into interstellar space,” said Nicola Fox, director of the Heliophysics Division at NASA Headquarters in Washington. “Over the last 45 years, the Voyager missions have been integral in providing this knowledge and have helped change our understanding of the Sun and its influence in ways no other spacecraft can.”
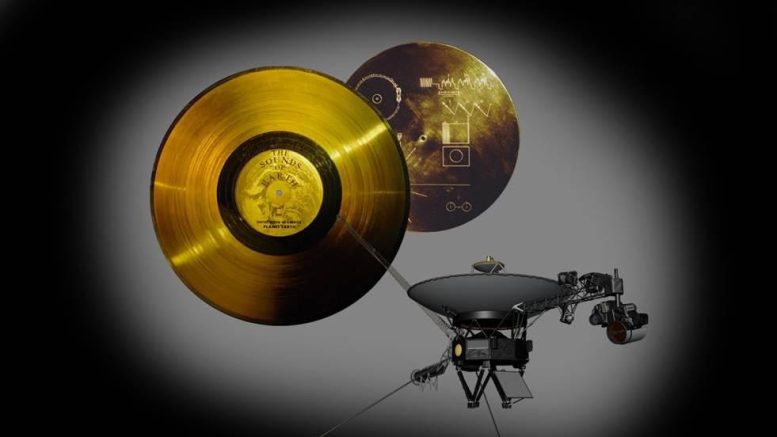

This image highlights the special cargo onboard NASA’s Voyager spacecraft: the Golden Record. Each of the two Voyager spacecraft launched in 1977 carry a 12-inch gold-plated phonograph record with images and sounds from Earth. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
The Voyagers are also ambassadors for humanity, each carrying a golden record containing images of life on Earth, diagrams of basic scientific principles, and audio that includes sounds from nature, greetings in multiple languages, and music. The gold-coated records serve as a cosmic “message in a bottle” for anyone who might encounter the space probes. At the rate gold decays in space and is eroded by cosmic radiation, the records will last more than a billion years.
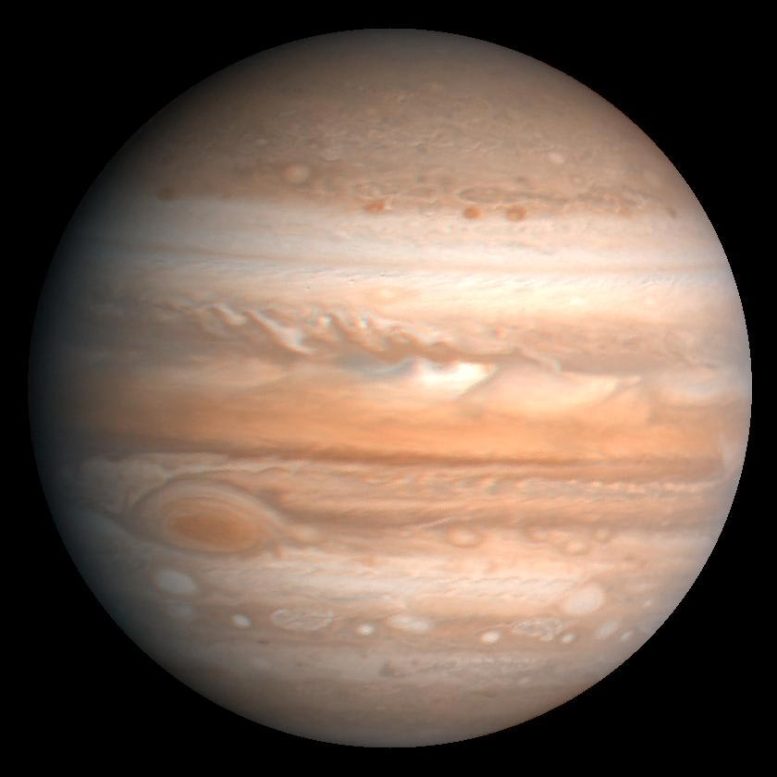

This processed color image of Jupiter was produced in 1990 by the U.S. Geological Survey from a Voyager image captured in 1979. Zones of light-colored, ascending clouds alternate with bands of dark, descending clouds. Credit: NASA/JPL/USGS
Beyond Expectations
Voyager 2 launched on August 20, 1977, quickly followed by Voyager 1 on September 5. Both probes traveled to Jupiter and Saturn , with Voyager 1 moving faster and reaching them first. Together, the probes unveiled much about the solar system’s two largest planets and their moons. Voyager 2 also became the first and only spacecraft to fly close to Uranus (in 1986) and Neptune (in 1989), offering humanity remarkable views of – and insights into – these distant worlds.
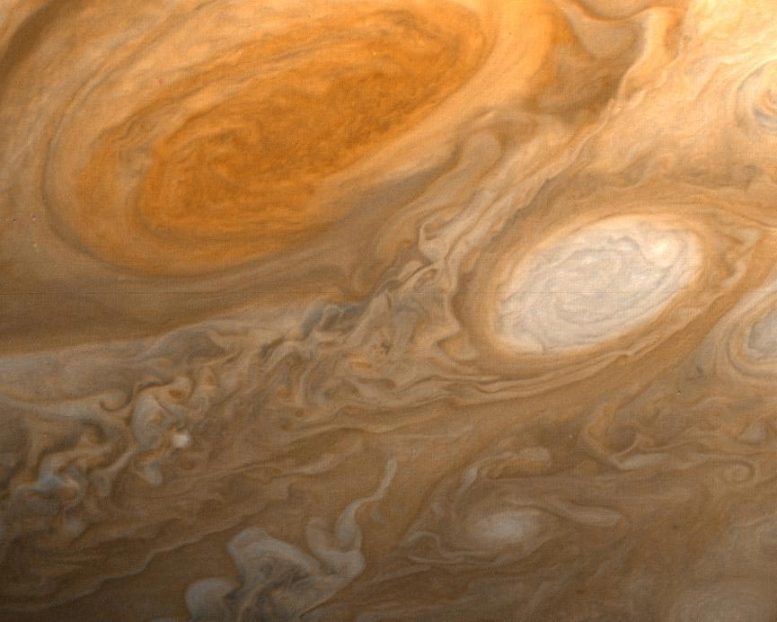

This photo of Jupiter was taken by NASA’s Voyager 1 on the evening of March 1, 1979, from a distance of 2.7 million miles (4.3 million kilometers). The photo shows Jupiter’s Great Red Spot (top) and one of the white ovals. Credit: NASA/JPL
While Voyager 2 was conducting these flybys, Voyager 1 headed toward the boundary of the heliosphere. Upon exiting it in 2012 , Voyager 1 discovered that the heliosphere blocks 70% of cosmic rays, or energetic particles created by exploding stars. Voyager 2, after completing its planetary explorations, continued to the heliosphere boundary, exiting in 2018 . The twin spacecraft’s combined data from this region has challenged previous theories about the exact shape of the heliosphere.
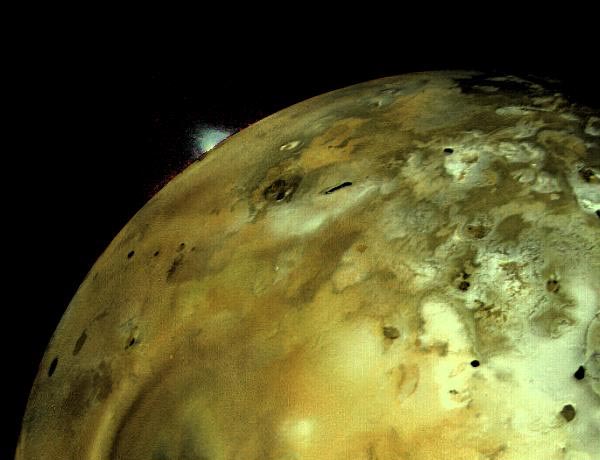

NASA’s Voyager 1 acquired this image of a volcanic explosion on Io on March 4, 1979, about 11 hours before the spacecraft’s closest approach to the moon of Jupiter. Credit: NASA/JPL
“Today, as both Voyagers explore interstellar space, they are providing humanity with observations of uncharted territory,” said Linda Spilker, Voyager’s deputy project scientist at JPL. “This is the first time we’ve been able to directly study how a star, our Sun, interacts with the particles and magnetic fields outside our heliosphere, helping scientists understand the local neighborhood between the stars, upending some of the theories about this region, and providing key information for future missions.”
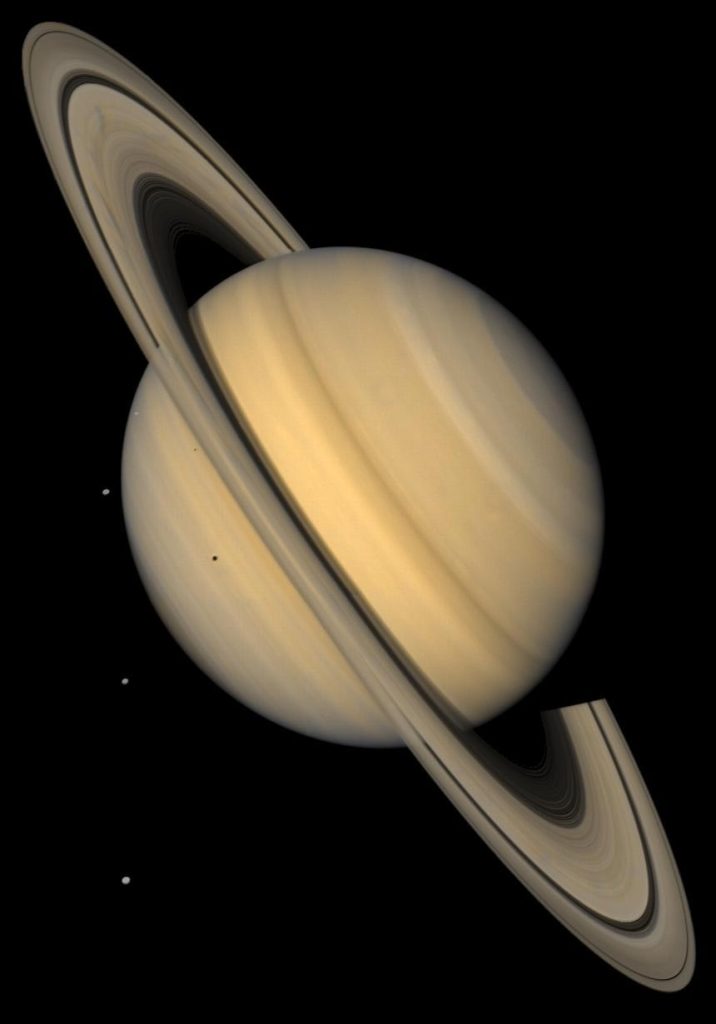
This approximate natural-color image from NASA’s Voyager 2 shows Saturn, its rings, and four of its icy satellites. Three satellites Tethys, Dione, and Rhea are visible against the darkness of space. Credit: NASA/JPL/USGS
The Long Journey
Over the years, the Voyager team has grown accustomed to surmounting challenges that come with operating such mature spacecraft, sometimes calling upon retired colleagues for their expertise or digging through documents written decades ago.
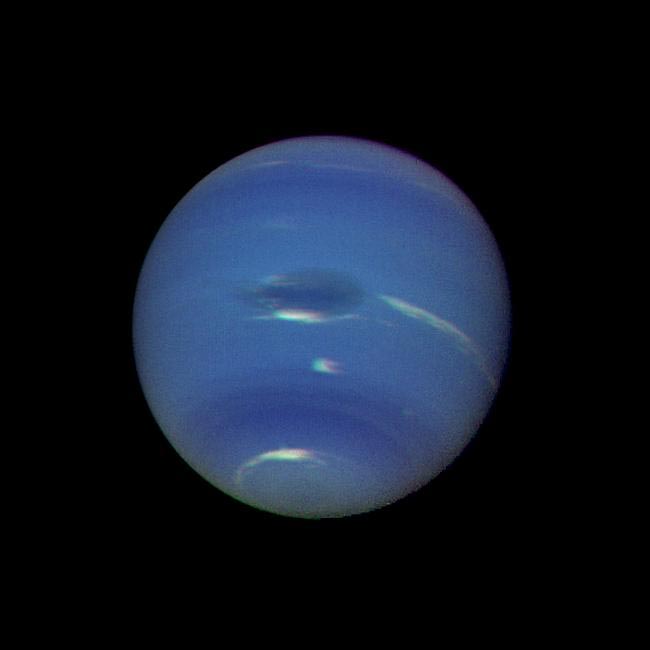

