

How to Write a Field Trip Report: A Comprehensive Guide for Students
- by Adam Davis
- October 18, 2023
Field trips are an exciting and educational opportunity for students to step outside the confines of the classroom and explore the real world. Whether you’re visiting a museum, a historical site, or a nature reserve, writing a field trip report is an essential task to document your experience and reflect on what you have learned.
In this blog post, we will guide you through the process of writing a field trip report. We’ll cover everything from understanding what a field study report is to providing examples of field research. Additionally, we’ll explore the importance of using transition words or phrases and how to write a fieldwork report specifically in geography.
By the end of this post, you’ll have a clear understanding of how to structure your field trip report, highlight key findings, and convey your observations effectively. So, let’s dive in and discover the art of crafting an impressive field trip report!

How to Write a Field Trip Report
Field trips are an exciting break from the monotony of the classroom, allowing students to explore the world outside the textbook. But what happens after the trip is over? That’s right, the dreaded field trip report. Don’t worry, though! I’m here to guide you through the ins and outs of writing a captivating field trip report that will impress your teachers and keep boredom at bay.
1. Start with a Catchy Introduction
No one likes a dull and lifeless introduction , especially not your teacher. Grab their attention right from the start by setting the scene of your field trip. Paint a vivid picture in their minds with words that transport them to the destination. Whether it was a visit to the local zoo or a thrilling adventure to a science museum, make them feel like they were right there with you.
2. Share Your Experiences, the Fun and the “Oops”
Now that you’ve captured your teacher’s attention, it’s time to dive into the juicy details of your field trip. Share the memorable moments, the funny anecdotes, and the exciting discoveries. Did your best friend accidentally step in elephant droppings? Did you get lost in the labyrinth of an art museum? These are the stories that will make your field trip report stand out from the rest.
3. Showcase Your Knowledge
A field trip is not just about having a grand adventure; it’s also an opportunity to learn. Impress your teacher by showcasing the knowledge you gained during the trip. Highlight the educational aspects , such as the new facts you learned, the exhibits that fascinated you, and any interactions with experts that expanded your understanding of the subject. Remember, knowledge is power, and it’s your time to shine!
4. Organize Your Thoughts
The last thing you want is for your field trip report to look like a chaotic jumble of random thoughts. Take a deep breath and organize your ideas before putting pen to paper (or in this case, fingers to keyboard). Divide your report into clear and logical sections, such as “Introduction,” “Highlights,” and “Key Learnings.” This will make it easier for your teacher to follow along and appreciate your well-structured masterpiece.
5. Sprinkle Some Humor
Writing a field trip report doesn’t have to be all serious business. Inject some humor into your writing to keep your teacher entertained. Share a witty remark or a funny observation that made everyone laugh during the trip. Just remember to strike a balance — you want to amuse, not distract. So, make your teacher chuckle while still maintaining the informative nature of your report.
6. Conclude with a Bang
It’s time to wrap it all up and leave a lasting impression. Summarize your key takeaways from the field trip and leave the reader with something to ponder. Perhaps a thought-provoking question or a call to action related to the topic. Let your creativity shine through, and make your conclusion a memorable one that ties together everything you’ve written.
Now that you know the secrets to writing an exceptional field trip report, go forth and conquer! Your teacher will be impressed by your storytelling skills, your knowledge retention, and your ability to entertain with a touch of humor. So, grab that pen or open that laptop, and let your field trip experiences come to life on the page. Happy writing!

FAQ: How to Write a Field Trip Report?
What are transition words or phrases.
Transition words and phrases are like secret passageways in your writing. They smoothly guide your readers from one idea to another, ensuring a seamless flow. It’s like taking your readers on a thrilling adventure rather than leaving them stranded in a maze of disconnected thoughts. So, grab your compass and sprinkle these magical words throughout your field trip report!
How Do You Write a Field Trip Report
Oh, the joys of sharing your field trip experiences with others! To write a captivating field trip report, follow these steps:
Step 1: Introduction, Ahoy!
Get your readers hooked from the get-go. Engage them with a brief overview of your field trip and its purpose. Remember, first impressions matter, even in the wondrous land of field trip reports!
Step 2: Choose Your Field Trip Highlights
No one wants to hear endless tales of every single droplet in that ocean of knowledge. Select the most exciting and educational parts of your trip, like spotting rare species or uncovering hidden treasures. These gems will make your report shine bright like a flashlight in a dark cave!
Step 3: Detailed Descriptions
Paint a vivid picture of your adventures using descriptive and colorful language. Imagine you’re setting the stage for a thrilling play. Make your readers feel like they’re right there with you, dodging hazards and exploring breathtaking sights!
Step 4: Data and Analysis
Numbers, graphs, and charts might not be as thrilling as sword fights and dragons, but they are vital to give your field trip report substance. Include any scientific data you collected, and analyze it like a detective, searching for hidden clues in the numbers.
Step 5: Conclusion and Reflections
Wrap up your field trip report with a strong conclusion that summarizes your most significant findings. Reflect on what you learned and how the trip impacted your understanding of the subject. Don’t be afraid to add a dash of introspection and personal growth.
What’s a Transitional Phrase
Ah, transitional phrases, the unsung heroes of coherent writing! These magical phrases connect your thoughts like puzzle pieces, guiding your readers effortlessly from one paragraph to another. Examples include “On the other hand,” “In addition,” or “As a result.” They’re like the smoothie in your writing blender, blending your ideas into a tasty concoction your readers will savor!
What Do You Mean by Field Study Report
A field study report is a formal document that recounts the details of a research or educational trip. It’s like a treasure map that guides readers through your exciting journey. This report usually includes an introduction, a description of the field trip, data analysis, and a conclusion. Think of it as your chance to become a storytelling scientist!
What Are Examples of Field Research
Field research, my dear adventurer, is a thrilling expedition that takes you out of the dull confines of a classroom or laboratory. It involves gathering data in the real world, beyond the pages of textbooks. Examples of field research include studying animal behavior in natural habitats, exploring geological formations, or investigating the impact of pollution in a local community. So pack your backpack and get ready for an unforgettable quest!
How Do You Write a Fieldwork Report in Geography
Ah, geography, the art of discovering the secrets this remarkable world holds! To write a captivating fieldwork report in geography, follow these steps:
Step 1: Research and Planning
Choose a fascinating research topic and plan your fieldwork accordingly. Whether you’re exploring rivers, mountains, or urban landscapes, ensure your adventure aligns with your research objectives. No need to pack a spyglass, but a map could come in handy!
Step 2: Data Collection
Get your detective hat on! Collect data through observations, surveys, interviews, or measurements. Just like a secret agent, remember to document everything meticulously, as accuracy is key.
Step 3: Analysis and Interpretation
Once you’ve gathered the data, it’s time to decode its hidden messages. Analyze and interpret the information you collected, using geographic tools and concepts to unveil the grand patterns of our wonderful planet.
Step 4: Results and Conclusions
Present your findings as if you were unveiling buried treasure. Summarize the results of your analysis and draw thoughtful conclusions. Reflect on the significance of your research and its implications for the wider world. You might just become a geography adventurer who changes the course of history!
And there you have it, your ultimate guide to writing a captivating field trip report! So, pick up your pen, grab your notebook, and embark on an adventure of words as you share your thrilling field trip experiences with the world!
- catchy introduction
- field research
- field trips
- fieldwork report
- grand adventure
- thrilling adventure
- transition words
Does Sure Jell Contain Gluten? Unveiling the Gluten Mystery in Fruit Preserves
Understanding the five levels of stakeholder engagement, you may also like, the mac user’s guide to creating subpages in onenote: a step-by-step tutorial.
- by Matthew Morales
- October 29, 2023
How Much Is Tesla the Band Worth?
- by Lindsey Smith
- October 8, 2023
Why is Peptone Used in Media Preparation?
- by Sean Brown
- October 7, 2023
Effective Communication Skills: Unlocking the Secret to Successful Relationships and Professional Growth
The son of a duke and duchess: what is he called.
- by Erin Fuentes
- October 30, 2023
Concave and Convex Slope: Understanding the Curvy Side of Mathematics
- by Jackie Hobbs
- October 12, 2023
Questions? Call us:
Email:
- How it works
- Testimonials
Essay Writing
- Essay service
- Essay writers
- College essay service
- Write my essay
- Pay for essay
- Essay topics
Term Paper Writing
- Term paper service
- Buy term papers
- Term paper help
- Term paper writers
- College term papers
- Write my term paper
- Pay for term paper
- Term paper topic
Research Paper Writing
- Research paper service
- Buy research paper
- Research paper help
- Research paper writers
- College research papers
- Write my research paper
- Pay for research paper
- Research paper topics
Dissertation Writing
- Dissertation service
- Buy dissertation
- Dissertation help
- Dissertation writers
- College thesis
- Write my dissertation
- Pay for dissertation
- Dissertation topics
Other Services
- Custom writing services
- Speech writing service
- Movie review writing
- Editing service
- Assignment writing
- Article writing service
- Book report writing
- Book review writing
Popular request:
Field report: writing guide from a to z.
February 18, 2021

So, you’ve just been given the difficult task of writing a field report. In most cases, this is your first field report. As such, you probably have absolutely no idea about what to do and how to do it. Fortunately, writing such a report is not as difficult as you imagine. In this blog post, we will discuss everything about the field report. What is a field report? Get all the answers in one blog post! We will also show you how to write a field trip report the easy way. You will find a nice little template you can use and we will also be more than happy to help you with a 100% original sample – upon your request. Read on!
So, What Is a Field Report?
Where can i get a field report example, a simple field report template, writing a field report from start to finish.
- FAQ About the Field Report
Need a Great Field Report Sample?
But what is field report? This is a very good question; one that we would like to answer right from the start. Why? Because if you don’t know the definition of field report, you have little chance of writing one correctly. After all, you can’t write about something you don’t understand, can you?
Basically, a field report is an academic paper that requires you to combine the theory you’ve learned in the classroom with specific methods of observation (applied in a specific environment, outside of class) to describe a subject. Said subject can be a person, a group of persons, an event, or even an animal. This is basically the field report definition.
But what are the objectives of field trip report? This is where it gets a bit tricky. Your report should be very comprehensive and you need to show your professor that you’ve mastered not only the theoretical parts of analysis, but also the practical ones. You need to observe the subject and take note of all things that are of interest. You need to be able to categorize, make connections, gather evidence, organize evidence, and even work with photographs, audio recordings and illustrations. Bottom line, the observation phase is not easy to do.
When it comes to getting a good field report example, there are several options you can explore. However, only one of them is viable for most students. Here are some of the things you can try:
- Go online and try to find an example on a websit e. Now, it’s true that you may be able to find several examples. However, many of them are poorly written. They are missing vital information and may even be missing certain parts. Be aware that some websites will attempt to sell you pre-written reports, which is something you need to stay away from at all costs.
- You can ask around on blogs, forums or social media if somebody has a report example they can share with you. While you may get lucky and get an example, you have no way of knowing whether or not it is correctly written.
- Many students try to hire a freelance writer to write the report . The idea is good, but you need much more than a freelance writer who probably doesn’t know how to write a field trip report After all, just 1% of freelance writers have academic writing experience (and these people are quite expensive to hire).
- You can hire a writing service to get the job done . This is the best way to go if you want to make sure you get a top quality, complete product. For instance, our ENL writers have written hundreds of these reports, so they definitely know what they’re doing. They have access to the best field scouting report forms and know how to write field report sections in a way that will make your professor give you some bonus points.
If you don’t know how to write a field report, it is important to get a good template. Obviously, you will need to learn how to write a field study report eventually. However, by using a good template, you make your life a lot easier. You will always have the basic structure of the report right there in front of you. This means that with a good field report template or daily field report template, you won’t miss any important sections or information. Here is how the basic structure of a field report home looks like:
- An introduction where you describe the objective of your report and underline specific concepts (if any).
- A Description of Activities section. This is where you describe everything that you observe, so that your readers know what is happening.
- An Interpretation and Analysis section. This is the part where you need to interpret and analyze the data you’ve gathered during your observations.
- A Conclusion and Recommendations section. This is the conclusion of your report, so you should never include any new information here.
If necessary, you can add a fifth section, the Appendix. This section will support your analysis in case you need to include lengthy information. Use the Appendix section to include any graphs, charts, graphics, tables, or illustrations.
Now that you know the field study report definition and have a template to work with, it’s time to show you how to write the report from start to finish. Let’s get started:
- Write the introduction . Don’t explain your readers what is field trip report. Instead, provide a bit of background information about the objective of your report. Describe the theoretical perspective and talk a bit about the various types of observations you’ve used.
- Write the Description of Activities section . In other words, describe everything that you have observed in an well organized, logical manner. Each observation needs to be written as a separate paragraph and needs to answer the five Ws: What, Where, When, Who, Why.
- Write the Interpretation and Analysis section . This is where you are free to interpret and analyze all the data you have gathered during your observations. In other words, this section can get pretty lengthy. You are not required to discuss each and every observation, so pick the most important ones (and explain why you consider them to be the most important ones). In this section, you need to convince your professor that you are talking from the perspective of a knowledgeable viewer by applying the theoretical knowledge you’ve accumulated in class.
- Write the field trip report conclusion and include any recommendations . You will basically need to summarize everything and show how your observations support your thesis. The recommendation can be used as a call to action to end the conclusion.
- As with any essay, you must edit the report . Eliminate the unnecessary information and don’t be afraid to delete entire sections if necessary. Your field report is, after all, an academic paper. It should be unbiased, objective and to the point. Also, make sure it is well organized.
- The last thing you need to do is proofread the paper . We would advise you to proofread the field report twice to make sure you didn’t miss anything. You can easily lose points over a few typos, so don’t risk it.
Frequently Asked Questions About the Field Report
Q: What are the differences between a daily field report and a regular report?
A: There are minor differences between field report types, and they all have to do with time. A daily field report is completed daily, while a regular report can take a couple of days or a couple of weeks to compile. The time span of the observations is different, that’s the major difference.
Q: What is the best field report app you can use?
A: Truth be told, we don’t know about any applications that can do a field report for you. In any case, you don’t even need such an app to do a field observation report. A notebook and a pen, a camera and a voice recorder are more than enough tools to record your observations.
Q: What are the top 3 tips you can give me?
A: Here they are:
- Before you begin writing the field experience report, you need to accurately record all aspects of the situation. It’s good to have a plan in place so you don’t miss anything.
- Analyze your observations and try to find the meaning of the things you are observing. Try to figure out what is happening and why it is happening.
- Remember that you need to write a report. Keep this in mind as you do the observations. Stay focused and pay attention to even minor details. Record every piece of new information.
Q: How to sample during the observations phase?
A: There are various methods to sample. For example, Ad Libitum sampling simply means observing what you deem important at a given moment. Behavior sampling translates to observing an entire group and noting specific individual behaviors. Continuous recording sampling and focal sampling are two other widely used methods for a field study report.
We realize you may not know how to write a field observation report. Or perhaps you want to learn how to write a field report for geography in just one day. However, there is an easy way to learn more about the field report. You can simply contact us and request a field report or an observation essay . The sample will be written just for you, so it will be 100% original.
Of course, you are free to use parts of our sample in your own writing. After all, you will own the sample and nobody else will have access to it. And did you know that our experienced writers and professional editors can help you with many other things? We can help you write intro or conclusion, edit your paper or even proofread your work. With our help, your essay will be perfect. So what are you waiting for? Learn how to write a report on a field trip with one of our awesome samples!

Take a break from writing.
Top academic experts are here for you.
- How To Write An Autobiography Guideline And Useful Advice
- 182 Best Classification Essay Topics To Learn And Write About
- How To Manage Stress In College: Top Practical Tips
- How To Write A Narrative Essay: Definition, Tips, And A Step-by-Step Guide
- How To Write Article Review Like Professional
- Great Problem Solution Essay Topics
- Creating Best Stanford Roommate Essay
- Costco Essay – Best Writing Guide
- How To Quote A Dialogue
- Wonderful Expository Essay Topics
- Research Paper Topics For 2020
- Interesting Persuasive Essay Topics
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
The purpose of a field report in the social sciences is to describe the deliberate observation of people, places, and/or events and to analyze what has been observed in order to identify and categorize common themes in relation to the research problem underpinning the study. The content represents the researcher's interpretation of meaning found in data that has been gathered during one or more observational events.
Flick, Uwe. The SAGE Handbook of Qualitative Data Collection . London: SAGE Publications, 2018; Lofland, John, David Snow, Leon Anderson, and Lyn H. Lofland. Analyzing Social Settings: A Guide to Qualitative Observation and Analysis. Long Grove, IL: Waveland Press, 2022; Baker, Lynda. "Observation: A Complex Research Method." Library Trends 55 (Summer 2006): 171-189.; Kellehear, Allan. The Unobtrusive Researcher: A Guide to Methods . New York: Routledge, 2020.
How to Approach Writing a Field Report
How to Begin
Field reports are most often assigned in disciplines of the applied social sciences [e.g., social work, anthropology, gerontology, criminal justice, education, law, the health care services] where it is important to build a bridge of relevancy between the theoretical concepts learned in the classroom and the practice of actually doing the work you are being taught to do. Field reports are also common in certain science disciplines [e.g., geology] but these reports are organized differently and serve a different purpose than what is described below.
Professors will assign a field report with the intention of improving your understanding of key theoretical concepts by applying methods of careful and structured observation of, and reflection about, people, places, or phenomena existing in their natural settings. Field reports facilitate the development of data collection techniques and observation skills and they help you to understand how theory applies to real world situations. Field reports are also an opportunity to obtain evidence through methods of observing professional practice that contribute to or challenge existing theories.
We are all observers of people, their interactions, places, and events; however, your responsibility when writing a field report is to conduct research based on data generated by the act of designing a specific study, deliberate observation, synthesis of key findings, and interpretation of their meaning.
When writing a field report you need to:
- Systematically observe and accurately record the varying aspects of a situation . Always approach your field study with a detailed protocol about what you will observe, where you should conduct your observations, and the method by which you will collect and record your data.
- Continuously analyze your observations . Always look for the meaning underlying the actions you observe. Ask yourself: What's going on here? What does this observed activity mean? What else does this relate to? Note that this is an on-going process of reflection and analysis taking place for the duration of your field research.
- Keep the report’s aims in mind while you are observing . Recording what you observe should not be done randomly or haphazardly; you must be focused and pay attention to details. Enter the observation site [i.e., "field"] with a clear plan about what you are intending to observe and record in relation to the research problem while, at the same time, being prepared to adapt to changing circumstances as they may arise.
- Consciously observe, record, and analyze what you hear and see in the context of a theoretical framework . This is what separates data gatherings from reporting. The theoretical framework guiding your field research should determine what, when, and how you observe and act as the foundation from which you interpret your findings in relation to the underlying assumptions embedded in the theoretical framework .
Techniques to Record Your Observations Although there is no limit to the type of data gathering techniques you can use, these are the most frequently used methods:
Note Taking This is the most common and easiest method of recording your observations. Tips for taking notes include: organizing some shorthand symbols beforehand so that recording basic or repeated actions does not impede your ability to observe, using many small paragraphs, which reflect changes in activities, who is talking, etc., and, leaving space on the page so you can write down additional thoughts and ideas about what’s being observed, any theoretical insights, and notes to yourself that are set aside for further investigation. See drop-down tab for additional information about note-taking.
Photography With the advent of smart phones, an almost unlimited number of high quality photographs can be taken of the objects, events, and people observed during a field study. Photographs can help capture an important moment in time as well as document details about the space where your observation takes place. Taking a photograph can save you time in documenting the details of a space that would otherwise require extensive note taking. However, be aware that flash photography could undermine your ability to observe unobtrusively so assess the lighting in your observation space; if it's too dark, you may need to rely on taking notes. Also, you should reject the idea that photographs represent some sort of "window into the world" because this assumption creates the risk of over-interpreting what they show. As with any product of data gathering, you are the sole instrument of interpretation and meaning-making, not the object itself. Video and Audio Recordings Video or audio recording your observations has the positive effect of giving you an unfiltered record of the observation event. It also facilitates repeated analysis of your observations. This can be particularly helpful as you gather additional information or insights during your research. However, these techniques have the negative effect of increasing how intrusive you are as an observer and will often not be practical or even allowed under certain circumstances [e.g., interaction between a doctor and a patient] and in certain organizational settings [e.g., a courtroom]. Illustrations/Drawings This does not refer to an artistic endeavor but, rather, refers to the possible need, for example, to draw a map of the observation setting or illustrating objects in relation to people's behavior. This can also take the form of rough tables, charts, or graphs documenting the frequency and type of activities observed. These can be subsequently placed in a more readable format when you write your field report. To save time, draft a table [i.e., columns and rows] on a separate piece of paper before an observation if you know you will be entering data in that way.
NOTE: You may consider using a laptop or other electronic device to record your notes as you observe, but keep in mind the possibility that the clicking of keys while you type or noises from your device can be obtrusive, whereas writing your notes on paper is relatively quiet and unobtrusive. Always assess your presence in the setting where you're gathering the data so as to minimize your impact on the subject or phenomenon being studied.
ANOTHER NOTE: Techniques of deliberate observation and data gathering are not innate skills; they are skills that must be learned and practiced in order to achieve proficiency. Before your first observation, practice the technique you plan to use in a setting similar to your study site [e.g., take notes about how people choose to enter checkout lines at a grocery store if your research involves examining the choice patterns of unrelated people forced to queue in busy social settings]. When the act of data gathering counts, you'll be glad you practiced beforehand.
YET ANOTHER NOTE: An issue rarely discussed in the literature about conducting field research is whether you should move around the study site while observing or remaining situated in one place. Moving around can be intrusive, but it facilitates observing people's behavior from multiple vectors. However, if you remain in one place throughout the observation [or during each observation], you will eventually blend into the background and diminish the chance of unintentionally influencing people's behavior. If the site has a complex set of interactions or interdependent activities [e.g., a play ground], consider moving around; if the study site is relatively fixed [e.g., a classroom], then consider staying in one place while observing.
Examples of Things to Document While Observing
- Physical setting . The characteristics of an occupied space and the human use of the place where the observation(s) are being conducted.
- Objects and material culture . This refers to the presence, placement, and arrangement of objects that impact the behavior or actions of those being observed. If applicable, describe the cultural artifacts representing the beliefs [i.e., the values, ideas, attitudes, and assumptions] of the individuals you are observing [e.g., the choice of particular types of clothing in the observation of family gatherings during culturally specific holidays].
- Use of language . Don't just observe but listen to what is being said, how is it being said, and the tone of conversations among participants.
- Behavior cycles . This refers to documenting when and who performs what behavior or task and how often they occur. Record at which stage this behavior is occurring within the setting.
- The order in which events unfold . Note sequential patterns of behavior or the moment when actions or events take place and their significance. Also, be prepared to note moments that diverge from these sequential patterns of behavior or actions.
- Physical characteristics of subjects. If relevant, document personal characteristics of individuals being observed. Note that, unless this data can be verified in interviews or from documentary evidence, you should only focus on characteristics that can be clearly observed [e.g., clothing, physical appearance, body language].
- Expressive body movements . This would include things like body posture or facial expressions. Note that it may be relevant to also assess whether expressive body movements support or contradict the language used in conversation [e.g., detecting sarcasm].
Brief notes about all of these examples contextualize your observations; however, your observation notes will be guided primarily by your theoretical framework, keeping in mind that your observations will feed into and potentially modify or alter these frameworks.
Sampling Techniques
Sampling refers to the process used to select a portion of the population for study . Qualitative research, of which observation is one method of data gathering, is generally based on non-probability and purposive sampling rather than probability or random approaches characteristic of quantitatively-driven studies. Sampling in observational research is flexible and often continues until no new themes emerge from the data, a point referred to as data saturation.
All sampling decisions are made for the explicit purpose of obtaining the richest possible source of information to answer the research questions. Decisions about sampling assumes you know what you want to observe, what behaviors are important to record, and what research problem you are addressing before you begin the study. These questions determine what sampling technique you should use, so be sure you have adequately answered them before selecting a sampling method.
Ways to sample when conducting an observation include:
- Ad Libitum Sampling -- this approach is not that different from what people do at the zoo; they observe whatever seems interesting at the moment. There is no organized system of recording the observations; you just note whatever seems relevant at the time. The advantage of this method is that you are often able to observe relatively rare or unusual behaviors that might be missed by more deliberately designed sampling methods. This method is also useful for obtaining preliminary observations that can be used to develop your final field study. Problems using this method include the possibility of inherent bias toward conspicuous behaviors or individuals, thereby missing mundane or repeated patterns of behavior, and that you may miss brief interactions in social settings.
- Behavior Sampling -- this involves watching the entire group of subjects and recording each occurrence of a specific behavior of interest and with reference to which individuals were involved. The method is useful in recording rare behaviors missed by other sampling methods and is often used in conjunction with focal or scan methods [see below]. However, sampling can be biased towards particular conspicuous behaviors.
- Continuous Recording -- provides a faithful record of behavior including frequencies, durations, and latencies [the time that elapses between a stimulus and the response to it]. This is a very demanding method because you are trying to record everything within the setting and, thus, measuring reliability may be sacrificed. In addition, durations and latencies are only reliable if subjects remain present throughout the collection of data. However, this method facilitates analyzing sequences of behaviors and ensures obtaining a wealth of data about the observation site and the people within it. The use of audio or video recording is most useful with this type of sampling.
- Focal Sampling -- this involves observing one individual for a specified amount of time and recording all instances of that individual's behavior. Usually you have a set of predetermined categories or types of behaviors that you are interested in observing [e.g., when a teacher walks around the classroom] and you keep track of the duration of those behaviors. This approach doesn't tend to bias one behavior over another and provides significant detail about a individual's behavior. However, with this method, you likely have to conduct a lot of focal samples before you have a good idea about how group members interact. It can also be difficult within certain settings to keep one individual in sight for the entire period of the observation without being intrusive.
- Instantaneous Sampling -- this is where observation sessions are divided into short intervals divided by sample points. At each sample point the observer records if predetermined behaviors of interest are taking place. This method is not effective for recording discrete events of short duration and, frequently, observers will want to record novel behaviors that occur slightly before or after the point of sampling, creating a sampling error. Though not exact, this method does give you an idea of durations and is relatively easy to do. It is also good for recording behavior patterns occurring at a specific instant, such as, movement or body positions.
- One-Zero Sampling -- this is very similar to instantaneous sampling, only the observer records if the behaviors of interest have occurred at any time during an interval instead of at the instant of the sampling point. The method is useful for capturing data on behavior patterns that start and stop repeatedly and rapidly, but that last only for a brief period of time. The disadvantage of this approach is that you get a dimensionless score for an entire recording session, so you only get one one data point for each recording session.
- Scan Sampling -- this method involves taking a census of the entire observed group at predetermined time periods and recording what each individual is doing at that moment. This is useful for obtaining group behavioral data and allows for data that are evenly representative across individuals and periods of time. On the other hand, this method may be biased towards more conspicuous behaviors and you may miss a lot of what is going on between observations, especially rare or unusual behaviors. It is also difficult to record more than a few individuals in a group setting without missing what each individual is doing at each predetermined moment in time [e.g., children sitting at a table during lunch at school]. The use of audio or video recording is useful with this type of sampling.
Alderks, Peter. Data Collection. Psychology 330 Course Documents. Animal Behavior Lab. University of Washington; Emerson, Robert M. Contemporary Field Research: Perspectives and Formulations . 2nd ed. Prospect Heights, IL: Waveland Press, 2001; Emerson, Robert M. et al. “Participant Observation and Fieldnotes.” In Handbook of Ethnography . Paul Atkinson et al., eds. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2001), 352-368; Emerson, Robert M. et al. Writing Ethnographic Fieldnotes . 2nd ed. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press, 2011; Ethnography, Observational Research, and Narrative Inquiry. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Hazel, Spencer. "The Paradox from Within: Research Participants Doing-Being-Observed." Qualitative Research 16 (August 2016): 446-457; Pace, Tonio. Writing Field Reports. Scribd Online Library; Presser, Jon and Dona Schwartz. “Photographs within the Sociological Research Process.” In Image-based Research: A Sourcebook for Qualitative Researchers . Jon Prosser, editor (London: Falmer Press, 1998), pp. 115-130; Pyrczak, Fred and Randall R. Bruce. Writing Empirical Research Reports: A Basic Guide for Students of the Social and Behavioral Sciences . 5th ed. Glendale, CA: Pyrczak Publishing, 2005; Report Writing. UniLearning. University of Wollongong, Australia; Wolfinger, Nicholas H. "On Writing Fieldnotes: Collection Strategies and Background Expectancies.” Qualitative Research 2 (April 2002): 85-95; Writing Reports. Anonymous. The Higher Education Academy.
Structure and Writing Style
How you choose to format your field report is determined by the research problem, the theoretical framework that is driving your analysis, the observations that you make, and/or specific guidelines established by your professor. Since field reports do not have a standard format, it is worthwhile to determine from your professor what the preferred structure and organization should be before you begin to write. Note that field reports should be written in the past tense. With this in mind, most field reports in the social sciences include the following elements:
I. Introduction The introduction should describe the research problem, the specific objectives of your research, and the important theories or concepts underpinning your field study. The introduction should describe the nature of the organization or setting where you are conducting the observation, what type of observations you have conducted, what your focus was, when you observed, and the methods you used for collecting the data. Collectively, this descriptive information should support reasons why you chose the observation site and the people or events within it. You should also include a review of pertinent literature related to the research problem, particularly if similar methods were used in prior studies. Conclude your introduction with a statement about how the rest of the paper is organized.
II. Description of Activities
Your readers only knowledge and understanding of what happened will come from the description section of your report because they were not witnesses to the situation, people, or events that you are writing about. Given this, it is crucial that you provide sufficient details to place the analysis that will follow into proper context; don't make the mistake of providing a description without context. The description section of a field report is similar to a well written piece of journalism. Therefore, a useful approach to systematically describing the varying aspects of an observed situation is to answer the "Five W’s of Investigative Reporting." As Dubbels notes [p. 19], these are:
- What -- describe what you observed. Note the temporal, physical, and social boundaries you imposed to limit the observations you made. What were your general impressions of the situation you were observing. For example, as a student teacher, what is your impression of the application of iPads as a learning device in a history class; as a cultural anthropologist, what is your impression of women's participation in a Native American religious ritual?
- Where -- provide background information about the setting of your observation and, if necessary, note important material objects that are present that help contextualize the observation [e.g., arrangement of computers in relation to student engagement with the teacher].
- When -- record factual data about the day and the beginning and ending time of each observation. Note that it may also be necessary to include background information or key events which impact upon the situation you were observing [e.g., observing the ability of teachers to re-engage students after coming back from an unannounced fire drill].
- Who -- note background and demographic information about the individuals being observed e.g., age, gender, ethnicity, and/or any other variables relevant to your study]. Record who is doing what and saying what, as well as, who is not doing or saying what. If relevant, be sure to record who was missing from the observation.
- Why -- why were you doing this? Describe the reasons for selecting particular situations to observe. Note why something happened. Also note why you may have included or excluded certain information.
III. Interpretation and Analysis
Always place the analysis and interpretations of your field observations within the larger context of the theoretical assumptions and issues you described in the introduction. Part of your responsibility in analyzing the data is to determine which observations are worthy of comment and interpretation, and which observations are more general in nature. It is your theoretical framework that allows you to make these decisions. You need to demonstrate to the reader that you are conducting the field work through the eyes of an informed viewer and from the perspective of a casual observer.
Here are some questions to ask yourself when analyzing your observations:
- What is the meaning of what you have observed?
- Why do you think what you observed happened? What evidence do you have for your reasoning?
- What events or behaviors were typical or widespread? If appropriate, what was unusual or out of the ordinary? How were they distributed among categories of people?
- Do you see any connections or patterns in what you observed?
- Why did the people you observed proceed with an action in the way that they did? What are the implications of this?
- Did the stated or implicit objectives of what you were observing match what was achieved?
- What were the relative merits of the behaviors you observed?
- What were the strengths and weaknesses of the observations you recorded?
- Do you see connections between what you observed and the findings of similar studies identified from your review of the literature?
- How do your observations fit into the larger context of professional practice? In what ways have your observations possibly changed or affirmed your perceptions of professional practice?
- Have you learned anything from what you observed?
NOTE: Only base your interpretations on what you have actually observed. Do not speculate or manipulate your observational data to fit into your study's theoretical framework.
IV. Conclusion and Recommendations
The conclusion should briefly recap of the entire study, reiterating the importance or significance of your observations. Avoid including any new information. You should also state any recommendations you may have based on the results of your study. Be sure to describe any unanticipated problems you encountered and note the limitations of your study. The conclusion should not be more than two or three paragraphs.
V. Appendix
This is where you would place information that is not essential to explaining your findings, but that supports your analysis [especially repetitive or lengthy information], that validates your conclusions, or that contextualizes a related point that helps the reader understand the overall report. Examples of information that could be included in an appendix are figures/tables/charts/graphs of results, statistics, pictures, maps, drawings, or, if applicable, transcripts of interviews. There is no limit to what can be included in the appendix or its format [e.g., a DVD recording of the observation site], provided that it is relevant to the study's purpose and reference is made to it in the report. If information is placed in more than one appendix ["appendices"], the order in which they are organized is dictated by the order they were first mentioned in the text of the report.
VI. References
List all sources that you consulted and obtained information from while writing your field report. Note that field reports generally do not include further readings or an extended bibliography. However, consult with your professor concerning what your list of sources should be included and be sure to write them in the preferred citation style of your discipline or is preferred by your professor [i.e., APA, Chicago, MLA, etc.].
Alderks, Peter. Data Collection. Psychology 330 Course Documents. Animal Behavior Lab. University of Washington; Dubbels, Brock R. Exploring the Cognitive, Social, Cultural, and Psychological Aspects of Gaming and Simulations . Hershey, PA: IGI Global, 2018; Emerson, Robert M. Contemporary Field Research: Perspectives and Formulations . 2nd ed. Prospect Heights, IL: Waveland Press, 2001; Emerson, Robert M. et al. “Participant Observation and Fieldnotes.” In Handbook of Ethnography . Paul Atkinson et al., eds. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2001), 352-368; Emerson, Robert M. et al. Writing Ethnographic Fieldnotes . 2nd ed. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press, 2011; Ethnography, Observational Research, and Narrative Inquiry. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Pace, Tonio. Writing Field Reports. Scribd Online Library; Pyrczak, Fred and Randall R. Bruce. Writing Empirical Research Reports: A Basic Guide for Students of the Social and Behavioral Sciences . 5th ed. Glendale, CA: Pyrczak Publishing, 2005; Report Writing. UniLearning. University of Wollongong, Australia; Wolfinger, Nicholas H. "On Writing Fieldnotes: Collection Strategies and Background Expectancies.” Qualitative Research 2 (April 2002): 85-95; Writing Reports. Anonymous. The Higher Education Academy.
- << Previous: Writing a Case Study
- Next: About Informed Consent >>
- Last Updated: Mar 6, 2024 1:00 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments

Field Trip Report

Who does not like field trips? When you were a kid or when you were still attending school, you would have gone through field trips and often than not asked to write a report about it. You get to visit different places and learn from it. A lot of people who have gone through field trips often expect to have a written report about it, but it is of course different from when you were a kid or a student. There are some who do go on field trips who are tasked to make reports like those in agricultural businesses or have graduated within the field of agriculture. To get to know more about what can be expected in a field trip report, let’s check out the example templates below for more information. Check out 10+ Trip Report Examples & Templates .
[bb_toc content=”][bb_toc]
10+ Field Trip Report Examples
1. data field trip report.

Size: 567 KB
2. Field Trip Report Template

Size: 41 KB
3. Formal Field Trip Report
Size: 730 KB
4. Professional Field Trip Report

Size: 61 KB
5. Field Trip Report in PDF

Size: 96 KB
6. General Field Trip Report

Size: 50 KB
7. Temple Field Trip Report

8. Field Trip Report Form

9. Draft Field Trip Report

Size: 43 KB
10. Construction Field Trip Report
Size: 19 KB
11. Printable Field Trip Report

Size: 86 KB
What Is a Field Trip Report?
What is a field trip report? A field trip report is a document that describes , summarizes and explains the things that have been done during the field trip. Whether or not the field trip may have been done as work related, school related, or even personal or family related. There is no denying, field trips can be fun and informative. A field trip report consists of an introduction, a body and a conclusion. Basically like writing a report. In addition, the field trip report contains information and the reason for the said field trip. Working in agriculture, a field trip report is a required paperwork to explain the process of the agricultural work and any issues that may slow down the agricultural business. Lastly, when you think of field trip reports, you think of information necessary to record and explain. The document is also used as a means of record to be sure that everything is going as it should. See 13 + Business Trip Report Examples .
How to Write a Field Trip Report
How do you write a report for a field trip? For students, they are given a template for them to follow and write down what they see and learn. On a work related or professional level, the person who went on the field trip is required to make a report of what they have observed and what they may take from the learning experience. Regardless of what the field trip may be and for who it is for, writing the report is needed. With that being said, a list of steps to take to make a field trip report. For students on a field trip see 12+ Permission Slip Templates .
1. Make an Interesting Title and Introduction
To start making a field trip report, you must also make an interesting title and an interesting introduction. What this simply means is that, to get your audiences’ attention, you must grab it with an interesting title. The title must be about the field trip you went on. The same goes for an introduction. Avoid adding too much detail in the introduction.
2. Tell It in Story Format
Telling your report in story format is fine, but do avoid making it sound fiction when it is supposed to be non-fiction. Writing the report can also be written in an essay format. Again as long as you avoid adding too many flimsy words that may make your report sound more fiction than non-fiction. Another way to make it is to outline your report to make it easier. Outlining helps a lot.
3. Jargon Must Be Clear and Concise
Jargon . There may be times that we are tempted to use different jargon to express what we feel and see in the field trip report. But make sure that the jargon you are using is easy enough for the audience to understand. The use of jargon must be clear and concise throughout your report. See 6+ Jargon Examples in Literature – PDF .
4. Review Your Trip Report
The last thing to do is to review the trip report. Just to be sure that you have added an introduction, the body and your conclusion. The jargon should be understandable, the details complete and of course check on your grammar and spelling throughout the report.
What is a field trip report?
When you hear the words field trip, the first thing that may come to mind is your childhood memories filled with those trips either made with family, friends or school. With school, you are asked to make a report or an essay about what you did on the field trip. A field trip report is a document that describes , summarizes and explains the things that have been done during the field trip. Whether or not the field trip may have been done as work related, school related, or even personal or family related.
How do you make a field trip report?
To make a field trip report, you must remember to make it interesting. Capture the attention of the audience. Add in some photos if you have any, but remember the main focus is in your words or how you express it in a story.
Why do you need a field trip report?
The need for making the report may vary. For students, it is a way for them to express what they felt during the field trip. For business purposes, it is to explain the ongoing projects or the ongoing business that they have.
Who does not like field trips? A lot of people may find it useless as they may not have had the best field trips growing up, but it’s not too late for that. Field trip reports are made for varying reasons, one reason would be to describe and talk about the things they see. For a business point of view, it would be for the prospect of expanding to other places.
Report Generator
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Generate a report on the impact of technology in the classroom on student learning outcomes
Prepare a report analyzing the trends in student participation in sports and arts programs over the last five years at your school.