Neptune’s green-blue atmosphere was shown in greater detail than ever before in this image from NASA’s Voyager 2 as the spacecraft rapidly approached its encounter with the giant planet in August 1989. Credit: NASA/JPL
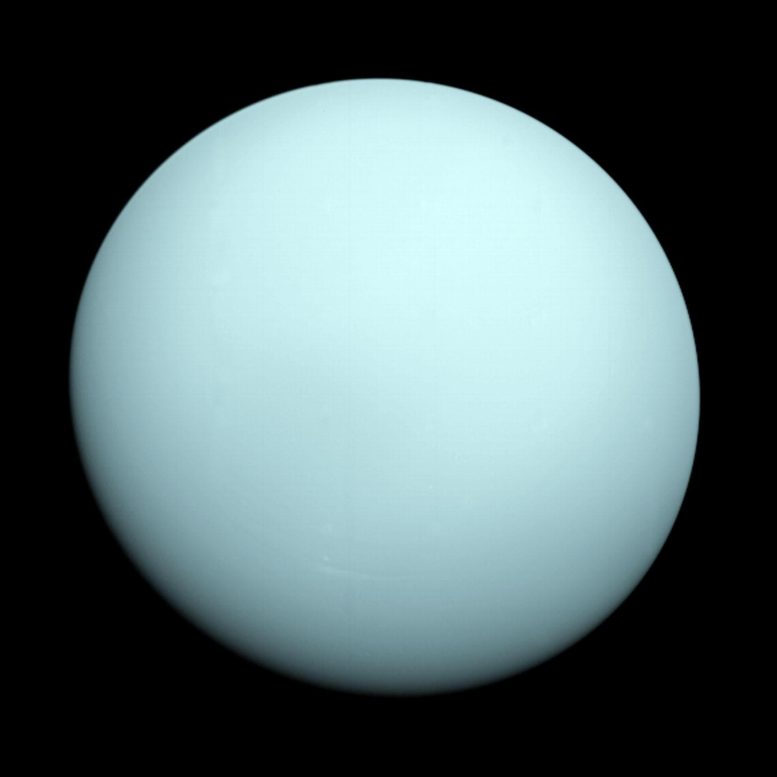

This is an image of the planet Uranus taken by the spacecraft Voyager 2 in 1986. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
This image, taken by NASA’s Voyager 2 early in the morning of August 23, 1989, is a false color image of Triton, Neptune’s largest satellite; mottling in the bright southern hemisphere is present. Credit: NASA/JPL
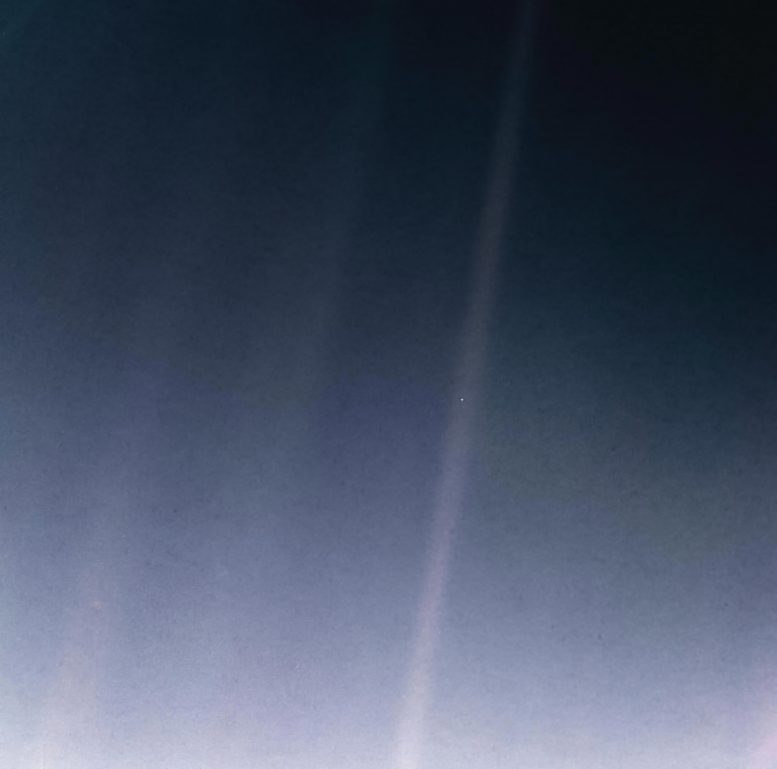

This updated version of the iconic “Pale Blue Dot” image taken by the Voyager 1 spacecraft uses modern image-processing software and techniques to revisit the well-known Voyager view while attempting to respect the original data and intent of those who planned the images. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Each Voyager is powered by a radioisotope thermoelectric generator containing plutonium, which gives off heat that is converted to electricity. As the plutonium decays, the heat output decreases and the Voyagers lose electricity. To compensate , the team turned off all nonessential systems and some once considered essential, including heaters that protect the still-operating instruments from the frigid temperatures of space. All five of the instruments that have had their heaters turned off since 2019 are still working, despite being well below the lowest temperatures they were ever tested at.
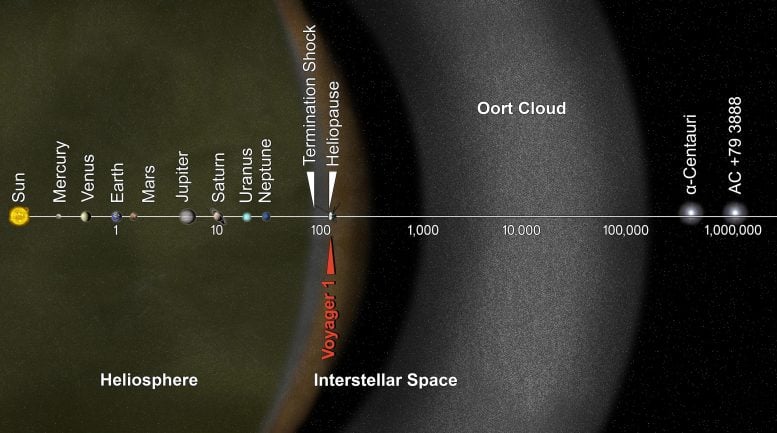
This illustrated graphic was made to mark Voyager 1’s entry into interstellar space in 2012. It puts solar system distances in perspective, with the scale bar in astronomical units and each set distance beyond 1 AU (the average distance between the Sun and Earth) representing 10 times the previous distance. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Recently, Voyager 1 began experiencing an issue that caused status information about one of its onboard systems to become garbled. Despite this, the system and spacecraft otherwise continue to operate normally, suggesting the problem is with the production of the status data, not the system itself. The probe is still sending back science observations while the engineering team tries to fix the problem or find a way to work around it.
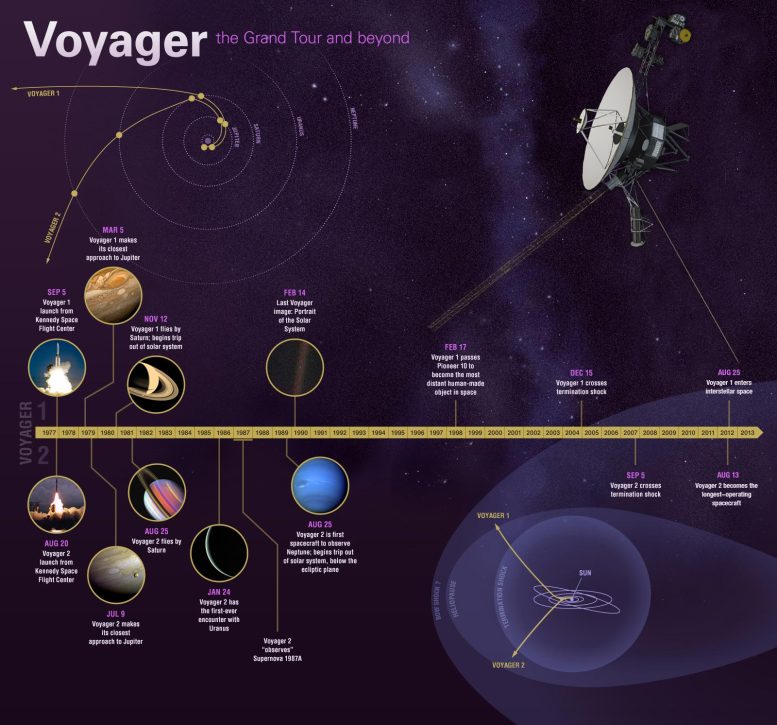
This graphic highlights some of the Voyager mission’s key accomplishments. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
“The Voyagers have continued to make amazing discoveries, inspiring a new generation of scientists and engineers,” said Suzanne Dodd, project manager for Voyager at JPL. “We don’t know how long the mission will continue, but we can be sure that the spacecraft will provide even more scientific surprises as they travel farther away from the Earth.”