How to Write a Field Trip Report

How to Create a Nursing Practicum Journal
Visiting the Air and Space Museum in Washington, D.C., or touring the wetlands in Florida are two examples of exciting and educational field trips for middle school and high school students. You might take notes during your trip, so you can come up with an interesting thesis for your assigned field trip report. For example, you might write about a shuttle launching or an unusual creature who lives in the wetlands. Field trip reports should include a compelling introduction, a well-structured body and a strong conclusion. Discuss your favorite elements of the trip, so your assignment reads like a personal observation report or narrative essay.
Lead with Interesting Introduction
Start your introduction with information that leads up to your thesis statement, which is usually the last sentence of your introduction. You might focus on an interesting anecdote from your trip or discuss particular features that made an impression on you. Use these tidbits to develop your thesis. For example, you might create a three-point thesis, such as "The wetlands in Florida have vulnerable ecosystems, experience climate changes and endure seasonal flooding." If your teacher wants a technical field trip report, start with an abstract -- a brief summary paragraph -- that clearly explains where you went and what you learned during the field trip. Use research or literature to support your statements in your field trip report. For example, if you visited a local arboretum, you might use information from display placards to describe your favorite types of foliage and their seasonal life cycles.
Provide Facility Details
Discuss the field trip location by describing the facilities and explaining what you saw or experienced. For example, if you visited an astronomy observatory, discuss viewing areas and the telescopes you used. If you were using inside telescopes, describe the height of the domed ceilings, the different types of lighting and the approximate distance to the stars or planets. By providing extensive details, you show your teacher that you were paying close attention to the instructor, or in the observatory example, to the astronomer's explanations. You might also discuss any handouts or educational materials you received during the field trip.
Discuss Surprising Findings
Explain in your field trip report any new information or details that took you by surprise and include statistical data to support your findings. This type of data shows that you learned something during the field trip. For example, if you visited an underground cave, you might discuss a particular type of bat or an unusual plant that grows in the cave. Use outside research or information from the tour guide to support your data, and cite your references clearly, so your teacher knows where you got the information. When possible, use academic journals or magazines to support details in your observation report of the field visit.
End with Compelling Conclusion
Conclude your field trip report with a summary of your overall experience, including reasons why others might want to visit the location. You might include a brief summary of a personal discussion you had with the tour guide or field trip facilitator or cite a distinguishable fact from your research. If you participated in any hands-on activities or your class was allowed to see behind the scenes, you might end your paper by discussing those highlights. For example, if you visited a science center, you might discuss fossils you examined, electricity experiments you participated in, or hands-on experiments with wind tunnels that allowed you to examine weather patterns.
Related Articles

How to Create an Animal School Project

How to Write a Practicum Report

How to Write a Short Report on Job Shadowing

How to Write Post-Doctoral Career Goals

How to Write an Autobiography in the 7th Grade

Does APA Style Recommend Using the Present Tense?

How to Write a Timeline Report

How to Create a Life Map
- Clayton State University: Natural Sciences: Report Format
- Purdue University Online Writing Lab: Using Research and Evidence
- University of Arkansas Newswire: Research: School Field Trips Give Significant Benefits
- Common Core State Standards Initiative: English Language Arts Standards: Writing: Grade 9-10
As curriculum developer and educator, Kristine Tucker has enjoyed the plethora of English assignments she's read (and graded!) over the years. Her experiences as vice-president of an energy consulting firm have given her the opportunity to explore business writing and HR. Tucker has a BA and holds Ohio teaching credentials.

Want to Write a Field Study Report? 6 Key Points to Consider!
Research conduction is not just limited to your laboratory, library, or work place setting. As part of your research you may have to step out in the field (any place other than your regular research lab or work station) to collect raw data for analysis and then publish it as a field study report. In this article, we will discuss the elements of a field study report and the key points to consider while writing one!
Table of Contents
What is a Field Study Report?
A field study report is defined as a documentation of analysis of particular phenomena, behaviors, processes based on theories and observations made by the researcher in the field. These observed and analyzed theories are used to identify solutions for a specific project or case report .
What is the Importance of Field Study Report?
- A field study report is important as part of many operational and technical documentation processes in various industries including field services, education, medicine, and management.
- Moreover, it gives detailed information of an observed subject or specimen which is used to analyze and compare data against a theoretical framework .
- It also helps in identifying challenges in implementing solutions to form a standardized protocol.
- Furthermore, it helps in capturing information on resource management and discovering new processes for effective and optimized solutions.
How to Write Field Research Notes?
A field study report begins with an idea and ends with a solution. Hence, while conducting field research, one must follow a planned route of taking notes for proper documentation of the observations made. A successful field study report begins when the researcher is involved in the observational research process of taking proper notes.
Based on the methods, the field research notes are categorized in four different types:
1. Job Notes:
- Researchers use this method of taking field notes whilst they are conducting the study.
- These notes are taken in close proximity and in open sight with the study’s subject.
- These notes are brief, concise, in the form that can be built on by the researcher later while creating the report.
2. Field Notes Proper:
- This method of taking field notes is to expand them immediately after the completion of study.
- These notes are detailed and the words have to be as close to the terms that will be used in the final field study report.
3. Methodological Notes:
- This type of field notes involve research methods used by the researcher, newly proposed research methods, and the way to monitor their progress.
- Methodological notes are either attached with field notes or filed separately. These notes are always placed at the end of the field study report.
4. Journals and Diaries:
- This method of taking notes is an insight into the researcher’s life as it tracks all aspects of the researcher’s life.
- It helps in eliminating any bias that may have affected the field research.
Examples of Things to Document During Field Study
1. Physical Setting:
Observe the characteristics of the space where the study is being conducted.
2. Objects and Material:
The presence, placement, and arrangement of objects that affect the behavior of the subject being studied.
3. Language Used:
Observe the language being used by study participants (in case of human participation).
4. Behavior Cycles:
Document who is performing what behavior at what time and situation.
5. Physical Characteristics of Participants/Subjects:
Observe and note personal characteristics of subjects.
6. Body Movements:
Things such as body posture or facial expressions and assess if these movements support or contradict the language used while communicating.
Data Collection in Field Report (Sampling Techniques)
Data collection process in field study is also known as sampling. It refers to the process used to select a portion of the population for study. Selection of an ideal sampling technique is imperative to obtain the richest possible source of information to answer the research questions.
Different Types of Sampling Techniques:
Ad Libitum Sampling
This technique involves observing whatever seems interesting at the moment. It does not follow an organized system of recording the observations.
Behavior Sampling
This sampling technique involves watching the entire group of subjects and recording each occurrence of a specific behavior of interest with reference to which individuals were involved.
Continuous Recording
This sampling technique includes recording of frequencies, durations, and latencies in a continuous and systematic pattern.
Focal Sampling
The focal sampling technique involves observing one individual/subject for a specified amount of time and recording all instances of that individual’s behavior.
Instantaneous Sampling
The technique of instantaneous sampling involves dividing observation sessions into short intervals by sample points.
One-Zero Sampling
The one-zero sampling technique is similar to instantaneous sampling. It involves recording only if the behaviors of interest have occurred at any time during an interval instead of at the instant of the sampling point.
Scan Sampling
The scan sampling technique involves taking a census of the entire observed group at predetermined time periods and recording what each individual is doing at that moment.
What is the Structure and Writing Style of Field Study Report?
A field study report does not have a standard format; however, the following factors determined its structure and writing style:
- Nature of research problem
- Theoretical perspective that drives the analysis
- Observations made by researcher
- Specific guidelines established by your professor/supervisor
A field study report includes 6 main elements as follows:
1. Introduction
The introduction section should describe the objective and important theories or concepts underpinning your field study. More importantly, it should describe the organization’s nature or setting where you are conducting the observation—the types of observations conducted, the focus of your research study, what was observed, and which methods were used for collecting the data. Furthermore, it is important to include a review of pertinent literature .
2. Description of Activities
It becomes imperative for researchers to provide the information to the readers about what happened during the field study. Hence, you must include the details of all events that take place during your field research.
The description section helps in answering the five “WH” questions as mentioned below:
What did you see and hear in your area of study?
Where does the background information of the research setting is observed and reported?
Why are you conducting this field research?,
The reason behind particular thing happening , and
Why have you included or excluded specific information?
Who are the participants in terms of gender, age, ethnicity, and other relevant variables from your observation?
When is the study being conducted (day or time when occurring actions are observed and noted)?
3. Analysis and Interpretation
While you are on the field conducting the study, you are likely to observe multiple things. However, it is up to you as to which observations do you want to interpret and record in the report. This allows you to show the reader that you are interpreting events like an informed observer. Furthermore, your theoretical framework helps you in making this decision. The analysis and interpretation of your field observations must always be placed in the larger context of the theories described in the introduction.
Some questions to ask yourself when analyzing your observations are as follows:
- What is the meaning of your observations?
- What are the reasons behind the occurrence of the things you observed?
- How typical or widespread are the events and behaviors of the things you observed?
- Are there any connections or patterns in your observations?
- What are the implications of your observations?
- Did your observations match the objective of your study?
- What were the merits of your observations?
- What were the strengths and weaknesses of your recorded observations?
- Are there any connections between your findings and the findings from pertinent literature?
- Do your observations fit into the larger context of the study’s theories?
4. Conclusion and Recommendations
The conclusion of your field study report should summarize your report and emphasize the importance of your observations. This section has to be concise and relevant to your field study and must not include any new information. Furthermore, it is imperative to highlight any recommendations that you may have for readers to consider while conducting similar study. Additionally, describe any unanticipated problems you encountered and note the limitations of your study. Limit your conclusion to around two to three paragraphs.
5. References
The reference section must include every source that you referred to and used while writing your field study report. Since format for writing references may differ for every university, you must consult your professor to understand the format and write it accordingly.
6. Appendix
This section includes information that is not essential to explain your findings, but supports your analysis [especially repetitive or lengthy information]. It validates your conclusions and contextualize a related point. This helps the reader to understand the overall field study report.

6 Key Points to Consider While Writing a Field Study Report
A field study report focuses on factual and observational details of a project case. It must help the reader understand how theory applies to real-world scenarios. Hence, it should cover the circumstances and contributing factors to derive conclusive results from the observed and collated raw data.
Below are the key points to consider while writing a field study report:
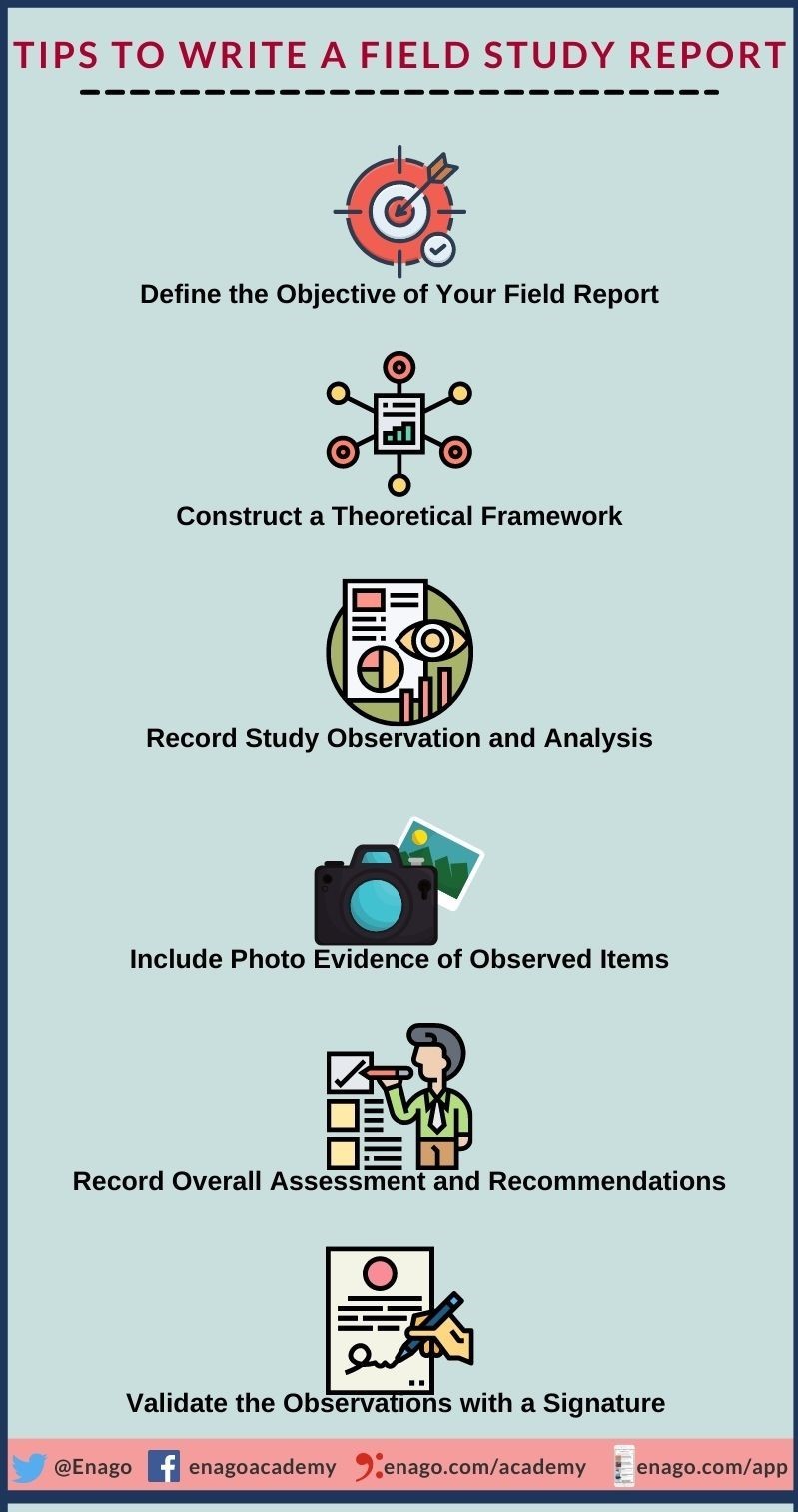
1. Define the Objective of Your Field Report
- Ensure that you state the purpose of your field study report clearly.
- Determine the focus of your study and provide the relevant information.
- Define the setting of observations, and the methods used to collect data.
2. Construct a Theoretical Framework
- Creating a theoretical framework helps you in garnering information based on statistics, news, and pertinent literature for better understanding.
- Additionally, it guides you in determining the data that need to be analyzed and set as a baseline for comparison to acquire necessary information.
3. Record Study Observations and Analysis
- Take notes of your observations based on the defined scope of work (SOW).
- Furthermore, achieve and record the detailed plan on how to achieve the set objectives.
4. Include Photo Evidence of Observed Items
- Validate gathered raw data with photographs or videos as evidences.
- This increases the authenticity of your report and the conclusions you derive from it.
5. Record Overall Assessment and Recommendations
- Document all the observed aspects of your study based on gathered analysis and observations.
- Furthermore, clearly explain the observations and discuss the challenges and limitations faced by you while conducting the study.
6. Validate the Observations with a Signature
- After completing your research and documenting it, it is important to declare who is responsible for the reported data.
- Additionally, you must validate your findings in the field study report by signing off with a digital signature at the end of the report.
Did you every try writing a field study report? How difficult or easy was it? What methods do you follow while writing a field report? Let us know about it in the comments section below!
very well written….the enumeration is really commendable dear Bhosale…sweet regards from Nepal..
Very well explained and detailed. The information was relevant to my research. thanks
Wow…. Thank you I find this useful 🙏
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Diversity and Inclusion
- Trending Now
The Silent Struggle: Confronting gender bias in science funding
In the 1990s, Dr. Katalin Kariko’s pioneering mRNA research seemed destined for obscurity, doomed by…

Addressing Barriers in Academia: Navigating unconscious biases in the Ph.D. journey
In the journey of academia, a Ph.D. marks a transitional phase, like that of a…

- Industry News
Attention Scopus Users! Study Reveals 67 Hijacked Journals Prompting Concerns
A recent study focused on indexjacking, warns that Scopus, a widely used scientific paper database…

- Manuscripts & Grants
- Reporting Research
Unraveling Research Population and Sample: Understanding their role in statistical inference
Research population and sample serve as the cornerstones of any scientific inquiry. They hold the…

- Manuscript Preparation
- Publishing Research
Research Problem Statement — Find out how to write an impactful one!
What Is a Research Problem Statement? A research problem statement is a clear, concise, and…
Unraveling Research Population and Sample: Understanding their role in statistical…
2022 in a Nutshell — Reminiscing the year when opportunities were seized and feats…
Write an Error-free Research Protocol As Recommended by WHO: 21 Elements You…

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?