This graphic provides some of the mission’s key statistics from 2018, when NASA’s Voyager 2 probe exited the heliosphere. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
More About the Mission
A division of Caltech in Pasadena, JPL built and operates the Voyager spacecraft. The Voyager missions are a part of the NASA Heliophysics System Observatory, sponsored by the Heliophysics Division of the Science Mission Directorate in Washington.
More on SciTechDaily

Voyager 2 Illuminates Boundary of Interstellar Space 11 Billion Miles From Earth

Voyager 2 Probe Enters Interstellar Space, Over 18 Billion Kilometers from Earth
Mysteries abound: nasa studying the edge of the sun’s magnetic bubble.

It’s Official – Voyager 1 Has Entered Interstellar Space

Hear the Eerie Sounds of Interstellar Space Captured by NASA’s Voyager
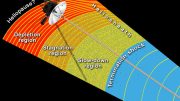
NASA’s Voyager 1 Explores the Outer Limits of Our Heliosphere
Nasa’s interstellar boundary explorer charts 11 years of change to heliosphere.

IBEX Reveals How Solar Wind Changes Our Heliosphere
9 comments on "nasa’s longest-lived mission: voyager probes log 45 years in space".
How is information transmitted from Voyager back to Earth and vice versa? WiFi? I want WiFi that strong for my house. Serious question.
“The uplink communications are executed via S-band microwave communications. The downlink communications are carried out by an X-band microwave transmitter on board the spacecraft, with an S-band transmitter as a back-up. All long-range communications to and from the two Voyagers have been carried out using their 3.7-meter (12 ft) high-gain antennas. The high-gain antenna has a beamwidth of 0.5° for X-band, and 2.3° for S-band.[38]: 17 (The low-gain antenna has a 7 dB gain and 60° beamwidth.)[38]: 17
Because of the inverse-square law in radio communications, the digital data rates used in the downlinks from the Voyagers have been continually decreasing the farther that they get from the Earth. For example, the data rate used from Jupiter was about 115,000 bits per second. That was halved at the distance of Saturn, and it has gone down continually since then.[38] Some measures were taken on the ground along the way to reduce the effects of the inverse-square law. In between 1982 and 1985, the diameters of the three main parabolic dish antennas of the Deep Space Network were increased from 64 to 70 m (210 to 230 ft)[38]: 34 dramatically increasing their areas for gathering weak microwave signals.
Whilst the craft were between Saturn and Uranus the onboard software was upgraded to do a degree of image compression and to use a more efficient Reed-Solomon error-correcting encoding.[38]: 33
Then between 1986 and 1989, new techniques were brought into play to combine the signals from multiple antennas on the ground into one, more powerful signal, in a kind of an antenna array.[38]: 34 This was done at Goldstone, California, Canberra, and Madrid using the additional dish antennas available there. Also, in Australia, the Parkes Radio Telescope was brought into the array in time for the fly-by of Neptune in 1989. In the United States, the Very Large Array in New Mexico was brought into temporary use along with the antennas of the Deep Space Network at Goldstone.[38]: 34 Using this new technology of antenna arrays helped to compensate for the immense radio distance from Neptune to the Earth.”
Amazing accomplishment for humanity. This shows what humans can do when their energy is not consumed by fighting with each other. Not only is this a model for scientific inspiration, it’s a great argument for world peace.
The Voyager probes are *not* the only interstellar vehicles. You forgot Pioneer 10.
There are five interstellar probes, all launched by the American space agency NASA: Voyager 1, Voyager 2, Pioneer 10, Pioneer 11 and New Horizons. As of 2019, Voyager 1, Voyager 2 and Pioneer 10 are the only probes to have actually reached interstellar space. The other two are on interstellar trajectories.
Good catch!
The communications accomplishment exceeds even the accomplishment of placing the probes on trajectory.
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Email address is optional. If provided, your email will not be published or shared.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Suggested Searches
- Climate Change
- Expedition 64
- Mars perseverance
- SpaceX Crew-2
- International Space Station
- View All Topics A-Z
Humans in Space
Earth & climate, the solar system, the universe, aeronautics, learning resources, news & events.

NASA’s Fermi Mission Sees No Gamma Rays from Nearby Supernova

The Ocean Touches Everything: Celebrate Earth Day with NASA

The April 8 Total Solar Eclipse: Through the Eyes of NASA
- Search All NASA Missions
- A to Z List of Missions
- Upcoming Launches and Landings
- Spaceships and Rockets
- Communicating with Missions
- James Webb Space Telescope
- Hubble Space Telescope
- Why Go to Space
- Astronauts Home
- Commercial Space
- Destinations
- Living in Space
- Explore Earth Science
- Earth, Our Planet
- Earth Science in Action
- Earth Multimedia
- Earth Science Researchers
- Pluto & Dwarf Planets
- Asteroids, Comets & Meteors
- The Kuiper Belt
- The Oort Cloud
- Skywatching
- The Search for Life in the Universe
- Black Holes
- The Big Bang
- Dark Energy & Dark Matter
- Earth Science
- Planetary Science
- Astrophysics & Space Science
- The Sun & Heliophysics
- Biological & Physical Sciences
- Lunar Science
- Citizen Science
- Astromaterials
- Aeronautics Research
- Human Space Travel Research
- Science in the Air
- NASA Aircraft
- Flight Innovation
- Supersonic Flight
- Air Traffic Solutions
- Green Aviation Tech
- Drones & You
- Technology Transfer & Spinoffs
- Space Travel Technology
- Technology Living in Space
- Manufacturing and Materials
- Science Instruments
- For Kids and Students
- For Educators
- For Colleges and Universities
- For Professionals
- Science for Everyone
- Requests for Exhibits, Artifacts, or Speakers
- STEM Engagement at NASA
- NASA's Impacts
- Centers and Facilities
- Directorates
- Organizations
- People of NASA
- Internships
- Our History
- Doing Business with NASA
- Get Involved
- Aeronáutica
- Ciencias Terrestres
- Sistema Solar
- All NASA News
- Video Series on NASA+
- Newsletters
- Social Media
- Media Resources
- Upcoming Launches & Landings
- Virtual Events
- Sounds and Ringtones
- Interactives
- STEM Multimedia
Rover Basics

Send Your Name to Mars Reservations Update

Amendment 9: New Opportunity: C.26 Rapid Mission Design Studies for Mars Sample Return

NASA Open Science Initiative Expands OpenET Across Amazon Basin

NASA Motion Sickness Study Volunteers Needed!

NASA Selects New Crew for Next Simulated Mars Journey

A.3 Ocean Biology and Biogeochemistry Inclusion Plan Correction
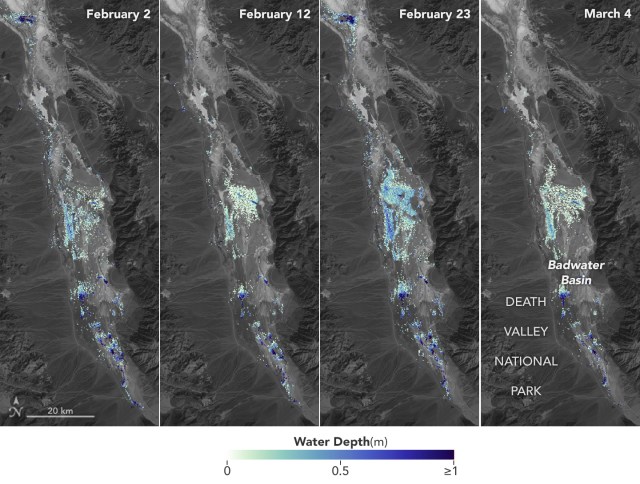
SWOT Satellite Helps Gauge the Depth of Death Valley’s Temporary Lake

Mars Exploration Science Goals
A Solar Neighborhood Census, Thanks to NASA Citizen Science

Hubble Spots a Galaxy Hidden in a Dark Cloud

NASA Langley Team to Study Weather During Eclipse Using Uncrewed Vehicles

ARMD Solicitations
NASA Noise Prediction Tool Supports Users in Air Taxi Industry

Tech Today: Folding NASA Experience into an Origami Toolkit

NASA’s SERT II: ‘A Genuine Space Success Story’

NASA Names Finalists of the Power to Explore Challenge
Earth Day 2024: Posters and Virtual Backgrounds

NASA Partnerships Bring 2024 Total Solar Eclipse to Everyone

NASA Receives 13 Nominations for the 28th Annual Webby Awards

La presentación del X-59 de la NASA personifica la tradición aeronáutica
Voyager 2 illuminates boundary of interstellar space.
Anthony Greicius
Pushing through plasma, leaking particles, magnetic field mystery.
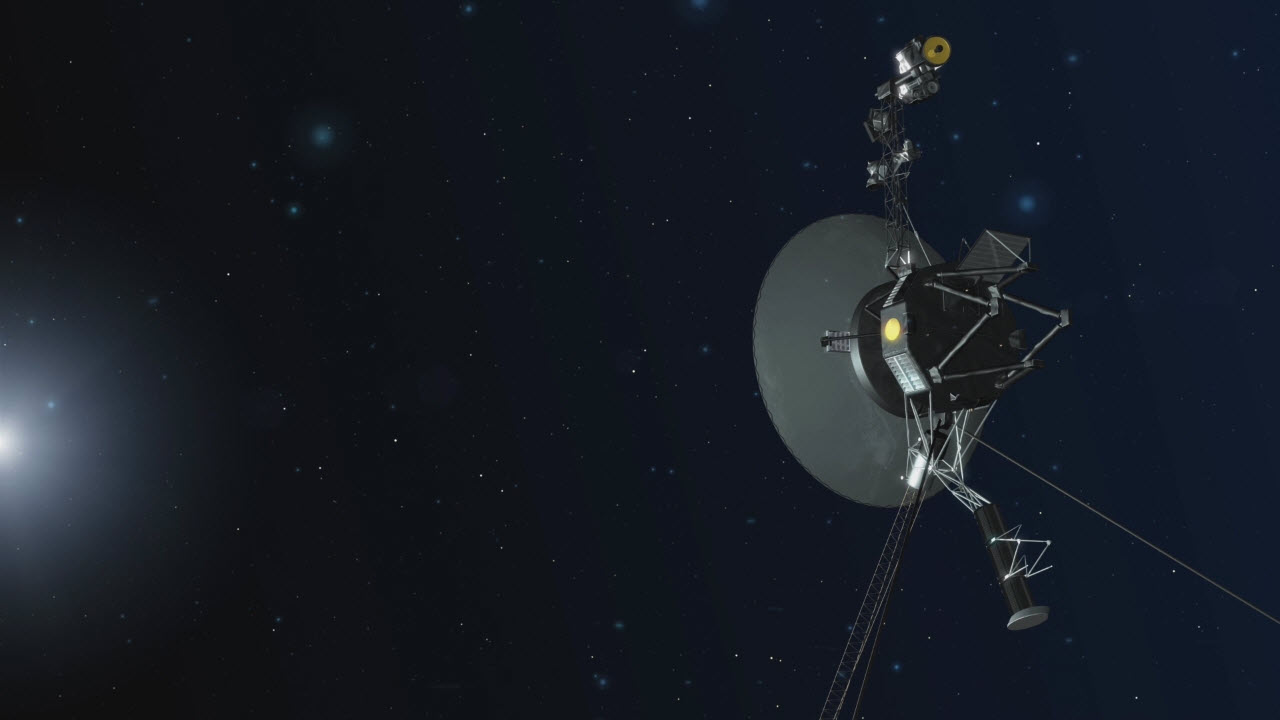