Organizing Academic Research Papers: Writing a Field Report
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Executive Summary
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tertiary Sources
- What Is Scholarly vs. Popular?
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Annotated Bibliography
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- How to Manage Group Projects
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Essays
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Acknowledgements
Field reports require the researcher to combine theory and analysis learned in the classroom with methods of observation and practice applied outside of the classroom. The purpose of field reports is to describe an observed person, place, or event and to analyze that observation data in order to identify and categorize common themes in relation to the research problem(s) underpinning the study. The data is often in the form of notes taken during the observation but it can also include any form of data gathering, such as, photography, illustrations, or audio recordings.
How to Approach Writing a Field Report
How to Begin
Field reports are most often assigned in the applied social sciences [e.g., social work, anthropology, gerontology, criminal justice, education, law, the health care professions] where it is important to build a bridge of relevancy between the theoretical concepts learned in the classroom and the practice of actually doing the work you are being taught to do. Field reports are also common in certain science and technology disciplines [e.g., geology] but these reports are organized differently and for different purposes than what is described below.
Professors will assign a field report with the intention of improving your understanding of key theoretical concepts through a method of careful and structured observation of and reflection about real life practice. Field reports facilitate the development of data collection techniques and observation skills and allow you to understand how theory applies to real world situations. Field reports are also an opportunity to obtain evidence through methods of observing professional practice that challenge or refine existing theories.
We are all observers of people, their interactions, places, and events; however, your responsibility when writing a field report is to create a research study based on data generated by the act of observation, a synthesis of key findings, and an interpretation of their meaning. When writing a field report you need to:
- Systematically observe and accurately record the varying aspects of a situation . Always approach your field study with a detailed plan about what you will observe, where you should conduct your observations, and the method by which you will collect and record your data.
- Continuously analyze your observations . Always look for the meaning underlying the actions you observe. Ask yourself: What's going on here? What does this observed activity mean? What else does this relate to? Note that this is an on-going process of reflection and analysis taking place for the duration of your field research.
- Keep the report’s aims in mind while you are observing . Recording what you observe should not be done randomly or haphazardly; you must be focused and pay attention to details. Enter the field with a clear plan about what you are intending to observe and record while, at the same time, be prepared to adapt to changing circumstances as they may arise.
- Consciously observe, record, and analyze what you hear and see in the context of a theoretical framework . This is what separates data gatherings from simple reporting. The theoretical framework guiding your field research should determine what, when, and how you observe and act as the foundation from which you interpret your findings.
Techniques to Record Your Observations Note Taking This is the most commonly used and easiest method of recording your observations. Tips for taking notes include: organizing some shorthand symbols beforehand so that recording basic or repeated actions does not impede your ability to observe, using many small paragraphs, which reflect changes in activities, who is talking, etc., and, leaving space on the page so you can write down additional thoughts and ideas about what’s being observed, any theoretical insights, and notes to yourself about may require further investigation. See drop-down tab for additional information about note-taking. Video and Audio Recordings Video or audio recording your observations has the positive effect of giving you an unfiltered record of the observation event. It also facilitates repeated analysis of your observations. However, these techniques have the negative effect of increasing how intrusive you are as an observer and will often not be practical or even allowed under certain circumstances [e.g., interaction between a doctor and a patient] and in certain organizational settings [e.g., a courtroom]. Illustrations/Drawings This does not an artistic endeavor but, rather, refers to the possible need, for example, to draw a map of the observation setting or illustrating objects in relation to people's behavior. This can also take the form of rough tables or graphs documenting the frequency and type of activities observed. These can be subsequently placed in a more readable format when you write your field report.
Examples of Things to Document While Observing
- Physical setting . The characteristics of an occupied space and the human use of the place where the observation(s) are being conducted.
- Objects and material culture . The presence, placement, and arrangement of objects that impact the behavior or actions of those being observed. If applicable, describe the cultural artifacts representing the beliefs--values, ideas, attitudes, and assumptions--used by the individuals you are observing.
- Use of language . Don't just observe but listen to what is being said, how is it being said, and, the tone of conversation among participants.
- Behavior cycles . This refers to documenting when and who performs what behavior or task and how often they occur. Record at which stage is this behavior occurring within the setting.
- The order in which events unfold . Note sequential patterns of behavior or the moment when actions or events take place and their significance.
- Physical characteristics of subjects. If relevant, note age, gender, clothing, etc. of individuals.
- Expressive body movements . This would include things like body posture or facial expressions. Note that it may be relevant to also assess whether expressive body movements support or contradict the use of language.
Brief notes about all of these examples contextualize your observations; however, your observation notes will be guided primarily by your theoretical framework, keeping in mind that your observations will feed into and potentially modify or alter these frameworks.
Sampling Techniques
Sampling refers to the process used to select a portion of the population for study . Qualitative research, of which observation is one method, is generally based on non-probability and purposive sampling rather than probability or random approaches characteristic of quantitatively-driven studies. Sampling in observational research is flexible and often continues until no new themes emerge from the data, a point referred to as data saturation.
All sampling decisions are made for the explicit purpose of obtaining the richest possible source of information to answer the research questions. Decisions about sampling assumes you know what you want to observe, what behaviors are important to record, and what research problem you are addressing before you begin the study. These questions determine what sampling technique you should use, so be sure you have adequately answered them before selecting a sampling method.
Ways to sample when conducting an observation include:
Ad Libitum Sampling -- this approach is not that different from what people do at the zoo--observing whatever seems interesting at the moment. There is no organized system of recording the observations; you just note whatever seems relevant at the time. The advantage of this method is that you are often able to observe relatively rare or unusual behaviors that might be missed by more deliberate sampling methods. This method is also useful for obtaining preliminary observations that can be used to develop your final field study. Problems using this method include the possibility of inherent bias toward conspicuous behaviors or individuals and that you may miss brief interactions in social settings.
Behavior Sampling -- this involves watching the entire group of subjects and recording each occurance of a specific behavior of particular interest and with reference to which individuals were involved. The method is useful in recording rare behaviors missed by other sampling methods and is often used in conjunction with focal or scan methods. However, sampling can be biased towards particular conspicuous behaviors.
Continuous Recording -- provides a faithful record of behavior including frequencies, durations, and latencies [the time that elapses between a stimulus and the response to it]. This is a very demanding method because you are trying to record everything within the setting and, thus, measuring reliability may be sacrificed. In addition, durations and latencies are only reliable if subjects remain present throughout the collection of data. However, this method facilitates analyzing sequences of behaviors and ensures obtaining a wealth of data about the observation site and the people within it. The use of audio or video recording is most useful with this type of sampling.
Focal Sampling -- this involves observing one individual for a specified amount of time and recording all instances of that individual's behavior. Usually you have a set of predetermined categories or types of behaviors that you are interested in observing [e.g., when a teacher walks around the classroom] and you keep track of the duration of those behaviors. This approach doesn't tend to bias one behavior over another and provides significant detail about a individual's behavior. However, with this method, you likely have to conduct a lot of focal samples before you have a good idea about how group members interact. It can also be difficult within certain settings to keep one individual in sight for the entire period of the observation.
Instantaneous Sampling -- this is where observation sessions are divided into short intervals divided by sample points. At each sample point the observer records if predetermined behaviors of interest are taking place. This method is not effective for recording discrete events of short duration and, frequently, observers will want to record novel behaviors that occur slightly before or after the point of sampling, creating a sampling error. Though not exact, this method does give you an idea of durations and is relatively easy to do. It is also good for recording behavior patterns occurring at a specific instant, such as, movement or body positions.
One-Zero Sampling -- this is very similar to instantaneous sampling, only the observer records if the behaviors of interest have occurred at any time during an interval instead of at the instant of the sampling point. The method is useful for capturing data on behavior patterns that start and stop repeatedly and rapidly, but that last only for a brief period of time. The disadvantage of this approach is that you get a dimensionless score for an entire recording session, so you only get one one data point for each recording session.
Scan Sampling -- this method involves taking a census of the entire observed group at predetermined time periods and recording what each individual is doing at that moment. This is useful for obtaining group behavioral data and allows for data that are evenly representative across individuals and periods of time. On the other hand, this method may be biased towards more conspicuous behaviors and you may miss a lot of what is going on between observations, especially rare or unusual behaviors.
Alderks, Peter. Data Collection. Psychology 330 Course Documents. Animal Behavior Lab. University of Washington; Emerson, Robert M. Contemporary Field Research: Perspectives and Formulations. 2nd ed. Prospect Heights, IL: Waveland Press, 2001; Emerson, Robert M. et al. “Participant Observation and Fieldnotes.” In Handbook of Ethnography. Paul Atkinson et al., eds. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2001), 352-368; Emerson, Robert M. et al. Writing Ethnographic Fieldnotes. 2nd ed. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press, 2011; Ethnography, Observational Research, and Narrative Inquiry . Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Pace, Tonio. Writing Field Reports . Scribd Online Library; Pyrczak, Fred and Randall R. Bruce. Writing Empirical Research Reports: A Basic Guide for Students of the Social and Behavioral Sciences. 5th ed. Glendale, CA: Pyrczak Publishing, 2005; Report Writing . UniLearning. University of Wollongong, Australia; Wolfinger, Nicholas H. On Writing Fieldnotes: Collection Strategies and Background Expectancies.” Qualitative Research 2 (April 2002): 85-95; Writing Reports . Anonymous. The Higher Education Academy.
Structure and Writing Style
How you choose to format your field report is determined by the research problem, the theoretical perspective that is driving your analysis, the observations that you make, and/or specific guidelines established by your professor. Since field reports do not have a standard format, it is worthwhile to determine from your professor what the preferred organization should be before you begin to write. Note that field reports should be written in the past tense. With this in mind, most field reports in the social sciences include the following elements:
I. Introduction The introduction should describe the specific objective and important theories or concepts underpinning your field study. The introduction should also describe the nature of the organization or setting where you are conducting the observation, what type of observations you have conducted, what your focus was, when you observed, and the methods you used for collecting the data. You should also include a review of pertinent literature.
II. Description of Activities
Your readers only knowledge and understanding of what happened will come from the description section of your report because they have not been witness to the situation, people, or events that you are writing about. Given this, it is crucial that you provide sufficient details to place the analysis that will follow into proper context; don't make the mistake of providing a description without context. The description section of a field report is similar to a well written piece of journalism. Therefore, a helpful approach to systematically describing the varying aspects of an observed situation is to answer the "Five W’s of Investigative Reporting." These are:
- What -- describe what you observed. Note the temporal, physical, and social boundaries you imposed to limit the observations you made. What were your general impressions of the situation you were observing. For example, as a student teacher, what is your impression of the application of iPads as a learning device in a history class; as a cultural anthropologist, what is your impression of women participating in a Native American religious ritual?
- Where -- provide background information about the setting of your observation and, if necessary, note important material objects that are present that help contextualize the observation [e.g., arrangement of computers in relation to student engagement with the teacher].
- When -- record factual data about the day and the beginning and ending time of each observation. Note that it may also be necessary to include background information or key events which impact upon the situation you were observing [e.g., observing the ability of teachers to re-engage students after coming back from an unannounced fire drill].
- Who -- note the participants in the situation in terms of age, gender, ethnicity, and/or any other variables relevant to your study. Record who is doing what and saying what, as well as, who is not doing or saying what. If relevant, be sure to record who was missing from the observation.
- Why -- why were you doing this? Describe the reasons for selecting particular situations to observe. Note why something happened. Also note why you may have included or excluded certain information.
III. Interpretation and Analysis
Always place the analysis and interpretations of your field observations within the larger context of the theories and issues you described in the introduction. Part of your responsibility in analyzing the data is to determine which observations are worthy of comment and interpretation, and which observations are more general in nature. It is your theoretical framework that allows you to make these decisions. You need to demonstrate to the reader that you are looking at the situation through the eyes of an informed viewer, not as a lay person.
Here are some questions to ask yourself when analyzing your observations:
- What is the meaning of what you have observed?
- Why do you think what you observed happened? What evidence do you have for your reasoning?
- What events or behaviors were typical or widespread? If appropriate, what was unusual or out of ordinary? How were they distributed among categories of people?
- Do you see any connections or patterns in what you observed?
- Why did the people you observed proceed with an action in the way that they did? What are the implications of this?
- Did the stated or implicit objectives of what you were observing match what was achieved?
- What were the relative merits of the behaviors you observed?
- What were the strengths and weaknesses of the observations you recorded?
- Do you see connections between what you observed and the findings of similar studies identified from your review of the literature?
- How do your observations fit into the larger context of professional practice? In what ways have your observations possibly changed your perceptions of professional practice?
- Have you learned anything from what you observed?
NOTE: Only base your interpretations on what you have actually observed. Do not speculate or manipulate your observational data to fit into your study's theoretical framework.
IV. Conclusion and Recommendations
The conclusion should briefly recap of the entire study, reiterating the importance or significance of your observations. Avoid including any new information. You should also state any recommendations you may have. Be sure to describe any unanticipated problems you encountered and note the limitations of your study. The conclusion should not be more than two or three paragraphs.
V. Appendix
This is where you would place information that is not essential to explaining your findings, but that supports your analysis [especially repetitive or lengthy information], that validates your conclusions, or that contextualizes a related point that helps the reader understand the overall report. Examples of information that could be included in an appendix are figures/tables/charts/graphs of results, statistics, pictures, maps, drawings, or, if applicable, transcripts of interviews. There is no limit to what can be included in the appendix or its format [e.g., a DVD recording of the observation site], provided that it is relevant to the study's purpose and reference is made to it in the report. If information is placed in more than one appendix ["appendices"], the order in which they are organized is dictated by the order they were first mentioned in the text of the report.
VI. References
List all sources that you consulted and obtained information from while writing your field report. Note that field reports generally do not include further readings or an extended bibliography. However, consult with your professor concerning what your list of sources should be included. Be sure to write them in the preferred citation style of your discipline [i.e., APA, Chicago, MLA, etc.].
Alderks, Peter. Data Collection. Psychology 330 Course Documents. Animal Behavior Lab. University of Washington; Emerson, Robert M. Contemporary Field Research: Perspectives and Formulations. 2nd ed. Prospect Heights, IL: Waveland Press, 2001; Emerson, Robert M. et al. “Participant Observation and Fieldnotes.” In Handbook of Ethnography. Paul Atkinson et al., eds. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2001), 352-368; Emerson, Robert M. et al. Writing Ethnographic Fieldnotes. 2nd ed. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press, 2011; Ethnography, Observational Research, and Narrative Inquiry . Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Pace, Tonio. Writing Field Reports . Scribd Online Library; Pyrczak, Fred and Randall R. Bruce. Writing Empirical Research Reports: A Basic Guide for Students of the Social and Behavioral Sciences. 5th ed. Glendale, CA: Pyrczak Publishing, 2005; Report Writing. UniLearning. University of Wollongong, Australia; Wolfinger, Nicholas H. On Writing Fieldnotes: Collection Strategies and Background Expectancies.” Qualitative Research 2 (April 2002): 85-95; Writing Reports. Anonymous. The Higher Education Academy.
- << Previous: Reviewing Collected Essays
- Next: About Informed Consent >>
- Last Updated: Jul 18, 2023 11:58 AM
- URL: https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803
- QuickSearch
- Library Catalog
- Databases A-Z
- Publication Finder
- Course Reserves
- Citation Linker
- Digital Commons
- Our Website
Research Support
- Ask a Librarian
- Appointments
- Interlibrary Loan (ILL)
- Research Guides
- Databases by Subject
- Citation Help
Using the Library
- Reserve a Group Study Room
- Renew Books
- Honors Study Rooms
- Off-Campus Access
- Library Policies
- Library Technology
User Information
- Grad Students
- Online Students
- COVID-19 Updates
- Staff Directory
- News & Announcements
- Library Newsletter
My Accounts
- Interlibrary Loan
- Staff Site Login
FIND US ON
404 Not found
- Business Templates
- Sample Reports
FREE 11+ Field Trip Report Samples [ Agriculture, Educational, Environmental ]