One year ago, on Nov. 5, 2018, NASA’s Voyager 2 became only the second spacecraft in history to leave the heliosphere — the protective bubble of particles and magnetic fields created by our Sun. At a distance of about 11 billion miles (18 billion kilometers) from Earth — well beyond the orbit of Pluto — Voyager 2 had entered interstellar space, or the region between stars. Today, five new research papers in the journal Nature Astronomy describe what scientists observed during and since Voyager 2’s historic crossing.
Each paper details the findings from one of Voyager 2’s five operating science instruments: a magnetic field sensor, two instruments to detect energetic particles in different energy ranges and two instruments for studying plasma (a gas composed of charged particles). Taken together, the findings help paint a picture of this cosmic shoreline, where the environment created by our Sun ends and the vast ocean of interstellar space begins.
The Sun’s heliosphere is like a ship sailing through interstellar space. Both the heliosphere and interstellar space are filled with plasma, a gas that has had some of its atoms stripped of their electrons. The plasma inside the heliosphere is hot and sparse, while the plasma in interstellar space is colder and denser. The space between stars also contains cosmic rays, or particles accelerated by exploding stars. Voyager 1 discovered that the heliosphere protects Earth and the other planets from more than 70% of that radiation.
When Voyager 2 exited the heliosphere last year , scientists announced that its two energetic particle detectors noticed dramatic changes: The rate of heliospheric particles detected by the instruments plummeted, while the rate of cosmic rays (which typically have higher energies than the heliospheric particles) increased dramatically and remained high. The changes confirmed that the probe had entered a new region of space.
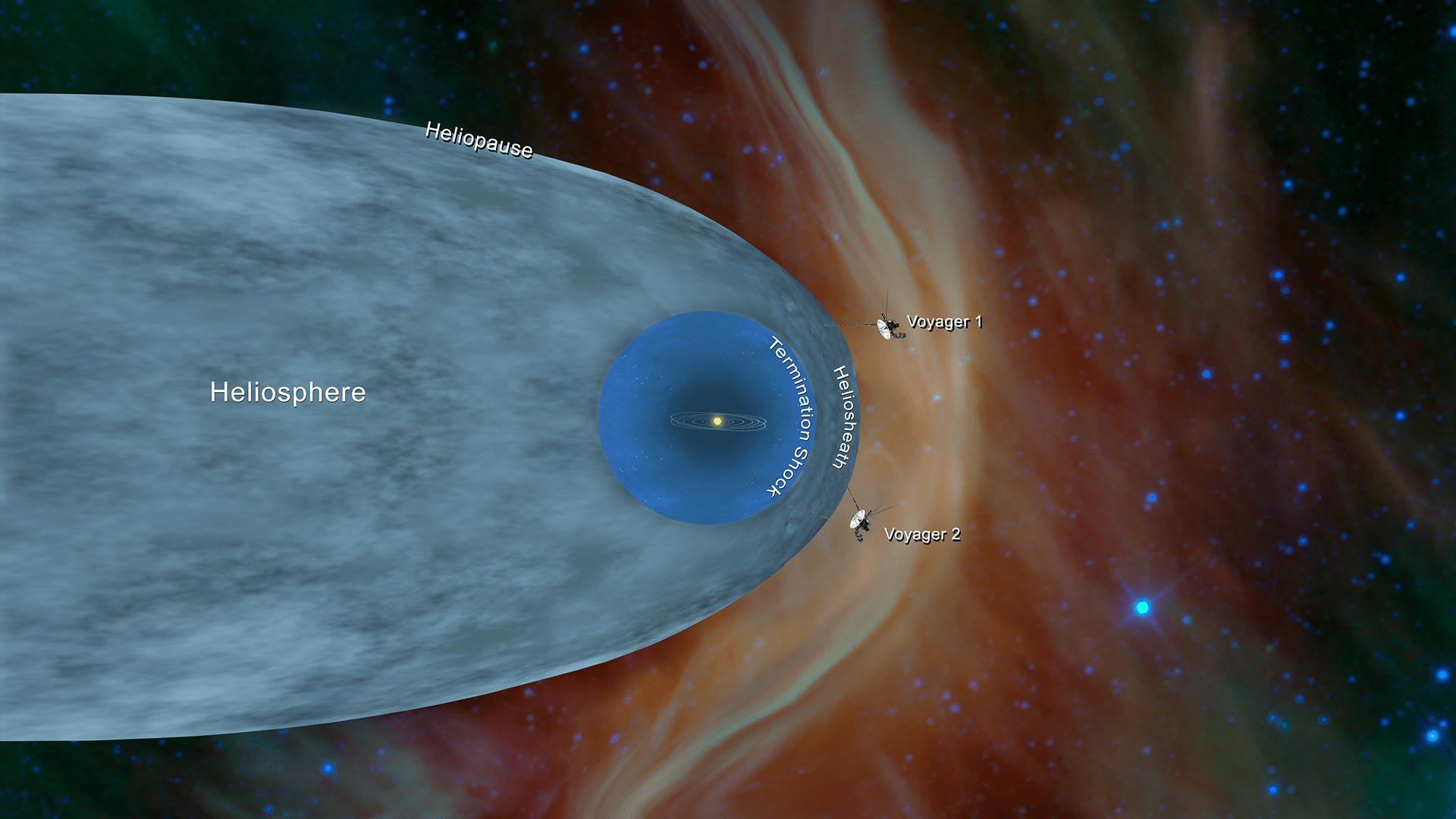
Before Voyager 1 reached the edge of the heliosphere in 2012, scientists didn’t know exactly how far this boundary was from the Sun. The two probes exited the heliosphere at different locations and also at different times in the constantly repeating, approximately 11-year solar cycle, over the course of which the Sun goes through a period of high and low activity. Scientists expected that the edge of the heliosphere, called the heliopause, can move as the Sun’s activity changes, sort of like a lung expanding and contracting with breath. This was consistent with the fact that the two probes encountered the heliopause at different distances from the Sun.
The new papers now confirm that Voyager 2 is not yet in undisturbed interstellar space: Like its twin, Voyager 1, Voyager 2 appears to be in a perturbed transitional region just beyond the heliosphere.
“The Voyager probes are showing us how our Sun interacts with the stuff that fills most of the space between stars in the Milky Way galaxy,” said Ed Stone, project scientist for Voyager and a professor of physics at Caltech. “Without this new data from Voyager 2, we wouldn’t know if what we were seeing with Voyager 1 was characteristic of the entire heliosphere or specific just to the location and time when it crossed.”
The two Voyager spacecraft have now confirmed that the plasma in local interstellar space is significantly denser than the plasma inside the heliosphere, as scientists expected. Voyager 2 has now also measured the temperature of the plasma in nearby interstellar space and confirmed it is colder than the plasma inside the heliosphere.
In 2012, Voyager 1 observed a slightly higher-than-expected plasma density just outside the heliosphere, indicating that the plasma is being somewhat compressed. Voyager 2 observed that the plasma outside the heliosphere is slightly warmer than expected, which could also indicate it is being compressed. (The plasma outside is still colder than the plasma inside.) Voyager 2 also observed a slight increase in plasma density just before it exited the heliosphere, indicating that the plasma is compressed around the inside edge of the bubble. But scientists don’t yet fully understand what is causing the compression on either side.
If the heliosphere is like a ship sailing through interstellar space, it appears the hull is somewhat leaky. One of Voyager’s particle instruments showed that a trickle of particles from inside the heliosphere is slipping through the boundary and into interstellar space. Voyager 1 exited close to the very “front” of the heliosphere, relative to the bubble’s movement through space. Voyager 2, on the other hand, is located closer to the flank, and this region appears to be more porous than the region where Voyager 1 is located.
An observation by Voyager 2’s magnetic field instrument confirms a surprising result from Voyager 1: The magnetic field in the region just beyond the heliopause is parallel to the magnetic field inside the heliosphere. With Voyager 1, scientists had only one sample of these magnetic fields and couldn’t say for sure whether the apparent alignment was characteristic of the entire exterior region or just a coincidence. Voyager 2’s magnetometer observations confirm the Voyager 1 finding and indicate that the two fields align, according to Stone.
The Voyager probes launched in 1977, and both flew by Jupiter and Saturn. Voyager 2 changed course at Saturn in order to fly by Uranus and Neptune, performing the only close flybys of those planets in history. The Voyager probes completed their Grand Tour of the planets and began their Interstellar Mission to reach the heliopause in 1989. Voyager 1, the faster of the two probes, is currently over 13.6 billion miles (22 billion kilometers) from the Sun, while Voyager 2 is 11.3 billion miles (18.2 billion kilometers) from the Sun. It takes light about 16.5 hours to travel from Voyager 2 to Earth. By comparison, light traveling from the Sun takes about eight minutes to reach Earth.
More information about Voyager is available at the following site:
https://voyager.jpl.nasa.gov/
Calla Cofield Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. 626-808-2469 [email protected]
- Mobile Site
- Staff Directory
- Advertise with Ars
Filter by topic
- Biz & IT
- Gaming & Culture
Front page layout
Hope returns —
Nasa knows what knocked voyager 1 offline, but it will take a while to fix, "engineers are optimistic they can find a way for the fds to operate normally.".
Stephen Clark - Apr 6, 2024 12:28 am UTC