Are you a student who recently went on an educational field trip? Or perhaps you are a professional researcher in agriculture who needs to conduct an observation and analysis of a particular farm? If you consider engaging in field research paper, and supporting research in difficult environments, you need to have the right skills and expertise in managing effective and safer research statement. Working on different types of field reports can be nerve-racking and challenging for most of the students or new researchers. Don’t fret because in this article, we have some downloadable field trip report samples to guide you. Keep on reading!
Field Trip Report
Free 11+ field trip report samples, 1. sample field trip report, 2. school field trip report sample pdf, 3. field trip report, 4. field trip report template, 5. student field visit report sample, 6. report writing on field trip, 7. field trip report sample pdf, 8. field trip report format, 9. field trip report example, 10. field visit report writing example, 11. educational field trip report sample, 12. field visit report sample, what is a field trip report, how to write a field trip report, 1. conduct field research , 2. collect fundamental data, 3. summarize the highlighted points of the field trip, 4. provide a simple overview of field trip activities , 5. develop a conclusion , what is the purpose of a field trip, how to write a brief summary for a field trip, what is the difference between a field report and a survey report, how do you describe a field trip, what is an example of a field trip.

- Google Docs

Size: 96 KB
Size: 115 KB

Size: 249 KB

Size: 48 KB

Size: 61 KB

Size: 19 KB

Size: 41 KB

Whether you are a graduate student who works with your academic advisors as you engage in field research or being one of the lead investigators of certain research projects, you need to be able to write a well-detailed and technical analysis field trip report. Additionally, you must use some diverse fieldwork methods such as ethnographic method, observational methods, comparative method, intersubjectivity, and other methods. To assist you in writing an informative field report, we provide you some downloadable and printable field trip report samples here in different formats. Simply click the field trip report templates in this article and start downloading now!
A field report is a clear and well-detailed report of a student or researcher while demonstrating primary activities, tasks, significant accomplishments, and other integral aspects of a field visit report in a certain place or event through writing.
Writing a clear and cohesive field report is essential to maintain the essence and content of the field trip. Thus, when you work on your field trip report, it must have good characteristics such as simplicity, consistency, precision and accuracy, topic relevance and many more. In order to guide you in preparing your narrative report of a field trip, we provide some useful tips that you should consider:
First, you must conduct field research in the place or event that you are visiting. Your objectives should be measurable, actionable results that will support your field report writing. Ask some questions to the people around the area. Some examples of field research are deciphering social metrics in a particular place, understanding the effects of food on child’s growth, etc.
Being cognizant on the specific figures can help you in completing the field report thoroughly. Know about the opinions, insights, and other quantitative data analysis which appear to be highly fundamental to your report. Collecting and preserving these figures in your field report will assist you and other researchers in understanding relevant themes of a research study plan .
After that, you need to summarize the highlighted points of the field trip . It should be less than one page and easy for readers to skim. Use subheaders, short sentences, and bullet points to emphasize your main idea accurately. Include facts such as primary research objectives, sample timeline , and many others
Provide a simple overview of field activities such as lectures, tours, sample worksheets, videos, and demonstrations. List down each of the activities and tasks involved in the place that you are covering.
Think deeply about the main purpose and benefits of visiting the area or place of your field research trip. Develop a conclusion of the entire field trip by presenting the useful elements of the field trip. Understand the key lessons you acquired from the field trip and explain how you have greatly benefited from them.
The purpose of a field trip is to help the students to conduct careful observation and sample assessment of people, places, and/or events, as well as a comprehensive analysis of the observation details. In this way, the students can determine and organize prevalent topics according to the research problem of a certain study.
If you need to write a sample brief summary for a field trip, indicate a clear and concise title and demonstrate the major elements in your introduction. Then, provide comprehensive information of the facility that you visited. Add several examples about the activities and tasks that happened in the field trip. Discuss what are the things that surprised you and other findings you gathered during the field trip.
A field report sample is necessary for the student or researcher when it comes to combining theory and analysis acquired through the application of observation techniques and practices. On the other hand, a survey report is a written document which contains the details collected during the survey.
A field trip is an educational outing where students or participants visit a location outside their regular classroom setting to explore and learn about specific subjects or concepts hands-on.
An example of a field trip is a visit to a natural history museum, where students can see and learn about fossils, dinosaurs, and various geological exhibits to enhance their understanding of Earth’s history.
In conclusion, this field trip report encapsulates the enriching experiences and educational insights gained during our excursion. The interactive learning opportunities provided a deeper understanding of [subject]. I extend gratitude to all participants, contributing to a memorable and valuable journey that enhances our collective knowledge and fosters a spirit of discovery.
Related Posts
Free 16+ sample marketing reports, free 16+ sample summary reports, free 14+ permission slip samples, free 14+ sample trip itinerary, free 11+ sample fall incident reports, free 8+ board memo templates, free 8+ accomplishment report samples, free 43+ report examples, free 18+ weekly report templates, free 16+ summary report templates, free 10+ retail trade report samples, free 9+ road trip itinerary samples, free 9+ stock audit report samples, free 9+ sample travel log, free 8+ sample parent release forms, how to write a visit report, free 47+ report format samples, free 21+ sample school reports, free 17+ sample visit reports.
Report on Field use for an Object
To analyze the fields for any object, including what percentage of the records (or a subset of your records) have that field populated, consider using the free "Field Trip" utility available on the AppExchange from Qandor.
The Field Trip utility includes the following features:
- Find out how often fields are being used
- Run Reports on fields
- Analyze all or a subset of your records
Once installed, click the "Field Trip" tab to get started, then create a new Field Trip Record by giving it a name, selecting an object (e.g. Accounts) and optionally a filter (in case you don't want to process all records in the data base).

Cookie Consent Manager
General information, required cookies, functional cookies, advertising cookies.
We use three kinds of cookies on our websites: required, functional, and advertising. You can choose whether functional and advertising cookies apply. Click on the different cookie categories to find out more about each category and to change the default settings. Privacy Statement
Required cookies are necessary for basic website functionality. Some examples include: session cookies needed to transmit the website, authentication cookies, and security cookies.
Functional cookies enhance functions, performance, and services on the website. Some examples include: cookies used to analyze site traffic, cookies used for market research, and cookies used to display advertising that is not directed to a particular individual.
Advertising cookies track activity across websites in order to understand a viewer’s interests, and direct them specific marketing. Some examples include: cookies used for remarketing, or interest-based advertising.
Cookie List

Report Writing on Educational Tour [With PDF]
In this article you are going to learn how to write a report on Educational Tour organize by your school. So with out much delay let’s jump in.

Educational Tour From School
By Ashlyn Tony
February 23, 2018; Karnataka: A bright morning, our tutor came in and announced we are going for a field trip. We were excited but most of us didn’t know what was a field trip and what was the motive behind it. We packed ourselves and led ourselves to our school bus.
During the ride, our tutor explained to us what a field trip was and why it was conducted. We went to a zoological park. It was a different experience from classroom learning. We students grasped the concept much faster. The method of learning through experience was different. We could learn things outside textbooks.
This is done so that students can look into a particular topic from all possible perspectives enabling them to learn everything. It has also been proved that field trips are an excellent way for incorporating knowledge into young minds. This also helps students to learn and understand topics on their own without further explanations.
They help indirect learning and help students in finding things by themselves which is better than spoon-feeding information. This experience helps students to retain in their memories what they have learnt for a much longer period.
Field Trip To A Butterfly Garden
By Rachel Harris
January 1, 2019; New Delhi: A field trip to a nearby butterfly garden was arranged for the kindergarten students. They were all excited about the idea of visiting a butterfly garden. We took the school bus to the garden. The students were so excited to see different types of butterflies.
Students observed different varieties and their teachers helped them understand the different features. They studied the different stages of growth. They saw a huge variety of butterflies. The students were so excited. By the end, students started recognising the different varieties of butterflies. They learnt all they could about Butterflies.
Also, they used this experience for instilling in students the importance of nature. They understood that the reason behind why they could not see butterflies like before is because of the disturbances humans create in the environment.
They were also taught the importance of trees in nature. They pledged that they would not hurt mother nature and will prevent unnecessary cutting of trees. Thus, the field trip was successful.
College Field Trip
By Saira Rajput
March 2, 2016; Bombay: We students were looking forward to the field trips. We were eagerly waiting for the days to come. We had pre-planned everything. Every single detail was planned and everything was set. We were visiting places with magnificent architectural designs.
The different varieties of ideas used made us think about the brilliance of the architecture. The designs, mural paintings, the statues, and the engraving on the walls. For some of us, this was the first experience. We learned about things that one should think about before planning and executing architectural designs.
This trip also taught us about the importance of precision in planning a design. One should be able to foresee everything before starting the actual construction. The quality of the materials, the materials used and also how much is the design applicable in a particular place.
Since some materials cannot be used in some climatic conditions, one should take utmost care in selecting materials for the construction. The trip made us realise our potential and also the importance of planning and precision in our field.
Field Trip To A Cow Farm
By Mark Anthony
September 5, 2015; Gujarat: This field trip was planned so as to make students understand how a farm works. On reaching the farm, students saw a large number of cows, of different varieties. One could see the huge machines used for milking the cows. The farm had a large number of workers. There was a veterinarian for weekly checkups.
There were employees cleaning the farms. There were separate employees for each pair of cows. Cows at this farm were given high-protein foods. The sheds were cleaned regularly to control diseases that might affect the cows. One could see the care given to the cows by looking at them. After the milking process, they are sent to a nearby plant for pasteurization and packaging.
There are special sheds for pregnant cows so as to give them special care. The calves are very well taken care of. The students could understand the importance of cleanliness and regular checkups. This experience made the students realise something new and made them learn new things.
There You Have It
So you have seen the example reports on Educational Tour, I hope these examples indeed help you.
Do let me know if you have any other topic ideas that you want me to cover by leaving a quick comment just below the article.
More from English Compositions
- Write Letter to the Editor about Poor Public Bus Service
- Madhyamik English Writing Suggestion 2022 [With PDF]
- Report Writing on Annual Sports Day Celebration in Your School [2023]
- Write a Report on Road Accident [4 Examples] 2023 Updated
- Report Writing Format | How to Write a Report | Example [PDF]
- Write a Diary Entry on Your Trip to an Amusement Park
- Write a Letter to Your Friend about Your Educational Tour
- Write a Letter of Complaint to a Book Dealer for the Delay in the Delivery of Books
- [FREE PDF] From The Diary Of Anne Frank MCQs | CBSE Class 10 English Chapter 4 [TERM 1]
- Write a Letter to Your Friend Describing How You Caught a Thief
- Write a Letter to Your Friend Telling Him About Your Visit to Shimla with Your Parents
- Short Essay on My Adventurous Trip [100, 200, 400 Words] With PDF
The Enlightened Mindset
Exploring the World of Knowledge and Understanding
Welcome to the world's first fully AI generated website!
What is a Field Trip: Exploring the Benefits, Challenges, and Creative Ideas
By Happy Sharer