Engineers have determined why NASA's Voyager 1 probe has been transmitting gibberish for nearly five months, raising hopes of recovering humanity's most distant spacecraft.
Voyager 1, traveling outbound some 15 billion miles (24 billion km) from Earth, started beaming unreadable data down to ground controllers on November 14. For nearly four months, NASA knew Voyager 1 was still alive—it continued to broadcast a steady signal—but could not decipher anything it was saying.
Confirming their hypothesis, engineers at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in California confirmed a small portion of corrupted memory caused the problem. The faulty memory bank is located in Voyager 1's Flight Data System (FDS), one of three computers on the spacecraft. The FDS operates alongside a command-and-control central computer and another device overseeing attitude control and pointing.
The FDS duties include packaging Voyager 1's science and engineering data for relay to Earth through the craft's Telemetry Modulation Unit and radio transmitter. According to NASA, about 3 percent of the FDS memory has been corrupted, preventing the computer from carrying out normal operations.
Optimism growing
Suzanne Dodd, NASA's project manager for the twin Voyager probes, told Ars in February that this was one of the most serious problems the mission has ever faced. That is saying something because Voyager 1 and 2 are NASA's longest-lived spacecraft. They launched 16 days apart in 1977, and after flying by Jupiter and Saturn, Voyager 1 is flying farther from Earth than any spacecraft in history. Voyager 2 is trailing Voyager 1 by about 2.5 billion miles, although the probes are heading out of the Solar System in different directions.
Normally, engineers would try to diagnose a spacecraft malfunction by analyzing data it sent back to Earth. They couldn't do that in this case because Voyager 1 has been transmitting data packages manifesting a repeating pattern of ones and zeros. Still, Voyager 1's ground team identified the FDS as the likely source of the problem.
The Flight Data Subsystem was an innovation in computing when it was developed five decades ago. It was the first computer on a spacecraft to use volatile memory. Most of NASA's missions operate with redundancy, so each Voyager spacecraft launched with two FDS computers. But the backup FDS on Voyager 1 failed in 1982.
Due to the Voyagers' age, engineers had to reference paper documents, memos, and blueprints to help understand the spacecraft's design details. After months of brainstorming and planning, teams at JPL uplinked a command in early March to prompt the spacecraft to send back a readout of the FDS memory.
The command worked, and Voyager1 responded with a signal different from the code it had been transmitting since November. After several weeks of meticulous examination of the new code, engineers pinpointed the location of the bad memory.
"The team suspects that a single chip responsible for storing part of the affected portion of the FDS memory isn’t working," NASA said in an update posted Thursday. "Engineers can’t determine with certainty what caused the issue. Two possibilities are that the chip could have been hit by an energetic particle from space or that it simply may have worn out after 46 years."
Voyager 1's distance from Earth complicates the troubleshooting effort. The one-way travel time for a radio signal to reach Voyager 1 from Earth is about 22.5 hours, meaning it takes roughly 45 hours for engineers on the ground to learn how the spacecraft responded to their commands.
NASA also must use its largest communications antennas to contact Voyager 1. These 230-foot-diameter (70-meter) antennas are in high demand by many other NASA spacecraft , so the Voyager team has to compete with other missions to secure time for troubleshooting. This means it will take time to get Voyager 1 back to normal operations.
"Although it may take weeks or months, engineers are optimistic they can find a way for the FDS to operate normally without the unusable memory hardware, which would enable Voyager 1 to begin returning science and engineering data again," NASA said.
reader comments
Channel ars technica.
We finally know why NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft stopped communicating — scientists are working on a fix
The first spacecraft to explore beyond the solar system started spouting gibberish late last year. Now, NASA knows why.

NASA engineers have discovered the cause of a communications breakdown between Earth and the interstellar explorer Voyager 1. It would appear that a small portion of corrupted memory exists in one of the spacecraft's computers.
The glitch caused Voyager 1 to send unreadable data back to Earth, and is found in the NASA spacecraft's flight data subsystem (FDS). That's the system responsible for packaging the probe's science and engineering data before the telemetry modulation unit (TMU) and radio transmitter send it back to mission control.
The source of the issue began to reveal itself when Voyager 1 operators sent the spacecraft a "poke" on March 3, 2024. This was intended to prompt FDS to send a full memory readout back to Earth.
The readout confirmed to the NASA team that about 3% of the FDS memory had been corrupted, and that this was preventing the computer from carrying out its normal operations.
Related: NASA finds clue while solving Voyager 1's communication breakdown case
Launched in 1977, Voyager 1 became the first human-made object to leave the solar system and enter interstellar space in 2012. Voyager 2 followed its spacecraft sibling out of the solar system in 2018, and is still operational and communicating well with Earth.
After 11 years of interstellar exploration, in Nov. 2023, Voyager 1's binary code — the computer language it uses to communicate with Earth — stopped making sense. Its 0's and 1's didn't mean anything anymore.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
"Effectively, the call between the spacecraft and the Earth was still connected, but Voyager's 'voice' was replaced with a monotonous dial tone," Voyager 1's engineering team previously told Space.com .

The team strongly suspects this glitch is the result of a single chip that's responsible for storing part of the affected portion of the FDS memory ceasing to work.
Currently, however, NASA can’t say for sure what exactly caused that particular issue. The chip could have been struck by a high-speed energetic particle from space or, after 46 years serving Voyager 1, it may simply have worn out.
— Voyager 2: An iconic spacecraft that's still exploring 45 years on
— NASA's interstellar Voyager probes get software updates beamed from 12 billion miles away
— NASA Voyager 2 spacecraft extends its interstellar science mission for 3 more years
Voyager 1 currently sits around 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) from Earth, which means it takes 22.5 hours to receive a radio signal from it — and another 22.5 hours for the spacecraft to receive a response via the Deep Space Network's antennas. Solving this communication issue is thus no mean feat.
Yet, NASA scientists and engineers are optimistic they can find a way to help FDS operate normally, even without the unusable memory hardware.
Solving this issue could take weeks or even months, according to NASA — but if it is resolved, Voyager 1 should be able to resume returning science data about what lies outside the solar system.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: [email protected].

Robert Lea is a science journalist in the U.K. whose articles have been published in Physics World, New Scientist, Astronomy Magazine, All About Space, Newsweek and ZME Science. He also writes about science communication for Elsevier and the European Journal of Physics. Rob holds a bachelor of science degree in physics and astronomy from the U.K.’s Open University. Follow him on Twitter @sciencef1rst.
Rocket Lab to launch NASA's new solar sail technology no earlier than April 24
SpaceX launches Starlink satellites on record 20th reflight of a Falcon 9 rocket first stage
Monster black hole seen feeding on nearby matter just 1 billion years after Big Bang (photos)
- jcs Funny timing for this article, when I am streaming an old Star Trek movie. So, surely this didn't cause a 3 byte glitch removing the O, Y and A from Voyager's name buffer? Get it? Reply
- bwana4swahili It is quite amazing it has lasted this long in a space environment. Reply
bwana4swahili said: It is quite amazing it has lasted this long in a space environment.
- HankySpanky So now we know even better for next time. Perhaps a spare chipset that is not redundant but is ready to take over, stored in a protective environment. A task NASA can handle. We'll find out in 100 year or so - if humanity still exists. Reply
HankySpanky said: So now we know even better for next time. Perhaps a spare chipset that is not redundant but is ready to take over, stored in a protective environment. A task NASA can handle. We'll find out in 100 year or so - if humanity still exists.
- Classical Motion I'm afraid it might self repair. And download galactic knowledge, then decide we are a danger. And turn around. Reply
Classical Motion said: I'm afraid it might self repair. And download galactic knowledge, then decide we are a danger. And turn around.
- jcs ROFLOL! And a hot bald chick delivering the bad news! Reply
- View All 8 Comments
Most Popular
- 2 Will the constellations ever change?
- 3 Switzerland signs Artemis Accords to join NASA in moon exploration
- 4 James Webb Space Telescope full-size model to be displayed by Space Foundation
- 5 Dark energy could be getting weaker, suggesting the universe will end in a 'Big Crunch'
Engineers Pinpoint Cause of Voyager 1 Issue, Are Working on Solution
Engineers have confirmed that a small portion of corrupted memory in one of the computers aboard NASA’s Voyager 1 has been causing the spacecraft to send unreadable science and engineering data to Earth since last November. Called the flight data subsystem (FDS), the computer is responsible for packaging the probe’s science and engineering data before the telemetry modulation unit (TMU) and radio transmitter send the data to Earth.
In early March , the team issued a “poke” command to prompt the spacecraft to send back a readout of the FDS memory, which includes the computer’s software code as well as variables (values used in the code that can change based on commands or the spacecraft’s status). Using the readout, the team has confirmed that about 3% of the FDS memory has been corrupted, preventing the computer from carrying out normal operations.
The team suspects that a single chip responsible for storing part of the affected portion of the FDS memory isn’t working. Engineers can’t determine with certainty what caused the issue. Two possibilities are that the chip could have been hit by an energetic particle from space or that it simply may have worn out after 46 years.
Although it may take weeks or months, engineers are optimistic they can find a way for the FDS to operate normally without the unusable memory hardware, which would enable Voyager 1 to begin returning science and engineering data again.
Launched in 1977 , the twin Voyager spacecraft flew by Saturn and Jupiter, and Voyager 2 flew by Uranus and Neptune. They are both exploring interstellar space, outside the bubble of particles and magnetic fields created by the Sun, called the heliosphere. Voyager 2 continues to operate normally.
News Media Contact Calla Cofield Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. 626-808-2469 [email protected]

NASA’s Voyager 2 Probe Enters Interstellar Space
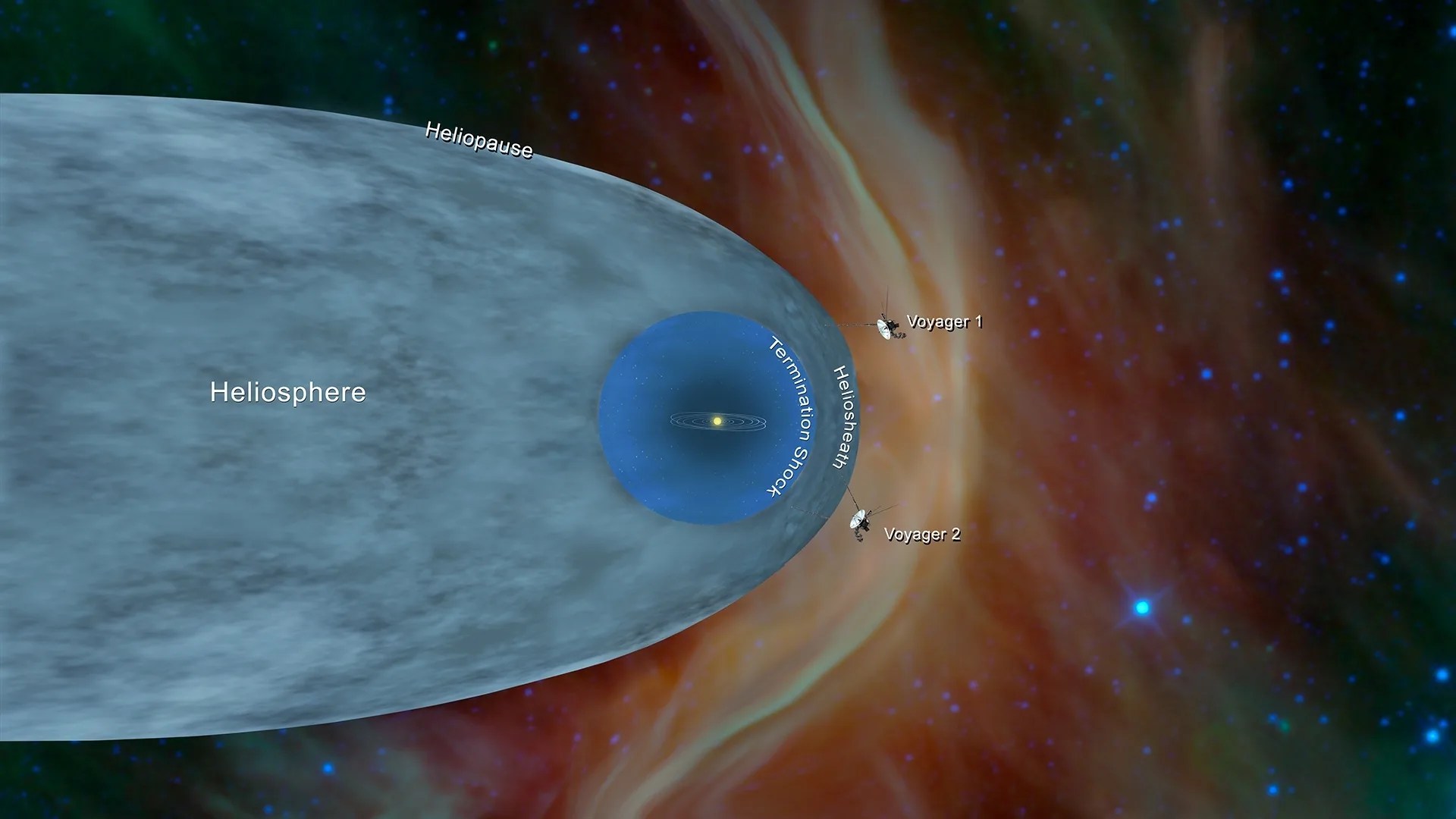
For the second time in history, a human-made object has reached the space between the stars. NASA’s Voyager 2 probe now has exited the heliosphere – the protective bubble of particles and magnetic fields created by the Sun.
Members of NASA’s Voyager team will discuss the findings at a news conference at 11 a.m. EST (8 a.m. PST) today at the meeting of the American Geophysical Union (AGU) in Washington. The news conference will stream live on the agency’s website .
Comparing data from different instruments aboard the trailblazing spacecraft, mission scientists determined the probe crossed the outer edge of the heliosphere on Nov. 5. This boundary, called the heliopause, is where the tenuous, hot solar wind meets the cold, dense interstellar medium. Its twin, Voyager 1 , crossed this boundary in 2012, but Voyager 2 carries a working instrument that will provide first-of-its-kind observations of the nature of this gateway into interstellar space.
Voyager 2 now is slightly more than 11 billion miles (18 billion kilometers) from Earth. Mission operators still can communicate with Voyager 2 as it enters this new phase of its journey, but information – moving at the speed of light – takes about 16.5 hours to travel from the spacecraft to Earth. By comparison, light traveling from the Sun takes about eight minutes to reach Earth.
The most compelling evidence of Voyager 2’s exit from the heliosphere came from its onboard Plasma Science Experiment ( PLS ), an instrument that stopped working on Voyager 1 in 1980, long before that probe crossed the heliopause. Until recently, the space surrounding Voyager 2 was filled predominantly with plasma flowing out from our Sun. This outflow, called the solar wind, creates a bubble – the heliosphere – that envelopes the planets in our solar system. The PLS uses the electrical current of the plasma to detect the speed, density, temperature, pressure and flux of the solar wind. The PLS aboard Voyager 2 observed a steep decline in the speed of the solar wind particles on Nov. 5. Since that date, the plasma instrument has observed no solar wind flow in the environment around Voyager 2, which makes mission scientists confident the probe has left the heliosphere.
“Working on Voyager makes me feel like an explorer, because everything we’re seeing is new,” said John Richardson, principal investigator for the PLS instrument and a principal research scientist at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in Cambridge. “Even though Voyager 1 crossed the heliopause in 2012, it did so at a different place and a different time, and without the PLS data. So we’re still seeing things that no one has seen before.”
In addition to the plasma data, Voyager’s science team members have seen evidence from three other onboard instruments – the cosmic ray subsystem, the low energy charged particle instrument and the magnetometer – that is consistent with the conclusion that Voyager 2 has crossed the heliopause. Voyager’s team members are eager to continue to study the data from these other onboard instruments to get a clearer picture of the environment through which Voyager 2 is traveling.
“There is still a lot to learn about the region of interstellar space immediately beyond the heliopause,” said Ed Stone, Voyager project scientist based at Caltech in Pasadena, California.
Together, the two Voyagers provide a detailed glimpse of how our heliosphere interacts with the constant interstellar wind flowing from beyond. Their observations complement data from NASA’s Interstellar Boundary Explorer ( IBEX ), a mission that is remotely sensing that boundary. NASA also is preparing an additional mission – the upcoming Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe ( IMAP ), due to launch in 2024 – to capitalize on the Voyagers’ observations.
“Voyager has a very special place for us in our heliophysics fleet,” said Nicola Fox, director of the Heliophysics Division at NASA Headquarters. “Our studies start at the Sun and extend out to everything the solar wind touches. To have the Voyagers sending back information about the edge of the Sun’s influence gives us an unprecedented glimpse of truly uncharted territory.”
While the probes have left the heliosphere, Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 have not yet left the solar system, and won’t be leaving anytime soon. The boundary of the solar system is considered to be beyond the outer edge of the Oort Cloud , a collection of small objects that are still under the influence of the Sun’s gravity. The width of the Oort Cloud is not known precisely, but it is estimated to begin at about 1,000 astronomical units (AU) from the Sun and to extend to about 100,000 AU. One AU is the distance from the Sun to Earth. It will take about 300 years for Voyager 2 to reach the inner edge of the Oort Cloud and possibly 30,000 years to fly beyond it.
The Voyager probes are powered using heat from the decay of radioactive material, contained in a device called a radioisotope thermal generator ( RTG ). The power output of the RTGs diminishes by about four watts per year, which means that various parts of the Voyagers, including the cameras on both spacecraft, have been turned off over time to manage power.
“I think we’re all happy and relieved that the Voyager probes have both operated long enough to make it past this milestone,” said Suzanne Dodd, Voyager project manager at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, California. “This is what we've all been waiting for. Now we’re looking forward to what we’ll be able to learn from having both probes outside the heliopause.”
Voyager 2 launched in 1977, 16 days before Voyager 1, and both have traveled well beyond their original destinations. The spacecraft were built to last five years and conduct close-up studies of Jupiter and Saturn. However, as the mission continued, additional flybys of the two outermost giant planets, Uranus and Neptune, proved possible. As the spacecraft flew across the solar system, remote-control reprogramming was used to endow the Voyagers with greater capabilities than they possessed when they left Earth. Their two-planet mission became a four-planet mission. Their five-year lifespans have stretched to 41 years, making Voyager 2 NASA’s longest running mission.
The Voyager story has impacted not only generations of current and future scientists and engineers, but also Earth's culture, including film, art and music. Each spacecraft carries a Golden Record of Earth sounds, pictures and messages. Since the spacecraft could last billions of years, these circular time capsules could one day be the only traces of human civilization.
Voyager’s mission controllers communicate with the probes using NASA’s Deep Space Network ( DSN ), a global system for communicating with interplanetary spacecraft. The DSN consists of three clusters of antennas in Goldstone, California; Madrid, Spain; and Canberra, Australia.
The Voyager Interstellar Mission is a part of NASA’s Heliophysics System Observatory, sponsored by the Heliophysics Division of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. JPL built and operates the twin Voyager spacecraft. NASA’s DSN, managed by JPL, is an international network of antennas that supports interplanetary spacecraft missions and radio and radar astronomy observations for the exploration of the solar system and the universe. The network also supports selected Earth-orbiting missions. The Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation, Australia’s national science agency, operates both the Canberra Deep Space Communication Complex, part of the DSN, and the Parkes Observatory, which NASA has been using to downlink data from Voyager 2 since Nov. 8.
For more information about the Voyager mission, visit:
https://www.nasa.gov/voyager
More information about NASA’s Heliophysics missions is available online at:
https://www.nasa.gov/sunearth
News Media Contact
Calla Cofield Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. 626-808-2469 [email protected]
Dwayne Brown / Karen Fox NASA Headquarters, Washington 202-358-1726 / 301-286-6284 [email protected] / [email protected]
Related Terms
- Voyager Program
Explore More

NASA’s Voyager Team Focuses on Software Patch, Thrusters
The efforts should help extend the lifetimes of the agency’s interstellar explorers. Engineers for NASA’s Voyager mission are taking steps to help make sure both spacecraft, launched in 1977, continue to explore interstellar space for years to come. One effort addresses fuel residue that seems to be accumulating inside narrow tubes in some of the […]

NASA Mission Update: Voyager 2 Communications Pause
Once the spacecraft’s antenna is realigned with Earth, communications should resume.

NASA’s Voyager Will Do More Science With New Power Strategy
The plan will keep Voyager 2’s science instruments turned on a few years longer than previously anticipated, enabling yet more revelations from interstellar space.
Discover More Topics From NASA

Facts About Earth

Asteroids, Comets & Meteors
Kuiper Belt


NASA tries to jog Voyager 1's memory from 15 billion miles away
Since you can't get a soldering iron out there, the fix will be in software.
Engineers at NASA have pinpointed some corrupted memory as the cause of Voyager 1's troubles and are working on a remote fix to deal with the hardware problem.…
The veteran probe began sending unreadable data back to Earth in late 2023, and engineers have tried to understand the nature of the issue. Last month, they sent a command – a "poke" to the spacecraft's Flight Data System (FDS) – and the resulting data stream contained a complete memory dump from the computer.
The team was able to use this readout, which contained the computer's code and variables, to ascertain that approximately 3 percent of the FDS memory had been corrupted. That corruption is preventing normal operation of the FDS, which is responsible for packaging the probe's engineering and science data before it gets passed to the Telemetry Modulation Unit (TMU), the radio transmitter and is sent back to Earth.
The Voyager team reckons that a single chip responsible for the corrupted portion of memory is at fault, although they can only make an informed guess with regard to what has happened.
Two leading theories are that the chip has simply worn out having spent 46 years in space, or that an energetic particle might have damaged it.
As Voyager 1 is well out of the reach of any physical intervention, the issue will need to be addressed in software.
According to NASA: "Although it may take weeks or months, engineers are optimistic they can find a way for the FDS to operate normally without the unusable memory hardware, which would enable Voyager 1 to begin returning science and engineering data again."
Computer problems caused by cosmic rays and energetic particles have long challenged spacecraft designers. Some might merely result in a bit flip, while others can leave satellites inoperable or damaged.
Voyager 2 suffered a bit flip in 2010, which caused problems with science data transmitted from the spacecraft and was traced to the FDS. A computer reset dealt with the problem.
This time, however, the hardware appears to have become inoperative, requiring engineers to devise something more complicated than a simple turn-it-off-and-on-again solution. ®