Introduction: What is a Field Trip?
A field trip is an educational excursion outside of the classroom environment. It is an opportunity for students to gain first-hand experience with the material they are learning in class. Field trips can take place at local attractions, museums, historic sites, nature centers, and more. They can also be conducted virtually, allowing students to explore faraway places without ever leaving the classroom.
Overview of Field Trips: Exploring the Benefits and Challenges
Field trips are an important part of any school curriculum. They provide an opportunity for students to gain real-world experience with the material they are learning in class. However, there are both benefits and challenges associated with field trips that must be considered before planning one.
Benefits of Field Trips
The most obvious benefit of field trips is that they give students the chance to experience the material they are learning in class in a real-world setting. According to a study conducted by the National Education Association, “Field trips provide students with experiences that cannot be replicated in the classroom. They offer opportunities to explore concepts from a different perspective, to observe firsthand what has been read about in textbooks, and to make connections between course content and real life.”
In addition to providing an opportunity for experiential learning, field trips can also help to engage student interest in the subject matter. A study conducted by the University of Texas found that students who went on field trips were more likely to remember the material they had learned than those who did not go on the trip. Furthermore, field trips can spark curiosity and inspire students to ask questions and seek out further knowledge.
Challenges of Field Trips
Despite their many benefits, field trips can present some challenges. One of the biggest challenges associated with field trips is the cost. Depending on where you are traveling and the size of your group, the expenses can quickly add up. Additionally, finding the time to plan and execute a successful field trip can be difficult for teachers who already have a full schedule.
Safety is another issue that must be taken into consideration when planning a field trip. It is important to ensure that all students are supervised at all times and that the destination is appropriate for the age and maturity level of the students.
Tips for Planning a Successful Field Trip
Planning a successful field trip requires careful consideration of multiple factors. Here are some tips to keep in mind when planning a field trip.
Establish Goals
Before planning a field trip, it is important to establish clear goals. Ask yourself why you are taking the students on the trip and what you hope to accomplish. This will help to ensure that the field trip is meaningful and relevant to the material being taught in class.
Choose an Appropriate Destination
Once you have established your goals, it is important to choose a destination that is appropriate for the age and maturity level of the students. When selecting a location, consider the interests and abilities of the students and make sure that the destination offers something that will be interesting and engaging for them.
Develop an Itinerary
Once you have selected a destination, it is important to develop an itinerary that outlines the activities for the day. Make sure there is enough time for each activity and that the activities are relevant to the goals you have established for the trip.
Manage Safety Issues
Safety should always be a top priority when planning a field trip. Make sure that all students are supervised at all times and that the destination is appropriate for the age and maturity level of the students. Additionally, be sure to review any safety policies or procedures with the students prior to the trip.

A Guide to Creating a Meaningful Field Trip Experience
Creating a meaningful field trip experience requires careful planning and preparation. Here are some tips to ensure that your students get the most out of their field trip.
Set Clear Expectations
Prior to the field trip, it is important to set clear expectations for the students. Explain to them the purpose of the trip and what you hope they will gain from the experience. Additionally, discuss any rules or guidelines that need to be followed during the trip.
Make Connections with Course Material
When planning the activities for the field trip, look for ways to connect the material to the course content. This will help to ensure that the students gain a deeper understanding of the material and that the trip is meaningful and relevant.
Utilize Time Wisely
Time management is key to ensuring a successful field trip. Make sure that all activities are planned in advance and that the students understand what is expected of them. Additionally, leave room for flexibility in case something unexpected arises.
How Field Trips Enhance Learning in the Classroom
Field trips can be an invaluable tool for enhancing learning in the classroom. Here are some of the ways that field trips can benefit students.
Engaging Student Interest
Field trips can help to engage student interest in the subject matter. Experiencing the material firsthand can make it easier for students to understand and relate to the material being taught in class.
Building Critical Thinking Skills
Field trips can also help to build critical thinking skills. Students are exposed to new information and must process it in order to gain a better understanding of the material. This helps to develop problem-solving abilities and encourages students to think more deeply about the material.
Developing Problem-Solving Abilities
Field trips can also help to develop problem-solving abilities. Students are exposed to new environments and must find ways to navigate them. This helps to build confidence and teaches students how to think on their feet.

The Value of Field Trips for Students
Field trips can be a valuable learning experience for students. Here are some of the ways that field trips can benefit students.
Developing Self-Confidence
Field trips can help to boost self-confidence. Being in unfamiliar surroundings can be intimidating, but it can also be a great opportunity for students to practice problem-solving skills and develop self-confidence.
Strengthening Interpersonal Relationships
Field trips can also help to strengthen interpersonal relationships among students. Working together to navigate new environments and solve problems can help to foster teamwork and collaboration.
Acquiring New Knowledge and Experiences
Finally, field trips can open students up to new knowledge and experiences. Seeing things firsthand can help to bring the material to life and make it easier for students to understand and remember.

Creative Ideas for Field Trips
There are many creative ways to incorporate field trips into the classroom. Here are some ideas for fun and engaging field trips.
Museum Visits
Museums are a great way to introduce students to a variety of topics. From art and history to science and technology, there are a variety of museums that offer educational experiences for students of all ages.
Local Attractions
Local attractions can be a great way to introduce students to the community and its culture. Consider visiting historical sites, parks, zoos, or aquariums for an interactive and fun learning experience.
Nature Walks
Nature walks are a great way to get students outdoors and exploring their natural surroundings. Not only can this be a fun activity, but it can also be a great way to introduce students to concepts such as ecology and conservation.

Virtual Field Trips: Taking Education Beyond the Classroom
Technology has opened up a world of possibilities for educators looking to take their students on field trips. Virtual field trips allow students to explore faraway places without ever leaving the classroom.
Advantages of Virtual Field Trips
Virtual field trips come with a number of advantages. They are often less expensive than traditional field trips, and they can be used to explore destinations that would otherwise be inaccessible. Additionally, virtual field trips can be tailored to fit the curriculum and the specific needs of the students.
Types of Virtual Field Trips
There are a variety of types of virtual field trips available. These include virtual tours of museums and historical sites, live video streams of events, and interactive simulations of different environments. Each type of virtual field trip offers a unique experience and can be used to enhance learning in the classroom.
Tips for Planning a Virtual Field Trip
When planning a virtual field trip, it is important to do your research. Check to see if the destination offers a virtual tour and make sure that the technology needed is available and easy to use. Additionally, make sure to set clear expectations and goals for the virtual field trip and to create an itinerary that outlines the activities for the day.
Field trips can be a valuable learning experience for students. They provide an opportunity for students to gain first-hand experience with the material they are learning in class and can help to engage student interest in the subject matter. Additionally, field trips can help to build critical thinking skills and develop problem-solving abilities. Finally, virtual field trips offer an exciting way to explore faraway places without ever leaving the classroom. With careful planning and preparation, field trips can be a fun and educational experience for everyone involved.
(Note: Is this article not meeting your expectations? Do you have knowledge or insights to share? Unlock new opportunities and expand your reach by joining our authors team. Click Registration to join us and share your expertise with our readers.)
Hi, I'm Happy Sharer and I love sharing interesting and useful knowledge with others. I have a passion for learning and enjoy explaining complex concepts in a simple way.
Related Post
Exploring japan: a comprehensive guide for your memorable journey, your ultimate guide to packing for a perfect trip to hawaii, the ultimate packing checklist: essentials for a week-long work trip, leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Expert Guide: Removing Gel Nail Polish at Home Safely
Trading crypto in bull and bear markets: a comprehensive examination of the differences, making croatia travel arrangements, make their day extra special: celebrate with a customized cake.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

ACADEMIC FIELD TRIP REPORT

Related Papers
Iorhom Ernest
FIELDWORK REPORT
Kennedy R Rogoi
At the end of the first semester of third year, the department of history, political science and public administration organizes an academic trip for students to embark on a week long field trip where they visit several occupational environments with the aim of providing students with a visual experience of what is learn in class. Given the fact that students have been well grounded in the theoretical underpinnings, this course exposes them to site personnel, knowledge and practices. At the conclusion of the field trip, students are expected to submit a written report, which should be a descriptive and critical analysis of their experience. The fieldwork trip to Coast region was from 4th to 10th August, 2013. In attendance were two lectures, four drivers, and a hundred and twenty two students from Moi Main Campus, Moi KPA Campus and Moi West Campus. The department of history, political science and public administration is sub-divided into two fields of discipline: 1. political science and public administration, and 2. penology and correctional Detailed information is provided in the annexes. Aim: To provide students with an avenue for practical learning in the field Objectives At the end of the field trip, the student is expected to have achieved the following objectives: 1. To gain visual experience of what is learnt in class; 2. To provide students with an avenue for interaction with other professionals in the field so as to gain a hands-on experience in the field situation; 3. To gain experience in practical work performance; In chapter one I will highlight history of the stations; vision, mission, core values, goals and objectives; Organizational structure; Roles and functions of the organization. Chapter two highlight the roles of the institutions visited in resource management, service delivery and administrative systems. Chapter three highlights the experience I personally in the course of fieldwork. Chapter four I will express challenges faced as individual or group during the field course and suggest recommendations to improve the fieldwork course schedule.
Iis Duwi Hartati
Musa Yarima Umar
Jurnal Onoma: Pendidikan, Bahasa, dan Sastra
Andi Halmina
This study aims to improve the students writing description skills of class XI through the application of the field trip method located at Senior High School 3 Wajo. This research is Classroom Action Research (CAR), which is aimed to improve the quality of learning practices in the classroom. The collected data were analysed critically by comparing the results of the actions in each cycle. The results obtained from this study include: (1) the application of the field trip method can improve writing learning. This is indicated by the increased activeness, attention, concentration, interest, and motivation of students in learning to write descriptions. (2) the application of the field trip method can improve students' ability to write descriptions. This is indicated by the increasing value of the students' writing. In cycle I the lowest score of students was 59 and the highest score of students was 82, while in cycle II the lowest score of students was 64 and the highest score...
Francis Ibama
Hodal BIZIMUNGU
It is understandable that it is not enough for students to only acquire theoretical skills without practical skills which is very important for them to do practices in order to become familiar with the day to day working environment, where pressure, constraints and challenges faced are totally different from those found in classes. The internship comes to remove the gap between the theory acquired in classes and the practical skills needed at work. It is in this perspective that Universities academically organize one-month internship for their students in order to acquire practical skills which can help them in their respective careers. Within the view of fulfilling my academic requirements, I conducted one month of Internship at the Ministry of East African community (MINEAC) which is responsible for coordinating the EAC Activities.
FIELD WORK EXPERIENCE IN IKOM - EXPLORING URBAN TOURISM ELEMENTS IN THE 21st CENTURY
COCOBASSEY DANY
ABSTRACT The field work is to explore on the Urban Tourism Elements in the 21st century in Ikom local government area and its environment both potential and in real term. Sufficient data was collected, analyzed and tested. The instrument used for collecting information was structured questionnaire and personal interaction with certain respondents. Discussion of findings was based on the results obtained from the study. It is recommended that more tourism event should be organized in the resort to attract more tourists’ visits to the area, and that the people in the area should also be supported through the provision of training, seminars, credit facilities and the provision of basic social amenities in the host community to help enhance their interest and participation in tourism activities.
SALTeL Journal (Southeast Asia Language Teaching and Learning)
firdayanti firdaus
Field trip programs as edu-tourism in university level were viewed as the great equalizer in terms of delivering students to cultural heritage awareness. So, they had seen these experiential learning as a central of educational mission. Higher level education especially university which implemented field trip programs as supporting activities in the English for tourism lesson was gladly endured the expense and disruption of providing field trips as the primary purpose to provide a learning opportunity. The aim of this study was to evaluate the implementation of educational field trips as edu-tourism at university level. This is a qualitative study which is carried out by survey and observation. The population of this study is the English Department students of Potensi Utama University. There were 150 respondents in this research which included of 50 teachers and 100 students were randomly selected. The instrument of this study used questionnaires and speaking test items. The questio...
Shiela Donna Gelua
RELATED PAPERS
Optical Materials
Gaetano Assanto
정읍콜걸샵【상담톡NW30 】ズ《SOD30점넷 》정읍출장샵ズ정읍출장아가씨ズ정읍출장샵ズ정읍출장마사지ズ정읍모텔출장ズ정읍출장샵추천
CteqJC ymir
Inorganic Chemistry
Antoni Llobet
The Yale Review
Susan Wheeler
Calidad en la educación
Journal of Studies in International Education
Kyra Garson
IP Journal of Nutrition, Metabolism and Health Science
Tanusree Debbarman
Revista Mediterránea de Comunicación
Cantillo Valero
Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry
Robindra Teron
Revista Cientifica E Curriculum Issn 1809 3876
JORGE LUIS ORDINOLA CORNEJO
Vincenzo Guidetti
Changwoo SHON
IEEE Access
Farrukh Hafeez
Zenodo (CERN European Organization for Nuclear Research)
Violetta Splitter
Revista de Gastroenterología del Perú
ROLANDO RENE SANCHEZ
Biological Psychiatry
adriana lori
International Journal on Perceptive and Cognitive Computing
Muhammad Ahmad
Agricultural Economics
Martin Nordin
The Civil War in Russia: Exit Problems, Historical Consequences, Lessons for Modernity
Oksana Pugovkina
Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition
Bruce Bistrian
Arthur Hunt
American Business Review
Richard Posthuma
International journal of progressive education
yener akman
Oleksandr Krupskyi
SSRN Electronic Journal
wayne holland
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- CBSSports.com
- Fanatics Sportsbook
Men's Brackets
Women's Brackets
Fantasy Baseball
Fantasy football, football pick'em, college pick'em, fantasy basketball, fantasy hockey, franchise games, 24/7 sports news network.
- CBS Sports Golazo Network
- PGA Tour on CBS
- UEFA Champions League
- UEFA Europa League
- Italian Serie A
- Watch CBS Sports Network
- TV Shows & Listings
The Early Edge
A Daily SportsLine Betting Podcast
With the First Pick
NFL Draft is coming up!
- Podcasts Home
- The First Cut Golf
- Beyond the Arc
- Eye On College Basketball
- NFL Pick Six
- Cover 3 College Football
- Fantasy Football Today
- My Teams Organize / See All Teams Help Account Settings Log Out
2024 Kentucky Derby prediction, odds, horses, and contenders: Surprising picks from horse racing insider
When is the 2024 kentucky derby the annual run for the roses takes place saturday, may 4 at churchill downs.
Newly elected Hall of Fame jockey Joel Rosario will try to add to his stellar career when he hops aboard the speedy Track Phantom in the 2024 Kentucky Derby on Saturday, May 4, at Churchill Downs in Louisville, Ky. On Tuesday, the National Museum of Racing and Hall of Fame announced that Rosario, 39, had been elected to the Hall as part of a nine-member 2024 class. Rosario has won more than 3,600 races in his career, including the 2013 Kentucky Derby aboard Orb. For this year's Derby, Rosario will ride the frontrunning Track Phantom, a 15-1 longshot to win. Meanwhile Florida Derby winner Fierceness is the favorite in the 2024 Kentucky Derby odds at 3-1.
The 2024 Kentucky Derby post time is 6:57 p.m. ET. With the Kentucky Derby annually featuring the largest field in North American racing, you'll want to see what Santa Anita-based racing reporter and analyst Michelle Yu has to say before making any 2024 Kentucky Derby picks, considering the success she's had handicapping this race .
Few people in racing are as well-connected as Yu. An on-air host and reporter who has provided racing analysis for TVG, HRTV and the Breeders' Cup, Yu has spent a lifetime in racing. Prior to her television career, she worked for trainers Steve Asmussen and Ron Moquett. She also is married to Santa Anita-based trainer Ryan Hanson.
Yu also has tremendous handicapping chops. In a wide-open Kentucky Derby in 2021, she gave out Medina Spirit, who crossed the finish line first, as the winner at 12-1. In Pool 5 of the Kentucky Derby Future Wager two years ago, she suggested a play on All Other 3-Year-Olds, which cashed at a whopping 18-1 when Rich Strike won the Derby.
Yu enters this year's Kentucky Derby on a roll. She correctly called National Treasure to win the Pegasus World Cup. In the month leading up to the Kentucky Derby, she predicted Stronghold's upset win in the Santa Anita Derby and smashed the exacta in the Apple Blossom Handicap.
For the first leg of the Triple Crown, Yu has handicapped the 2024 Kentucky Derby lineup, made her picks and constructed her best bets. You can head to SportsLine now to see them .
Top 2024 Kentucky Derby predictions
One surprise: Yu is fading Fierceness, even though he is the 3-1 Kentucky Derby favorite. The 3-1 morning line favorite, Fierceness owns Beyer Speed Figures of 110 (Florida Derby) and 105 (Breeders' Cup Juvenile). The next best figure is a 101 by longshot Mystik Dan, who earned that figure in the slop at Oaklawn Park.
But this Todd Pletcher-trained colt earned those big figures under ideal circumstances, and the 20-horse Kentucky Derby is the race every year in which a horse is most likely to not get ideal circumstances. "I can't see him being a lonely leader again in the Derby, and he has thrown in the towel the two times someone eyeballed him," Yu told SportsLine.
Another curveball: Yu is high on Just a Touch, even though he's a huge longshot at 20-1 in the Kentucky Derby odds 2024. A son of 2018 Triple Crown winner Justify, Just a Touch is looking to become just the fourth horse to win the Kentucky Derby having started just three previous times, joining his sire, Big Brown (2008) and Mage (2023).
Horses who run on or near the lead have done well in the Kentucky Derby over the last decade, and Just a Touch has the tactical speed to sit near the front. In his last race, he pressed a fast pace in the Blue Grass Stakes. "This is the kind of year that a horse with one lifetime win can capture the blanket of roses with the right trip," Yu told SportsLine. You can see all of Yu's 2024 Kentucky Derby bets here .
How to make 2024 Kentucky Derby picks
Moreover, Yu's top pick is a horse who "will be happy to get the added ground" at Churchill Downs. She's also high on a massive double-digit longshot who "showed some grit" in his last race. She is including these horses in her 2024 Kentucky Derby bets, and so should you. She's sharing which 2024 Kentucky Derby horses to back at SportsLine .
So who wins the 2024 Kentucky Derby? What double-digit longshot is a must-back? And how has Yu constructed her wagers? Visit SportsLine to see Yu's picks for the Kentucky Derby, all from the Santa Anita-based racing insider who has a long history of success in the Kentucky Derby , and find out.
2024 Kentucky Derby odds, contenders
Our latest general stories.
2024 Kentucky Derby: Exacta, trifecta and superfecta
Cbs sports staff • 4 min read.
2024 Kentucky Derby odds, futures picks, exotics
2024 Oaklawn Handicap odds, horse racing picks, bets
Cbs sports staff • 2 min read.
Howie Schwab, star of 'Stump the Schwab' dies at 63
Austin nivison • 1 min read.
Federal court overturns WV transgender athlete ban
2024 apple blossom odds, top horse racing expert picks, cbs sports staff • 3 min read, share video.

2024 Kentucky Derby picks by insider with long history

Ranking the biggest NFL Draft bust for all 32 teams

NFL mock: Four trades lead to five QBs

Holmgren answers physicality questions

Shaq correctly predicts Heat upset by exact margin

Butler trolls Celtics on Instagram after Heat upset

CFP solves Army-Navy issue, simulates 12-team field

Landing spots for Bengals wide receiver Higgins

Report: Jayden Daniels has two ideal landing spots

Knicks coach on G2 ending: 'They couldn't call a foul'

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
It will begin with a short explanation of field trip reports and their objectives. It will focus on the stages necessary to create a trip report and offer the structure of one. Finally, it will provide a field report example. What is a Field Trip Report. If you need to write a field trip report, let's start with the field trip itself.
A field study report is a formal document that recounts the details of a research or educational trip. It's like a treasure map that guides readers through your exciting journey. This report usually includes an introduction, a description of the field trip, data analysis, and a conclusion.
Write the introduction. Don't explain your readers what is field trip report. Instead, provide a bit of background information about the objective of your report. Describe the theoretical perspective and talk a bit about the various types of observations you've used. Write the Description of Activities section.
How to Begin. Field reports are most often assigned in disciplines of the applied social sciences [e.g., social work, anthropology, gerontology, criminal justice, education, law, the health care services] where it is important to build a bridge of relevancy between the theoretical concepts learned in the classroom and the practice of actually doing the work you are being taught to do.
Regardless of what the field trip may be and for who it is for, writing the report is needed. With that being said, a list of steps to take to make a field trip report. For students on a field trip see 12+ Permission Slip Templates. 1. Make an Interesting Title and Introduction.
If your teacher wants a technical field trip report, start with an abstract -- a brief summary paragraph -- that clearly explains where you went and what you learned during the field trip. Use research or literature to support your statements in your field trip report. For example, if you visited a local arboretum, you might use information ...
Ensure that you state the purpose of your field study report clearly. Determine the focus of your study and provide the relevant information. Define the setting of observations, and the methods used to collect data. 2. Construct a Theoretical Framework.
How to Begin. Field reports are most often assigned in the applied social sciences [e.g., social work, anthropology, gerontology, criminal justice, education, law, the health care professions] where it is important to build a bridge of relevancy between the theoretical concepts learned in the classroom and the practice of actually doing the work you are being taught to do.
Write a field trip report. Audubon Research Ranch (ARR) Field Trip. Field trip report is due 15 February. Field trip reports should be approximately 1.5-2 pages in length (single spaced, 12 pt font, typed, 1-1.25 in margins and 2 line breaks between paragraphs). Give a full answer at least. 2 questions (from 1-8) as well as 9.
Sample Field Trip Reports. Below are links to five sample field trip reports. They are actual student reports in their original form (no editing or spelling correction), except that the names and photos have been removed. Use them as a guideline or a model for preparing your own reports. There are many different possibilitites, so if you want ...
Sample Field Trip Report Introduction. The the 22nd of January 2021, 15 students from my class, our teacher, my mom, the I went toward London to get an excursion to Madame Tussauds Museum. We studied the history to European countries and their places of interest. When his teacher asked us to select who place to visit and investigate, we pick ...
Journalist Tan Shiow Chin shares tips for getting the best out of visits to scientists in their natural habitats.. Field trips are a crucial — and exciting — aspect of science journalism. They let you see where science is done, whether in a laboratory at your local university, an international research institute or even on scientists' field trips and projects.
An example of a field trip is a visit to a natural history museum, where students can see and learn about fossils, dinosaurs, and various geological exhibits to enhance their understanding of Earth's history. In conclusion, this field trip report encapsulates the enriching experiences and educational insights gained during our excursion.
GG 101 Sample Field Trip Report. When Buying a House in Terms of Geology For sale: a newly built house located in Manoa Valley surrounded by luscious and plentiful vegetation, and a spectacular overview of downtown Honolulu.Fee simple $3.5 million for this four bedroom three and a half bathroom, 2 car garage, and private gateway entry
All field reports, regardless of subject matter and intended academic discipline, aim to inform readers about the result and impact of an observed person, place, or event. ... Keep in mind that part of your field report includes providing a description of your activities, so make sure to capture important aspects of the place or event that you ...
Report on Field use for an Object. Publish Date: Oct 13, 2022. Description. To analyze the fields for any object, including what percentage of the records (or a subset of your records) have that field populated, consider using the free "Field Trip" utility available on the AppExchange from Qandor. The Field Trip utility includes the following ...
September 5, 2015; Gujarat: This field trip was planned so as to make students understand how a farm works. On reaching the farm, students saw a large number of cows, of different varieties. One could see the huge machines used for milking the cows. The farm had a large number of workers.
SCIENCE AND NATURE FIELD TRIP REPORT. 1. SCIENCE AND NATURE FIELD TRIP REPORT. 2018 SUMMER SCIENCE EXPLORATIONS & THE 2018-2019 SCHOOL YEAR FIELD TRIPS. We made a ton of improvements to better serve our diverse student body, and teachers noticed! "I have now attended the field trip 15 years in a row and it keeps getting better!
Field trips can take place at local attractions, museums, historic sites, nature centers, and more. They can also be conducted virtually, allowing students to explore faraway places without ever leaving the classroom. Overview of Field Trips: Exploring the Benefits and Challenges. Field trips are an important part of any school curriculum.
At the conclusion of the field trip, students are expected to submit a written report, which should be a descriptive and critical analysis of their experience. The fieldwork trip to Coast region was from 4th to 10th August, 2013. In attendance were two lectures, four drivers, and a hundred and twenty two students from Moi Main Campus, Moi KPA ...
Plan Your Schedule. Arrange Your Supervision. Create a Permission Form. Decide Who's Allowed To Go. Tie in Your Field Trip to Your Curriculum. These are the steps you will need to cover for your field trip plan. The order of these steps may be different for you, but be sure to think about all of these points. 1.
Summary. This chapter describes writing of incident reports, field trip reports and inspection reports, which are short in length. The chapter presents an example of an incident report, which explains a project delay. Field trip reports are written whenever people leave their usual place of work to do something elsewhere.
Field Trip Report, April 4th. HOURS REPORT 04042024.pdf, 578.08 KB; (Last Modified on Thursday at 10:36 AM)
Newly elected Hall of Fame jockey Joel Rosario will try to add to his stellar career when he hops aboard the speedy Track Phantom in the 2024 Kentucky Derby on Saturday, May 4, at Churchill Downs ...