- The Contents
- The Making of
- Where Are They Now
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Q & A with Ed Stone
golden record
Where are they now.
- frequently asked questions
- Q&A with Ed Stone

NASA’s Voyager Team Focuses on Software Patch, Thrusters

NASA Mission Update: Voyager 2 Communications Pause

NASA's Voyager Will Do More Science With New Power Strategy

Edward Stone Retires After 50 Years as NASA Voyager's Project Scientist
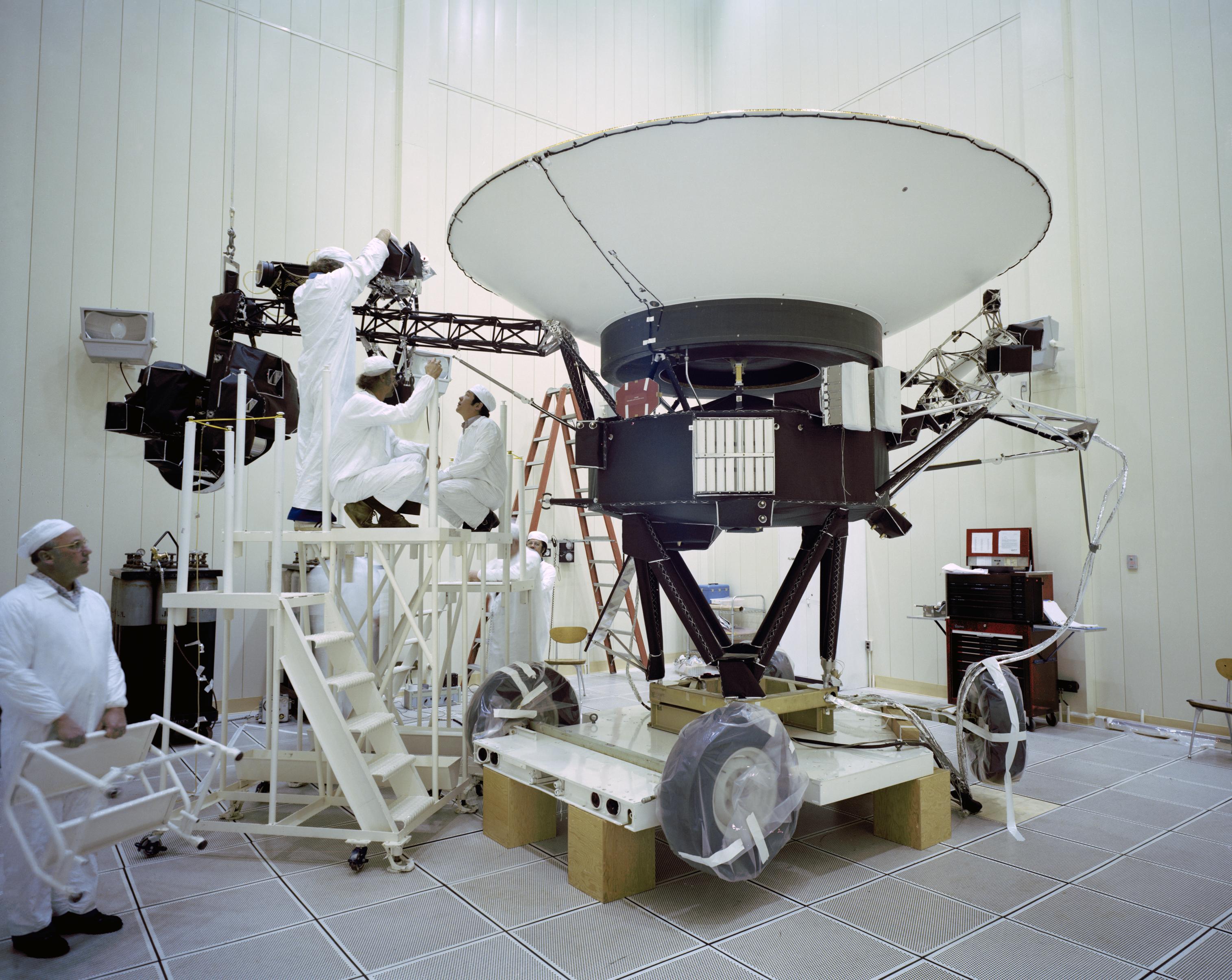

Voyager, NASA's Longest-Lived Mission, Logs 45 Years in Space
Voyager 1 distance from earth, voyager 1 distance from sun, voyager 1 one-way light time, voyager 1 cosmic ray data, voyager 2 distance from the earth, voyager 2 distance from the sun, voyager 2 one-way light time, voyager 2 cosmic ray data, what's happening now.

Since November 2023, NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft has been sending a steady radio signal to Earth, but the signal does not contain usable data.
Engineers are working to resolve an issue with one of Voyager 1’s three onboard computers, called the flight data system (FDS).

The efforts should help extend the lifetimes of the agency's interstellar explorers.

Download the Voyager 40th Anniversary posters.

NASA engineers discover why Voyager 1 is sending a stream of gibberish from outside our solar system
Voyager 1 has been sending a stream of garbled nonsense since November. Now NASA engineers have identified the fault and found a potential workaround.

For the past five months, the Voyager 1 spacecraft has been sending a steady stream of unreadable gibberish back to Earth. Now, NASA engineers finally know why.
The 46-year-old spacecraft sends regular radio signals as it drifts further from our solar system . But in November 2023, the signals suddenly became garbled, meaning scientists were unable to read any of its data, and they were left mystified about the fault's origins.
In March, NASA engineers sent a command prompt, or "poke," to the craft to get a readout from its flight data subsystem (FDS) — which packages Voyager 1's science and engineering data before beaming it back to Earth.
After decoding the spacecraft's response, the engineers have found the source of the problem: The FDS's memory has been corrupted.
Related: NASA's Voyager 1 sends readable message to Earth after 4 nail-biting months of gibberish
"The team suspects that a single chip responsible for storing part of the affected portion of the FDS memory isn't working," NASA said in a blog post Wednesday (March 13) . "Engineers can't determine with certainty what caused the issue. Two possibilities are that the chip could have been hit by an energetic particle from space or that it simply may have worn out after 46 years."
— NASA hears 'heartbeat' signal from Voyager 2 probe a week after losing contact
— Historic space photo of the week: Voyager 2 spies a storm on Saturn 42 years ago
— NASA reestablishes full contact with Voyager 2 probe after nail-biting 2-week blackout
Although it may take several months, the engineers say they can find a workaround to run the FDS without the fried chip — restoring the spacecraft's messaging output and enabling it to continue to send readable information from outside our solar system.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Launched in 1977, Voyager 1 zipped past Saturn and Jupiter in 1979 and 1980 before flying out into interstellar space in 2012. It is now recording the conditions outside of the sun's protective magnetic field , or heliosphere, which blankets our solar system.
Voyager 1 is currently more than 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) from Earth, and it takes 22.5 hours for any radio signal to travel from the craft to our planet.

Ben Turner is a U.K. based staff writer at Live Science. He covers physics and astronomy, among other topics like tech and climate change. He graduated from University College London with a degree in particle physics before training as a journalist. When he's not writing, Ben enjoys reading literature, playing the guitar and embarrassing himself with chess.
NASA spacecraft snaps mysterious 'surfboard' orbiting the moon. What is it?
The moon is getting its own time zone, White House memo to NASA reveals
Cancer patients can now be 'matched' to best treatment with DNA and lab-dish experiments
- TorbjornLarsson Bon voyage, Voyager! Reply
- Jay McHue What if aliens are doing it to try to communicate with us? 🤪 Reply
Jay McHue said: What if aliens are doing it to try to communicate with us? 🤪
admin said: Voyager 1 has been sending a stream of garbled nonsense since November. Now NASA engineers have identified the fault and found a potential workaround. NASA engineers discover why Voyager 1 is sending a stream of gibberish from outside our solar system : Read more
sourloaf said: What does FSB mean?
Rusty Lugnuts said: Where are you seeing "FSB"? The closest thing I can see in the article is "FDS". In modern computers, FSB would most likely refer to the Fr0nt S1ide Bu5, though I have no idea if a system as old as Voyagers, let alone engineered so specifically, would have an FSB. (apparently I can't spell out "Fr0nt S1ide Bu5" or my post gets flagged as spam or inappropriate??)
- SkidWard Just cut the % of ram needed... skip the bad sectors Reply
- kloudykat FDS = fl1ght da1a sub5ystem5 Reply
- 5ft24dave This is pretty old news, like 6 months old. Are you guys just now discovering this? Reply
Commodore Browncoat said: That's about as sane a theory as many of the others that have become ridiculously popular in the past several years, so sure - why not? What reply do you think we should send?
- View All 11 Comments
Most Popular
- 2 'Exceptional' prosthesis of gold, silver and wool helped 18th-century man live with cleft palate
- 3 Mass die-off half a billion years ago caused by shifting tectonic plates, ancient rocks reveal
- 4 Prehistoric henge accidentally discovered in England in search for Anglo-Saxon hermit
- 5 Space photo of the week: NASA spots enormous pink 'flames' during total solar eclipse. What are they?
- 2 Cancer patients can now be 'matched' to best treatment with DNA and lab-dish experiments
- 3 Space photo of the week: NASA spots enormous pink 'flames' during total solar eclipse. What are they?
- 4 Ancient Indigenous lineage of Blackfoot Confederacy goes back 18,000 years to last ice age, DNA reveals

COMMENTS
In the NASA Eyes on the Solar System app, you can see the real spacecraft trajectories of the Voyagers, which are updated every five minutes. Distance and velocities are updated in real-time. For a full 3D, immersive experience click on View Voyagers link below to launch the NASA Eyes on the Solar System app. View Voyager.
Launched in 1977, the twin Voyager probes are NASA's longest-operating mission and the only spacecraft ever to explore interstellar space. Read more. Voyager 1 Distance from Earth. This is a real-time indicator of Voyager 1's distance from Earth in astronomical units (AU) and either miles (mi) or kilometers (km). Note: Because Earth moves ...
A poster of the planets and moons visited during the Voyager program. The Voyager program is an American scientific program that employs two interstellar probes, Voyager 1 and Voyager 2.They were launched in 1977 to take advantage of a favorable alignment of the two gas giants Jupiter and Saturn and the ice giants, Uranus and Neptune, to fly near them while collecting data for transmission ...
Mission Overview. The twin Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft are exploring where nothing from Earth has flown before. Continuing on their more-than-40-year journey since their 1977 launches, they each are much farther away from Earth and the sun than Pluto. In August 2012, Voyager 1 made the historic entry into interstellar space, the region between ...
Launched in 1977, the twin Voyager probes are NASA's longest-operating mission and the only spacecraft ever to explore interstellar space. NASA's twin Voyager probes have become, in some ways, time capsules of their era: They each carry an eight-track tape player for recording data, they have about 3 million times less memory than modern cellphones, and they transmit data about 38,000 ...
NASA's twin Voyager probes have become, in some ways, time capsules of their era: They each carry an eight-track tape player for recording data, they have about 3 million times less memory than modern cellphones, and they transmit data about 38,000 times slower than a 5G internet connection.. Yet the Voyagers remain on the cutting edge of space exploration.
Voyager 1 and its twin Voyager 2 are the only spacecraft ever to operate outside the heliosphere, the protective bubble of particles and magnetic fields generated by the Sun. Voyager 1 reached the interstellar boundary in 2012, while Voyager 2 (traveling slower and in a different direction than its twin) reached it in 2018. Mission Type.
For the second time in history, a human-made object has reached the space between the stars. NASA's Voyager 2 probe now has exited the heliosphere - the protective bubble of particles and magnetic fields created by the Sun.. Members of NASA's Voyager team will discuss the findings at a news conference at 11 a.m. EST (8 a.m. PST) today at the meeting of the American Geophysical Union (AGU ...
For the second time in history, a human-made object has reached the space between the stars. NASA's Voyager 2 probe now has exited the heliosphere - the protective bubble of particles and magnetic fields created by the Sun.. Members of NASA's Voyager team will discuss the findings at a news conference at 11 a.m. EST (8 a.m. PST) today at the meeting of the American Geophysical Union (AGU) in ...
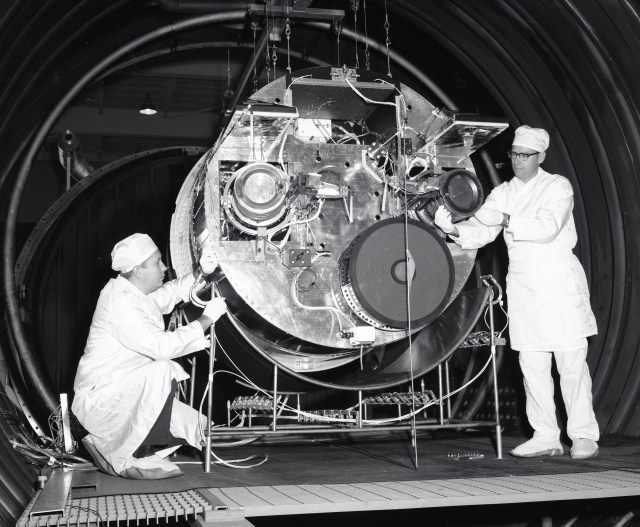
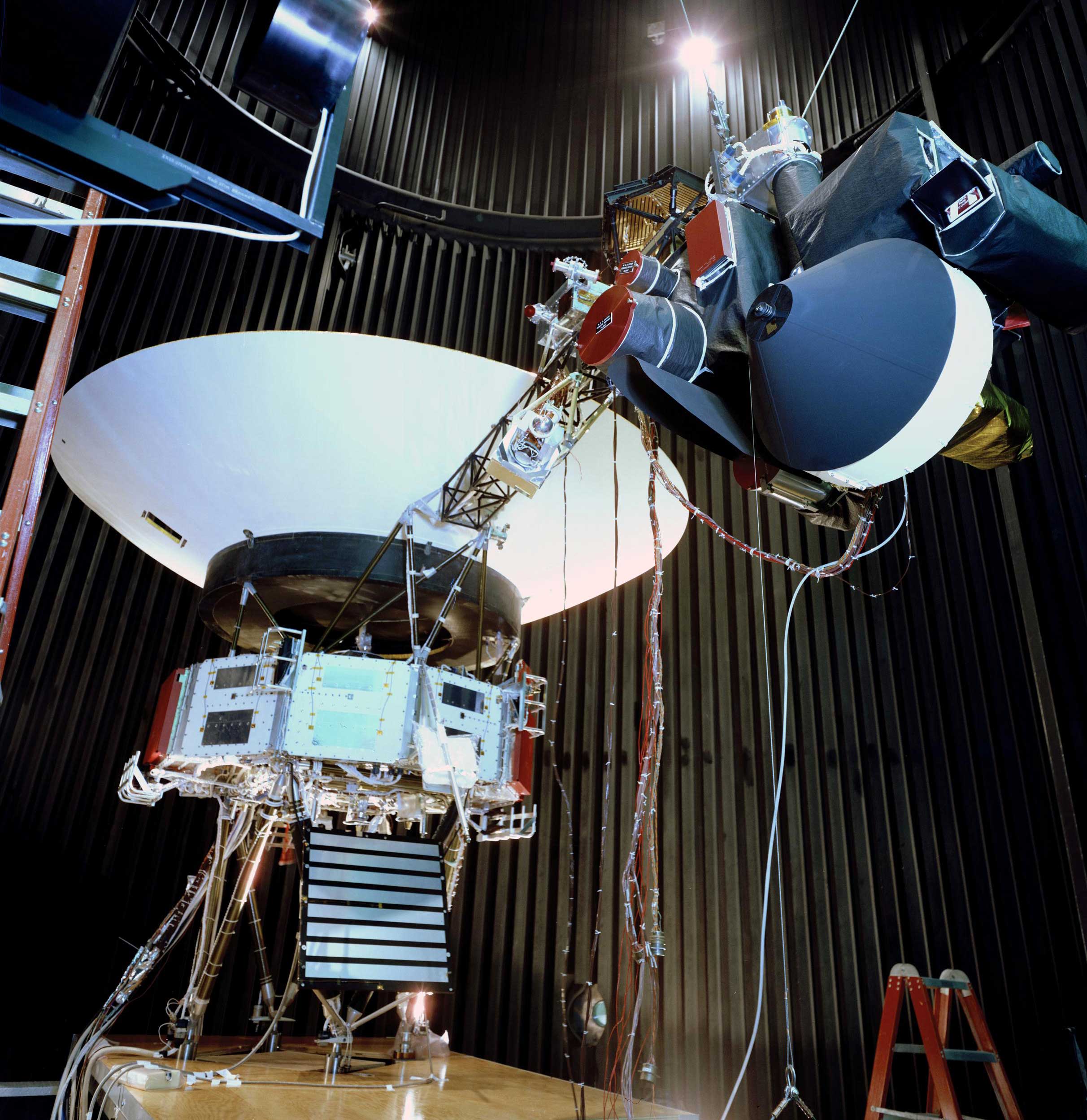
The Voyager proof test model, shown in a space simulator chamber at JPL in 1976, was a replica of the twin Voyager space probes that launched in 1977. The model's scan platform stretches to the right, holding several of the spacecraft's science instruments in their deployed positions. ... Each of NASA's Voyager probes are equipped with ...
For the second time in history, a human-made object has reached the space between the stars. NASA's Voyager 2 probe now has exited the heliosphere - the protective bubble of particles and magnetic fields created by the Sun.. Members of NASA's Voyager team will discuss the findings at a news conference at 11 a.m. EST (8 a.m. PST) today at the meeting of the American Geophysical Union (AGU) in ...
Voyager, NASA's Longest-Lived Mission, Logs 45 Years in Space. 6 min read. Launched in 1977, the twin Voyager probes are NASA's longest-operating mission and the only spacecraft ever to explore interstellar space. NASA's twin Voyager probes have become, in some ways, time capsules of their era: They each carry an eight-track tape….
Both Voyager probes have outlived their original missions and are exploring interstellar space more than 45 years after launch. The mission team has made clever decisions to manage the power ...
Launched in 1977, NASA's twin Voyager spacecraft are the agency's longest-operating and farthest-flung probes. Voyager 1 visited Jupiter and Saturn, revealing new features of both planets and their moons. Voyager 2 followed its twin to Jupiter and Saturn before changing its trajectory to fly by Uranus and Neptune.
Launched in 1977, the twin Voyager probes are NASA 's longest-operating mission and the only spacecraft ever to explore interstellar space.. Launched in 1977, NASA's twin Voyager spacecraft inspired the world with pioneering visits to Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.Their journey continues 45 years later as both probes explore interstellar space, the region outside the protective ...
Launched in 1977, the twin Voyager probes are NASA's longest-operating mission and the only spacecraft ever to explore interstellar space. NASA's twin Voyager probes have become, in some ways, time capsules of their era: They each carry an eight-track tape…
The Voyager probes completed their Grand Tour of the planets and began their Interstellar Mission to reach the heliopause in 1989. Voyager 1, the faster of the two probes, is currently over 13.6 billion miles (22 billion kilometers) from the Sun, while Voyager 2 is 11.3 billion miles (18.2 billion kilometers) from the Sun.
Voyager. NASA's interstellar Voyager probes get software updates beamed from 12 billion miles away. News. By Rahul Rao. published 23 October 2023. "This far into the mission, the engineering team ...
Engineers have determined why NASA's Voyager 1 probe has been transmitting gibberish for nearly five months, raising hopes of recovering humanity's most distant spacecraft. Voyager 1, traveling ...
The glitch caused Voyager 1 to send unreadable data back to Earth, and is found in the NASA spacecraft's flight data subsystem (FDS). That's the system responsible for packaging the probe's ...
Engineers have confirmed that a small portion of corrupted memory in one of the computers aboard NASA's Voyager 1 has been causing the spacecraft to send unreadable science and engineering data to Earth since last November. Called the flight data subsystem (FDS), the computer is responsible for packaging the probe's science and engineering ...
Its twin, Voyager 1, crossed this boundary in 2012, but Voyager 2 carries a working instrument that will provide first-of-its-kind observations of the nature of this gateway into interstellar space. Voyager 2 now is slightly more than 11 billion miles (18 billion kilometers) from Earth. Mission operators still can communicate with Voyager 2 as ...
Voyager 1 has four active scientific instruments, while Voyager 2 has five. Voyager 2 was launched two weeks earlier than Voyager 1. Interstellar 8-track tape. When they were launched, Voyager probes were state-of-the-art machines. So much so, NASA separated the twin spacecraft from the Mariner program which they initially were a part of.
Engineers at NASA have pinpointed some corrupted memory as the cause of Voyager 1's troubles and are working on a remote fix to deal with the hardware problem.…. The veteran probe began sending ...
Launched in 1977, the twin Voyager probes are NASA's longest-operating mission and the only spacecraft ever to explore interstellar space. Read more. Voyager 1 Distance from Earth. This is a real-time indicator of Voyager 1's distance from Earth in astronomical units (AU) and either miles (mi) or kilometers (km). Note: Because Earth moves ...
Launched in 1977, Voyager 1 zipped past Saturn and Jupiter in 1979 and 1980 before flying out into interstellar space in 2012. It is now recording the conditions outside of the sun's protective ...
There are volcanoes erupting hundreds of millions of miles beyond Earth. And a NASA spacecraft is watching it happen. The space agency's Juno probe, which has orbited Jupiter since 2016, swooped ...